Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITOR'S RECOMMENDATION
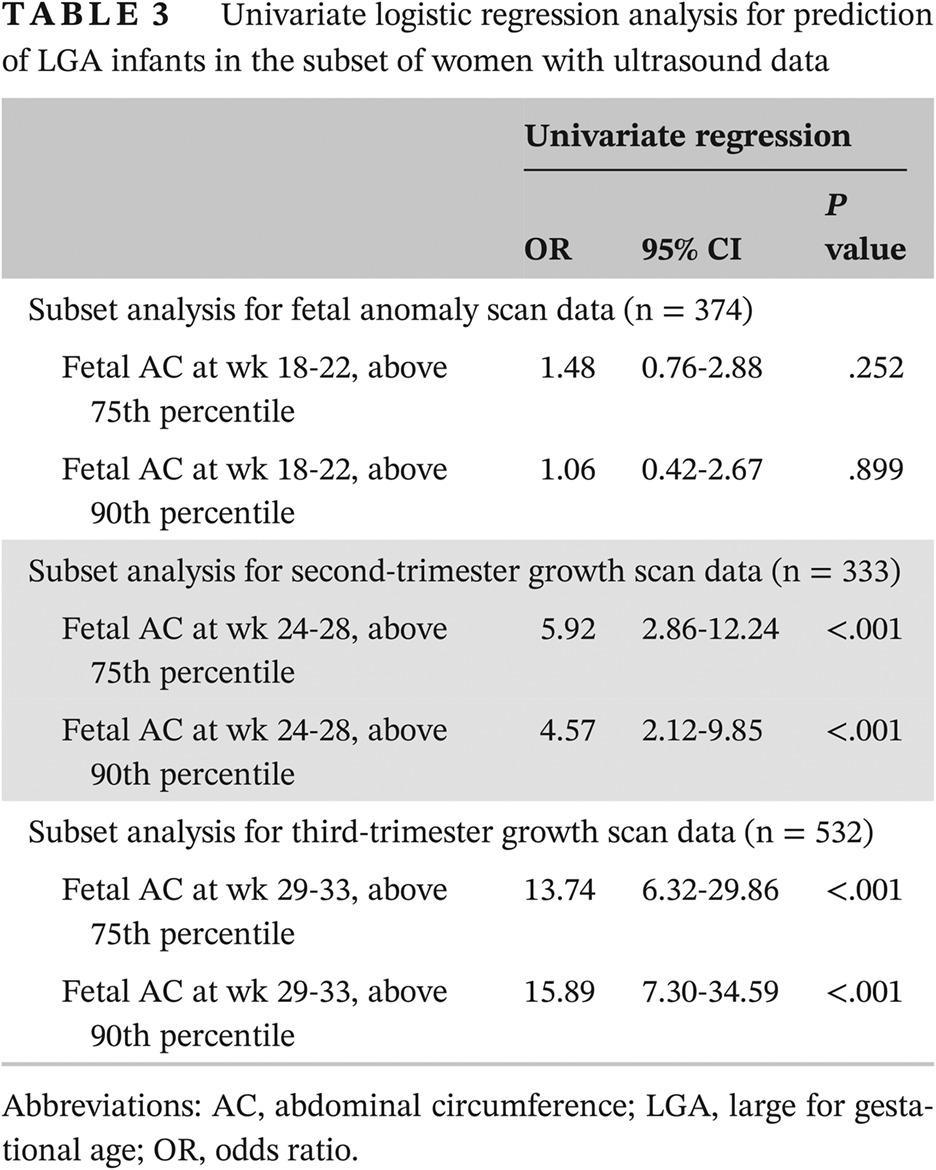
Sonographic and other nonglycemic factors can predict large-for-gestational-age infants in diet-managed gestational diabetes mellitus: A retrospective cohort study
超声和其他非血糖因素可以预测饮食管理中的妊娠糖尿病孕妇中的大于胎龄儿:一项回顾性队列研究
- Pages: 562-572
- First Published: 06 April 2020
Highlights
- In diet-managed gestational diabetes mellitus pregnancies, the novel large-for-gestational-age (LGA) risk factor of fetal abdominal circumference determined at 24- to 28-week fetal ultrasound can identify women at risk as well as the known risk factors of maternal parity, prepregnancy body mass index, and gestational age.
