Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Open Access
oa
Risks and benefits of vaccines in diabetes
- Pages: 806-807
- First Published: 26 September 2023
EDITOR'S RECOMMENDATION
Open Access
oa
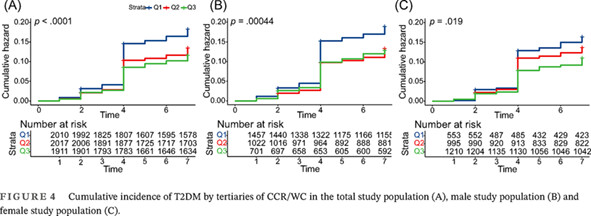
The serum creatinine to cystatin C to waist circumference ratios predicts risk for type 2 diabetes: A Chinese cohort study
血清肌酐/胱抑素C与腰围比例预测2型糖尿病的风险: 一项中国队列研究
- Pages: 808-816
- First Published: 05 July 2023
REVIEW ARTICLES
Open Access
oa
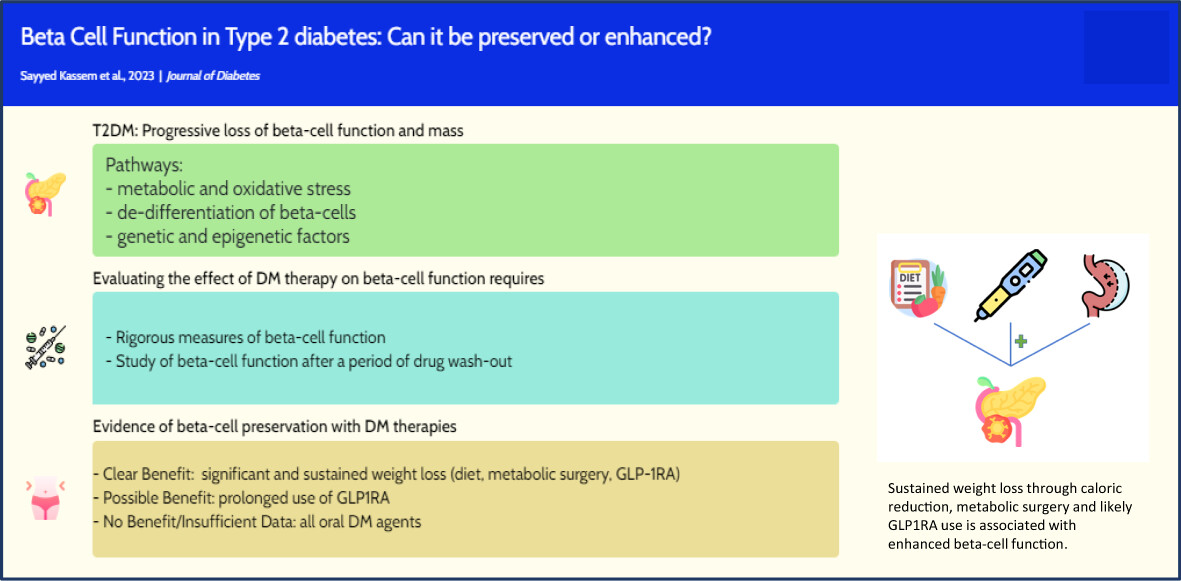
Beta-cell function in type 2 diabetes (T2DM): Can it be preserved or enhanced?
2型糖尿病患者的β细胞功能:能被保留或增强吗?
- Pages: 817-837
- First Published: 31 July 2023
Highlights
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is characterized by progressive loss of beta-cell function and mass. Numerous mechanisms of beta-cell failure are involved.
- Preservation and/or enhancement of beta-cell function is of great importance in delaying the progression of T2DM and the burden of its complications.
- Accurate evaluation of the effects of T2DM therapies on beta-cell function require assessments of beta-cell function following a washout period. This review focuses primarily on such assessments.
- Of all available therapies for T2DM, significant and sustained weight loss as well as prolonged therapy with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists are associated with preservation and perhaps enhancement of beta-cell function.
