Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Fournier's gangrene and sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors: Is there a causal association?
Fournier’s坏疽与钠-葡萄糖共转运体-2抑制剂:存在因果关系吗?
- Pages: 340-341
- First Published: 02 January 2019
NEWS
World Congress on Clinical Trials in Diabetes 2018
- Pages: 342-344
- First Published: 08 January 2019
EDITORS' RECOMMENDATION
Incidence of type 1 diabetes and distance from the sea: A descriptive epidemiological study
1型糖尿病的发病率与离海距离:一项描述性的流行病学研究
- Pages: 345-347
- First Published: 28 September 2018
Highlights
- A negative correlation was found between distance from the sea and the incidence of type 1 diabetes (T1D), which was independent of latitude, mean temperature, and mean hours of sunshine.
- This may help explain the increasing global incidence of T1D; the data suggest that climatic factors or factors related to human activity may be important in the etiology of T1D.
Fournier's gangrene in a patient on dapagliflozin treatment for type 2 diabetes
一名接受达格列净治疗的2型糖尿病患者发生的Fournier's坏疽
- Pages: 348-350
- First Published: 02 January 2019
REVIEW ARTICLE
Endoscopic bariatric and metabolic therapies: Another tool for the management of diabetes and obesity
内镜下减肥与代谢治疗:糖尿病与肥胖的另外一种管理方法
- Pages: 351-358
- First Published: 17 November 2018
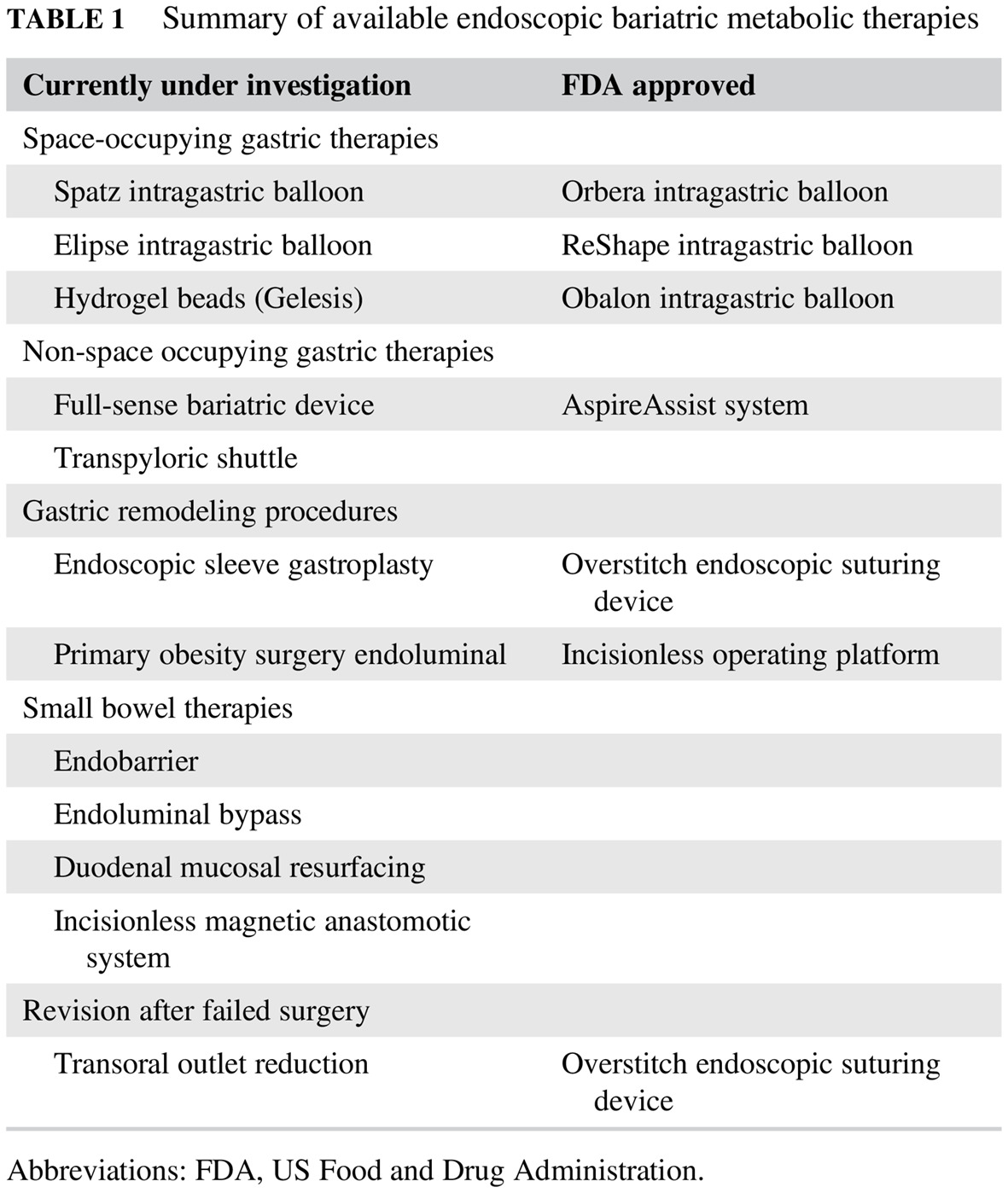
Highlights
- Bariatric endoscopy is a promising therapy in the treatment of patients with obesity and diabetes.
- Endoscopic procedures can be used for primary therapy of obesity, as a bridge to surgery, or for revision of failed surgical procedures.
- Current available endoscopic treatments for weight loss include intragastric balloons, aspiration therapy, and endoscopic suturing.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Autologous platelet-rich gel treatment for diabetic chronic cutaneous ulcers: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
自体富血小板凝胶治疗糖尿病慢性皮肤溃疡:随机对照试验的meta分析
- Pages: 359-369
- First Published: 05 September 2018
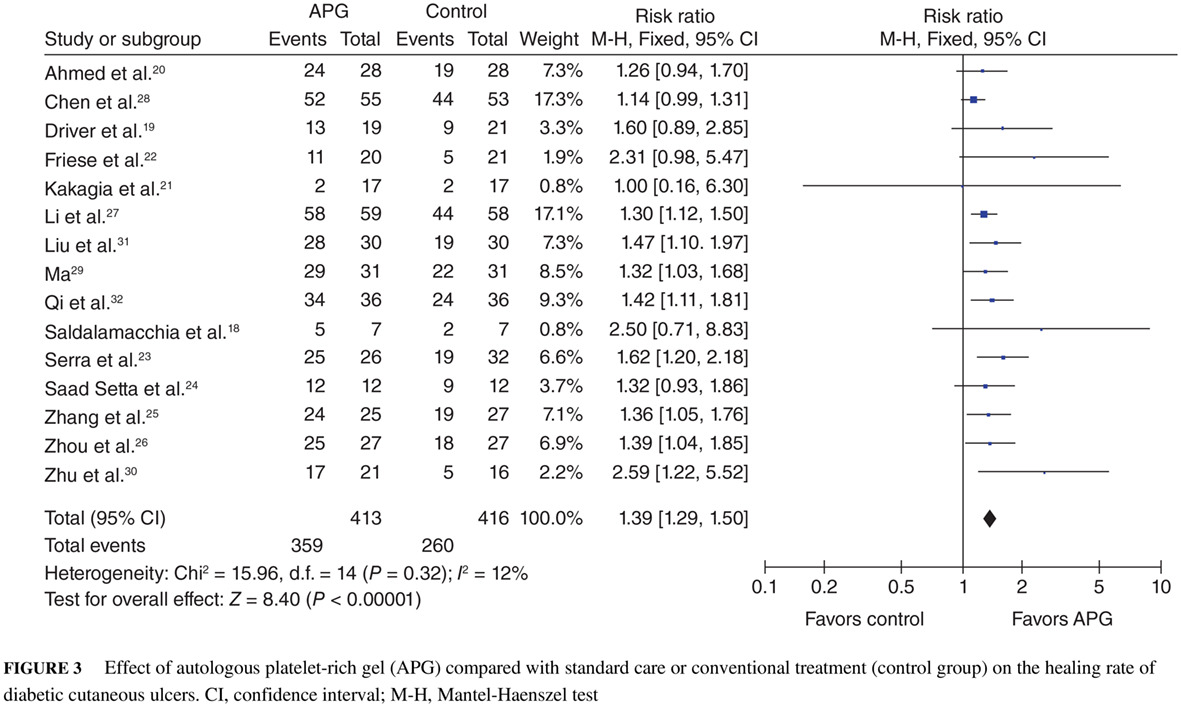
Highlights
- Autologous platelet-rich gel significantly improved the healing rate, shortened the healing time, and reduced the incidence of infection in patients with diabetic chronic cutaneous ulcers.
