Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Serum sodium as a diabetes risk factor?
- Pages: 84-85
- First Published: 16 February 2023
EDITOR'S RECOMMENDATION
Noninsulin-based antihyperglycemic medications in patients with diabetes and COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis
糖尿病合并COVID-19患者的非胰岛素类降糖药物治疗:一项系统综述和荟萃分析
- Pages: 86-96
- First Published: 23 January 2023
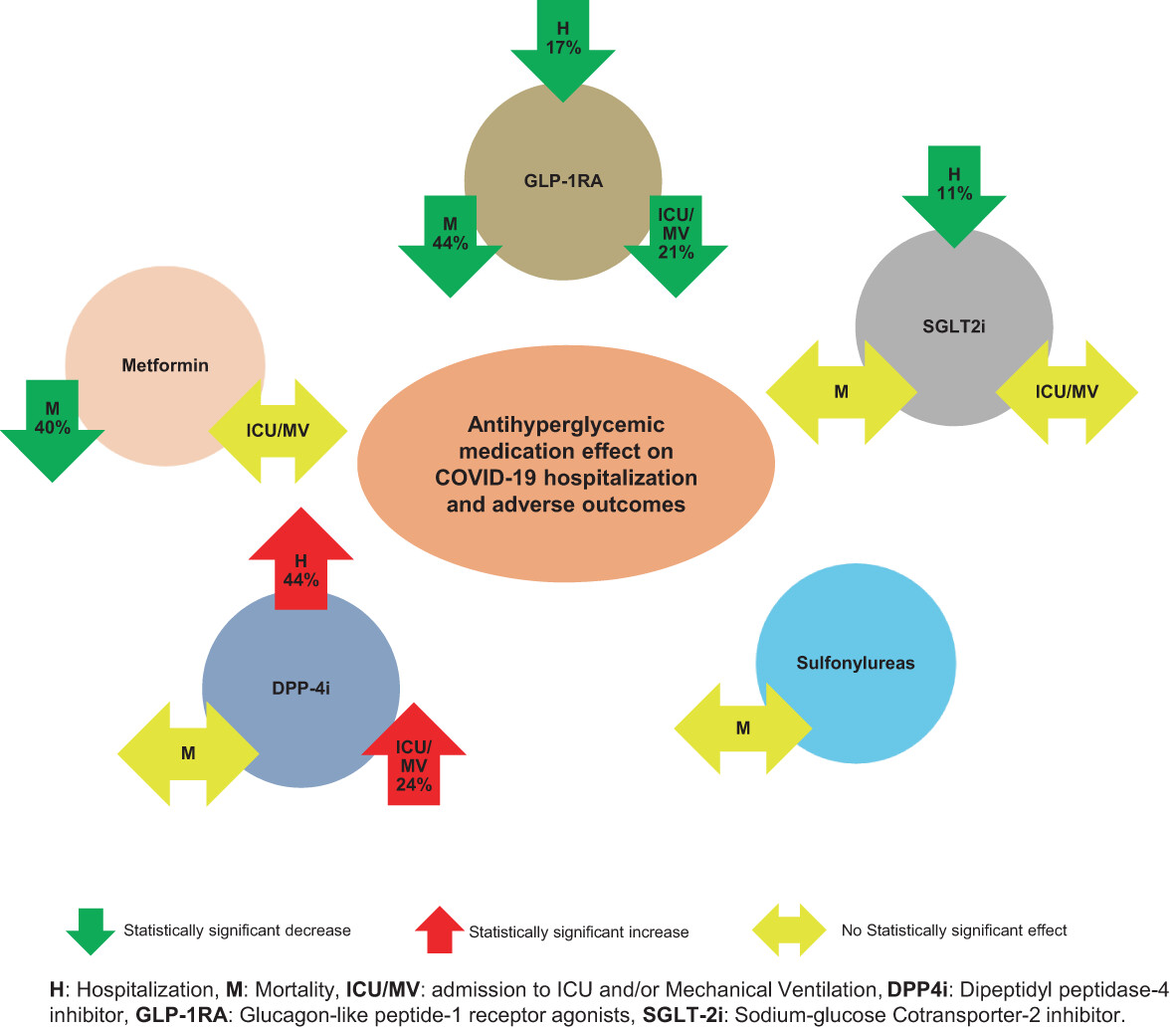
Highlights
- Metformin was associated with statistically significantly lower overall mortality for inpatients and outpatients.
- Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor use was associated with statistically significant higher hospitalization risk and higher risk of intensive care unit (ICU) admissions and/or mechanical ventilation.
- There was a statistically significant decrease in hospitalization for sodium glucose transporter 2 inhibitor) users vs. nonusers.
- Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist use was associated with a statistically significant decrease in mortality, ICU admission and/or mechanical ventilation, and hospitalization.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Thiazolidinedione use is associated with reduced risk of dementia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A retrospective cohort study
噻唑烷二酮的使用与2型糖尿病患者痴呆风险降低相关:一项回顾性队列研究
- Pages: 97-109
- First Published: 20 January 2023
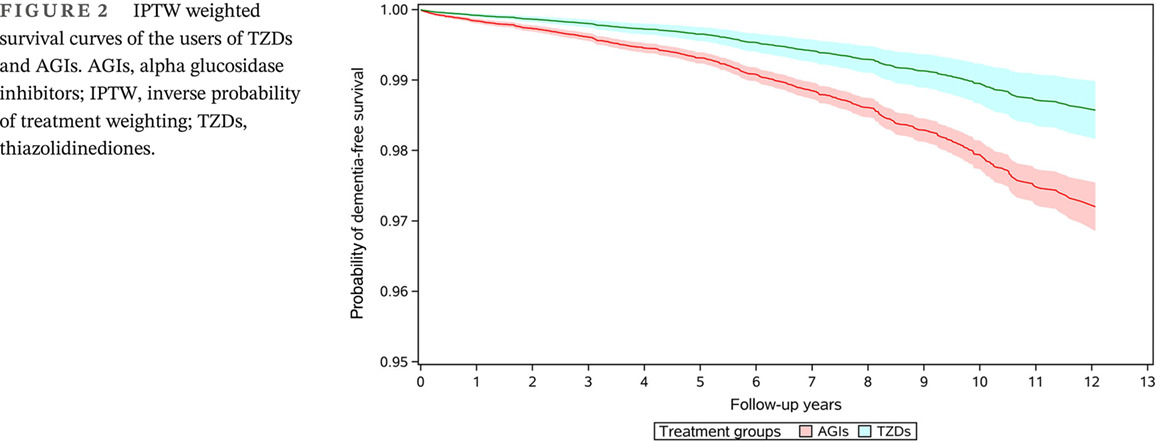
Highlights
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and dementia cause heavy health burden in China.
- This was the first cohort study investigating the association between TZD use and dementia incidence in a mainland Chinese population.
- We found that TZD use was associated with a 49% reduction in incidence of dementia.
- Our results could provide some insights into developing effective prevention and control measures to reduce the future disease burden of dementia.