Open Access
oa
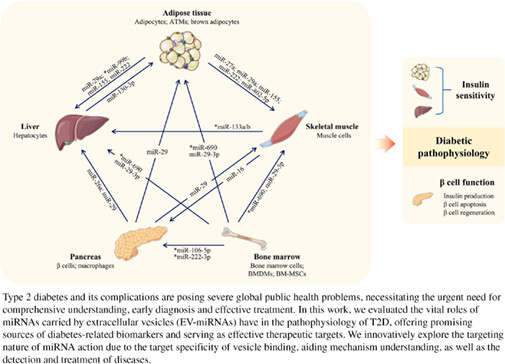
The role of miRNAs carried by extracellular vesicles in type 2 diabetes and its complications
外泌体miRNA在2型糖尿病及其并发症中的作用
- Pages: 838-852
- First Published: 16 August 2023
Highlights
- This review outlines the history of miRNA discovery and its major advances in the field of metabolism.
- We explore the roles of miRNAs in diabetes-related cognitive impairment.
- We innovatively propose that miRNAs also act with a certain organ-targeting specificity due to the organ-targeting nature of extracellular vesicles, which may aid disease detection and treatment and help interpret the mechanisms beneath.
- This review is highly concise and includes the latest research advances, allowing readers to gain a basic framework of the role of EV-miRNAs in T2D and its complications quickly.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Open Access
oa
Associations of blood biomarkers with arterial stiffness in patients with diabetes mellitus: A population-based study
糖尿病患者血液生物标志物与动脉硬化的关系: 一项基于人群的研究
- Pages: 853-865
- First Published: 16 June 2023
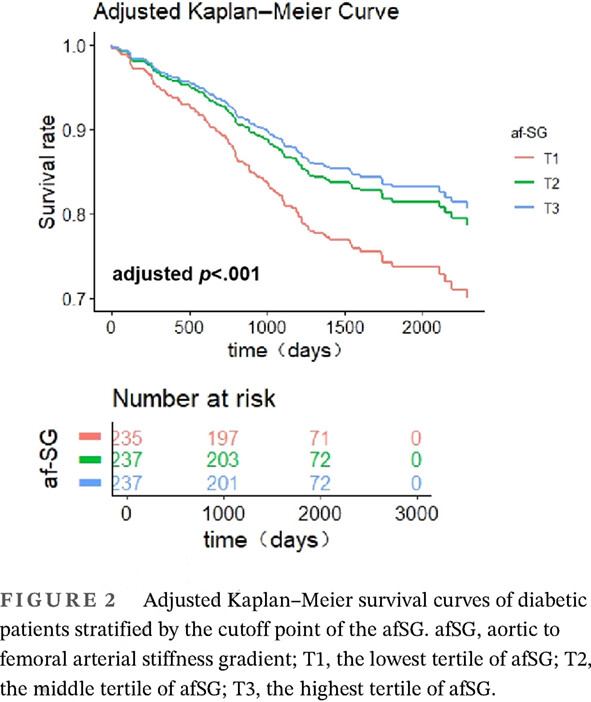
Highlights
- Few studies have investigated the association of large-scale biomarkers and pulse wave velocity (PWV) among diabetic patients.
- This study investigates the relationships of serum laboratory tests with PWV and explored the associations between PWV and all-cause mortality among diabetic patients.
- Certain biomarkers related to blood glucose monitoring, myocardial injury, and renal function significantly correlated with PWV among diabetic patients.
- Our research was the first to demonstrate that higher aortic-femoral arterial stiffness gradient was associated with lower all-cause mortality in diabetic patients, independent of a wide range of covariates.
