Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
EDITOR'S RECOMMENDATION
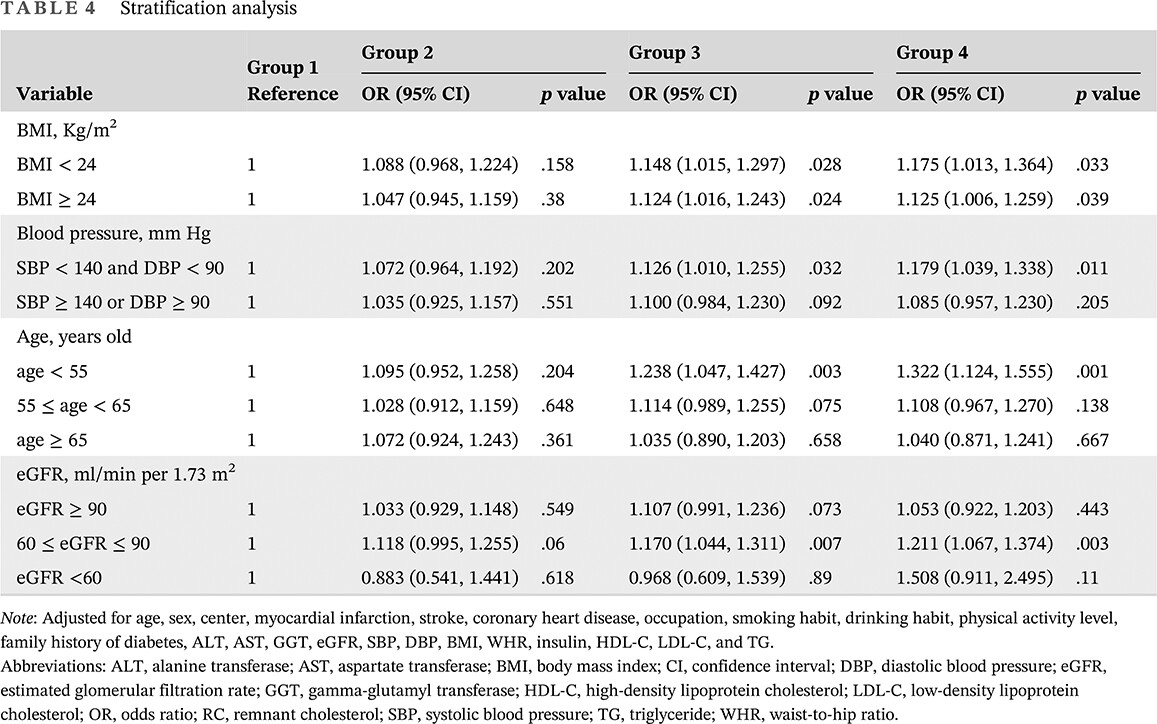
Remnant cholesterol is independently associated with diabetes, even if the traditional lipid is at the appropriate level: A report from the REACTION study
即使传统脂质处于适当水平, 残留胆固醇与糖尿病独立相关:来自REACTION研究的报告
- Pages: 204-214
- First Published: 05 February 2023
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
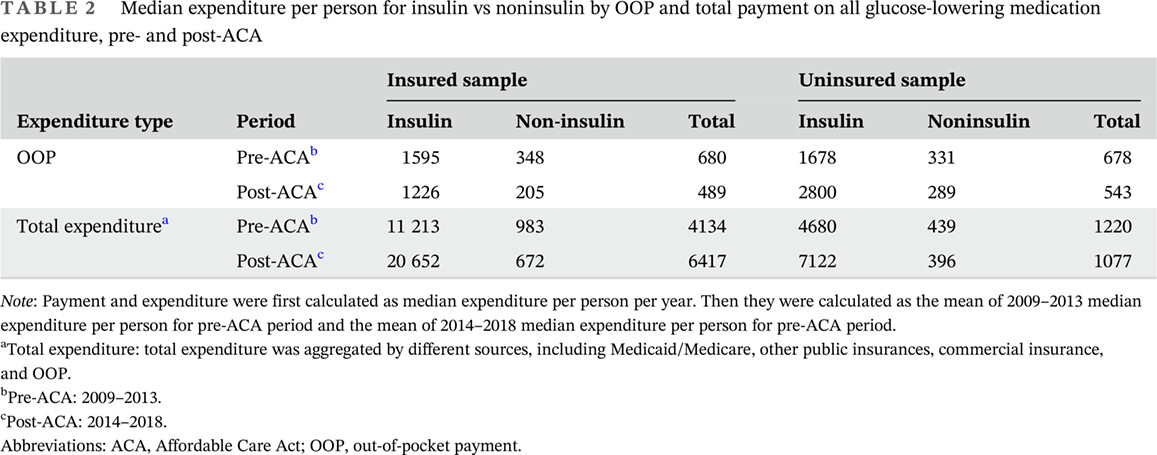
Exacerbation of financial burden of insulin and overall glucose-lowing medications among uninsured population with diabetes
在无保险的糖尿病人群中,胰岛素和降糖药物的经济负担正在加重
- Pages: 215-223
- First Published: 07 February 2023
Highlights
- Approximately 7.4 million Americans with diabetes use one or more formulations of insulin and the price of insulin tripled from 2002 to 2013. There are limited studies to explore the impact of insulin price, particularly on the uninsured population.