Changes in fasting blood glucose status and incidence of cardiovascular disease: The China-PAR project
空腹血糖状态变化与心血管疾病发病率:中国动脉粥样硬化性心血管疾病预测项目
- Pages: 110-120
- First Published: 13 January 2023
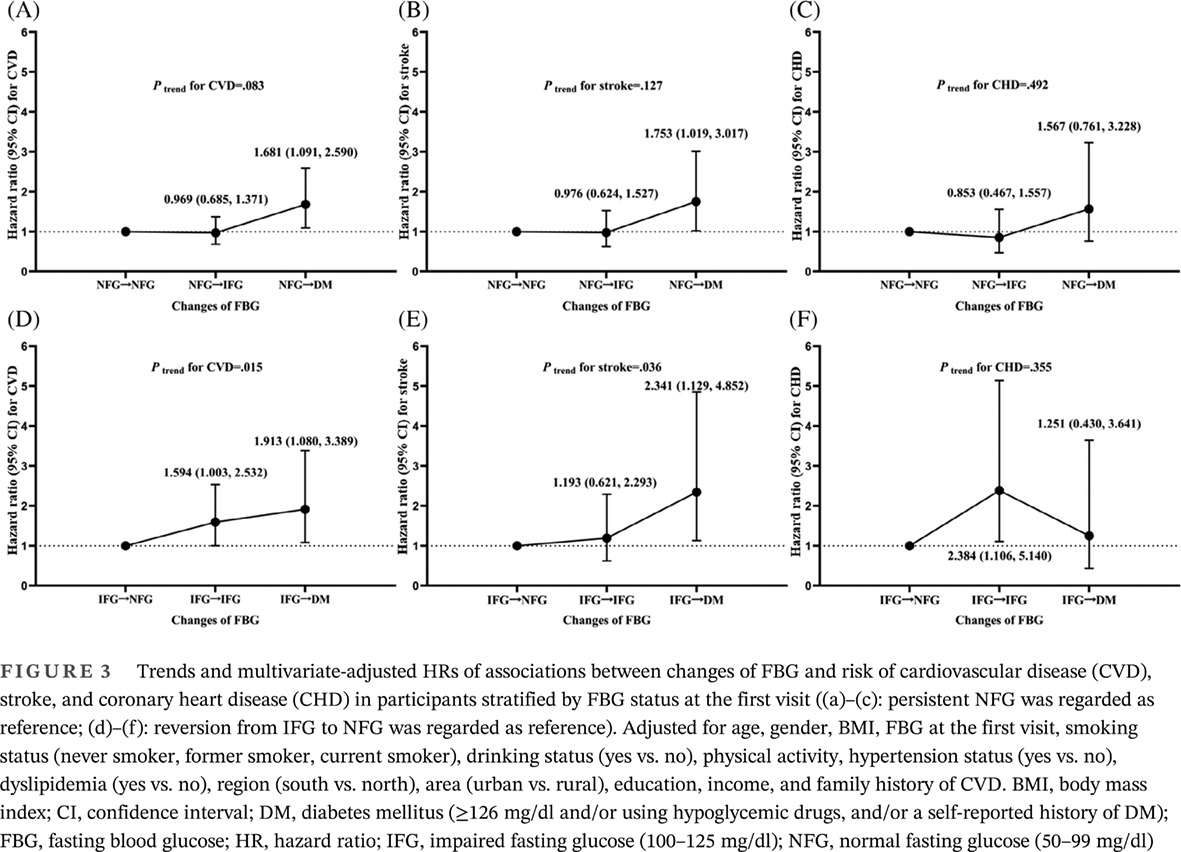
Highlights
- Adjusted for age, gender, BMI, FBG at the first visit, smoking status (never smoker, former smoker, current smoker), drinking status (yes vs no), physical activity, hypertension status (yes vs no), dyslipidemia (yes vs no), region (south vs north), area (urban vs rural), education, income and family history of CVD.
- BMI, body mass index; FBG, fasting blood glucose; NFG, normal fasting glucose (50-99 mg/dL); IFG, impaired fasting glucose (100-125 mg/dL); DM, diabetes mellitus (≥126 mg/dL and/or using hypoglycemic drugs, and/or a self-reported history of DM); CVD, cardiovascular disease.
