Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Monitoring Sarcopenia With Incretin Receptor Activator Treatment
- First Published: 18 June 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
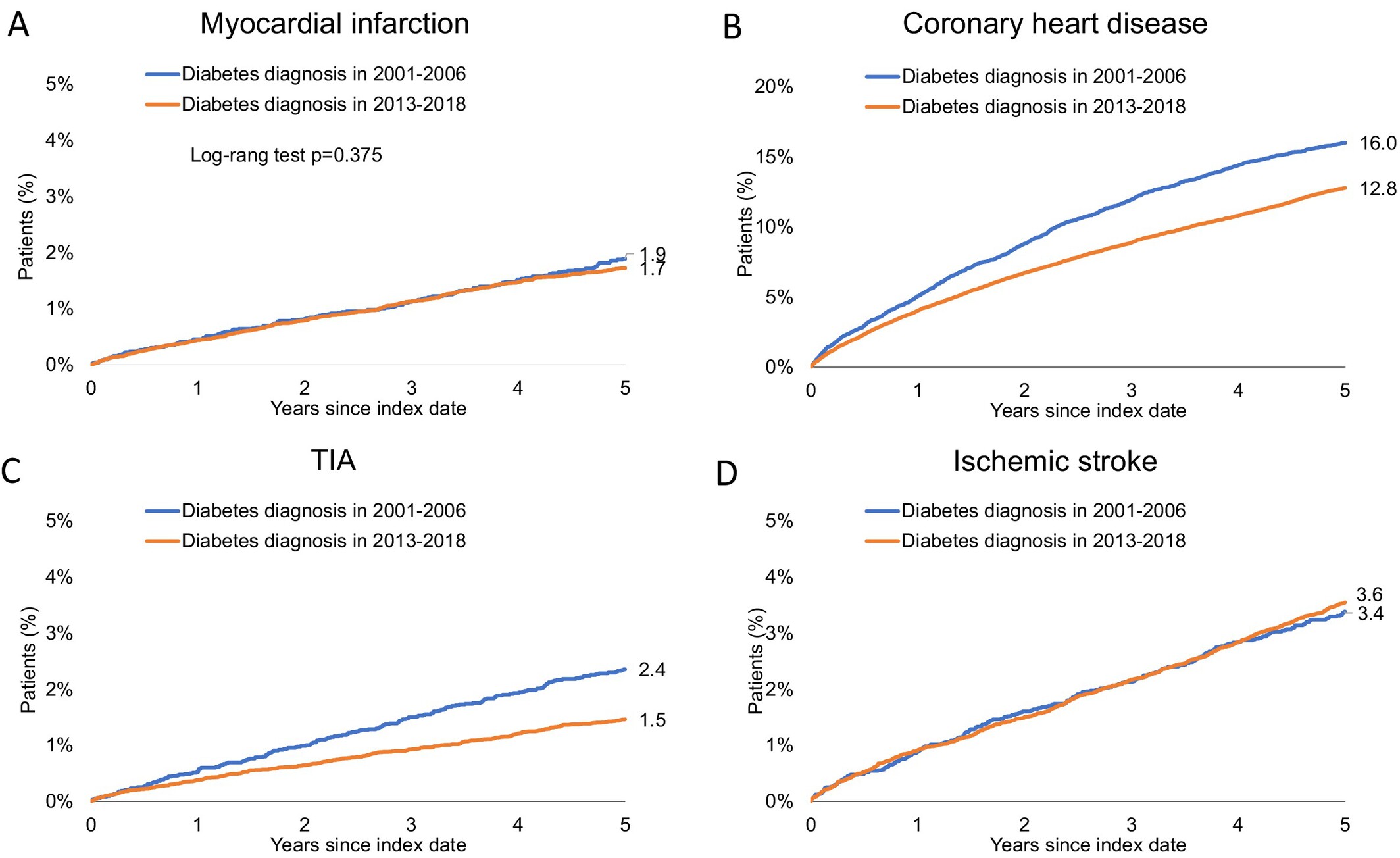
Time Trends in Cardiovascular Event Incidence in New-Onset Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-Based Cohort Study From Germany
- First Published: 02 June 2025
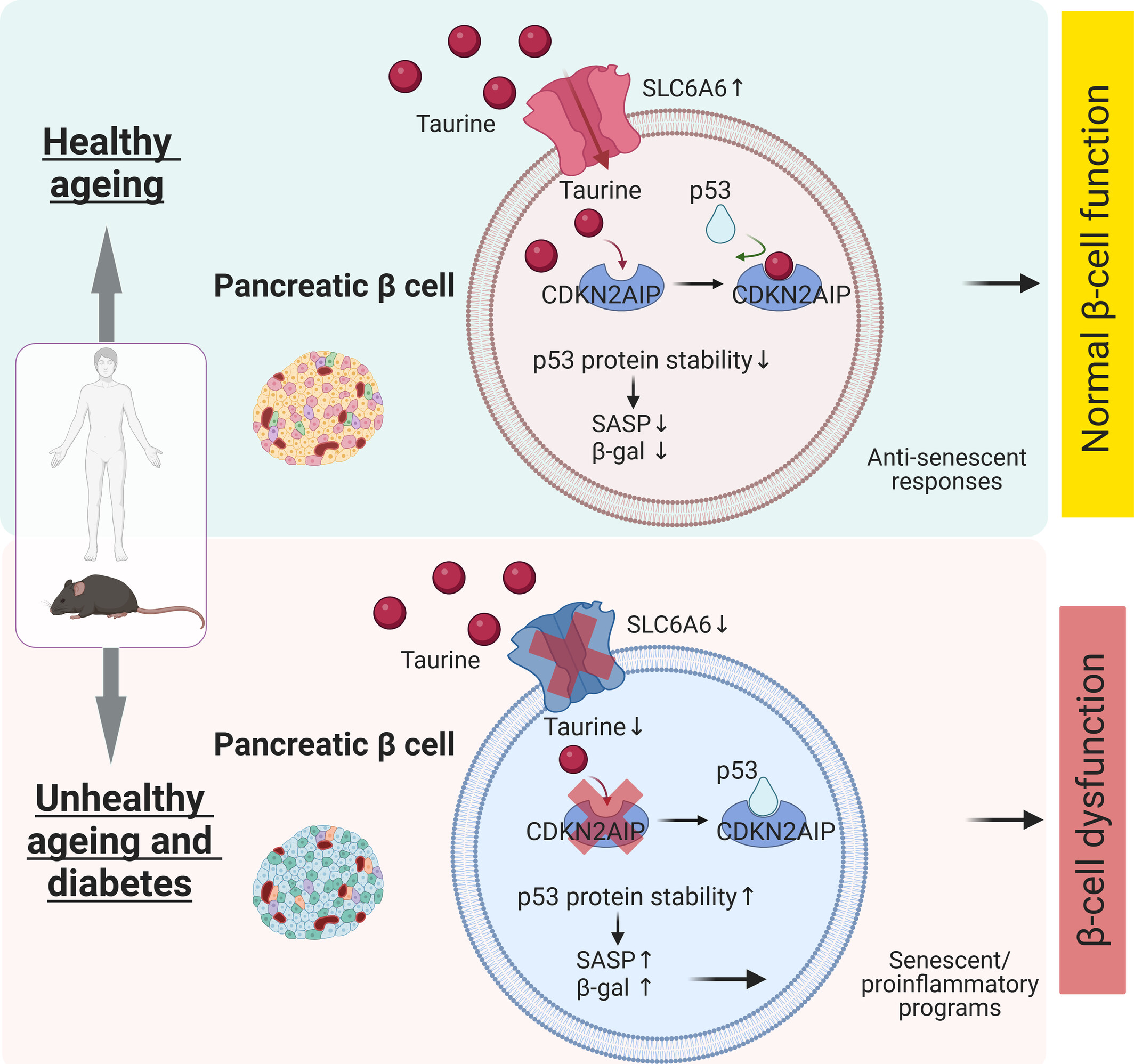
