Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Is the type of diabetes treatment relevant to outcome of COVID-19?
糖尿病的治疗类型与COVID-19的预后相关吗?
- Pages: 486-487
- First Published: 30 April 2020
EDITOR'S RECOMMENDATIONS
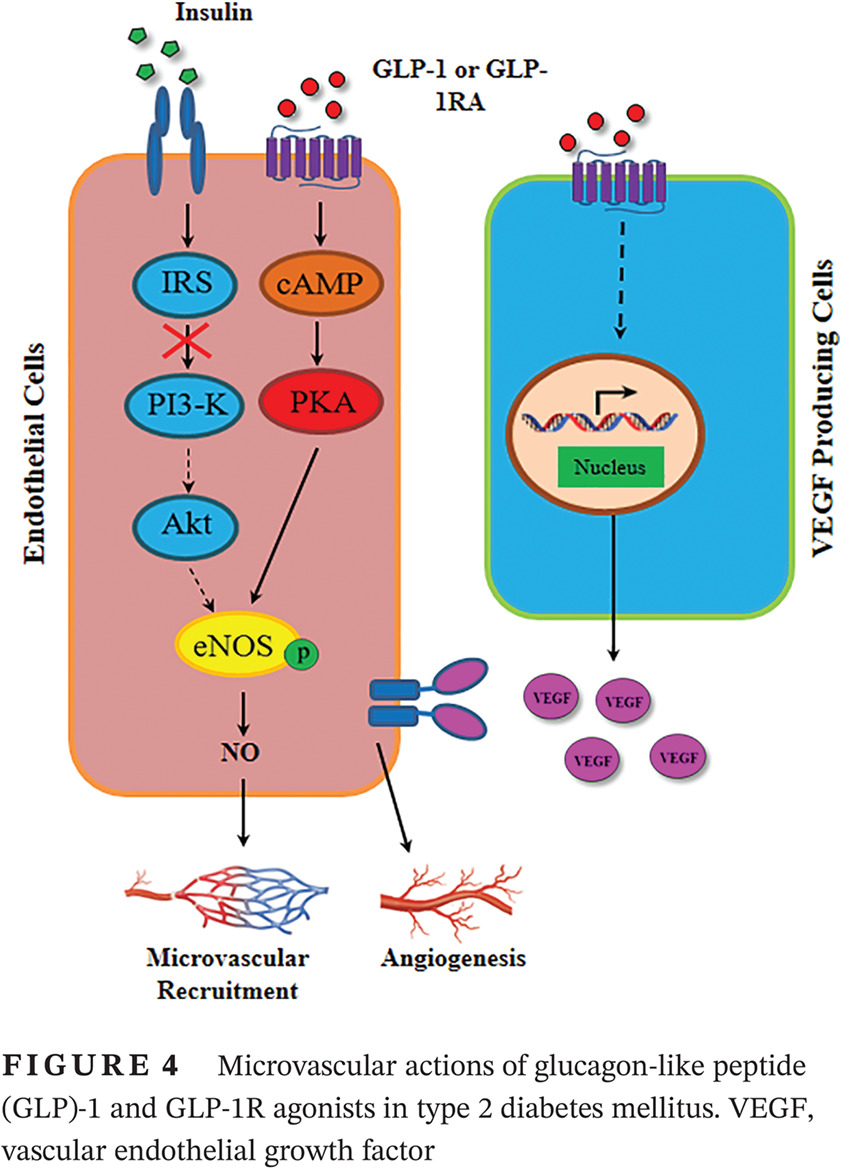
GLP-1 and insulin regulation of skeletal and cardiac muscle microvascular perfusion in type 2 diabetes
GLP-1和胰岛素对2型糖尿病骨骼肌和心肌微血管灌注的调节作用
- Pages: 488-498
- First Published: 09 April 2020
Highlights
- Skeletal and cardiac muscle microvasculature critically regulates tissue perfusion and the delivery of nutrients, oxygen, and hormones and thus the health and function of skeletal and cardiac muscle. Both insulin and GLP-1 increase skeletal and cardiac muscle microvascular perfusion but insulin's action is blunted whereas GLP-1's effect is preserved in obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. This may contribute to the salutary cardiovascular protective effects of the GLP-1 receptor agonists seen in multiple clinical trials.
A lion in the room: Has the CAROLINA trial definitely resolved the issue of the cardiovascular safety of sulfonylureas?
房间里的狮子:CAROLINA试验解决了磺脲类药物的心血管安全性问题吗?
