Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Should glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist treatment be withheld in preoperative management?
- Pages: 712-713
- First Published: 19 September 2023
EDITOR'S RECOMMENDATION
Association of glycemic gap with stroke recurrence in patients with ischemic stroke
缺血性卒中患者血糖间隙与卒中复发的相关性
- Pages: 714-723
- First Published: 09 June 2023
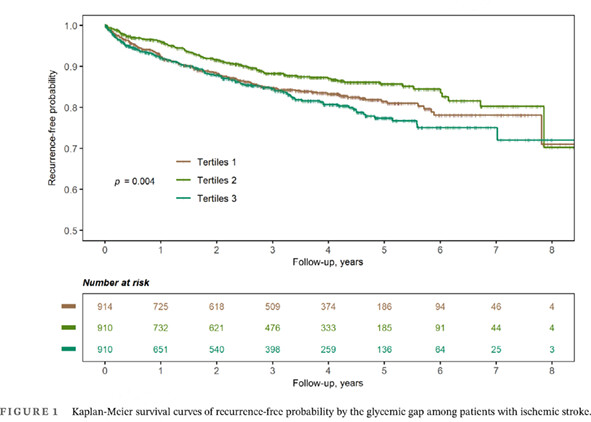
Highlights
- There was a U-shaped relationship between glycemic gap and stroke recurrence during a long-term follow-up in a Chinese ischemic stroke registry.
- Clinical physicians should remain vigilant in the fluctuation of glucose level and use individualized glucose control strategies in patients with ischemic stroke.
REVIEW ARTICLES
The impact of health literacy interventions on glycemic control and self-management outcomes among type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review
健康素养干预对2型糖尿病患者血糖控制和自我管理结果的影响:一项系统综述
- Pages: 724-735
- First Published: 05 July 2023
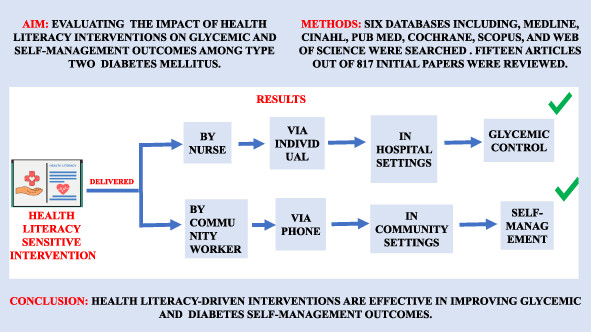
Highlights
- Health literacy (H)L-driven interventions were effective in controlling glycemic levels and improving diabetes self-management outcomes.
- The level of glycemic control and self-management skills were improved better through individual and telephone-based intervention, respectively, in comparing group intervention.
- Community worker led interventions were effective in improvements in diabetes knowledge and self-care behaviors; however, nurse-led interventions were more effective in glycemic control.
- Better glycemic control was achieved in hospital settings compared with outpatient settings.
- HL interventions yielded better improvement in self-management among people with a longer diabetes duration (more than 7 years) than those with short duration of diabetes.
- It was possible to achieve a significant reduction in HbA1c level after a 3-month intervention in hospital settings.
Mechanisms of bariatric surgery for weight loss and diabetes remission
减重手术减轻体重和缓解糖尿病的机制
- Pages: 736-752
- First Published: 13 July 2023
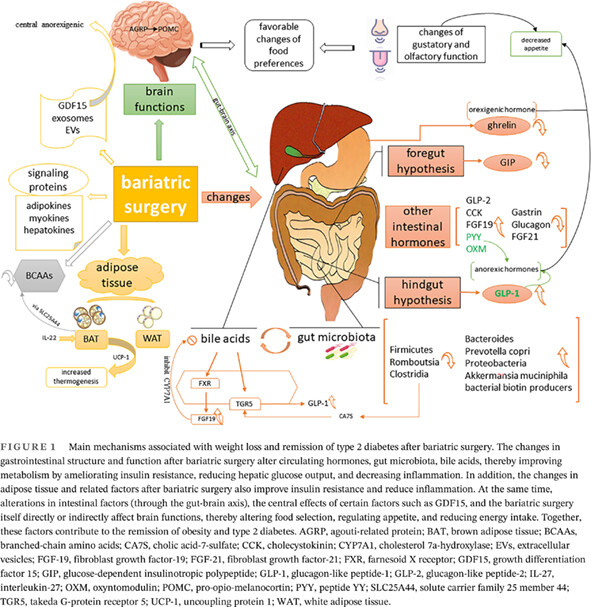
Highlights
- Controversial changes in intestinal hormones after bariatric surgery (BS) were summarized.
- The changes of signaling proteins involved in insulin resistance and the newly proposed changes in growth differentiation factor 15, exosomes, and extracellular vesicles after BS were elucidated.