- For insured people, there was little impact on the out-of-pocket (OOP) payment for patients with diabetes using insulin treatment during the insulin price rise. The burden was borne mainly by insurance.
- When the high insulin price issue came into the uninsured population, the financial burden became urgent because the consequences of rationing insulin are deadly. After the Affordable Care Act was enacted, the uninsured population had $403.96 and $143.64 more OOP payments than people with public and private insurance, respectively.
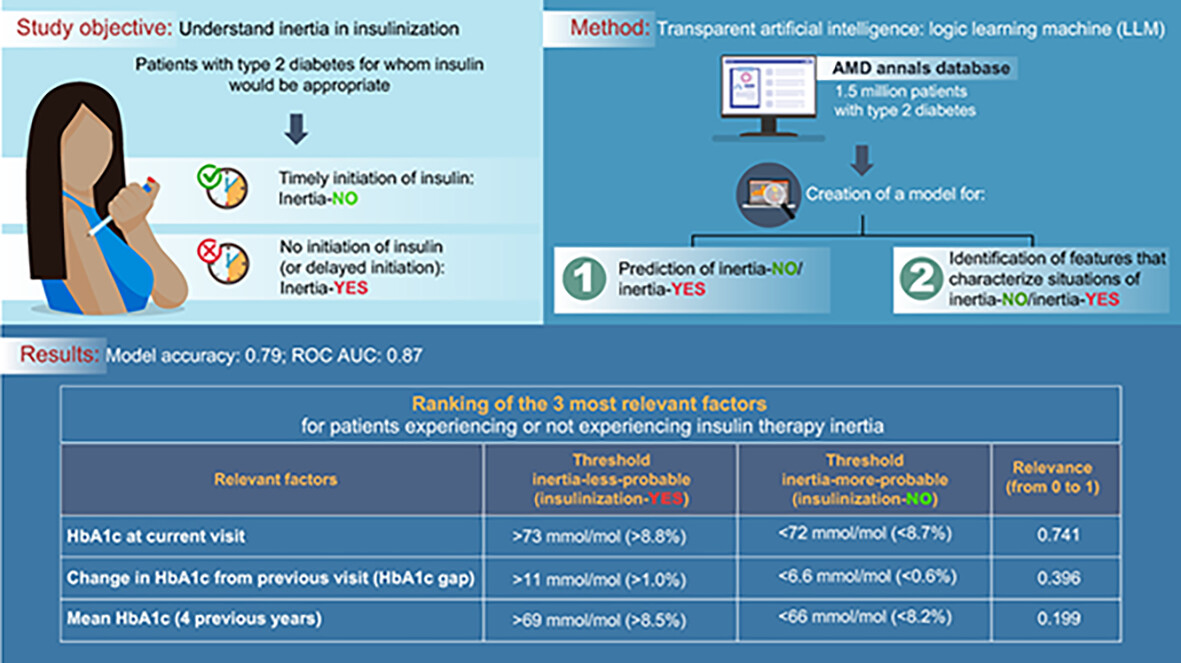
Transparent machine learning suggests a key driver in the decision to start insulin therapy in individuals with type 2 diabetes
透明机器学习预测决定2型糖尿病患者开始胰岛素治疗的关键驱动因素
- Pages: 224-236
- First Published: 08 March 2023
Highlights
ML suggests that when the HbA1c gap from a previous visit is >11 mmol/mol (1.0%) there is a greater probability that insulin therapy will be initiated, but when HbA1c gap is <6.6 mmol/mol (0.6%), a timely initiation of insulin therapy is less probable. Furthermore, for individuals initiated on insulin in a timely manner, the HbA1c gap is systematically higher than for those patients who have experienced clinical inertia. This key driver correlated with insulin therapy initiation could help combat clinical inertia.