- Pages: 499-502
- First Published: 23 March 2020
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
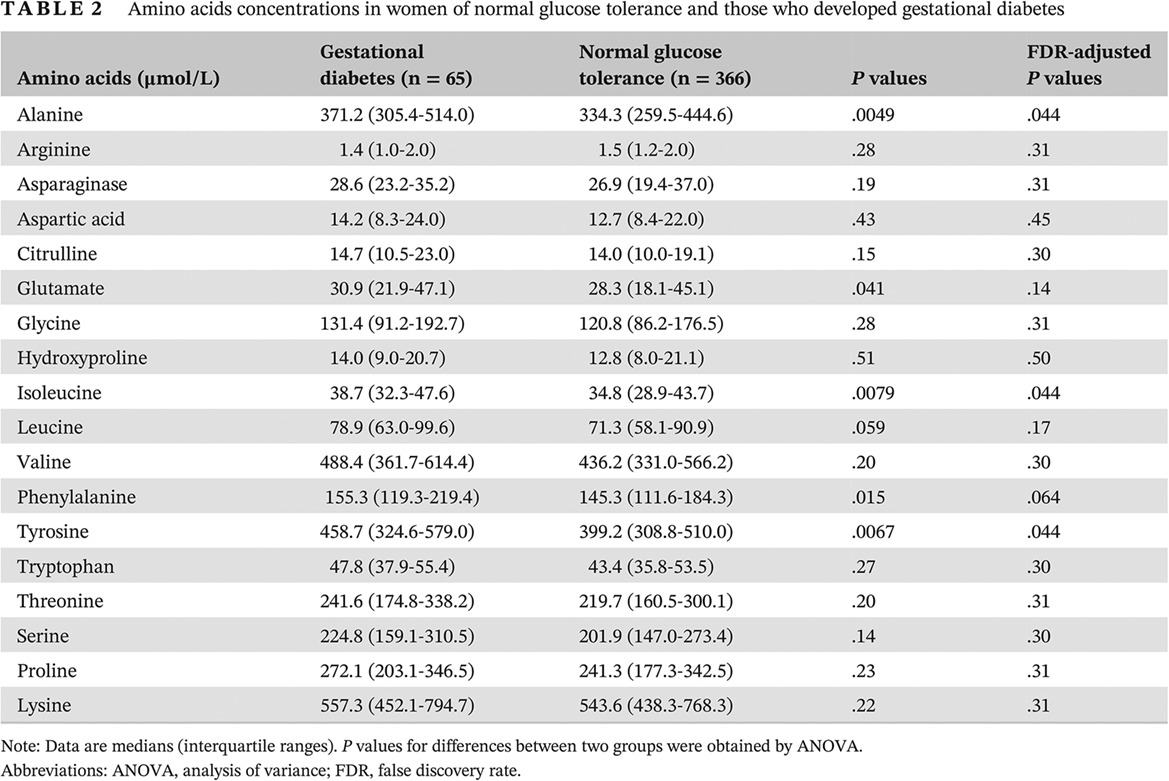
Amino acids levels in early pregnancy predict subsequent gestational diabetes
妊娠早期氨基酸水平可用于预测妊娠期糖尿病
- Pages: 503-511
- First Published: 27 December 2019
Highlights
- Elevated isoleucine, tyrosine, and alanine levels in early pregnancy are independently and significantly associated with subsequent gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM).
- Incorporating isoleucine and tyrosine into the conventional model modestly increased the discrimination ability but significantly improved the reclassification ability of the new model.
- New GDM risk prediction models including amino acids levels in early pregnancy might help clinicians to identify high-risk population of GDM.
TXNIP hypomethylation and its interaction with obesity and hypertriglyceridemia increase type 2 diabetes mellitus risk: A nested case-control study
TXNIP低甲基化及其与肥胖和高甘油三酯血症的交互作用可增加2型糖尿病的风险:巢式病例对照研究
- Pages: 512-520
- First Published: 09 January 2020
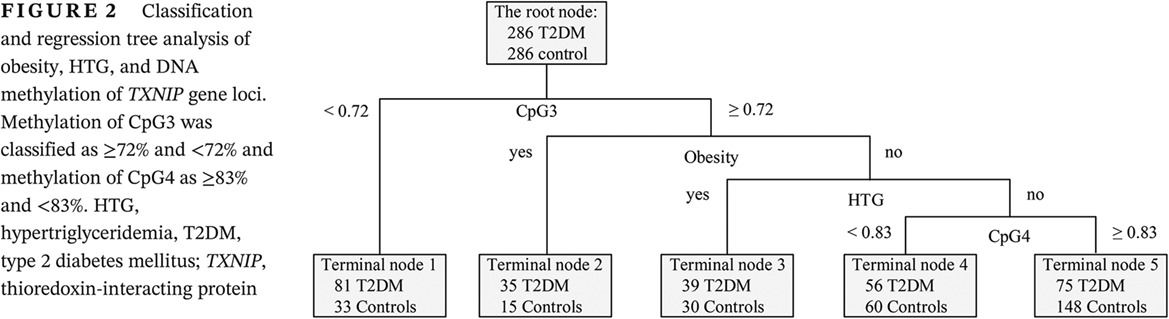
Highlights
- This is the first prospective nested case-control study in rural Chinese people to estimate the association of the methylation level of the thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) gene and its interaction with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) risk.
