Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
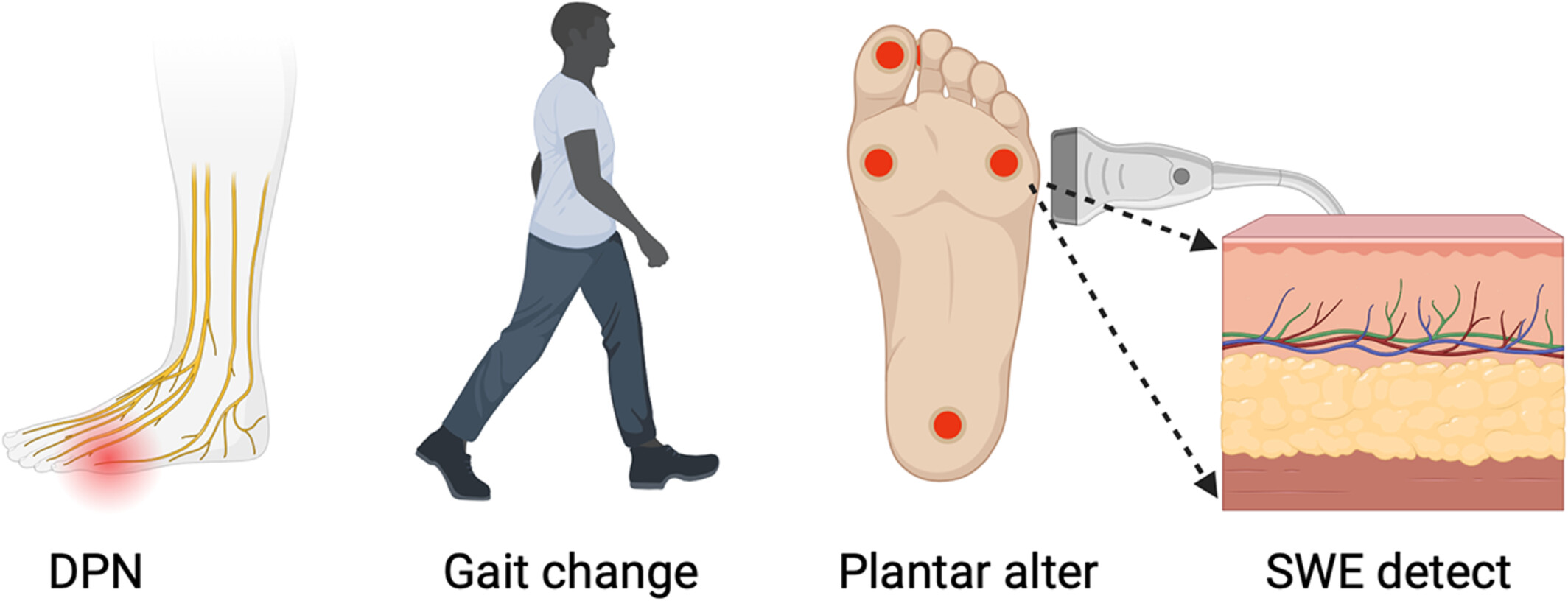
Plantar Tissue Characteristics in People With Diabetes With and Without Peripheral Neuropathy: A Novel Explanatory Model for DPN Risk Assessment
- First Published: 06 May 2025
Telemedicine's Impact on Diabetes Care During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cohort Study in a Large Integrated Healthcare System
- First Published: 12 May 2025