Open Access
oa
Protective effects of nattokinase against microvasculopathy and neuroinflammation in diabetic retinopathy
纳豆激酶对糖尿病视网膜病变微血管病变和神经炎症的保护作用
- Pages: 866-880
- First Published: 04 July 2023
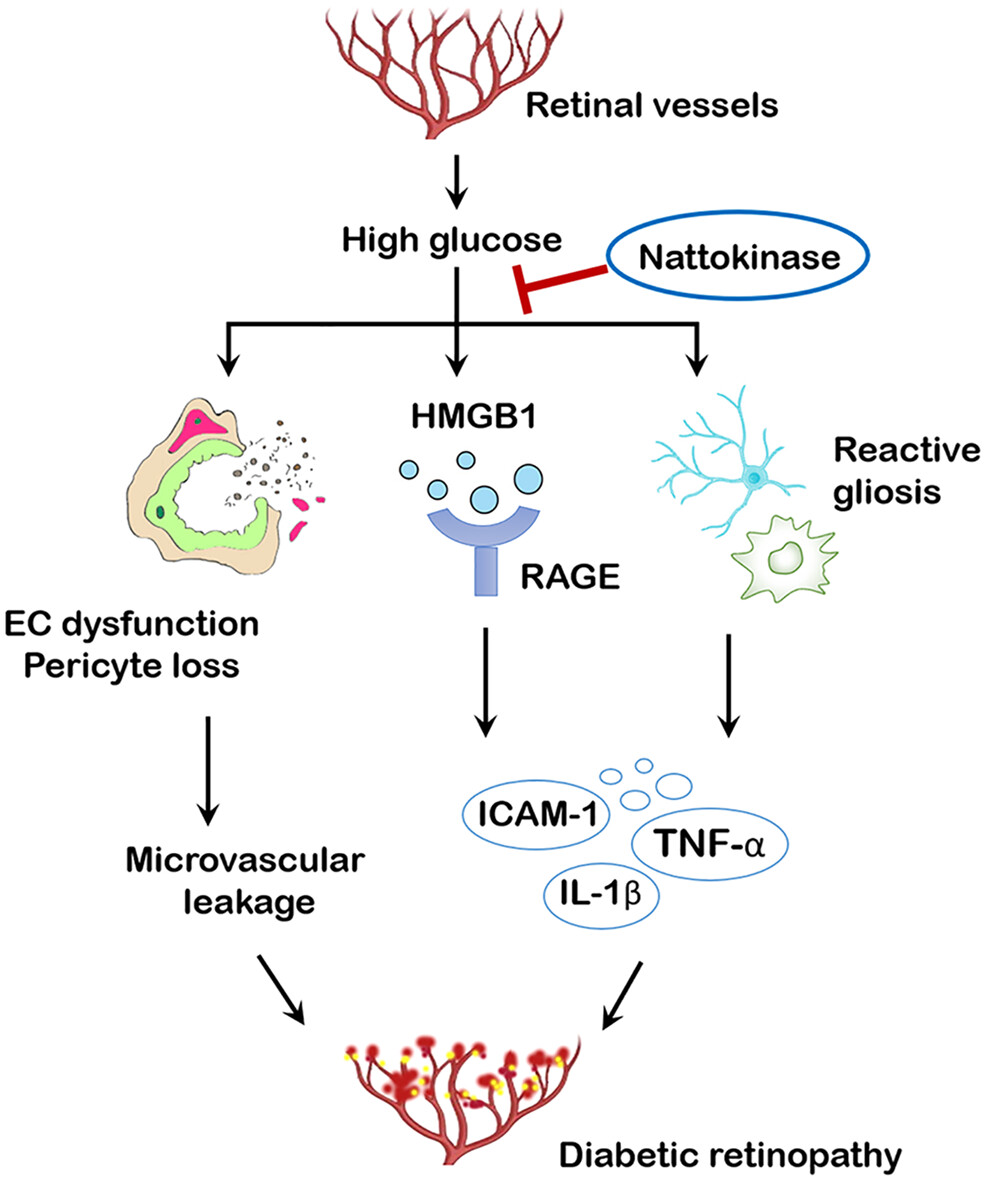
Highlights
- Nattokinase rescued endothelial dysfunction and pericyte loss in the diabetic retina.
