Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Notes from the world congress on insulin resistance, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease
来自胰岛素抵抗、糖尿病与心血管疾病世界大会 (WCIRDC) 的记录
- Pages: 258-260
- First Published: 18 December 2018
NEWS
American Heart Association Scientific Sessions 2018
- Pages: 261-264
- First Published: 11 December 2018
EDITORS' RECOMMENDATION
Cardiovascular, cancer and mortality events after bariatric surgery in people with and without pre-existing diabetes: A nationwide study
既往存在或者不存在糖尿病的患者接受减肥手术 (bariatric surgery) 后的心血管、癌症以及死亡事件:一项全国性的研究
- Pages: 265-272
- First Published: 07 September 2018
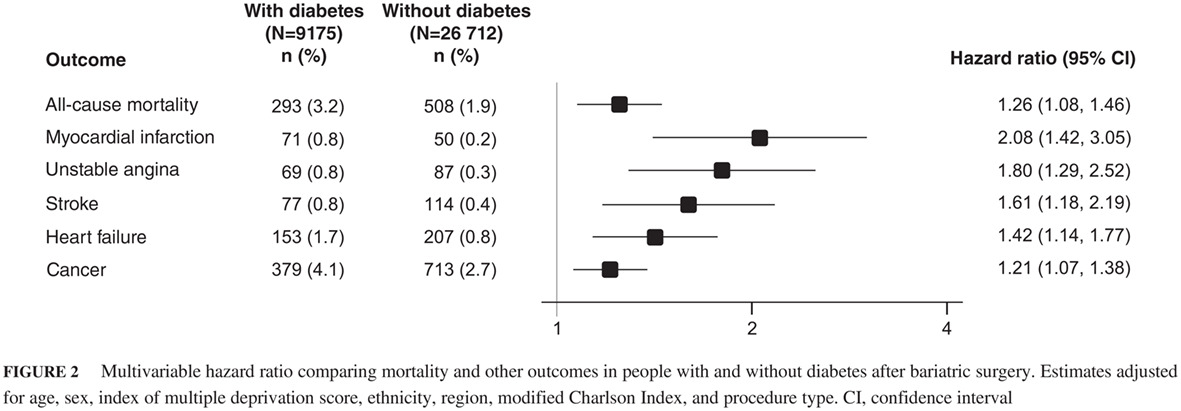
Highlights
- Patients with diabetes carry a residual risk of cardiovascular, cancer, and mortality events after bariatric surgery: compared with patients without diabetes, the risk is 26%, 21%, 42%, and 61% higher for all-cause mortality, cancer, heart failure, and stroke, respectively, and double for myocardial infarction.
- The risk of death after bariatric surgery remains higher in patients without diabetes than in subjects of same age from the general population.
High prevalence of comorbid autoimmune diseases in adults with type 1 diabetes from the HealthFacts database
在HealthFacts数据库中成年1型糖尿病患者合并自身免疫性疾病的患病率高
- Pages: 273-279