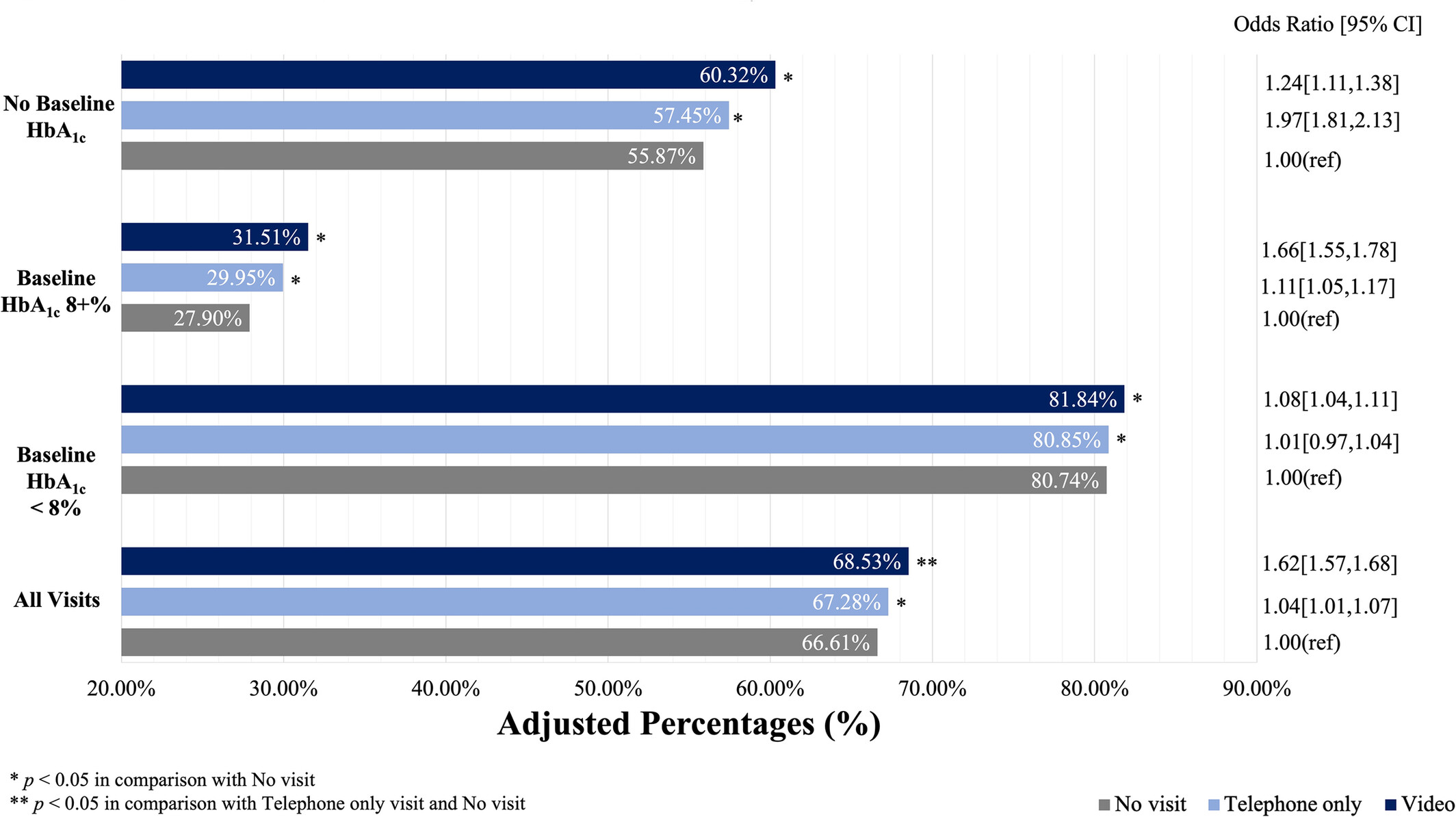
Adjusted association of pandemic telemedicine PCP visit with a HbA1c < 8% during the outcome period. Among those with an HbA1c measured, the proportion with an HbA1c < 8% in the second year of the COVID-19 pandemic was statistically significantly higher among people with telemedicine exposure in the prior year than those with no visits in the prior year (68.5% for video visits, 67.3% for telephone visits, 66.6% for no visits, p < 0.05).