Taurine Alleviates Pancreatic β-Cell Senescence by Inhibition of p53 Pathway
- First Published: 03 June 2025
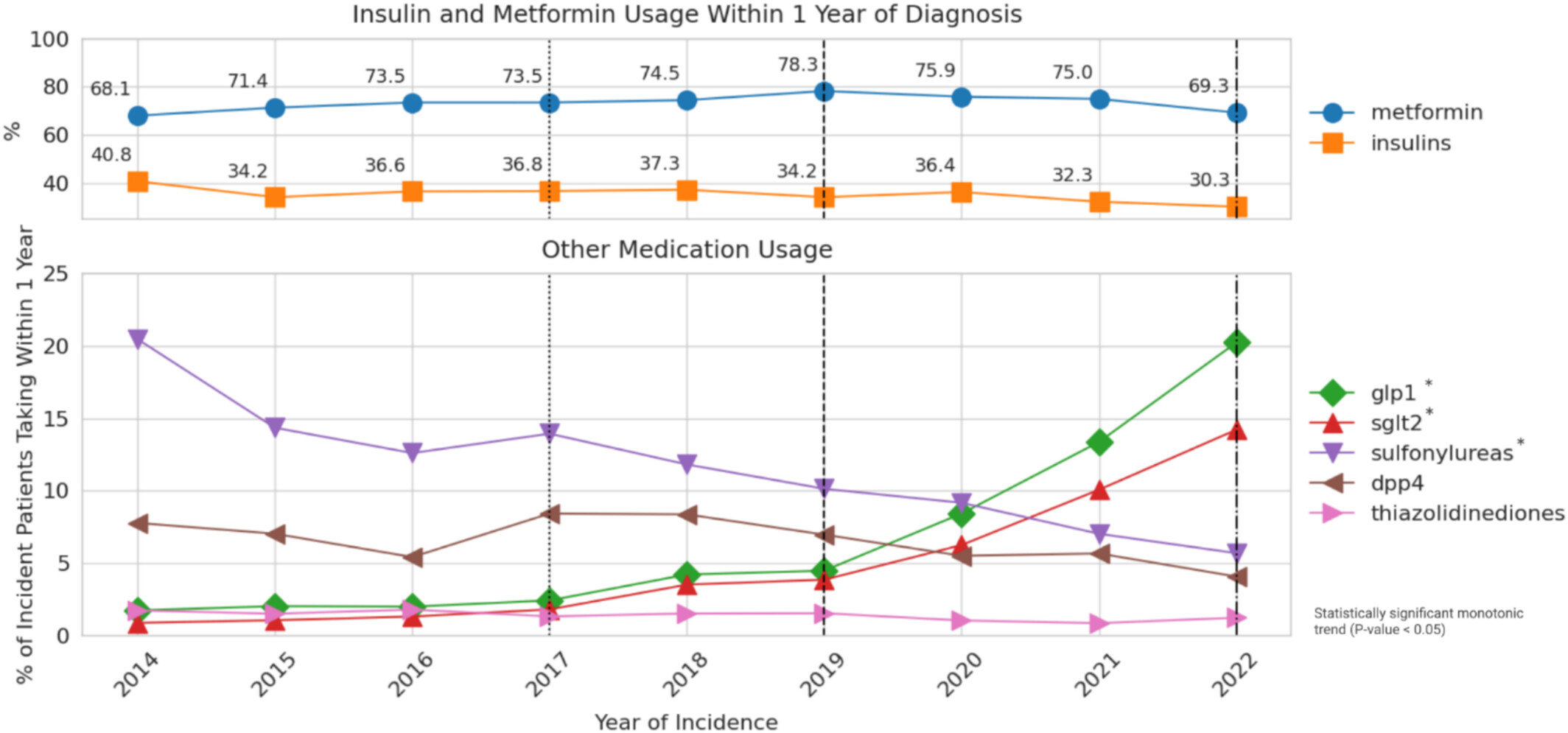
Trends in Pharmacological Treatment of Patients With New Onset Type 2 Diabetes: Usage Patterns in an Evolving Guideline Landscape
- First Published: 04 June 2025
Disease Progression Modeling of Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR): A Pharmacometrics Approach