- Autologous platelet-rich gel may be recommended for use as an adjuvant treatment for diabetic ulcers, especially for chronic refractory ulcers.
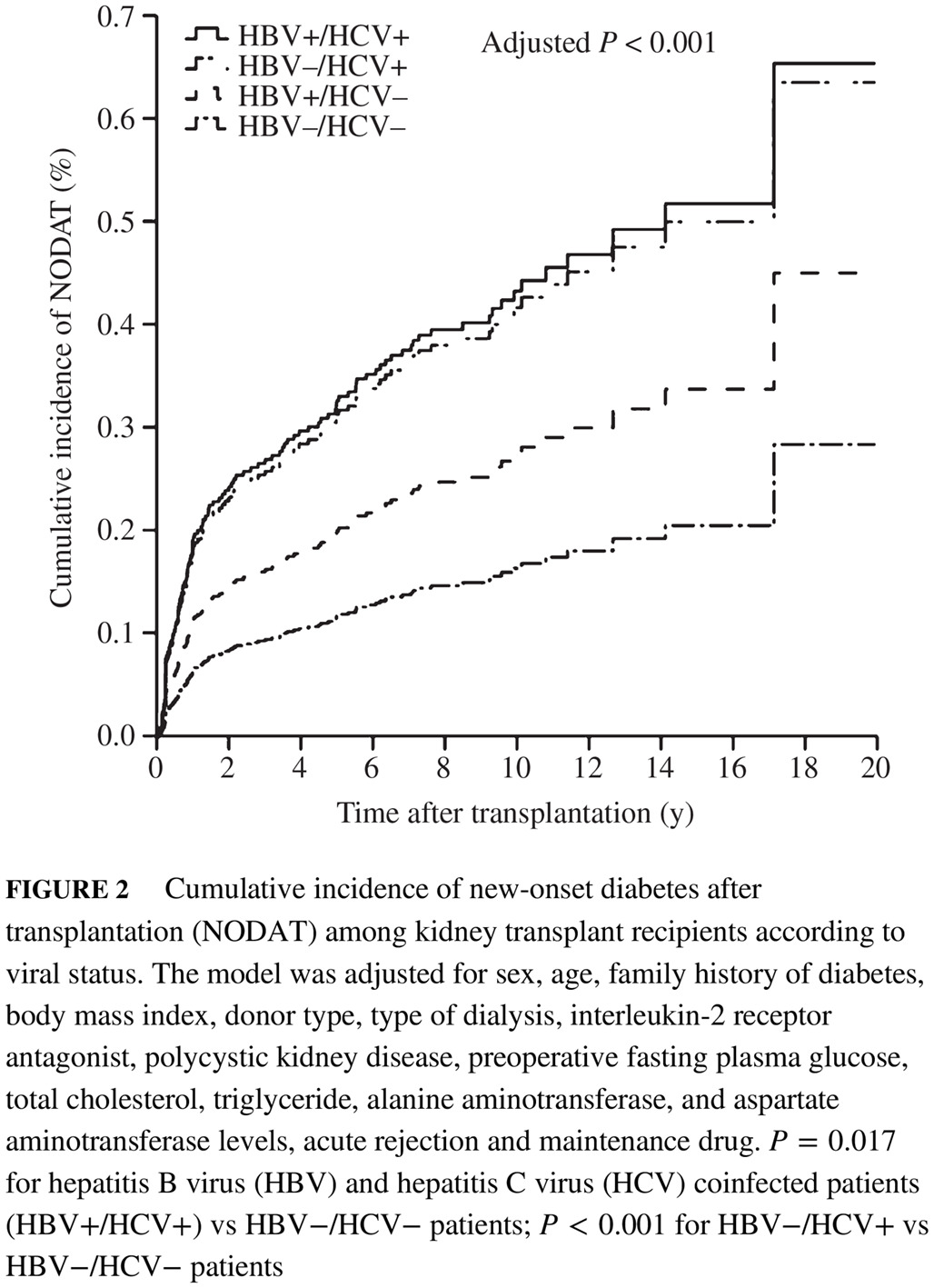
Effects of preoperative hepatitis B virus infection, hepatitis C virus infection, and coinfection on the development of new-onset diabetes after kidney transplantation
肾移植术前乙肝病毒感染、丙肝病毒感染及其共感染对移植后新发糖尿病发病的影响
- Pages: 370-378
- First Published: 11 September 2018
Highlights
- A retrospective cohort study of preoperative hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, and HBV and HCV coinfection was conducted to determine their effects on new-onset diabetes after transplantation (NODAT) among Chinese kidney transplant recipients (KTRs).
