Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Free Access
free
COVID-19 in the United States: Where are we now? Where have we been?
美国的COVID-19:我们现在怎么样?我们经历了什么?
- Pages: 98-100
- First Published: 11 November 2020
EDITORS' RECOMMENDATIONS
Free Access
free
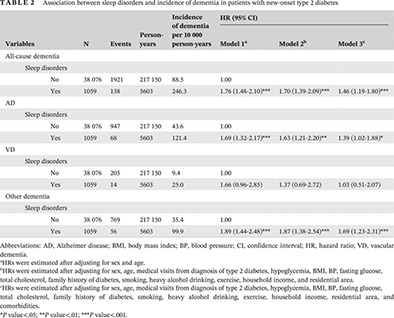
Sleep disorders and risk of dementia in patients with new-onset type 2 diabetes: A nationwide population-based cohort study
新发2型糖尿病患者的睡眠障碍和痴呆风险:一项基于全国人群的队列研究
- Pages: 101-110
- First Published: 18 July 2020
Highlights
- Sleep management plays a role as a potential target to prevent dementia, and sleep problems are common in patients with type 2 diabetes.
- Type 2 diabetes patients with sleep disorders were found to have more incidence of all cause dementia, Alzheimer disease, and other dementia.
- In patients with type 2 diabetes, men and older adults with sleep disorders were associated with an increased risk of dementia compared to their counterparts without sleep disorders.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
no
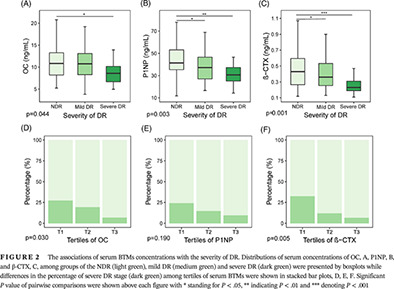
Low serum levels of bone turnover markers are associated with the presence and severity of diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
2型糖尿病患者中低血清水平的骨转换标志物与糖尿病视网膜病变的存在及严重程度相关
- Pages: 111-123
- First Published: 16 July 2020
Highlights
- To our best knowledge, this is the first study evaluating the association of bone turnover markers with the severity of diabetic retinopathy.
- Lower serum levels of procollagen type 1 N-terminal propeptide and β-cross-linked C-telopeptide of type I collagen (β-CTX) were associated with higher odds for DR, while β-CTX was associated with its severity.
no
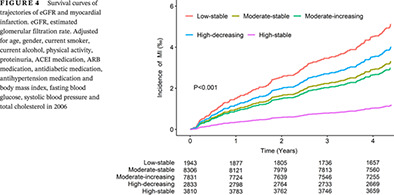
Distinct eGFR trajectories are associated with risk of myocardial infarction in people with diabetes or prediabetes
糖尿病或糖尿病前期患者中不同肾小球滤过率轨迹与心肌梗死风险的研究
- Pages: 124-133
- First Published: 16 July 2020
Highlights
- Distinct trajectories of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) were associated with myocardial infarction (MI) risk in a diabetic or prediabetic population.
- The MI risk was higher in the high-decreasing group although the eGFR levels were similar to the moderate-stable group during the last exposure period.
- The moderate-increasing group still had a significantly increased MI risk when reaching the normal range.
no
Five-year follow-up observation of interventional therapy for lower extremity vascular disease in type 2 diabetes and analysis of risk factors for restenosis
2型糖尿病下肢血管病变介入治疗5年随访观察及再狭窄危险因素分析
- Pages: 134-142
- First Published: 22 July 2020
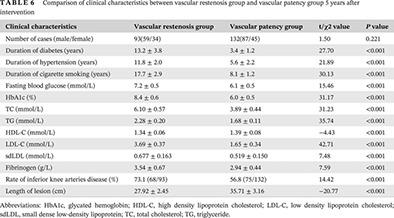
Highlights
- The survival rate and the limb salvage rate of patients in this study were 76.8% and 97.6%.
- This study suggested that fibrinogen may be used as an index to predict restenosis after interventional intervention.
- The results indicated that the detection of sdLDL may provide a new research direction for preventing restenosis after intervention.
Open Access
oa
Prediction of the development of islet autoantibodies through integration of environmental, genetic, and metabolic markers
通过整合环境、遗传和代谢标记物预测胰岛自身抗体的发展
- Pages: 143-153
- First Published: 22 July 2020
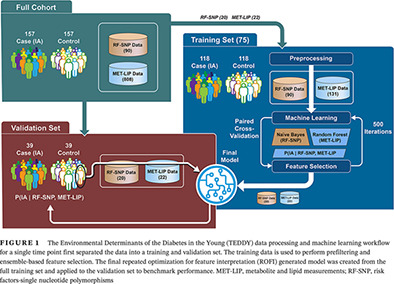
Highlights
- A machine learning model can significantly predict imminent development of islet autoimmunity based on environmental, genetic, and metabolic features.
- The machine learning algorithm feature selection identified type 1 diabetes-associated single nucleotide polymorphisms from The Environmental Determinants of the Diabetes in the Young (TEDDY) analysis are correlated to related data from the Diabetes Autoimmunity Study in the Young (DAISY) study.
- Most of the metabolic features predicting the development of islet autoantibodies belonged to three pathways; lipid oxidation, phospholipase A2 signaling, and pentose phosphate.
no
Clinical and laboratory clues of maturity-onset diabetes of the young and determination of association with molecular diagnosis
青少年发病的成人型糖尿病临床和实验室线索及其对分子诊断相关性的确定性
- Pages: 154-163
- First Published: 24 July 2020
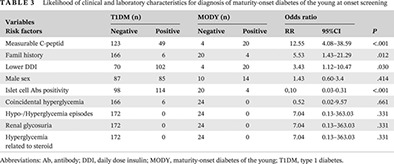
Highlights
- MODY is mostly overlooked due to uncertain clinical presentations and is often misdiagnosed as T1DM.
- This paper presents possible clinical and laboratory clues to consider a diagnosis of MODY in children presenting with hyperglycaemia.
- In addition, this paper reviews the association of these probable markers with MODY-causing genes.
no
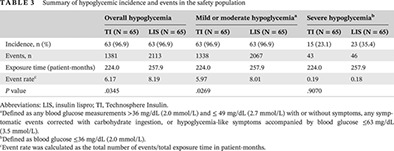
Understanding inhaled Technosphere Insulin: Results of an early randomized trial in type 1 diabetes mellitus
了解吸入性胰岛素:1型糖尿病早期随机试验的结果
- Pages: 164-172
- First Published: 31 July 2020
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
no
Comprehensive analysis of compliance with self-care guidelines and use of health services for patients with diabetes
糖尿病患者自我护理的指南依从性及卫生服务利用度的综合分析
- Pages: 173-174
- First Published: 10 September 2020
no
Differences between processes of diabetes care and diabetes self-care and their respective perspectives
糖尿病护理过程与糖尿病自我护理的区别及各自的视角
- Pages: 175-176
- First Published: 24 September 2020
no
Is newly diagnosed diabetes a stronger risk factor than pre-existing diabetes for COVID-19 severity?
与既往糖尿病相比,新诊断的糖尿病是否是新冠肺炎严重程度的更强危险因素?
- Pages: 177-178
- First Published: 27 October 2020
no
Response to: Is newly diagnosed diabetes a stronger risk factor than pre-existing diabetes for COVID-19 severity?
对以下问题的回应:与既往糖尿病相比,新诊断的糖尿病是否是新冠肺炎严重程度的更强危险因素?
- Pages: 179-180
- First Published: 30 October 2020