Sex differences in the risk of arterial stiffness among adults with different glycemic status and modifications by age
不同血糖状态和年龄变化的成年人动脉硬化风险的性别差异
- Pages: 121-132
- First Published: 17 January 2023
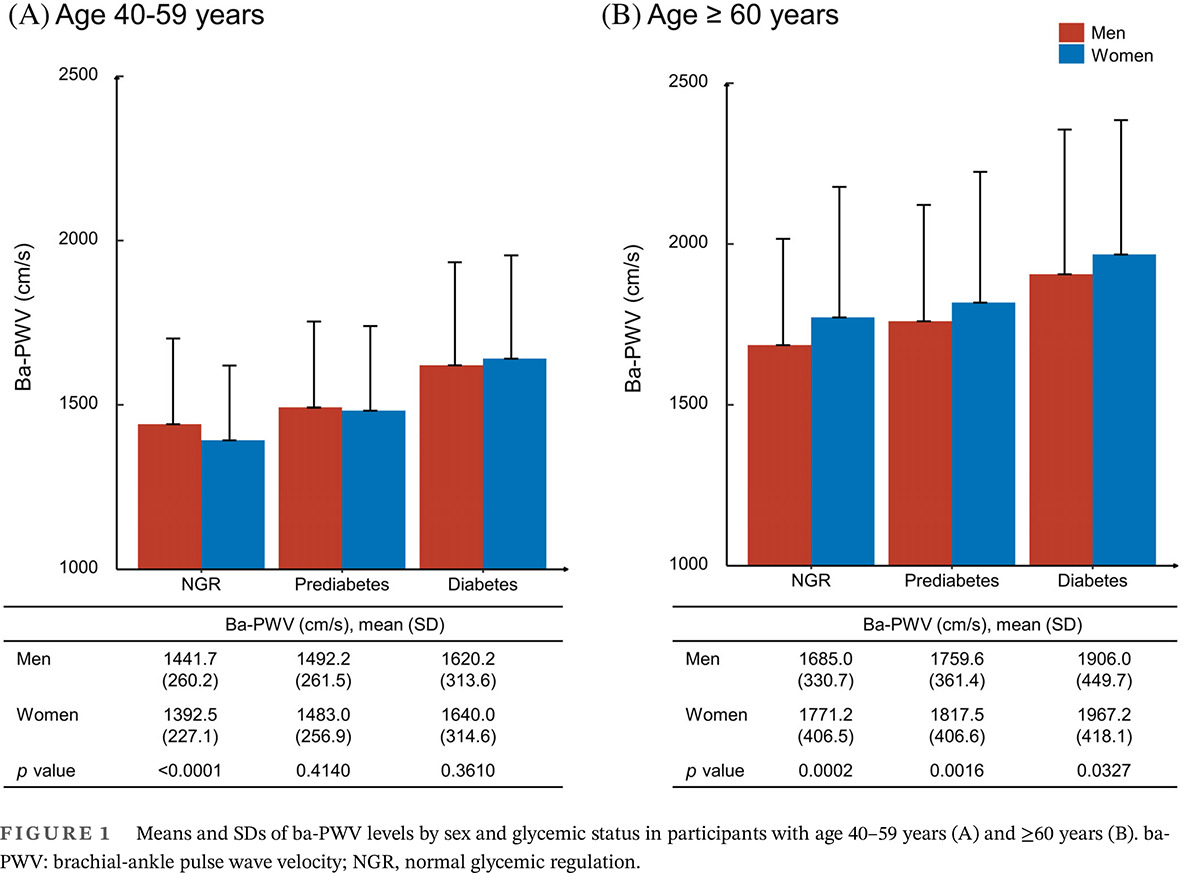
Highlights
- Sex difference regarding arterial stiffness in different glycemic status and whether aging plays a role remains uncertain.
- In participants aged 40–59 years, women were associated with lower ba-PWV levels in generally all glycemic strata after multivariable adjustment. In participants aged ≥60 years, women were associated with significantly higher ba-PWV levels in the group of normal glycemic regulation after multivariable adjustment and this sex difference was attenuated in the groups of prediabetes and diabetes.
- Our findings provided additional evidence for targeted sex-specific prevention of atherosclerosis in participants with different glycemic status.