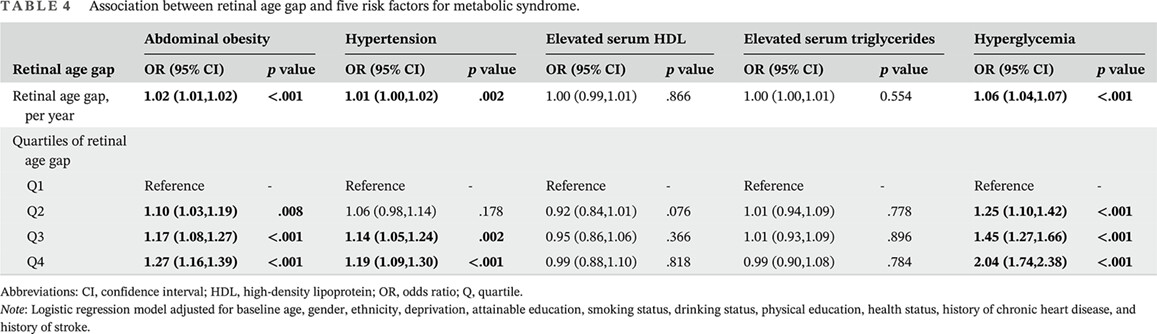
The Association of Retinal age gap with metabolic syndrome and inflammation
视网膜年龄差与代谢综合征和炎症的关系
- Pages: 237-245
- First Published: 14 March 2023
Sex differences in risk factors for end-stage kidney disease and death in type 2 diabetes: A retrospective cohort study
2型糖尿病终末期肾病和死亡危险因素的性别差异:一项回顾性队列研究
- Pages: 246-254
- First Published: 13 February 2023
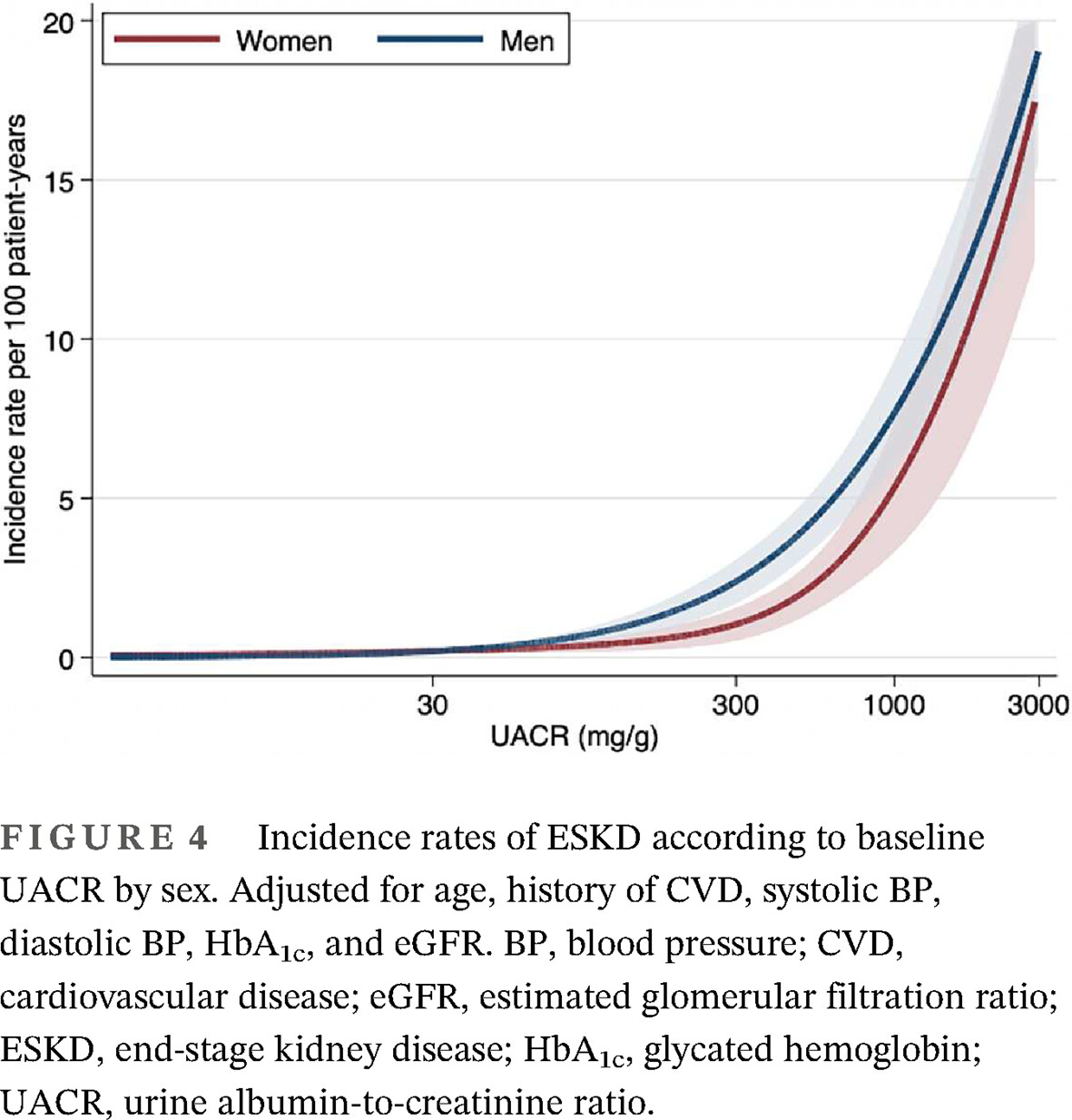
Highlights
- Sex differences are observed in the progression of chronic kidney disease; however, it is uncertain whether sex is associated with the risk of kidney failure in type 2 diabetes.