- Smoking reduces LGA risk but has other harms.
- Early identification of risk factors for LGA allows early intervention to mitigate LGA risk, such as restriction of excessive further maternal gestational weight gain and other therapies, which may include insulin, though unproven.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
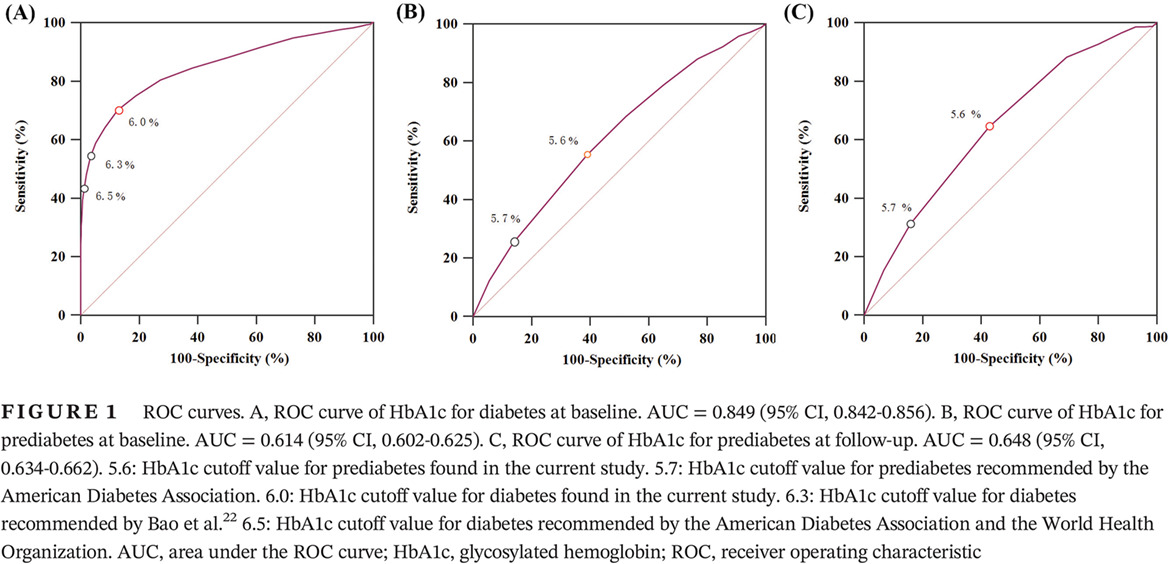
Detection of diabetes and prediabetes using glycosylated hemoglobin in Chinese adults living in Shanghai: A prospective analysis
使用糖化血红蛋白诊断中国上海成人糖尿病和糖尿病前期:一项前瞻性分析
- Pages: 573-582
- First Published: 02 March 2020
Highlights
- A glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) value ≥6.0% could be used to detect diabetes in Chinese adults aged ≥40 years.
- Although an HbA1c value of 5.6% to 5.9% was indicated to detect prediabetes in the current study using both cross-sectional and follow-up data, the overall discrimination of HbA1c for prediabetes was poor.