- First Published: 06 June 2025
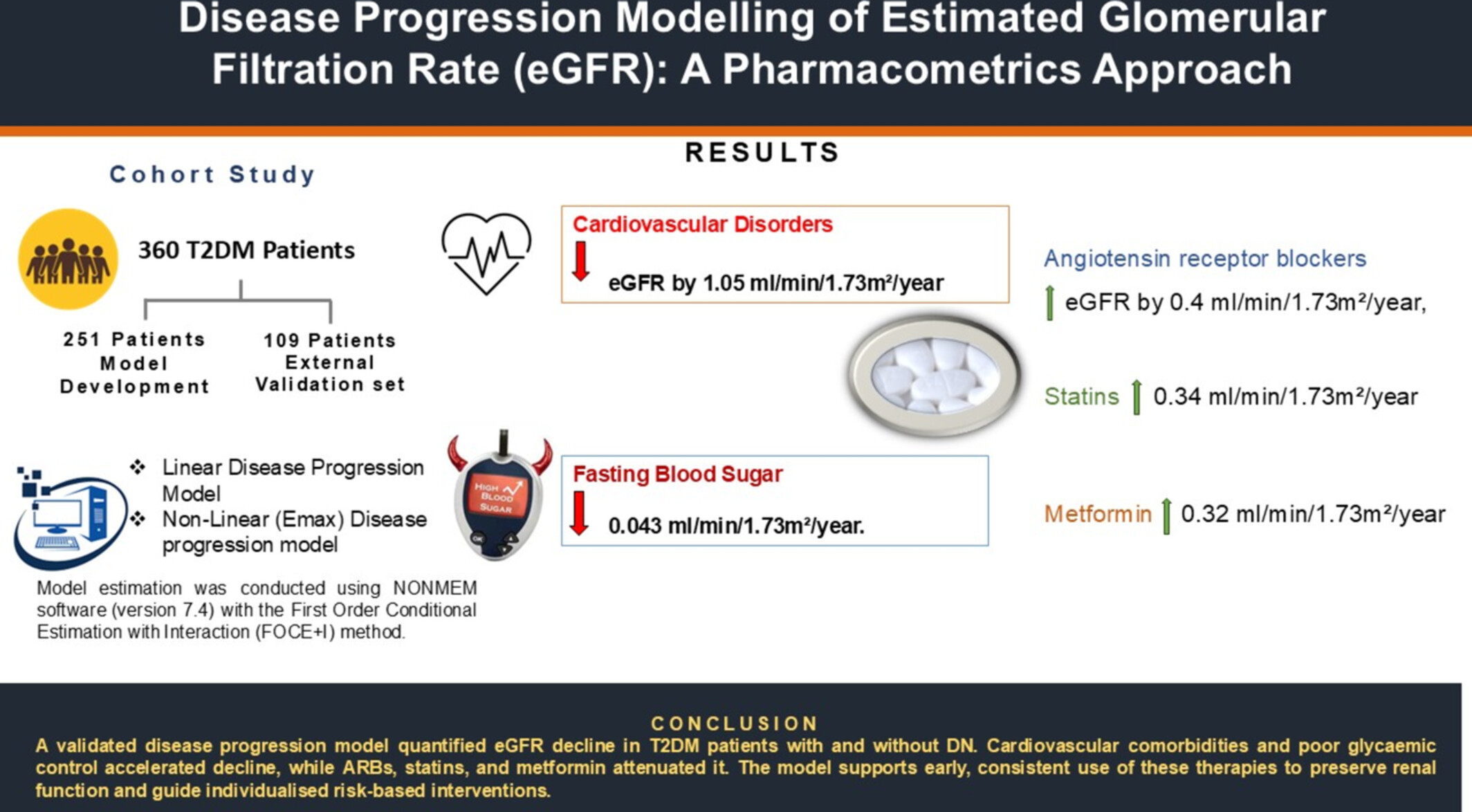
A validated disease progression model quantified eGFR decline in T2DM patients with and without DN. Cardiovascular comorbidities and poor glycaemic control accelerated decline, while ARBs, statins, and metformin attenuated it. The model supports early, consistent use of these therapies to preserve renal function and guide individualized risk-based interventions.
