Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW ARTICLE
From the infant to the geriatric patient—Strategies for inhalation therapy in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Pages: 487-498
- First Published: 13 April 2023
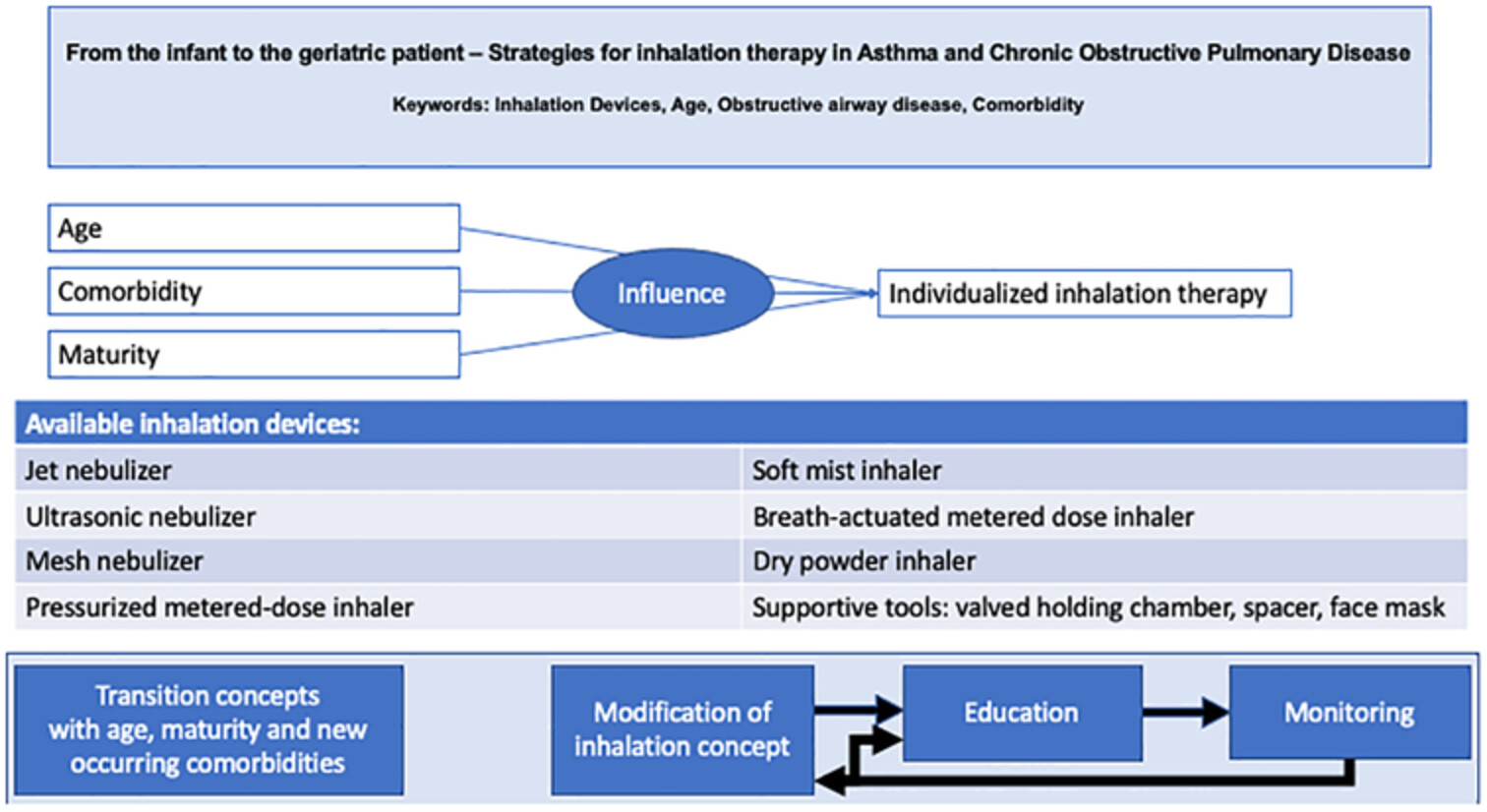
Inhalation therapy is a highly individualized concept of therapy. Age, maturity and comorbidities have to be considered when choosing a specific inhalation device. Standardized algorithms may support this decision process. A close monitoring is essential as it may detect handling mistakes and the need to modify the device concept. A routine reevaluation of the inhalation concept should be implemented with age, maturation and new occurring comorbidities.