- Preoperative HCV infection was significantly correlated with the risk of NODAT.
- Preoperative HBV and HBV plus HCV coinfection did not independently increase the risk of NODAT.
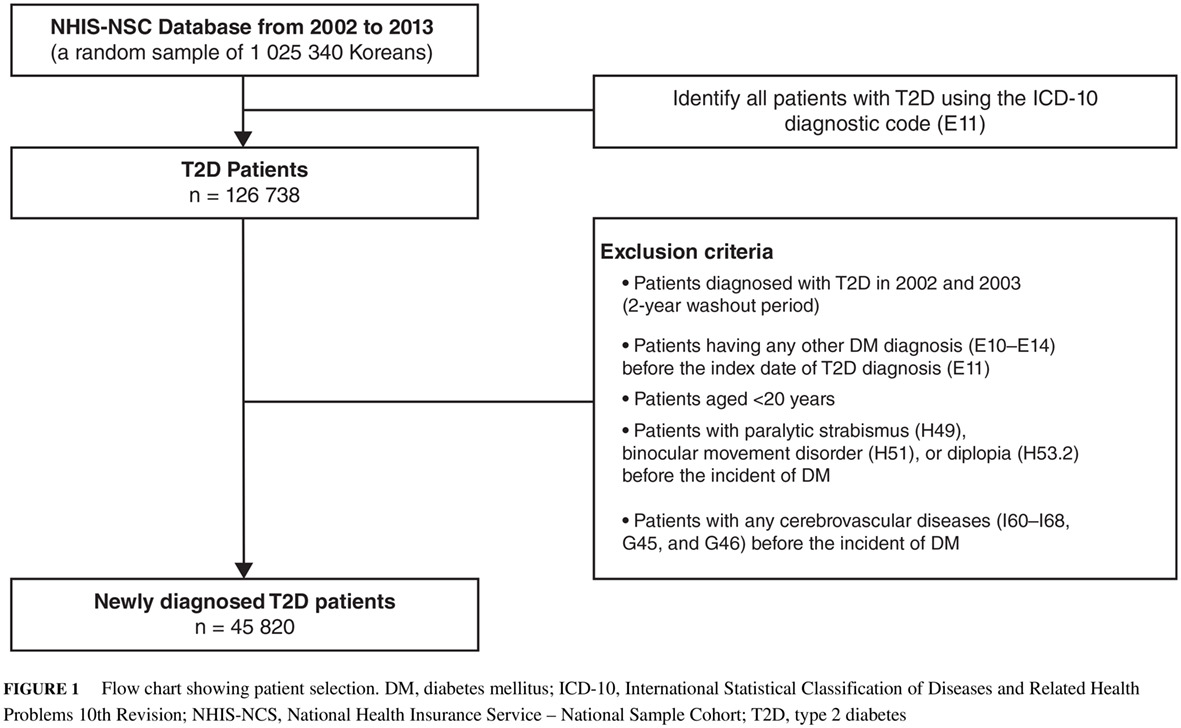
Risk of ischemic stroke after third, fourth, and sixth cranial nerve palsies in type 2 diabetes
2型糖尿病患者第三、第四以及第六颅神经麻痹后的缺血性卒中风险
- Pages: 379-385
- First Published: 24 September 2018
Highlights
- A nationwide cohort study was conducted on newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes (T2D) patients to evaluate the risk of ischemic stroke in those who developed isolated ocular motor nerve palsy.