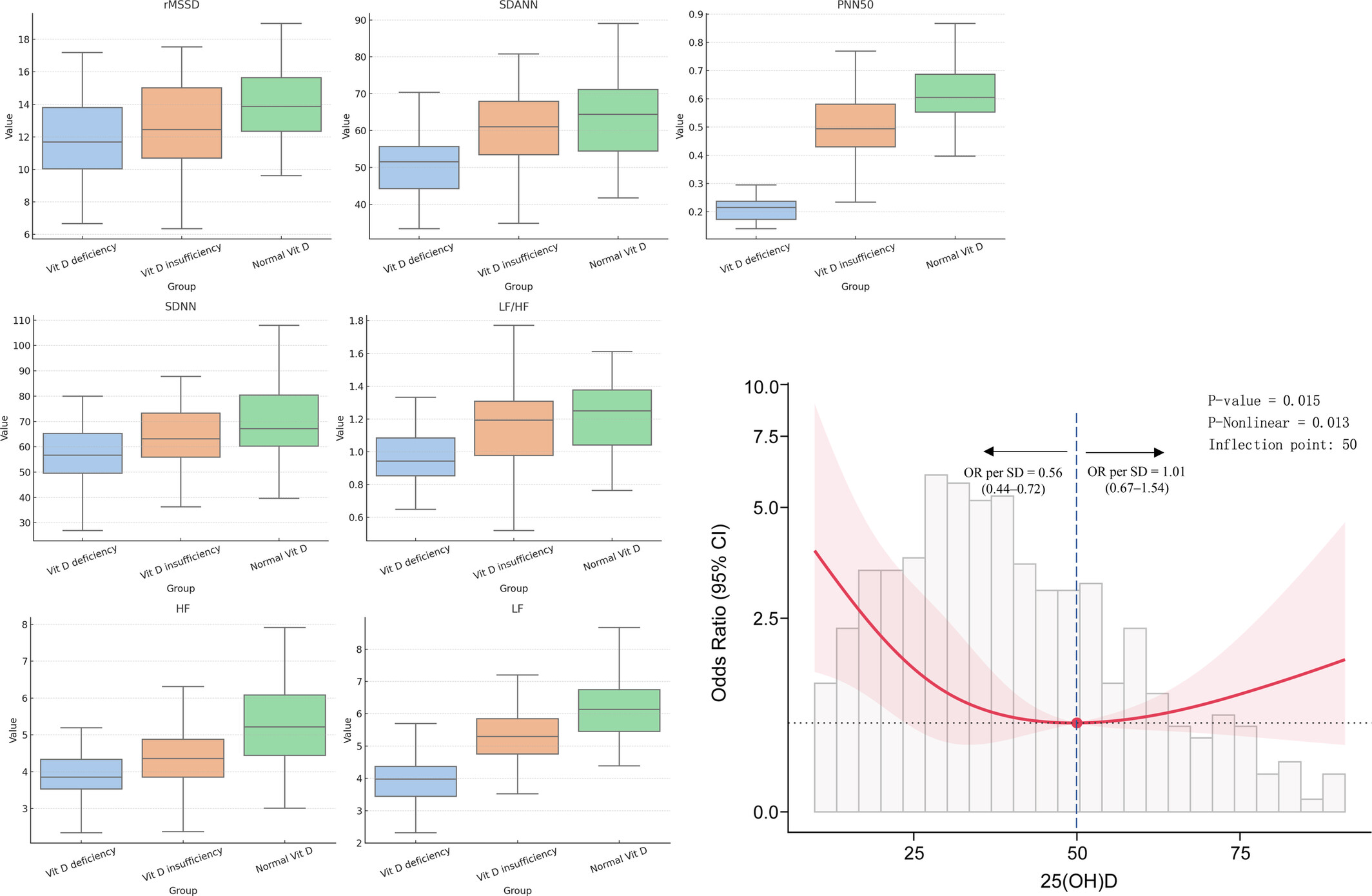
Nonlinear Association Between Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D and Cardiac Autonomic Dysfunction in Diabetic Foot: A Threshold Effect on Heart Rate Variability
- First Published: 10 June 2025
Phenotypic Spectrum at Diagnosis of Age-Related Endotypes of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-Sectional Study in China
- First Published: 12 June 2025
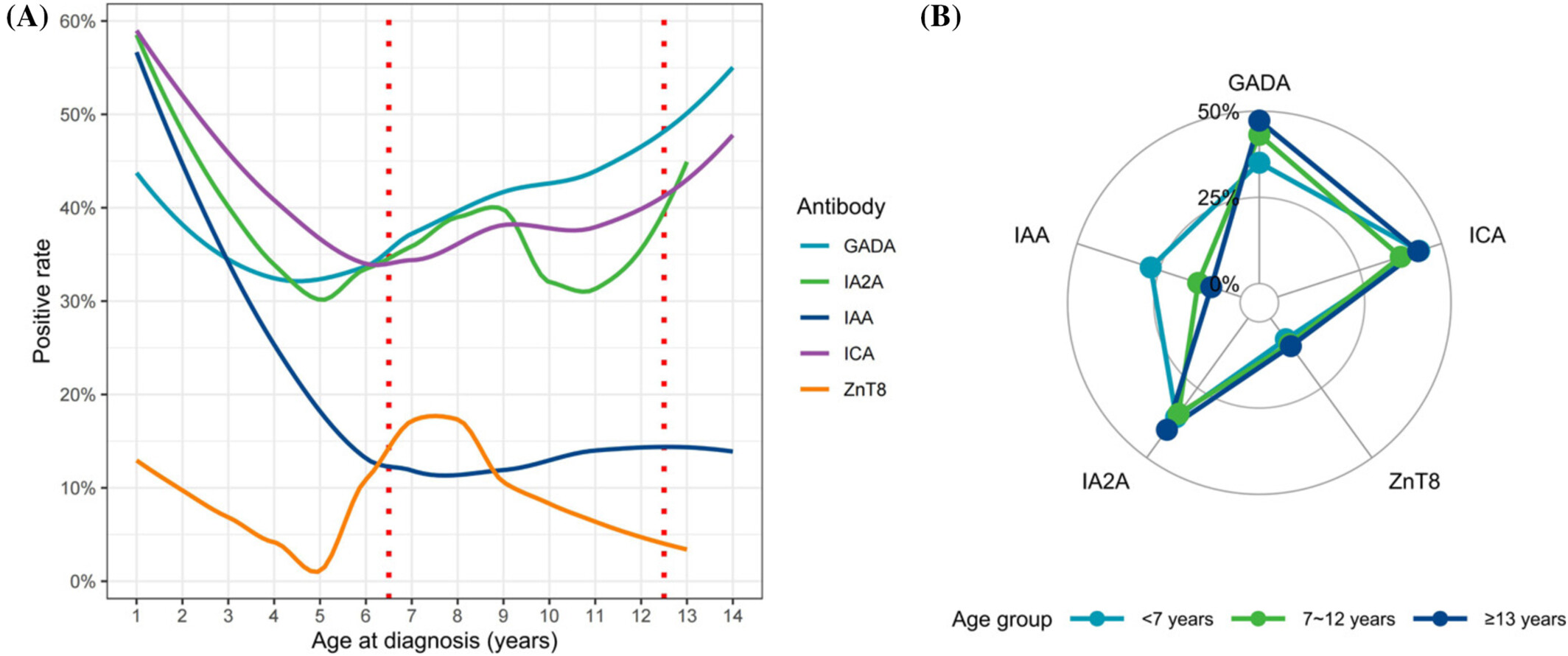
Emerging evidence points to distinct endotypes of T1DM: T1DE1 (diagnosed < 7 years) and T1DE2 (diagnosed ≥ 13 years). To explore phenotypic heterogeneity in Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) with