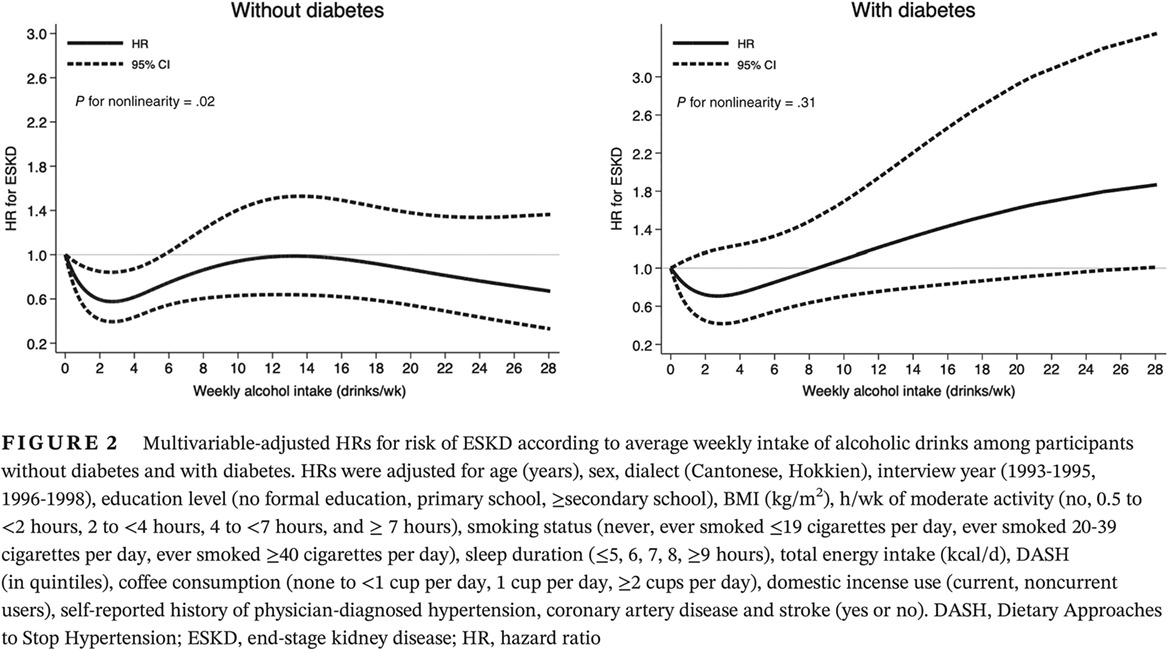
The impact of diabetes on the association between alcohol intake and the risk of end-stage kidney disease in the Singapore Chinese Health Study
在新加坡华人健康研究中探讨糖尿病对酒精摄入与终末期肾病风险关系的影响
- Pages: 583-593
- First Published: 06 March 2020
Highlights
- Low-dose intake of alcohol is associated with a lower risk of end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) in nondiabetic participants.
- Joint exposure to heavy drinking and diabetes is associated with a substantially higher risk of ESKD.
- Recommendations on alcohol intake among patients at risk of ESKD should consider the presence of diabetes as a comorbidity.
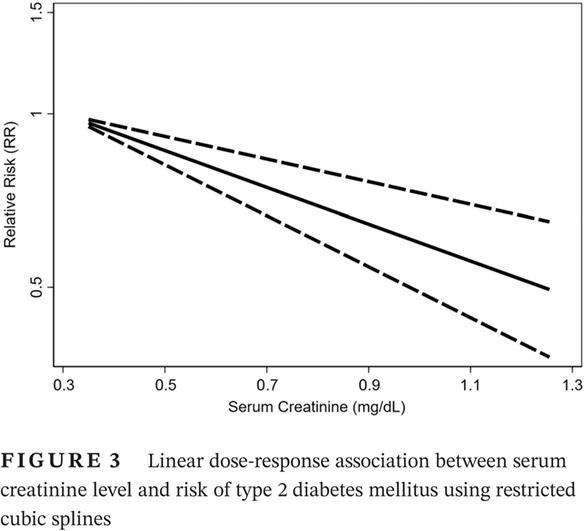
Dose-response associations between serum creatinine and type 2 diabetes mellitus risk: A Chinese cohort study and meta-analysis of cohort studies
血肌酐和2型糖尿病风险之间的剂量反应关联:一项中国队列研究和基于队列研究的meta分析
- Pages: 594-604
- First Published: 17 March 2020
Interactions among endotoxin, uric acid, and lactate in relation to the risk of type 2 diabetes: A population-based study
内毒素、尿酸和乳酸之间的相互作用与2型糖尿病风险的关系:一项基于人群的研究
- Pages: 605-615
- First Published: 25 March 2020