Association of Serum Total Bilirubin to Cholesterol Ratio With Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- First Published: 13 May 2025
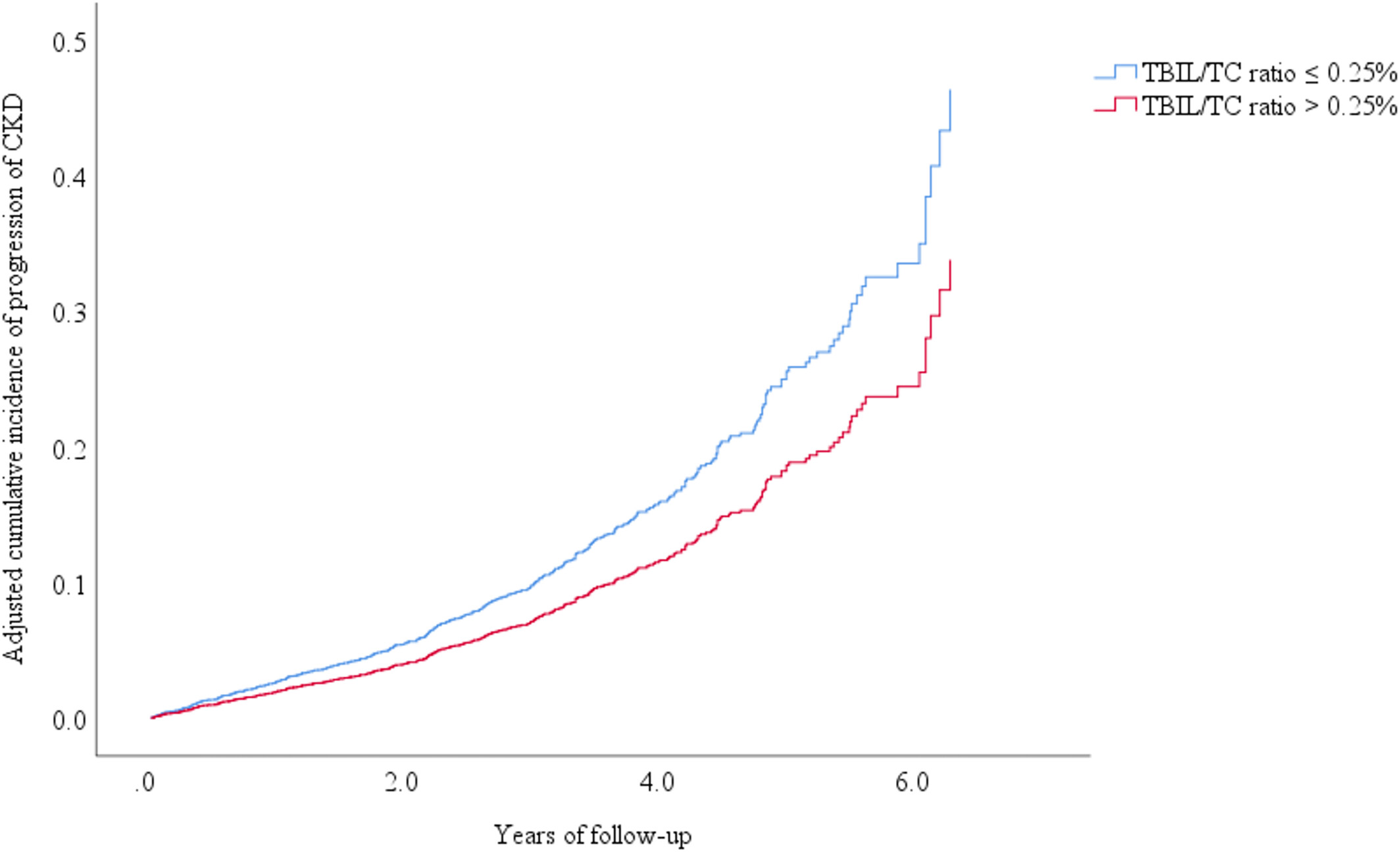
The time-based correlation between the bilirubin-lipid ratio and chronic kidney disease in people with diabetes has not been well elaborated. This retrospective cohort study reported that a high level of serum total bilirubin to total cholesterol ratio was significantly associated with a low risk for chronic kidney disease progression in patients with type 2 diabetes. This suggests that it may be a novel prognostic factor in these populations.