Evaluating the role of time in range as a glycemic target during short-term intensive insulin therapy in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes
在新诊断的2型糖尿病患者中评估短期胰岛素强化治疗期间血糖达标时间作为血糖目标的作用
- Pages: 133-144
- First Published: 17 January 2023
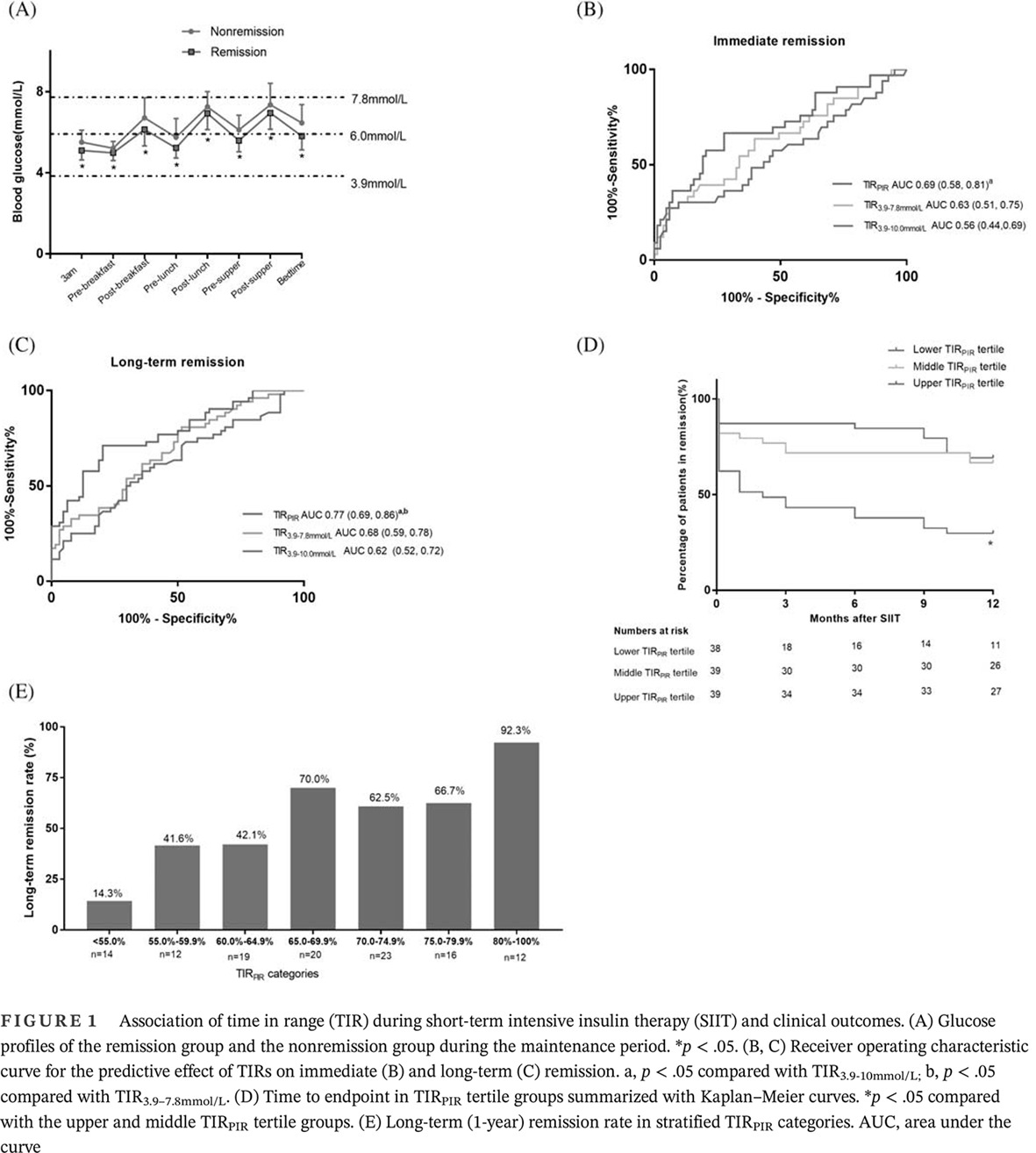
Highlights
- Whether time in range (TIR) during short-term intensive insulin therapy (SIIT) was associated with treatment response to the therapy in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes was uncertain.
- TIRPIR, which was calculated according to the percentage of glucose points within predefined glycemic targets, was superior to TIR3.9–7.8mmol/L, TIR3.9–10.0mmol/L, and other glycemic markers in predicting recovery of β-cell function, improvement of insulin sensitivity, and 1-year remission.
- Patients with TIRPIR ≥ 65% had a 1-year remission rate of 60% or higher.