respect to age-related endotypes. A cross-sectional study of 1204 newly diagnosed T1DM children in China (2010–2023), divided into three age groups: T1DE1, 7–12 years, and T1DE2. Age-specific phenotypic heterogeneity in pediatric T1DM indicates distinct endotypes, suggesting potential for precise treatment strategies.
REVIEW ARTICLE
The Effectiveness of Psychological Interventions for Families of Children With Type 1 Diabetes on Caregiver and Child Functioning: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- First Published: 17 June 2025
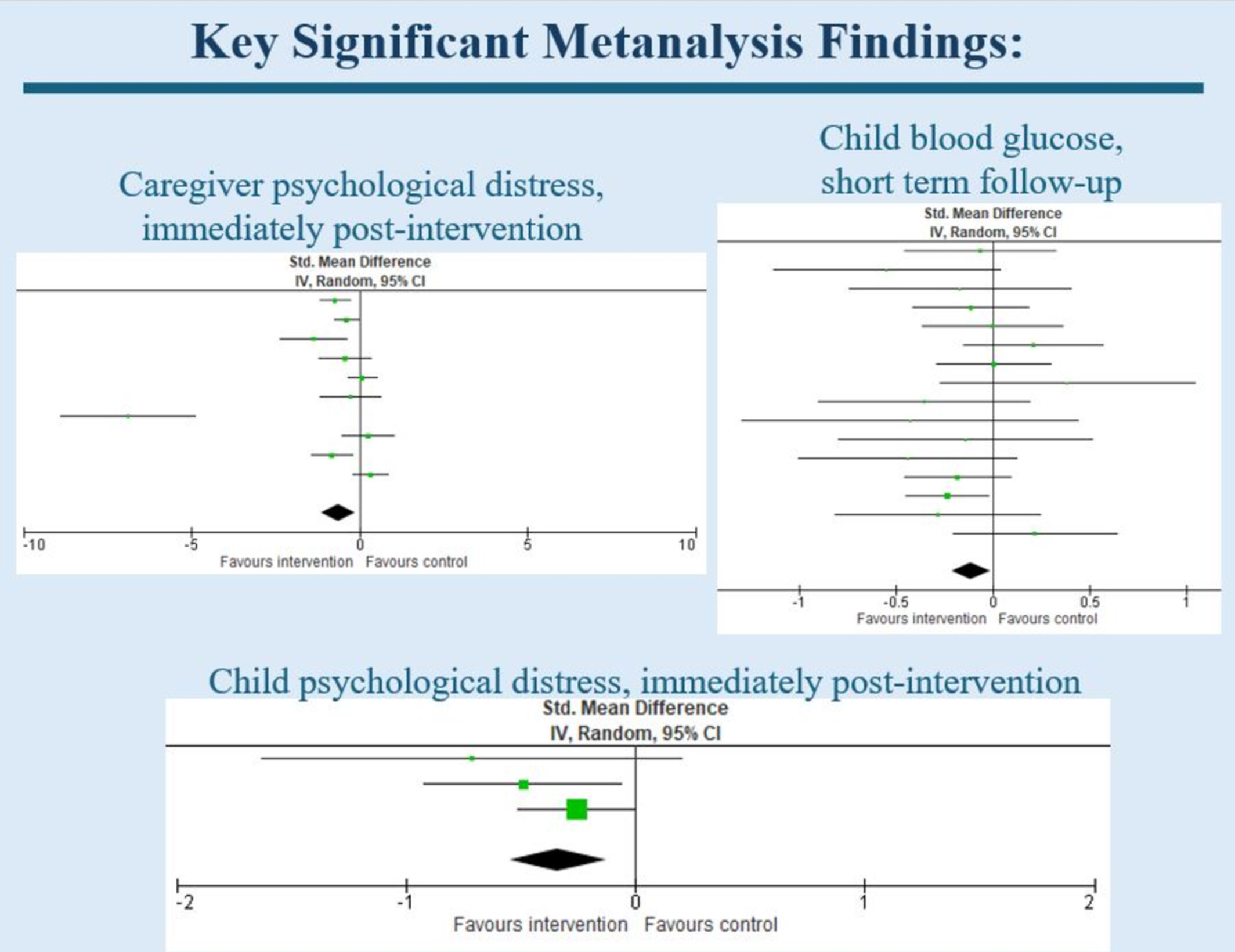