- First Published: 18 September 2018
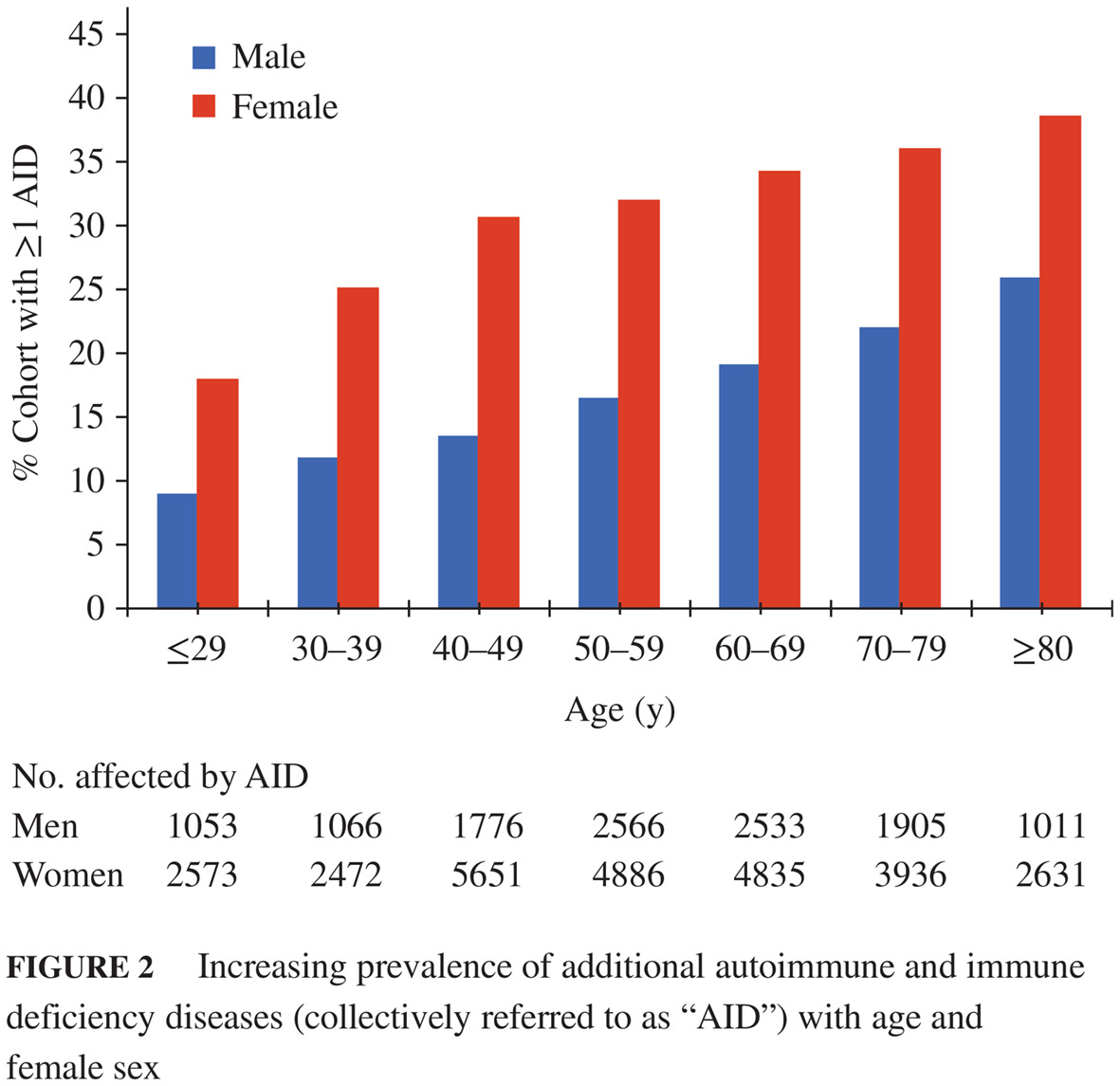
Highlights
- Patients with type 1 diabetes are at risk for other autoimmune diseases (ie polyautoimmunity); the most common autoimmune diseases were thyroid disease (20.1%), systemic rheumatic diseases (3.4%), rheumatoid arthritis specifically (2.0%), and gastrointestinal autoimmune diseases (1.4%).
- Caucasians were more likely than other ethnicities to have an additional autoimmune disease.
- Autoimmune disease prevalence increased with age, significantly in women, with 38.5% of women over 80 years of age having an additional autoimmune disease.
REVIEW ARTICLES
Linking of metabolomic biomarkers with cardiometabolic health in Chinese population
中国人群代谢组学标记物与心血管代谢健康的关联研究
- Pages: 280-291
- First Published: 21 September 2018
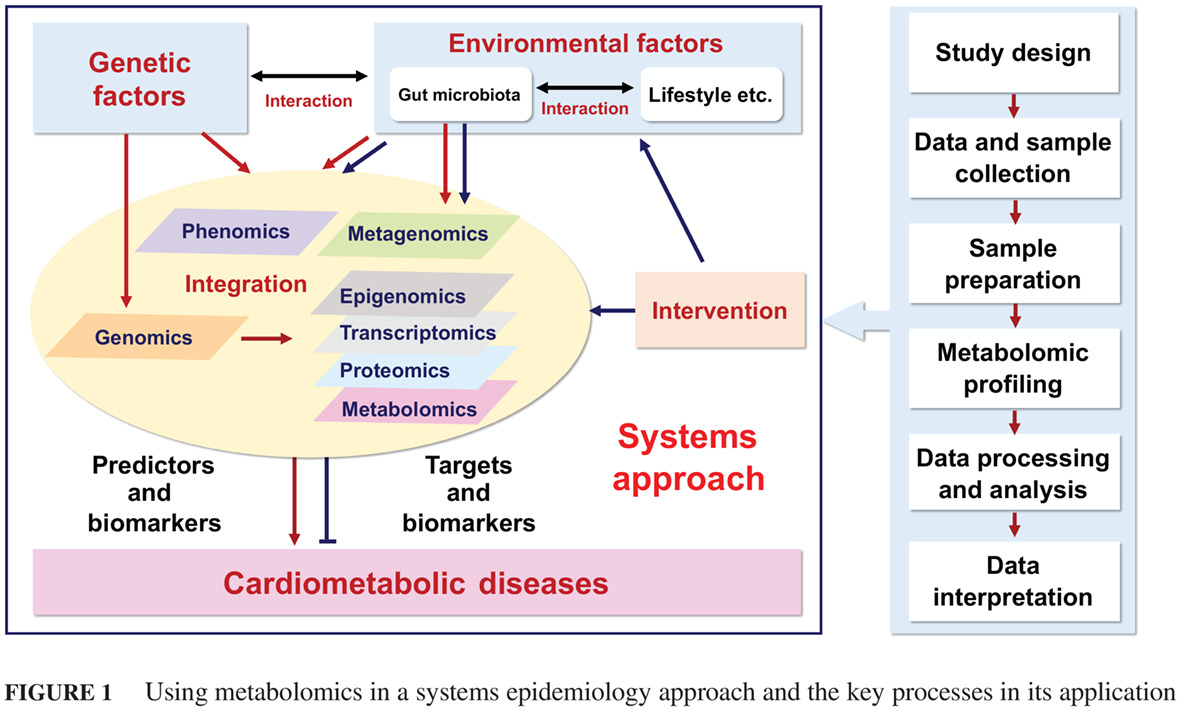
Highlights
- Given the increased prevalence of and higher susceptibility to cardiometabolic diseases in the Chinese population, understanding the roles of genetic and non-genetic factors in the pathogenesis of diseases, identifying novel biomarkers for disease prediction, and eventually developing more effective intervention strategies are urgently needed.
- “Omics”-based technologies, especially newly emerged metabolomics, have shown great potential in discovering novel biomarkers for precision health. However, there are still many challenges to be overcome.