Nailfold capillaroscopy and deep learning in diabetes
甲襞毛细血管镜检测与深度学习在糖尿病中的应用
- Pages: 145-151
- First Published: 15 January 2023
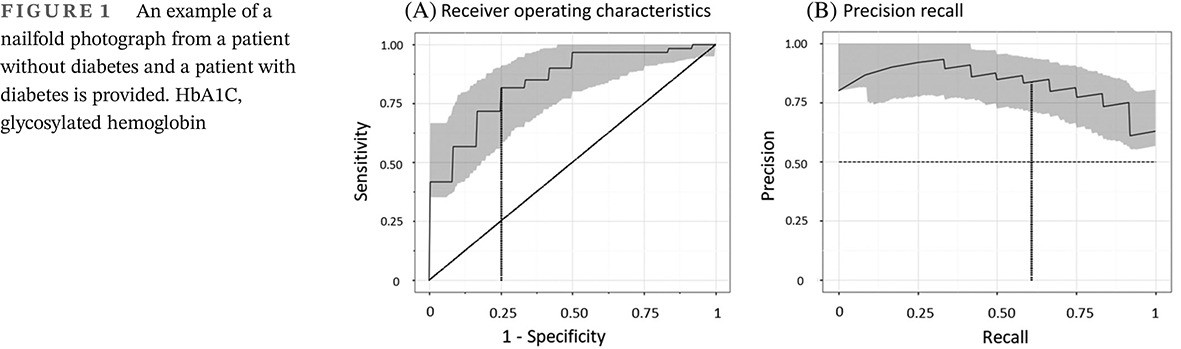
Highlights
- Nailfold capillary images were obtained by performing nailfold video capillaroscopy in 120 adult patients with and without diabetes.
- Over 5000 photographs were analyzed using machine-learning approaches, and these models were clearly able to distinguish people based on diabetes status.
- This proof-of-concept study demonstrates the potential of machine learning for identifying people with microvascular capillary changes from diabetes based on nailfold images and for possibly identifying those likely to have diabetes-related complications.
The relationship between well-being and HbA1c in adults with type 1 diabetes: A systematic review
成人1型糖尿病患者幸福感和HbA1c之间的关系:一项系统综述
- Pages: 152-164
- First Published: 16 February 2023
Highlights
- Subjective well-being (SWB) is an important variable to consider, given its association with positive outcomes in people with diabetes and the general population.
- The main aim of this study is to systematically review how SWB factors are related to type 1 diabetes management through the glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) index in adults.
- The overall data suggested that the cognitive well-being is negatively related to HbA1c in this population, but these results are inconclusive.
Fasting and refeeding triggers specific changes in bile acid profiles and gut microbiota
禁食和再进食触发胆汁酸谱和肠道微生物群的特异性变化
- Pages: 165-180
- First Published: 22 January 2023
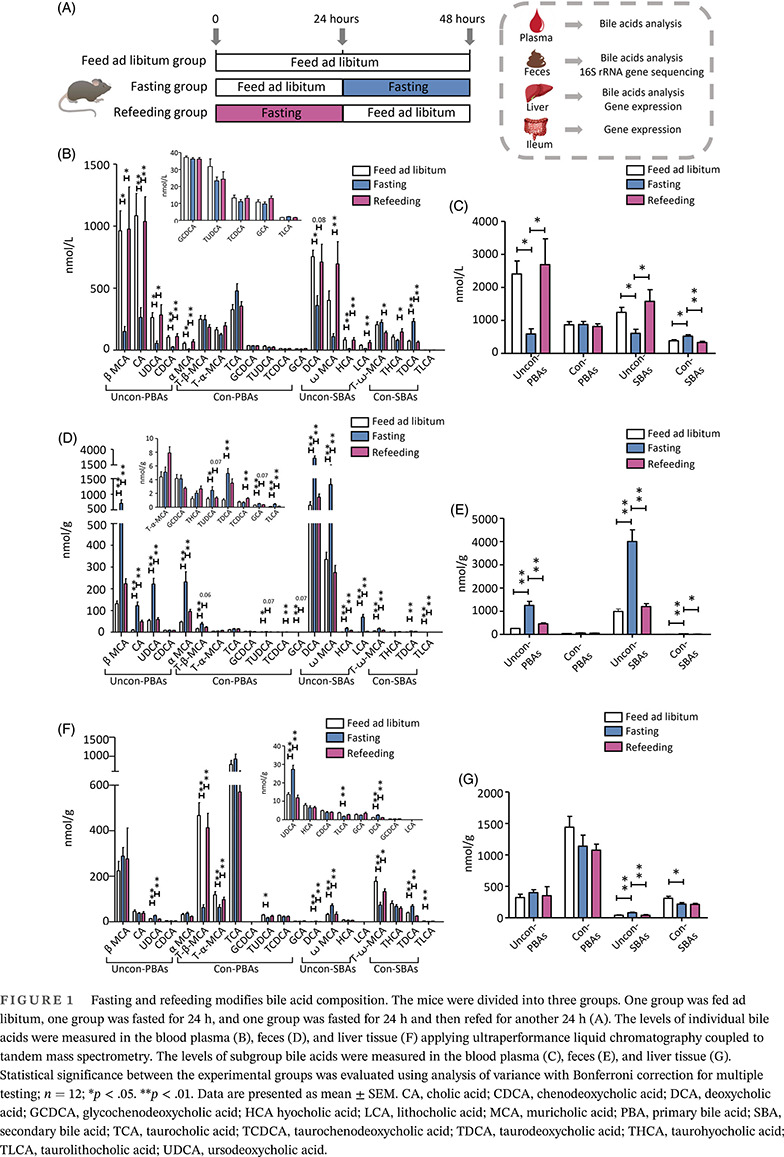
Highlights
- For the first time, our study contributed a systematic evaluation of bile acid (BA) profiles in plasma, feces and liver tissue and gut microbiota changes triggered by fasting-refeeding cycle in mice.
- Our work clearly demonstrated that overnight fasting leads to significant, but reversible changes in BA profiles and gut microbiota composition.
- Our results demonstrated that gene expression responsible for BA biosynthesis and intestinal reabsorption were suppressed under fasting status, whereas refeeding ameliorated this effect.
- Our study emphasized the important and rapid effects of nutrient supply on BA profiles and gut microbiota.
RESEARCH LETTERS