- In this multicenter cohort study, men had a higher risk of end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) than women, and moderately increased albuminuria was strongly associated with sex difference in developing ESKD in patients with type 2 diabetes.
- Sex differences may affect the risk of kidney disease progression because of type 2 diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes management: Room for improvement
1型糖尿病管理的改进空间
- Pages: 255-263
- First Published: 17 February 2023
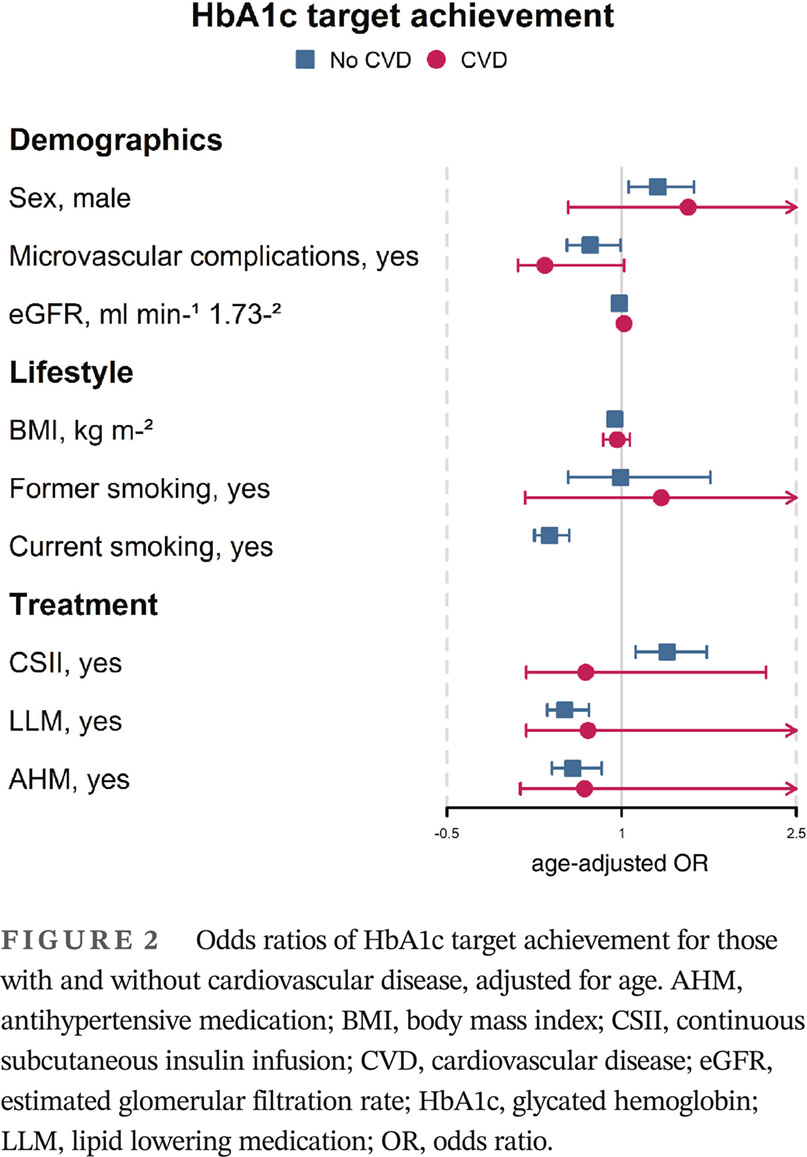
Highlights
- Achievement of glycemic, lipid, and blood pressure targets are suboptimal.
