Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
The potential of β-cell growth promotion, continued
- Pages: 366-367
- First Published: 27 April 2023
EDITOR'S RECOMMENDATION
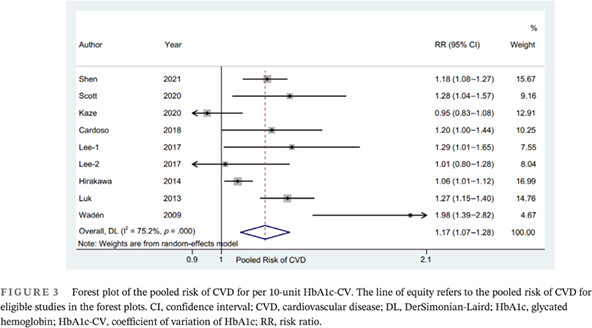
Higher glucose fluctuation is associated with a higher risk of cardiovascular disease: Insights from pooled results among patients with diabetes
较高的血糖波动与较高的心血管疾病风险相关:来自糖尿病患者汇总分析的观点
- Pages: 368-381
- First Published: 18 April 2023
Highlights
- This study is the first registered meta-analysis with three different insights to explore the relationship between the glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) variability and the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD).
- Our study suggests that the higher glucose fluctuation is significantly associated with the higher CVD risk in diabetes patients based on HbA1c variability.
- The CVD risk associated with per HbA1c-SD might be higher among patients type 1 diabetes than patients with type 2 diabetes.
REVIEW ARTICLES
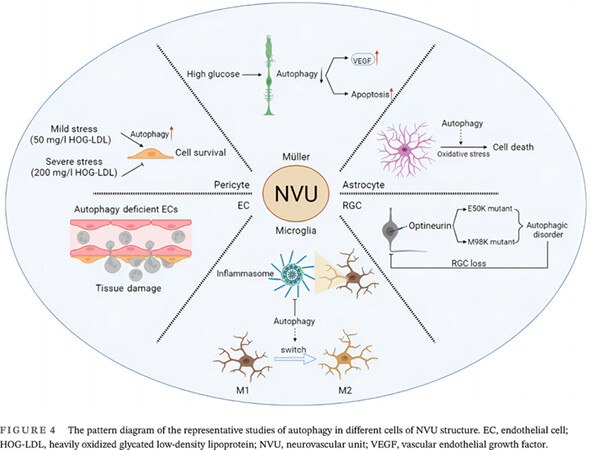
Autophagy in the retinal neurovascular unit: New perspectives into diabetic retinopathy
视网膜神经血管单元自噬:糖尿病视网膜病变的新视角
- Pages: 382-396
- First Published: 02 March 2023
Highlights
Autophagy is closely related to retinal neurovascular units in diabetes retinopathy. Different cells participate in the occurrence and development of diseases through autophagy, and targeted autophagy may be a new direction of treatment in the future.
- Emphasized the close relationship between diabetic retinopathy (DR) and autophagy
- Summarized the autophagy molecular mechanism of DR pathophysiology in the neurovascular unit
- Proposed potential targets for DR treatment
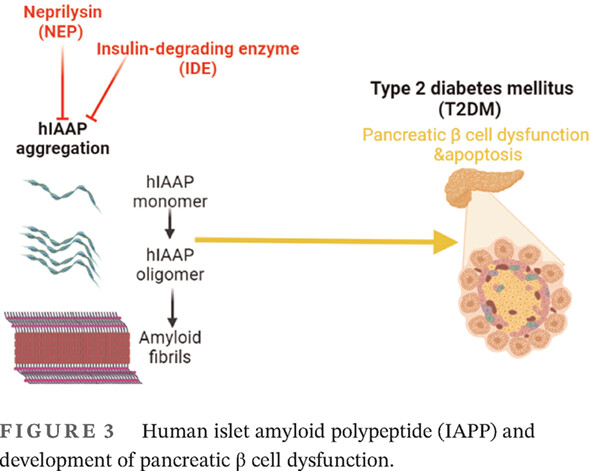
Effects of neprilysin and neprilysin inhibitors on glucose homeostasis: Controversial points and a promising arena
脑啡肽酶和脑啡肽酶抑制剂对葡萄糖稳态的影响:一个有争议的观点和有前景的领域
- Pages: 397-408
- First Published: 19 April 2023
Highlights
- Neprilysin (NEP) inhibitors may lead to beneficial effects through inhibition of NEP, which involves impairment of glucose homeostasis through modulation of insulin resistance and the development of pancreatic β cell dysfunction as observed in type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- NEP increases dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4) activity and contributes to increasing active glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) proteolysis so NEP inhibitors may improve glycemic control through increasing endogenous GLP-1 activity and reduction of DPP4 activity.
- NEP inhibitors have beneficial effects on glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity by increasing oxytocin and various substrates including GLP-1.