- Nattokinase attenuated diabetes-induced retinal inflammation and neurodegeneration.
- High mobility group box 1 signaling was involved in nattokinase-mediated retinal protection.
- Nattokinase might be developed as a pharmaceutical product for early diabetic retinopathy.
Open Access
oa
Association between serum LDL-C concentrations and risk of diabetes: A prospective cohort study
血清低密度脂蛋白胆固醇浓度与糖尿病风险之间的关联: 一项前瞻性队列研究
- Pages: 881-889
- First Published: 17 July 2023
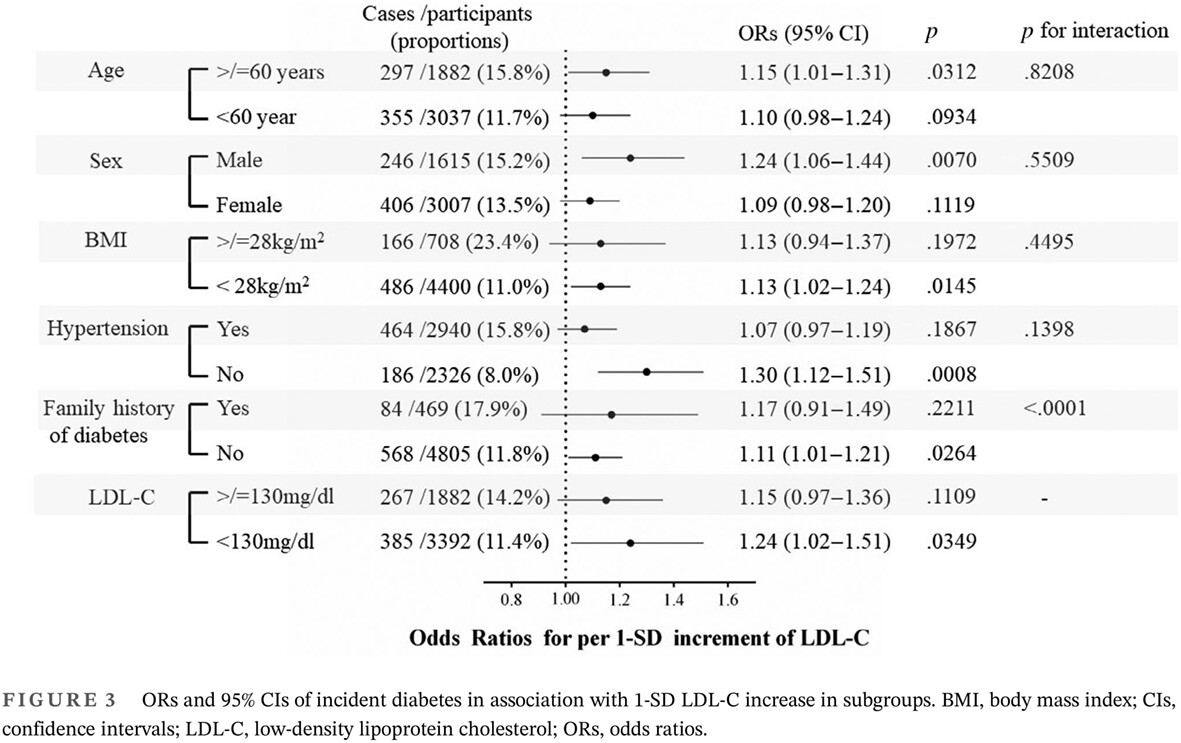
Highlights
- Serum low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels were positively and significantly associated with a high risk of incident diabetes.
- Even in participants with normal LDL-C levels (<130 mg/dL), a 1-SD increase in LDL-C levels was significantly associated with a higher risk of diabetes development.
- More attention and health management should be implemented on patients with elevated LDL-C to reduce diabetes risk.