- The interactions between bile acids and gut microbiota and the gut–brain axis play an indispensable role in BS.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Development and validation of a multivariable risk prediction model for identifying ketosis-prone type 2 diabetes
酮症倾向2型糖尿病多变量风险预测模型的建立与验证
- Pages: 753-764
- First Published: 10 May 2023
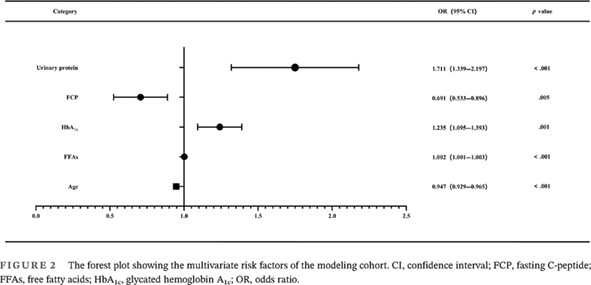
Highlights
- Ketosis-prone type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a novel type of diabetes mellitus, distinguished from type 1 diabetes mellitus and T2DM. Its clinical characteristics are complex and there is a lack of auxiliary tools for differential diagnosis.
- Ketosis-prone T2DM is a specific but common subtype in newly diagnosed T2DM patients in China, with specific clinical characteristics.
- Based on age, fasting C-peptide, free fatty acids, glycated hemoglobin A1c and urinary protein, our study provided an effective clinical risk prediction model for ketosis-prone T2DM, which could help for precise classification and management.
The effects of daily dose and treatment duration of metformin on the prevalence of vitamin B12 deficiency and peripheral neuropathy in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A multicenter cross-sectional study
二甲双胍日剂量和治疗时间对中国2型糖尿病患者维生素B12缺乏和周围神经病变患病率的影响:一项多中心横断面研究
- Pages: 765-776
- First Published: 13 June 2023
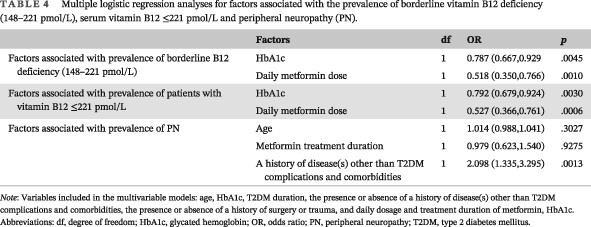
Highlights
- This is the first multicenter, cross-sectional study on the prevalence of vitamin B12 deficiency in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) receiving metformin treatment.
- About one out of five patients with T2DM receiving ≥1500 mg/day metformin could develop vitamin B12 deficiency.
- High daily dosage of metformin (≥1500 mg/day) played an important role in metformin-related vitamin B12 deficiency while not contributing to the risk of peripheral neuropathy.
Increased glutamate in type 2 diabetes in the Korean population is associated with increased plasminogen levels
韩国2型糖尿病患者谷氨酸升高与纤溶酶原水平升高有关
- Pages: 777-786
- First Published: 14 June 2023
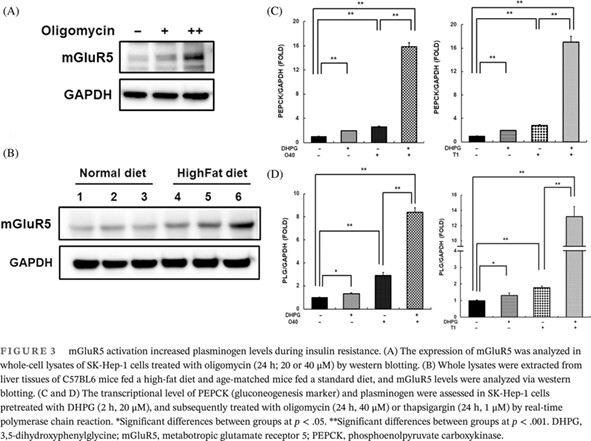
Highlights
- Increased glutamate is associated with the development of diabetes.
- Glutamate increases plasminogen (PLG) levels through glutamate metabotropic receptor 5 activation with various insulin resistance-related stresses.
- Glutamate inhibits the conversion of PLG to plasmin by increasing plasminogen activator inhibitor-1.
Weight loss and metabolic benefits of bariatric surgery in China: A multicenter study
减重手术的减重和代谢获益:一项中国多中心研究
- Pages: 787-798
- First Published: 06 July 2023
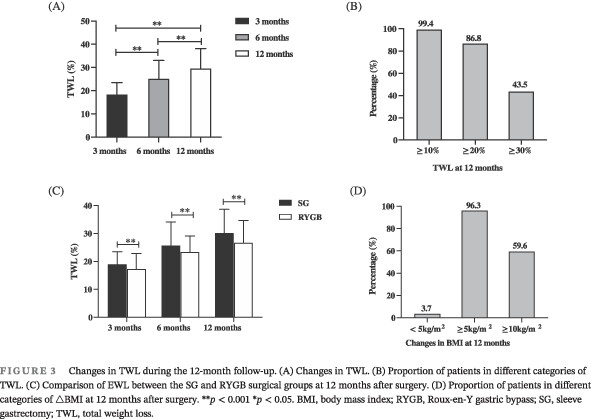
Highlights
Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy and laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass are effective for reducing weight and improving metabolic parameters in Chinese patients with obesity. These interventions resulted in improved glycemic control, as evidenced by decreased glycated hemoglobin levels, reduced insulin resistance, and improved cardiovascular profiles.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Bioinformatic and rare-variant collapsing analyses for type 1 and type 2 diabetes in the UK Biobank reveal novel pleiotropic susceptibility loci
- Pages: 799-802
- First Published: 01 August 2023