Concentrated insulins: History and critical reappraisal
浓缩胰岛素:历史以及关键的再评价
- Pages: 292-300
- First Published: 28 September 2018
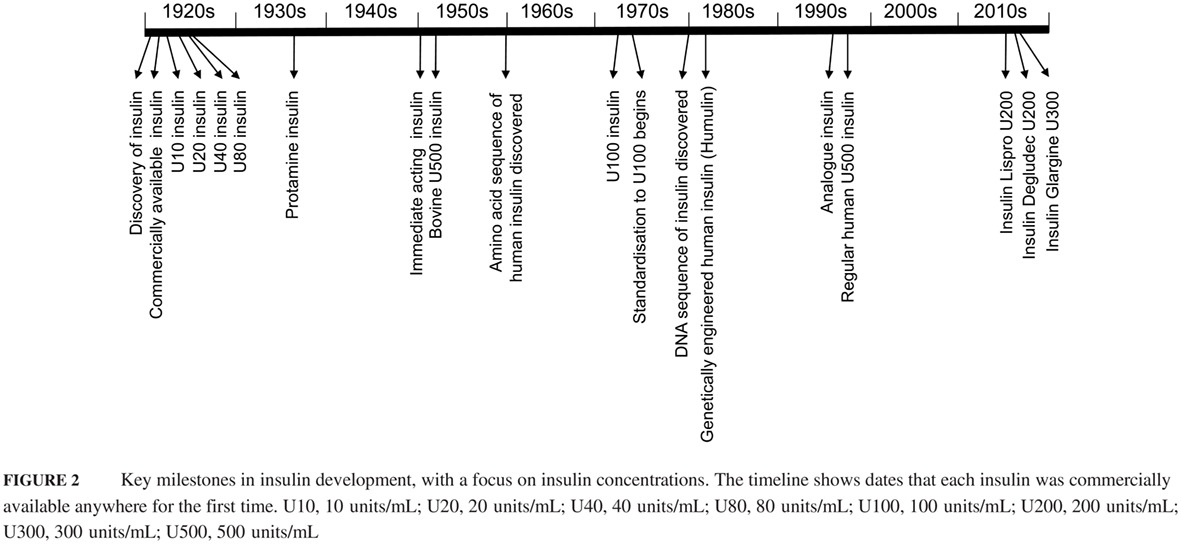
Highlights
- Since its first development, manufactured insulin has become increasingly concentrated.
- Concentrated insulins expand the options currently available to healthcare professionals in optimizing treatment for patients. Concentrated insulins provide changes in time-action profiles, smaller injection volumes, and potentially fewer injections, which may improve patients’ experience with insulin and may lead to better adherence.
- Healthcare professionals need to understand concentrated insulins to advise their patients. Patient education concerning concentrated insulins is key to their safe and effective use.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Crossing family histories of diabetes and cardiovascular disease leads to unexpected outcomes in diabetic offspring
糖尿病与心血管疾病交叉家族史可使糖尿病后代出现意料之外的结果
- Pages: 301-308
- First Published: 13 August 2018
Highlights
- Common family histories of diabetes mellitus and early onset coronary heart disease predispose to increased microvascular or macrovascular risk, respectively, in diabetic offspring.