Open Access
oa
Computerized nailfold video-capillaroscopy in type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study on 102 outpatients
计算机化甲襞视频毛细血管镜在2型糖尿病中的运用: 对102例门诊患者的横断面研究
- Pages: 890-899
- First Published: 09 July 2023
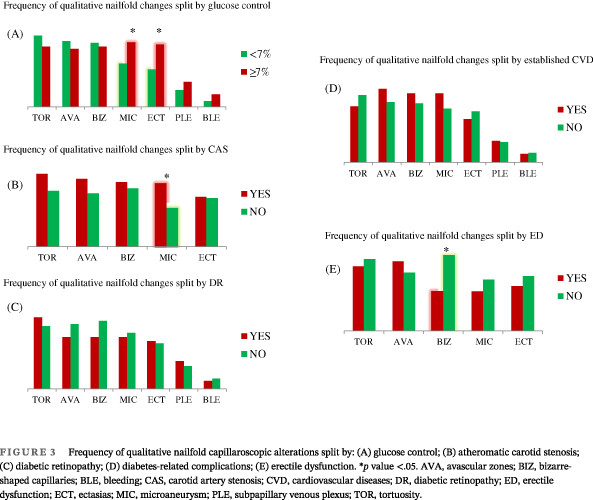
Highlights
- Patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) are prone to developing chronic diabetes-related complications at the microvascular and macrovascular levels. The Computerized Nailfold Video-Capillaroscopy (CNVC) provides specific information on both quantitative and qualitative characteristics of microvasculature at the level of fingers.
- The present study aims to characterize nailfold microvascular changes in T2D patients and better describe specific nailfold patterns related to poor glucose control (ie, HbA1c ≥7%) and chronic complications, such as diabetic retinopathy, chronic kidney impairment, atherosclerosis, established cardiovascular disease, and erectile dysfunction (ED). This cross-sectional cohort study was conducted on 102 consecutive and unselected outpatients with T2D. Patients underwent a comprehensive assessment of nailfold microvasculature by CNVC.
- Specific patterns of nailfold microvascular alteration are observed in T2D, such as tortuosity, ectasias, microaneurysms, and enlarged capillaries. Poor glycemic control is associated with dilated and longer capillaries and a higher frequency of ectasias and microaneurysms. Men with ED had fewer bizarre-shaped capillaries (a sign of impaired angiogenesis), and those with clinical signs of atherosclerosis (ie, carotid stenosis >20%) had more microaneurysms. Future studies are needed to understand better the role of the CNVC in identifying at-risk patients requiring specific therapeutic management to prevent the onset and evolution of severe chronic complications.
Open Access
oa
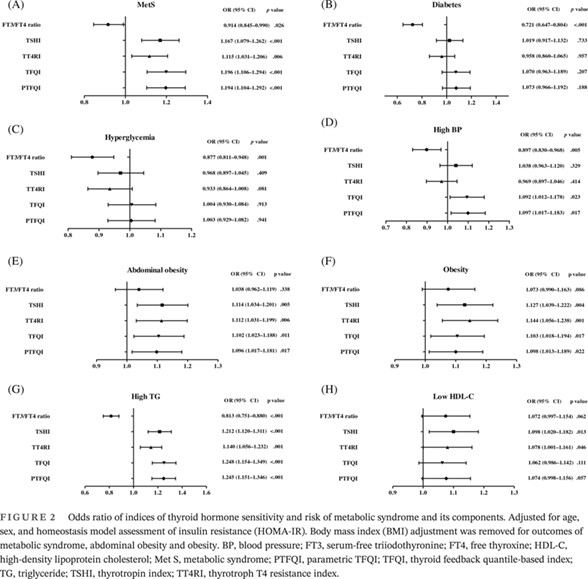
Sensitivity to thyroid hormone and risk of components of metabolic syndrome in a Chinese euthyroid population
中国甲状腺功能正常人群对甲状腺激素的敏感性和代谢综合征组分的风险
- Pages: 900-910
- First Published: 10 July 2023
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Open Access
oa
Should patient enrollment criteria for anti-VEGF phase III trials be reconsidered
- Pages: 911-912
- First Published: 20 September 2023