- Incident ocular motor cranial nerve palsy was associated with a subsequent risk of ischemic stroke in T2D patients.
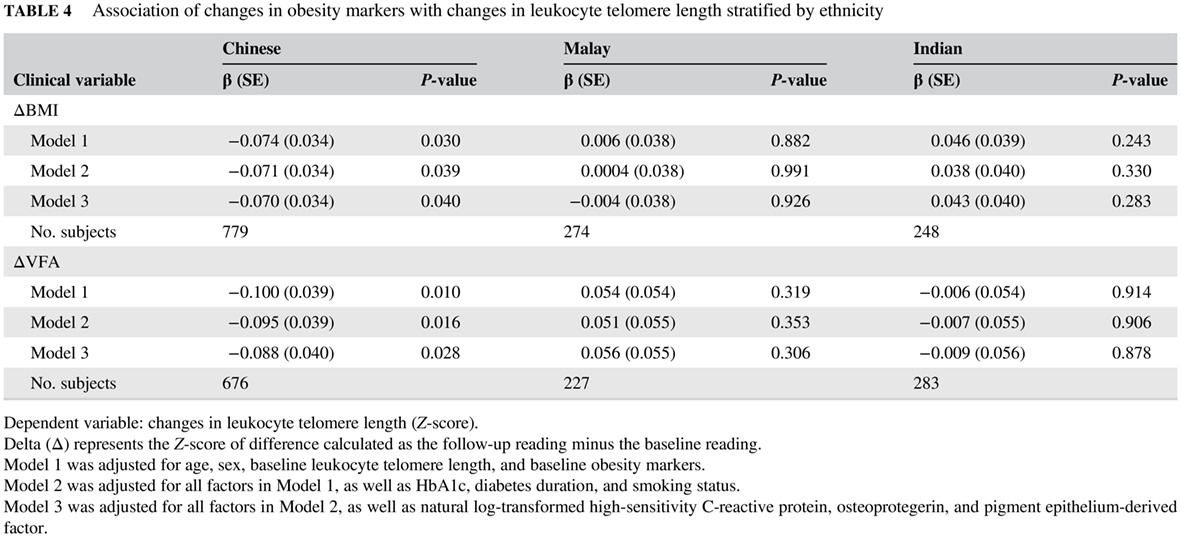
Ethnic disparities in relationships of obesity indices with telomere length in Asians with type 2 diabetes
亚洲2型糖尿病患者肥胖指数与端粒长度关系的种族差异
- Pages: 386-393
- First Published: 03 October 2018
Highlights
- In individual with type 2 diabetes, telomere length varied among ethnic groups in an Asian population, independent of metabolic conditions, smoking status, and levels of inflammation markers.
- Cross-sectional and longitudinal ethnic disparities were also observed in the inverse association of obesity indices with telomere length.
- Increased central obesity (visceral fat area) was associated with larger telomere attrition than general obesity (body mass index).