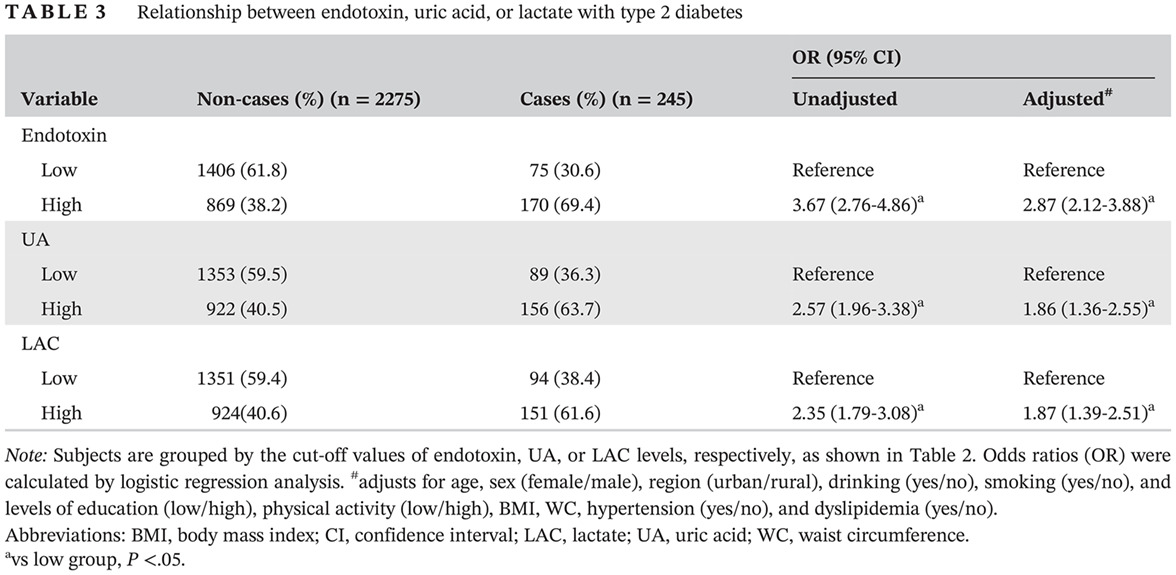
Highlights
- Blood levels of endotoxin, uric acid (UA), or lactate (LAC) were associated with systemic inflammation, insulin resistance, and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
- The interaction between levels of endotoxin and UA or levels of endotoxin and LAC was related to an increased systemic inflammation, insulin resistance, and T2DM.
Serum total bile acids associate with risk of incident type 2 diabetes and longitudinal changes in glucose-related metabolic traits
血清总胆汁酸与2型糖尿病发生风险和血糖代谢指标纵向变化的相关性研究
- Pages: 616-625
- First Published: 27 March 2020
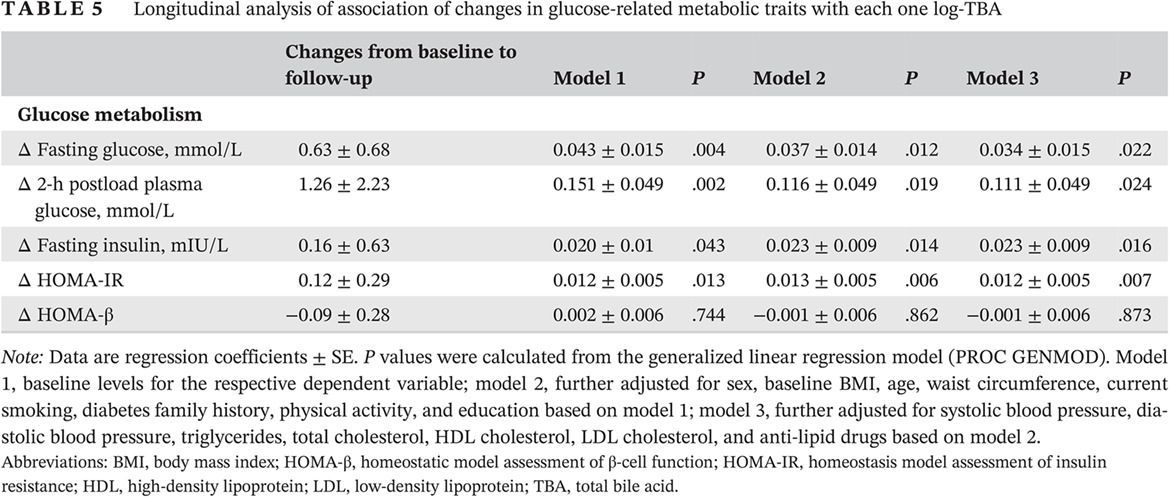
Highlights
- Serum total bile acids (TBAs) are significantly associated with a high risk of incident type 2 diabetes (T2D).
- Serum TBAs are positively associated with longitudinal changes in glucose-related metabolic traits.
- Insulin resistance indicated by homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) might partially mediate this association of TBAs with T2D.
- Our findings spark novel therapeutic approaches for metabolic diseases depending on bile acids.