- We found a significant negative association between the methylation level of TXNIP gene and T2DM incidence.
- Interaction among TXNIP gene hypomethylation, obesity, and hypertriglyceridemia increased the risk of T2DM.
Implications of immunoglobulin G deposit in glomeruli in Chinese patients with diabetic nephropathy
肾小球IgG沉积在中国糖尿病肾病患者中的临床意义
- Pages: 521-531
- First Published: 07 February 2020
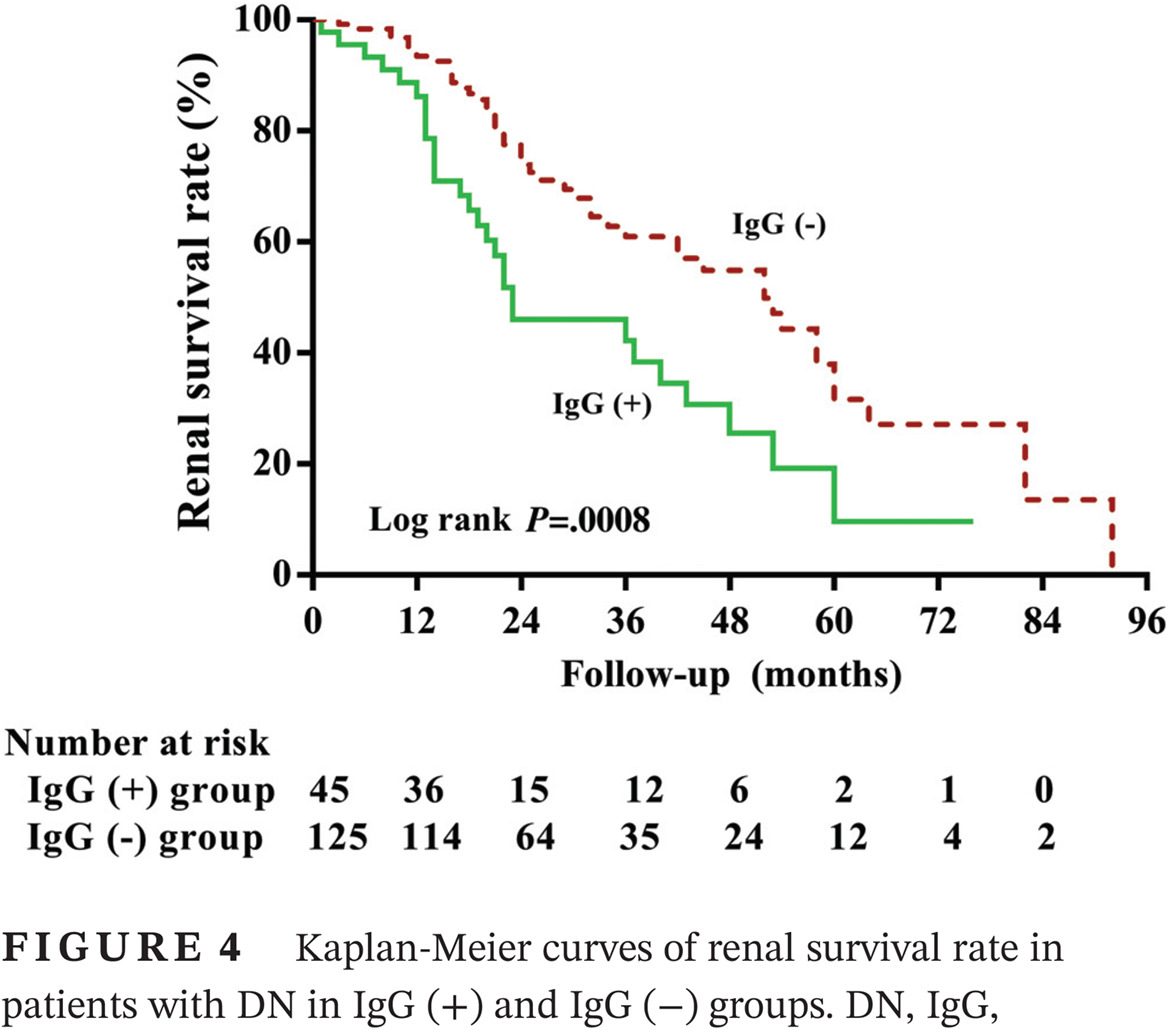
Highlights
- This study included a large sample of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients who underwent renal biopsy and were followed-up for more than 1 year.