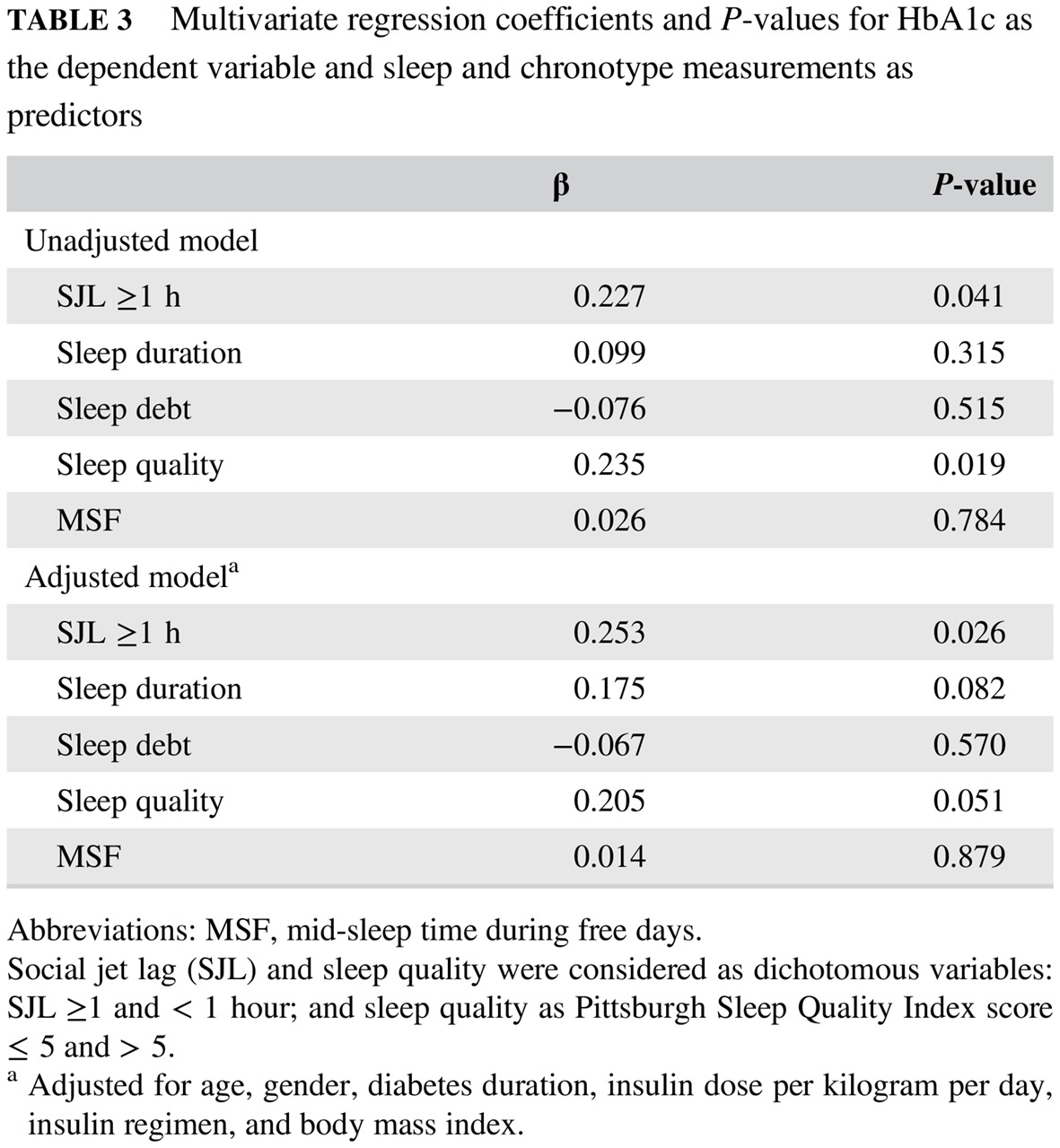
Social jetlag, sleep-related parameters, and glycemic control in adults with type 1 diabetes: Results of a cross-sectional study
成年1型糖尿病患者的社交时差、睡眠相关参数与血糖控制:一项横断面研究结果
- Pages: 394-401
- First Published: 10 October 2018
Highlights
- In patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D), small recurrent circadian rhythm disruption (social jetlag) is associated with a poor glycemic control and this association is independent of age, sex, diabetes duration, total daily insulin dose, body mass index, and other sleep and circadian rhythm measurements.
- Social jetlag does not interact with sleep quality in exerting a deleterious effect on glycemic control in T1D patients.