The systematic review and meta-analysis of psychological interventions for families of children with Type 1 Diabetes on caregiver and child functioning found psychological interventions significantly reduced parent and child psychological distress post-intervention and improved child blood glucose at short-term follow-up, relative to controls.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
A New Era in Obesity Treatment: The Evolution of Antiobesity Medications (AOMs) Based on Clinical Trials
- First Published: 17 June 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
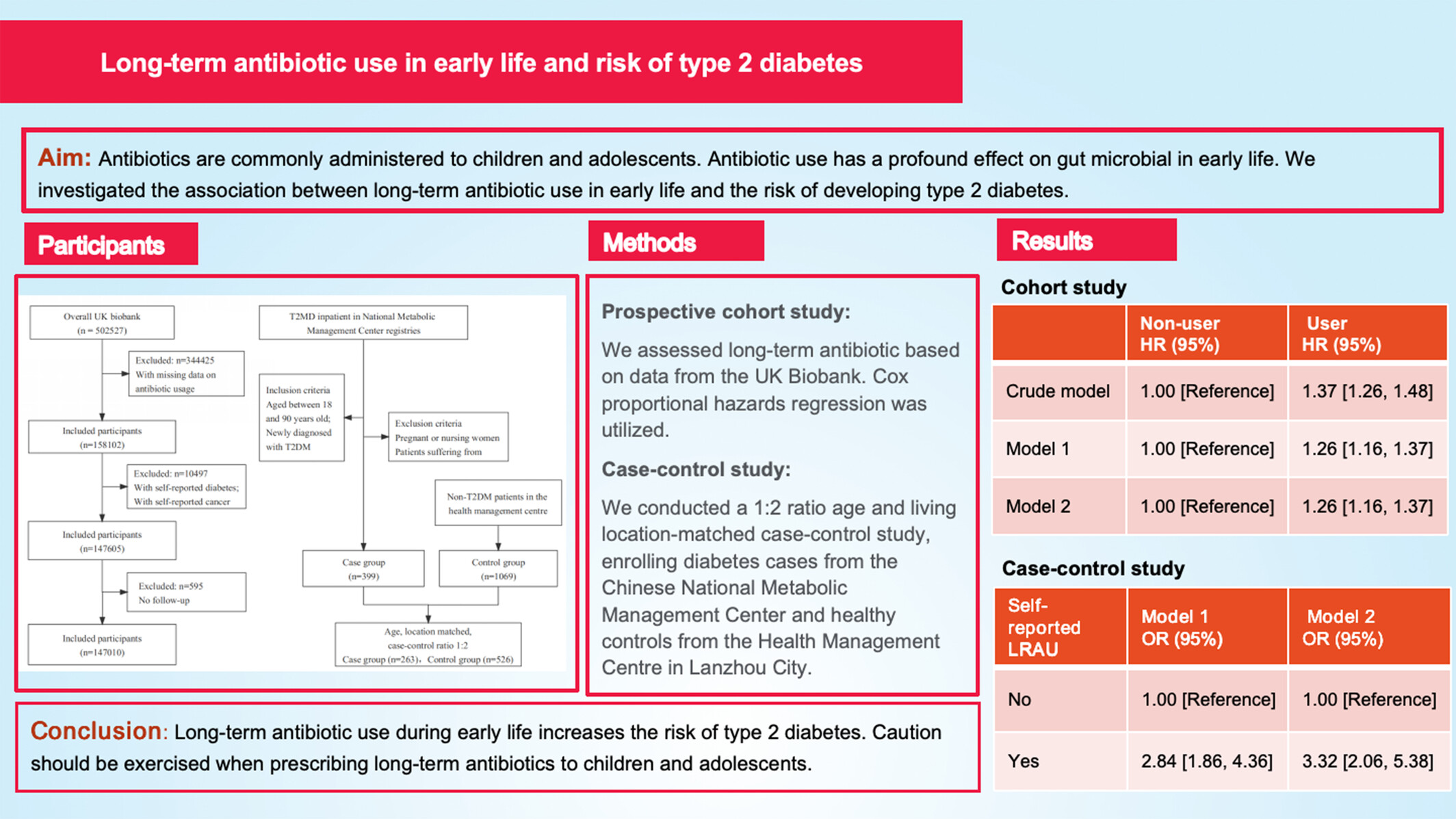
Long-Term or Recurrent Antibiotic Use in Early Life and the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-Based Prospective Cohort and a Case–Control Study