- Individuals with type 1 diabetes and cardiovascular disease (CVD) have more difficulty reaching treatment targets than individuals with diabetes without CVD.
- More consideration may be required for individuals with a previous cardiovascular event and type 1 diabetes.
Assessment of subclinical left ventricular systolic dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes: Relationship with HbA1c and microvascular complications
2型糖尿病患者亚临床左心室收缩功能障碍的评估:与糖化血红蛋白和微血管并发症的关系
- Pages: 264-274
- First Published: 22 February 2023
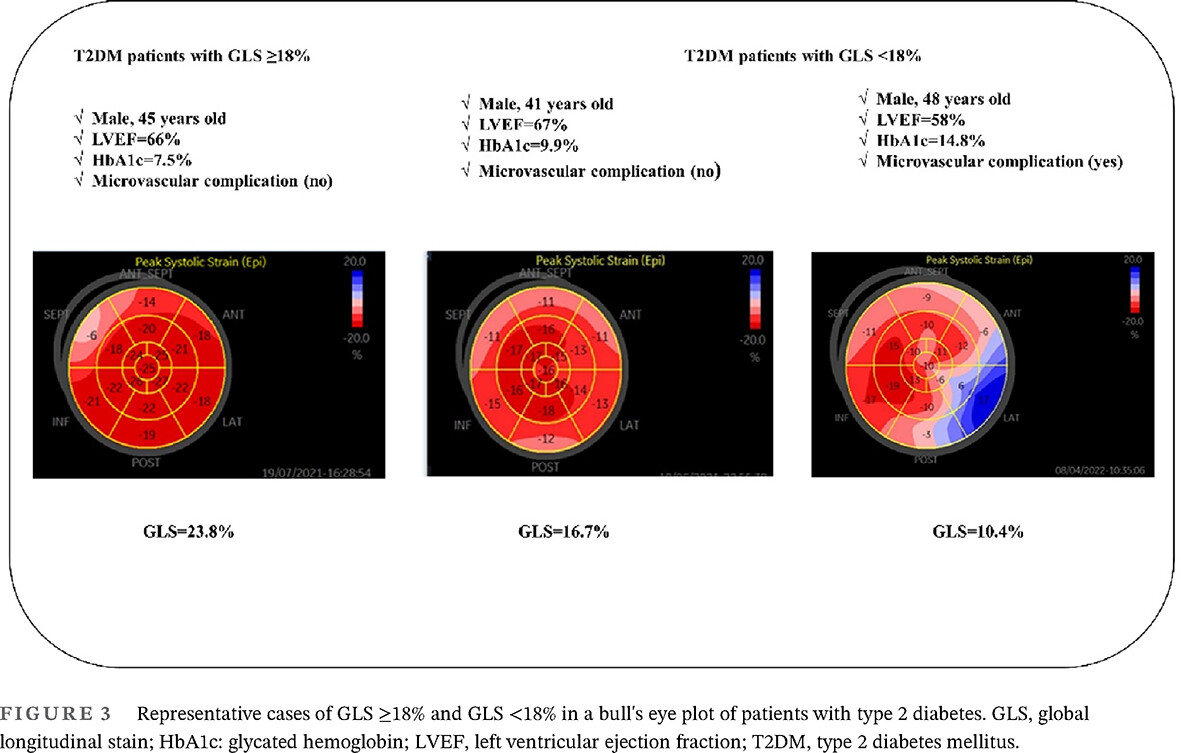
Highlights
In asymptomatic type 2 diabetic patients with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction, a negative correlation of glycated hemoglobin with subclinical left ventricular systolic dysfunction was revealed. Furthermore, glycated hemoglobin may make prognostic significance for the progression of myocardial damage.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Association of serum sodium levels and diabetes: A critical analysis
- Pages: 275-276
- First Published: 03 February 2023
RESEARCH LETTER
Expansion of human alpha-cell area is associated with a higher maximum body mass index before the onset of type 2 diabetes
- Pages: 277-282
- First Published: 26 February 2023
Highlights
- We examined whether maximum body mass index (BMI) before the onset of diabetes (MBBO) affects histological findings of islet cells.
- We divided patients into two groups according to an MBBO cutoff of 25 kg/m2 or BMI cutoff of 21 kg/m2. We compared immunohistochemical parameters between the MBBO groups or BMI groups.
- The relative alpha-cell area in the high MBBO group was significantly higher than that in the low MBBO group. There was no difference in the other parameters between the MBBO groups or BMI groups.