- The implication of immunofluorescence in patients with diabetic nephropathy (DN) may have been overlooked by clinicians. In this study, we intended to pinpoint the association between the glomerular immunoglobulin G (IgG) deposit and the clinicopathological features and renal prognosis in patients with DN and further determine the patterns of the IgG subclass deposit on the kidney tissues.
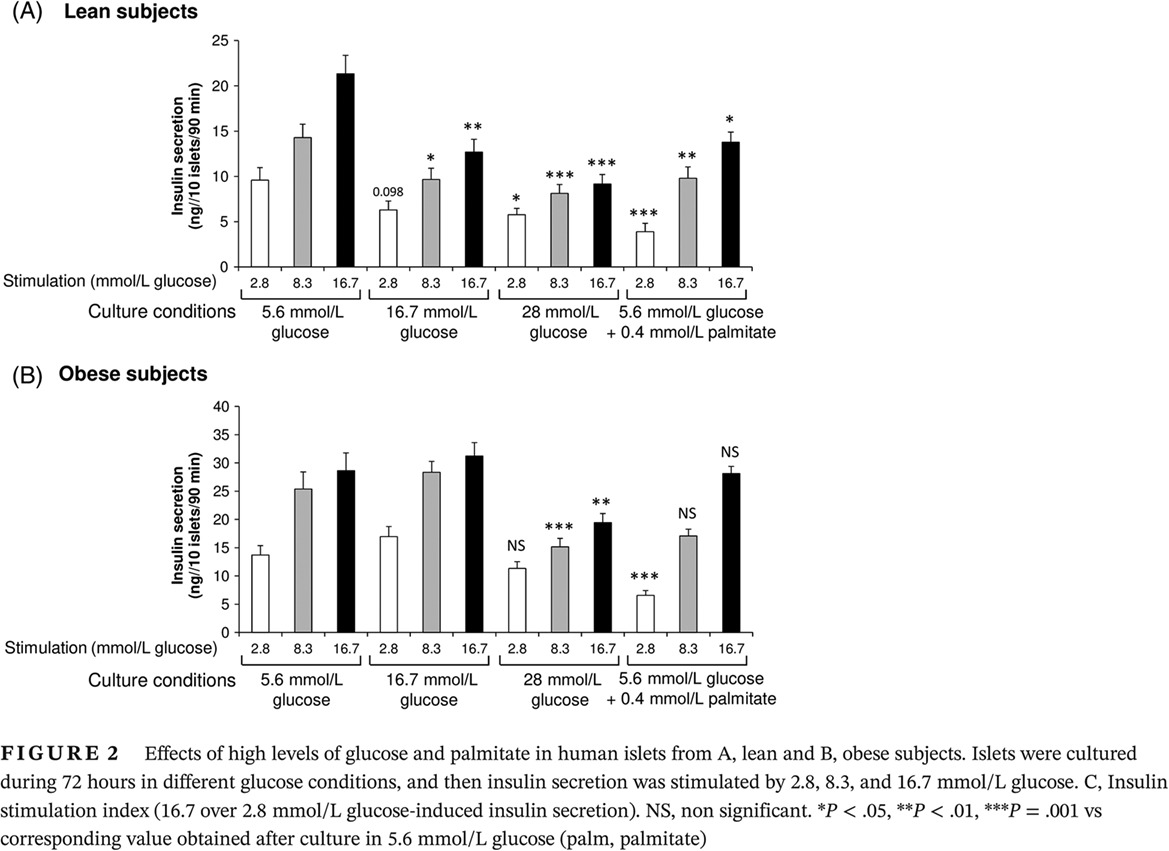
Differential sensitivity of human islets from obese versus lean donors to chronic high glucose or palmitate
肥胖和消瘦捐献者的胰岛对慢性高糖或棕榈酸盐的不同敏感性
- Pages: 532-541
- First Published: 23 February 2020
COMMENTARY
Diabetes during the COVID-19 pandemic: A global call to reconnect with patients and emphasize lifestyle changes and optimize glycemic and blood pressure control
COVID-19大流行期间的糖尿病:全球呼吁与患者重新建立联系, 强调改变生活方式, 优化血糖和血压控制
- Pages: 556-557
- First Published: 17 May 2020