- Crossing these histories does not randomly redistribute vascular risk, because patients with dual familial burden see their macrovascular phenotype mitigated by having parental diabetes.
- Hyperinsulinemia, dysfunctional high-density lipoproteins and lipoprotein[a] emerge from this analysis as potential mediators of inherited macrovascular risk.
Peripheral pain is enhanced by insulin-like growth factor 1 and its receptors in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes mellitus
在2型糖尿病小鼠模型中胰岛素样生长因子1及其受体可增强周围疼痛
- Pages: 309-315
- First Published: 13 August 2018
Highlights
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1) has a hyperalgesic effect in diabetic mice, which is related to the IGF1 receptor/c-raf/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway.
- We further explored the possible signaling pathways of pain in this study.
Gain in adiposity over 3 years is associated with progressive renal decline in multi-ethnic South-east Asians with type 2 diabetes
在多民族的东南亚2型糖尿病患者中超过3年的肥胖可导致肾功能逐渐下降
- Pages: 316-325
- First Published: 03 September 2018
Highlights
- This analysis of multiethnic South-east Asians with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) showed that longitudinal gain in adiposity, albeit relatively modest, was sufficient to be associated with annual estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) decline, but only in men.
- Increased adiposity also predicted rapid eGFR decline and progression of albuminuria.
- The findings suggest that increased adiposity over time adversely affects renal outcomes, highlighting the importance of carefully designing weight-neutral or -loss antidiabetic treatment regimes when managing T2DM in the clinic to ameliorate progressive kidney disease.
Effects of combined treatment with blood flow restriction and low-intensity electrical stimulation on diabetes mellitus-associated muscle atrophy in rats
限制血流与低强度电刺激联合治疗对大鼠糖尿病相关肌肉萎缩的影响
- Pages: 326-334
- First Published: 18 September 2018
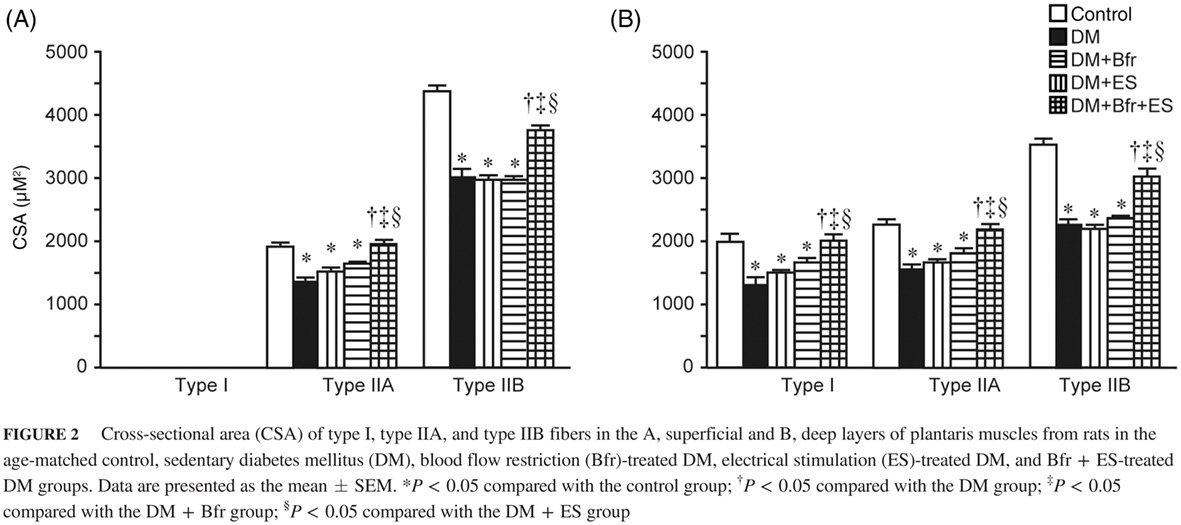
Highlights
- Combined treatment of blood flow restriction and low-intensity electrical stimulation (ES) can rescue diabetes mellitus-associated downregulation of protein synthesis and decreased translational activity and capacity.
- The study findings suggest that combined treatment with blood flow restriction and low-intensity ES has the potential to become an effective therapeutic intervention to prevent diabetes-associated muscle atrophy.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Carotid artery stenosis, diabetes mellitus, and TCD4+ lymphocyte subpopulations
颈动脉狭窄、糖尿病与TCD4+淋巴细胞亚群分布情况
- Pages: 335-336
- First Published: 09 November 2018