MINI REVIEW
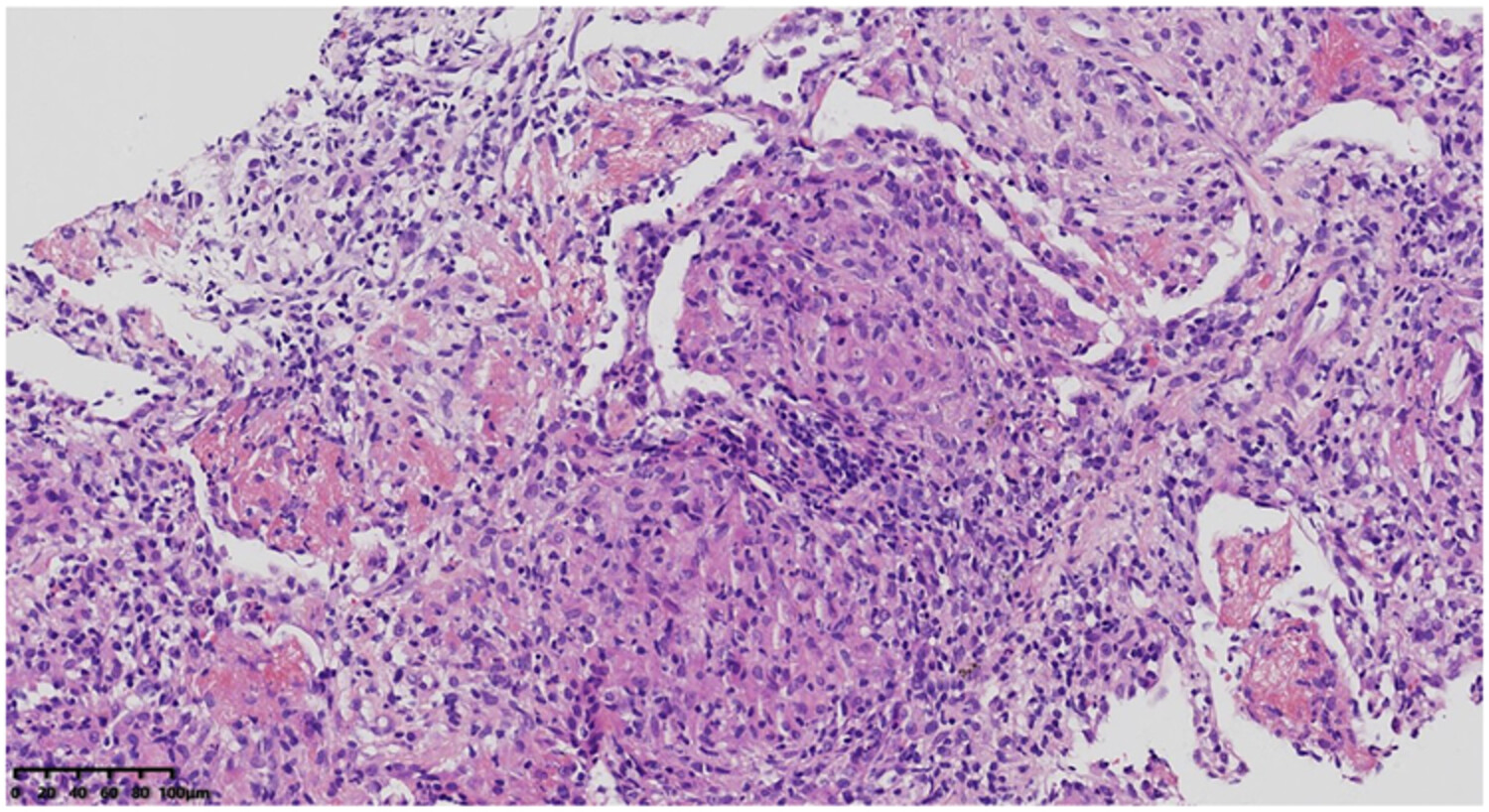
Pulmonary tuberculosis associated acute fibrinous and organizing pneumonia: A case report and literature review
- Pages: 499-506
- First Published: 08 May 2023
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
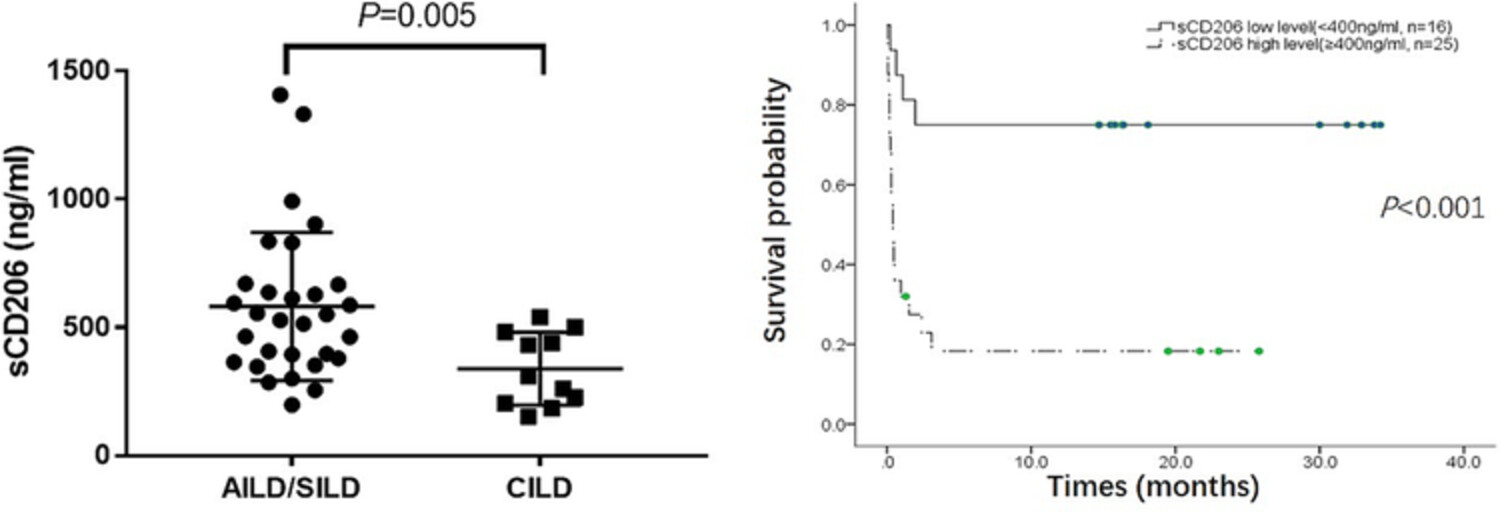
Soluble CD206 levels correlate with disease deterioration and predict prognosis of anti-MDA5 antibody-positive dermatomyositis related interstitial lung disease
- Pages: 507-515
- First Published: 11 April 2023
Association of nitric oxide synthase gene polymorphism with asthma: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 516-526
- First Published: 19 April 2023
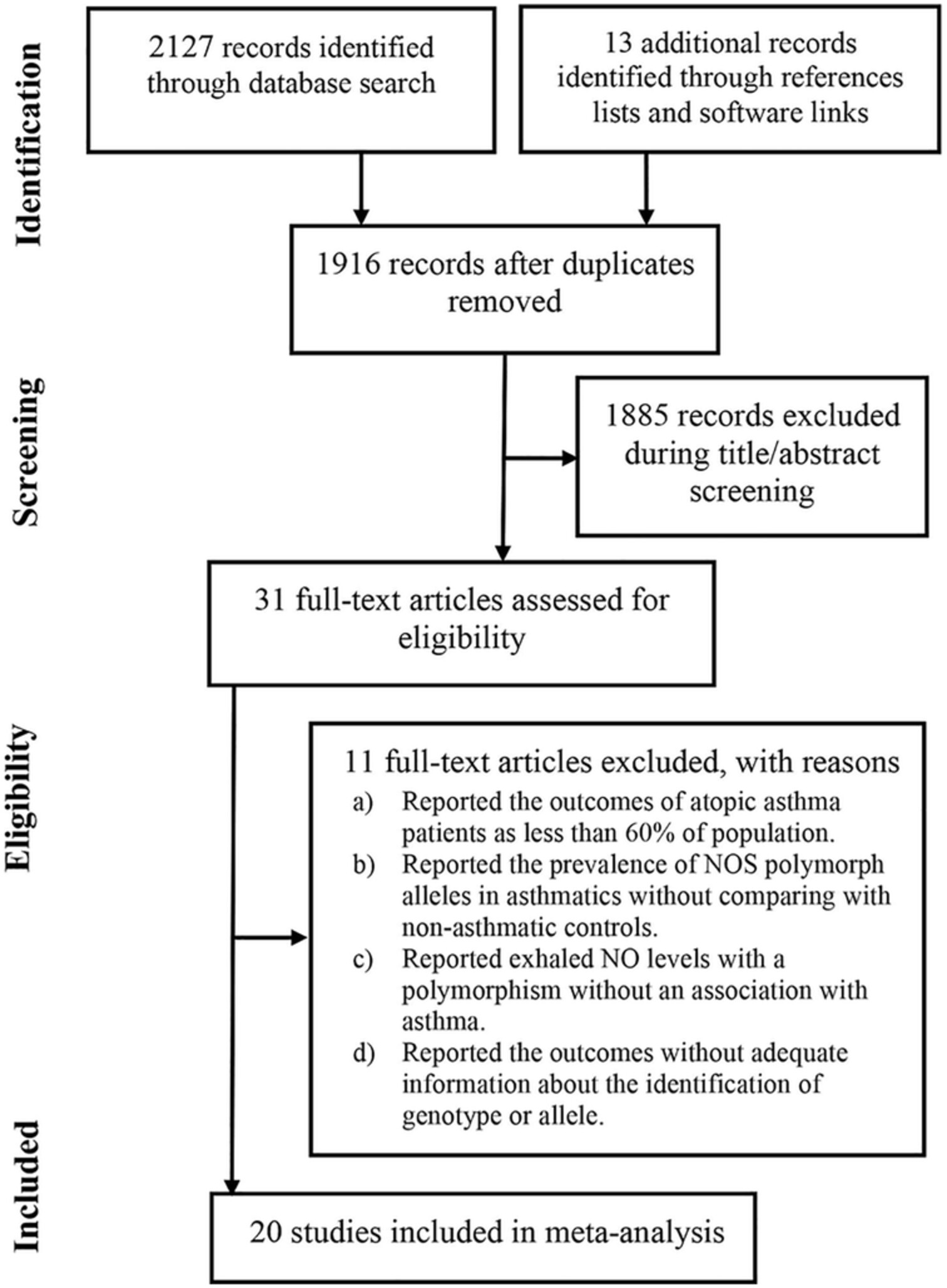