- First Published: 18 June 2025
REVIEW ARTICLE
Potential Significance of Targeting Ferroptosis for Intervention of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
- First Published: 19 June 2025
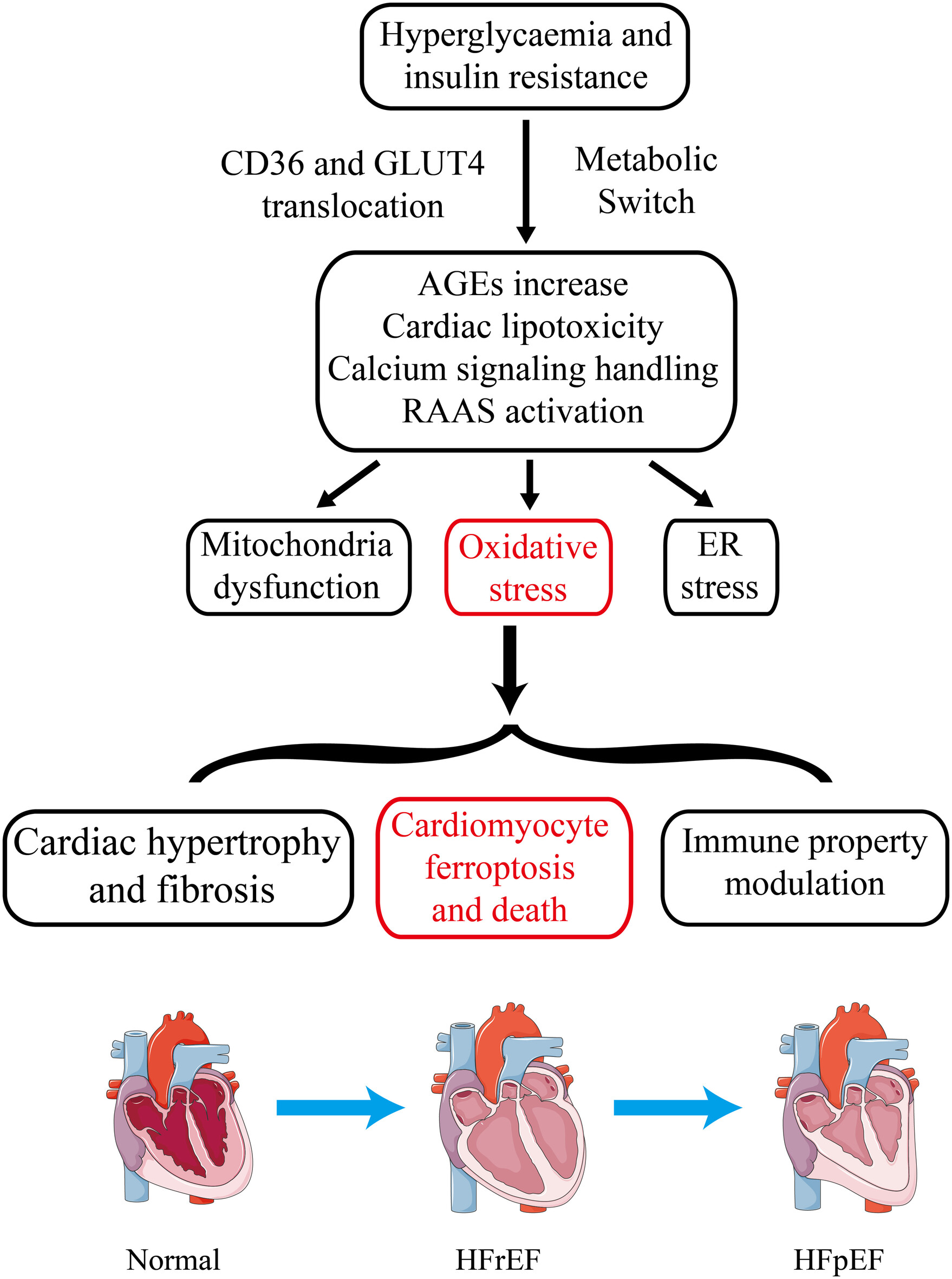
The pathophysiology of DCM encompasses insulin resistance and hyperglycemia-induced metabolic alterations in cardiomyocytes, mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress, cardiac lipotoxicity, dysregulation of immune responses, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, impaired calcium handling, and activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). Oxidative