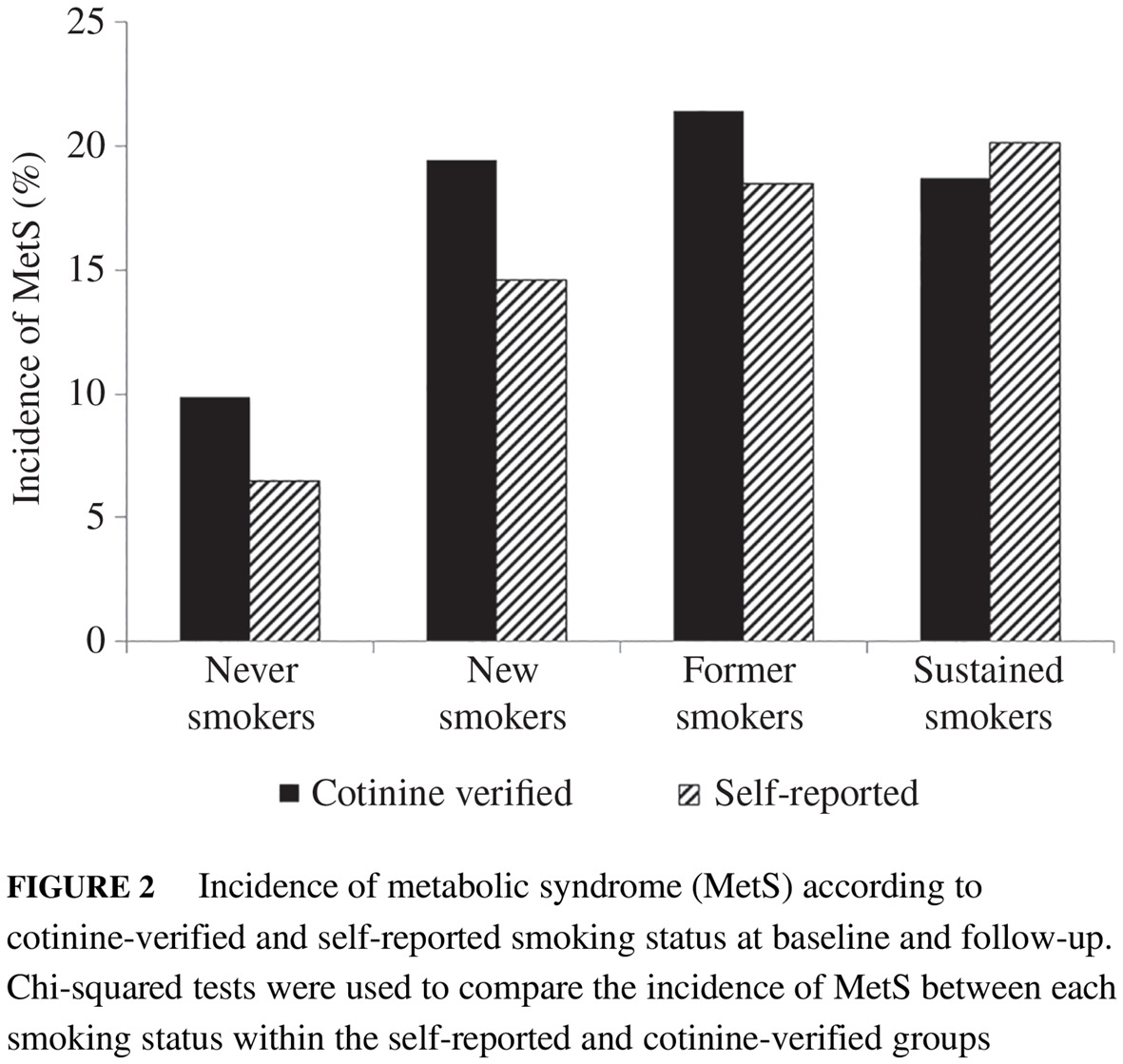
Association of self-reported and cotinine-verified smoking status with incidence of metabolic syndrome in 47 379 Korean adults
47379名韩国成年人自我报告的吸烟状态以及可替宁证实的吸烟状态与代谢综合征发生率之间的关系
- Pages: 402-409
- First Published: 11 October 2018