- NEP inhibitors may lead to a detrimental effect on insulin sensitivity and glucose homeostasis as well as pancreatic β cell dysfunction through different mechanisms including augmentation of some substrates and pancreatic amyloid deposition.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
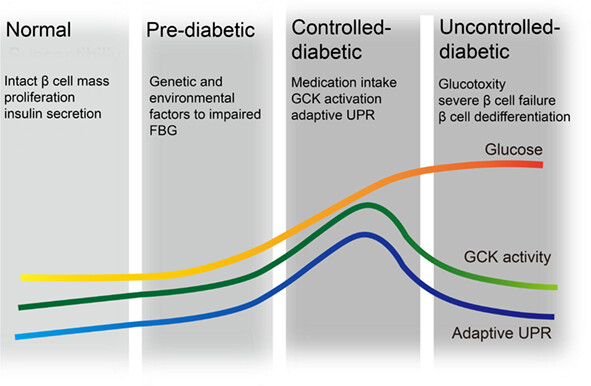
β-Cell glucokinase expression was increased in type 2 diabetes subjects with better glycemic control
血糖控制较好的2型糖尿病患者β细胞葡萄糖激酶表达增加
- Pages: 409-418
- First Published: 20 March 2023
Highlights
- A significant upregulation of glucokinase (GCK) expression was found in type 2 diabetes (T2D) subjects with adequate glucose control, but such increase was undetected in T2D with poor glycemic control.
- A strong positive correlation between GCK levels and spliced X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1s)/activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) expressions was observed in β-cells from T2D patients.
- Successful GCK activation to induce adaptive unfolded protein response in human β-cells might be an adaptive mechanism for maintaining appropriate glycemia.
Effectiveness, safety, initial optimal dose, and optimal maintenance dose range of basal insulin regimens for type 2 diabetes: A systematic review with meta-analysis
基础胰岛素治疗2型糖尿病的有效性、安全性、初始最佳剂量和最佳维持剂量范围:一项meta分析的系统综述
- Pages: 419-435
- First Published: 10 April 2023
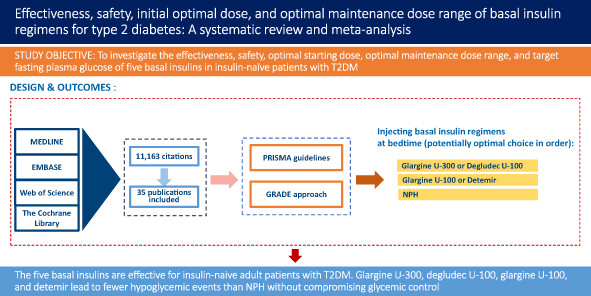
Highlights
This is a systematic review and meta-analysis. MEDLINE, EMBASE, Web of Science, and the Cochrane Library were searched from January 2000 to February 2022. Among 11,163 citations retrieved, 35 publications met the pre-planned criteria. The five basal insulins are effective for insulin-naive adult patients with T2DM. Glargine U-300, degludec U-100, glargine U-100, and detemir lead to fewer hypoglycemic events than NPH without compromising glycemic control.
Association of obesity under different metabolic status with adverse outcomes in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia: A retrospective cohort study
慢性髓系白血病患者不同代谢状态下肥胖与不良结局的相关性:一项回顾性队列研究
- Pages: 436-447
- First Published: 28 April 2023
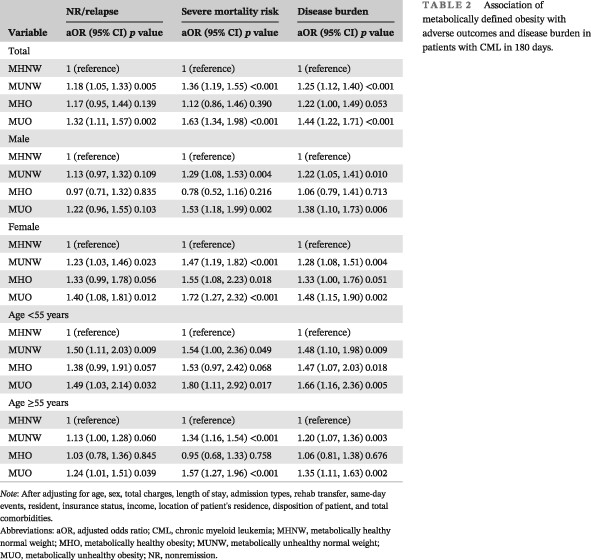
Highlights
- To our knowledge, our study is the first to date to investigate the association between metabolically defined obesity and adverse outcomes in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML).
- Metabolic abnormalities were associated with adverse outcomes in patients with CML, irrespective of obesity status.
- There were sex modifications in metabolically defined obesity and the nonremission/relapse risk of CML.
The use of nomogram for detecting mild cognitive impairment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
使用列线图筛查2型糖尿病轻度认知障碍
- Pages: 448-458
- First Published: 13 April 2023
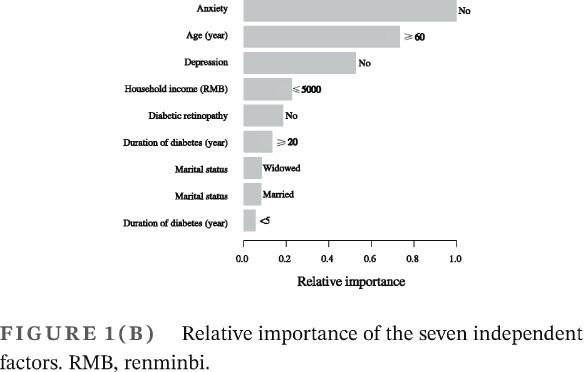
Highlights
- Almost one in three patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus suffered from mild cognitive impairment.
- Age, marital status, household income, diabetes duration, diabetic retinopathy, anxiety, and depression were associated with mild cognitive impairment.
- Nomograms could provide a clinical basis for detecting mild cognitive impairment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.