stress results in cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, myocardial fibrosis, cardiomyocyte ferroptosis and immune property modulation and ultimately lead to HFpEF. Ferroptosis inhibitors hold great promise as therapeutic agents for the intervention of DCM.
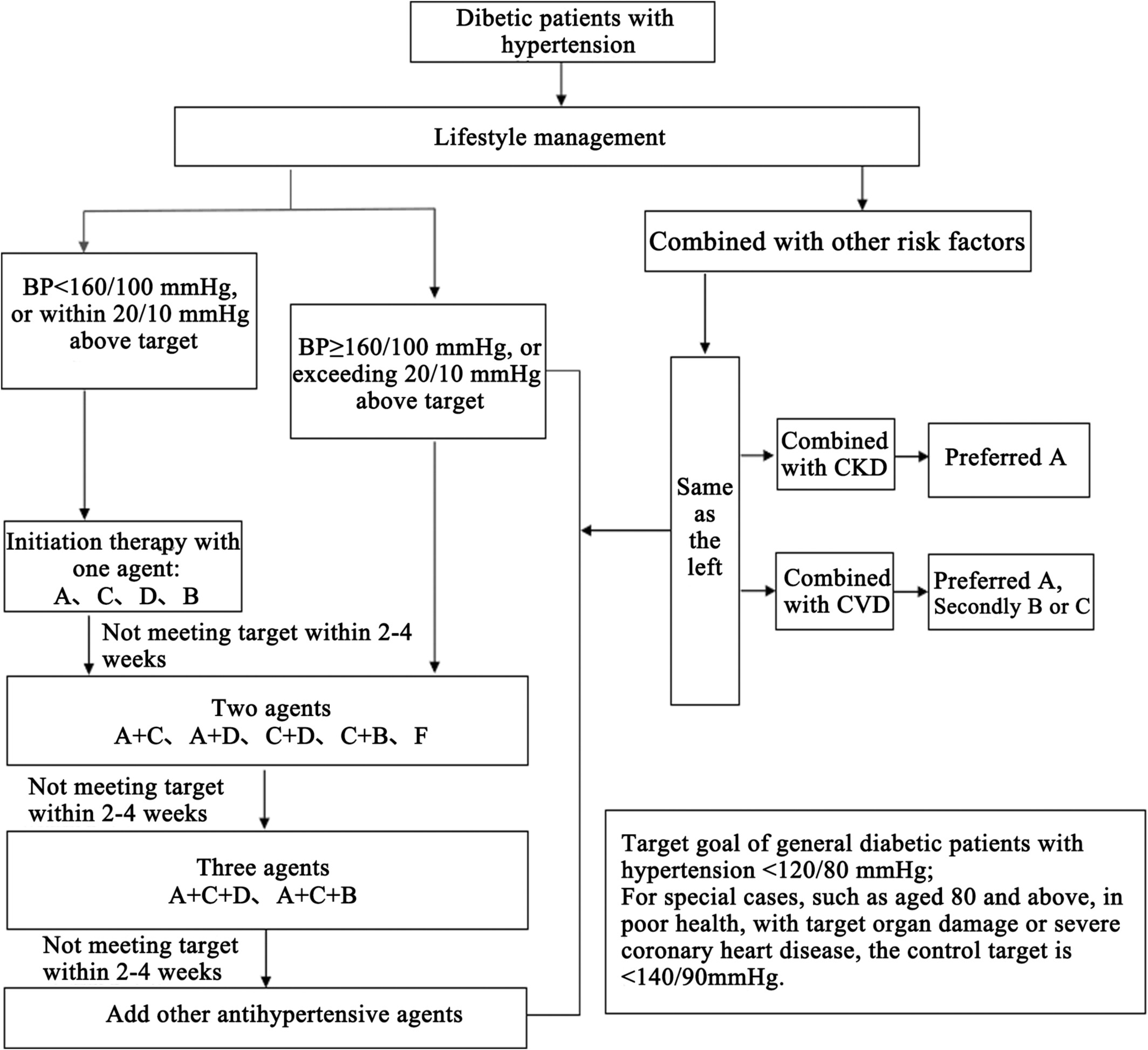
Management Guidelines for Diabetic Patients With Hypertension
- First Published: 22 June 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
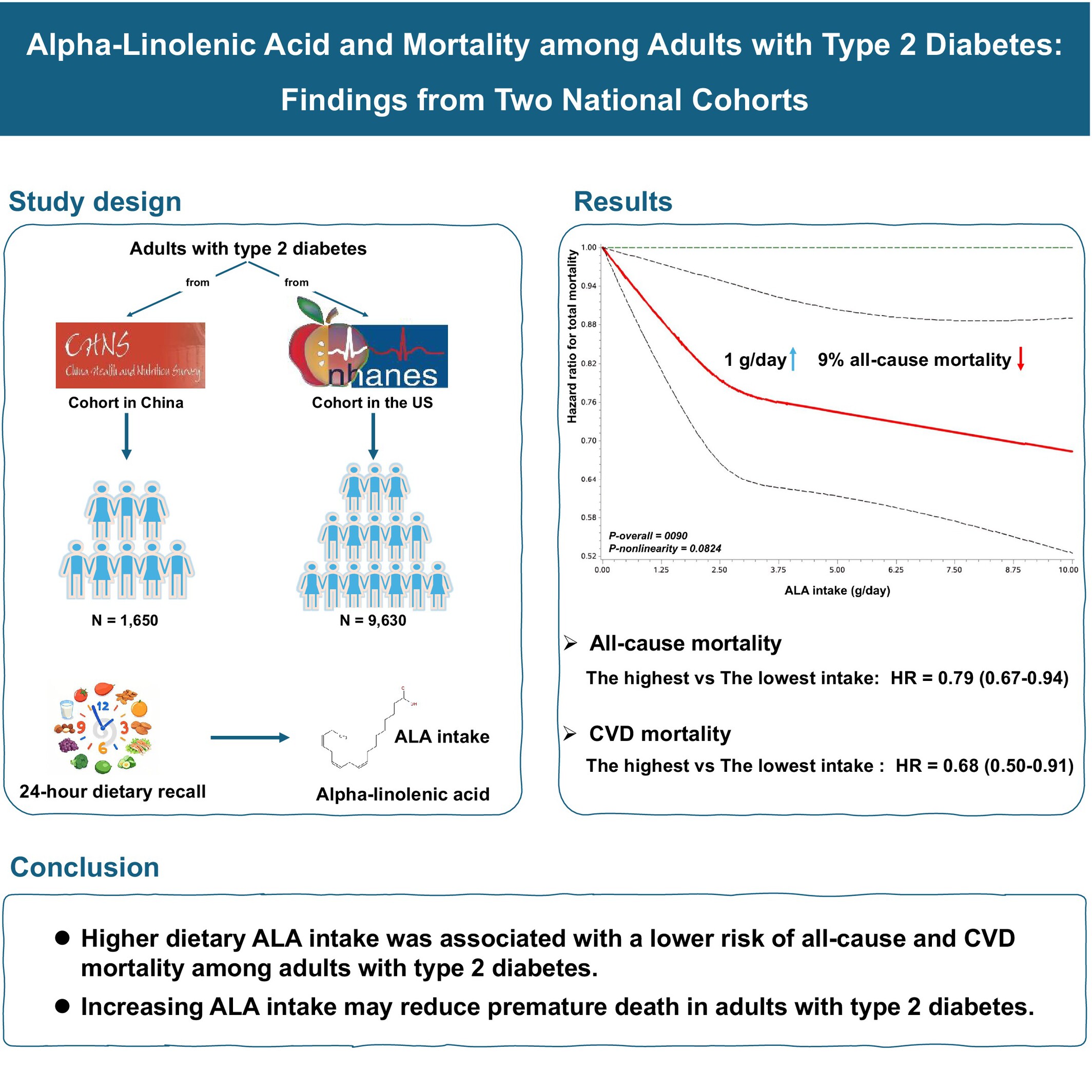
Alpha-Linolenic Acid and Mortality Among Adults With Type 2 Diabetes: Findings From Two National Cohorts
- First Published: 22 June 2025