EDITORIAL
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
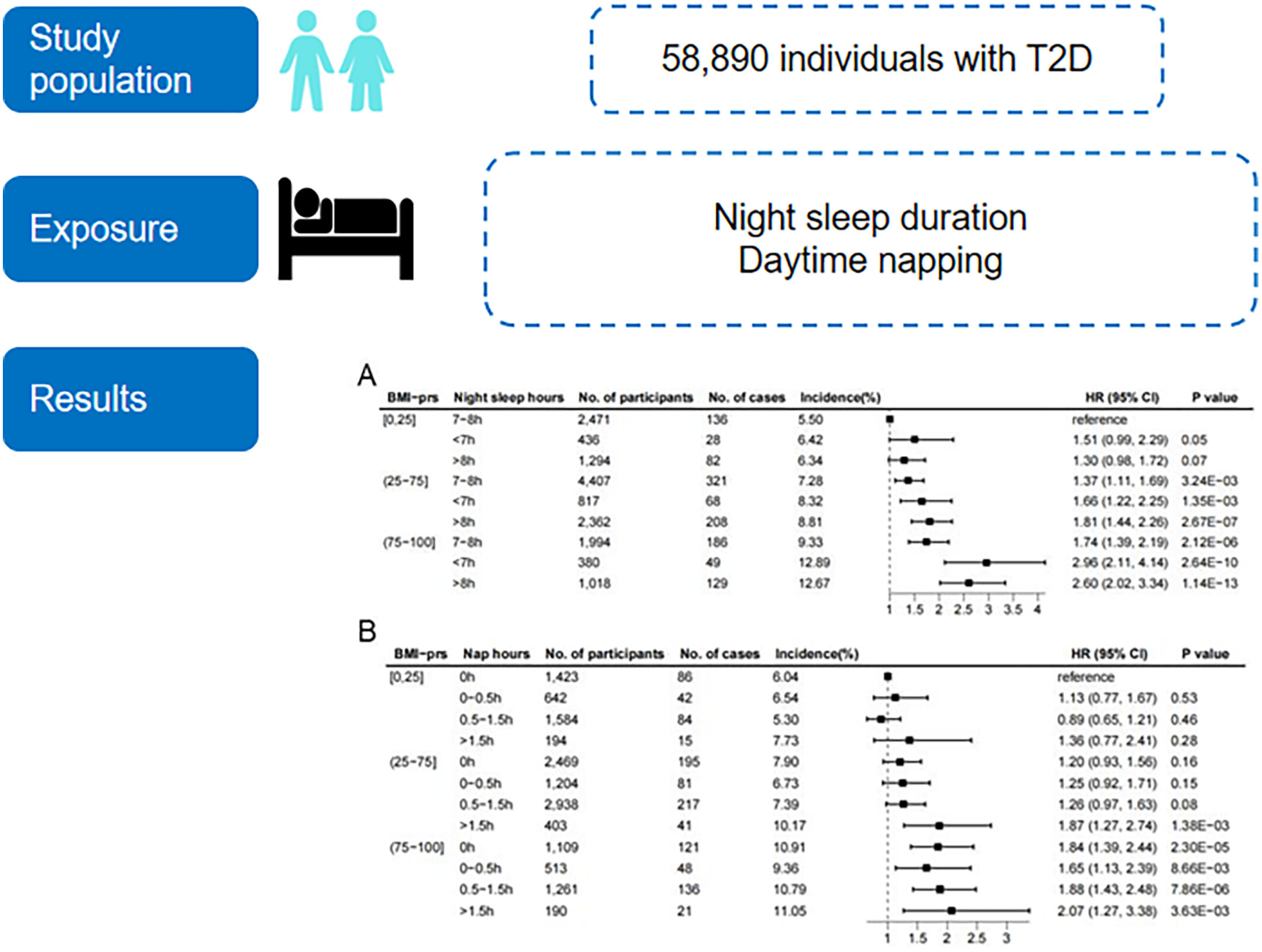
Sleep Phenotypes, Genetic Susceptibility, and Risk of Obesity in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A National Prospective Cohort Study
- First Published: 20 May 2025
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Potential Detrimental Interactions Between Metformin and Supplemental Dietary Fiber in Type 2 Diabetes
- First Published: 21 May 2025
Real-World Persistence and Characteristics of Type 2 Diabetes Patients Prescribed Semaglutide in Scotland
- First Published: 21 May 2025