Changes in dietary intake of aspartic acid during and after intermittent fasting correlate with an improvement in fasting glucose in overweight individuals
- Pages: 181-184
- First Published: 09 January 2023
Highlights
- We investigated a potential correlation between amino acid intake and glycemic markers among individuals who practiced intermittent fasting and controls.
- Reduced aspartic acid intake during and after intermittent fasting presented a positive correlation with fasting glucose.
- The positive effects of intermittent fasting on glucose metabolism could be partially related to a decrease in the ingestion of specific amino acids.
Sex differences in prognostic role of fasting glucose, Oral glucose tolerance, and HbA1c in diabetic cardiovascular disease
- Pages: 185-189
- First Published: 14 February 2023
Highlights
- Fasting glucose-defined prediabetes and undiagnosed diabetes based on the American Diabetes Association criteria were associated with a greater risk of coronary heart disease, stroke, and composite atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in women. In contrast, oral glucose tolerance-defined prediabetes and undiagnosed diabetes were associated with a greater risk of all cardiovascular outcomes in men.
- Intermediate A1c was associated with a more pronounced effect on the risk of coronary heart disease and stroke in women, whereas the above diagnostic level of A1c was associated with a higher magnitude of coronary heart risk in undiagnosed men but a higher magnitude of stroke risk in undiagnosed women.
Patterns of new glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist use in patients with type 2 diabetes during 2014–2019 from a US database: prescriber and patient characteristics
- Pages: 190-195
- First Published: 16 February 2023
Highlights This study demonstrates that initiation of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists among individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2D), including those with concomitant atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), has remained low in the United States between 2014 and 2019, despite clinical evidence supporting their use for cardiovascular risk reduction. These findings add to the existing literature to highlight a gap in adherence to current practice guidelines, which suggests that most patients with T2D and ASCVD in the United States may not be receiving optimal risk-reducing therapies.