Several lines of evidence suggest the role of polymorphisms in NOS genes to affect asthma etiology or prognosis. However, data are varying depending on the nature of variant, ethnicity, study and comparison design differences, and disease parameters. Moreover, a very few polymorphisms are studied in different ethnic groups or localities. Thus, replication of available data will refine the evidence regarding the role of various NOS gene polymorphisms in affecting the etiology and prognosis of asthma.
An investigation on the respiratory mechanics of mechanically ventilated patients during spontaneous breathing trials with enhanced low-level pressure support ventilation
- Pages: 527-535
- First Published: 09 May 2023

Low-level pressure support ventilation (PSV) is most commonly adopted in spontaneous breathing trials (SBTs). This study aims to investigate the effects of two PSV protocols on the patients' respiratory mechanics. These findings suggest that the enhanced low-level PSV protocol was more likely to induce a higher number of patient–ventilator asynchronies in difficult-to-wean patients.
Aetiological distribution of pulmonary hypertension and the value of transthoracic echocardiography screening in the respiratory department: A retrospective analysis from China
- Pages: 536-547
- First Published: 04 May 2023

This study confirmed that the distribution of PH aetiology in respiratory department differs from the total population. TTE is more suitable for the diagnosis of pulmonary artery obstructive pulmonary hypertension in the respiratory department, but overall, there are still limitations compared to RHC and further studies are needed to set the threshold values.
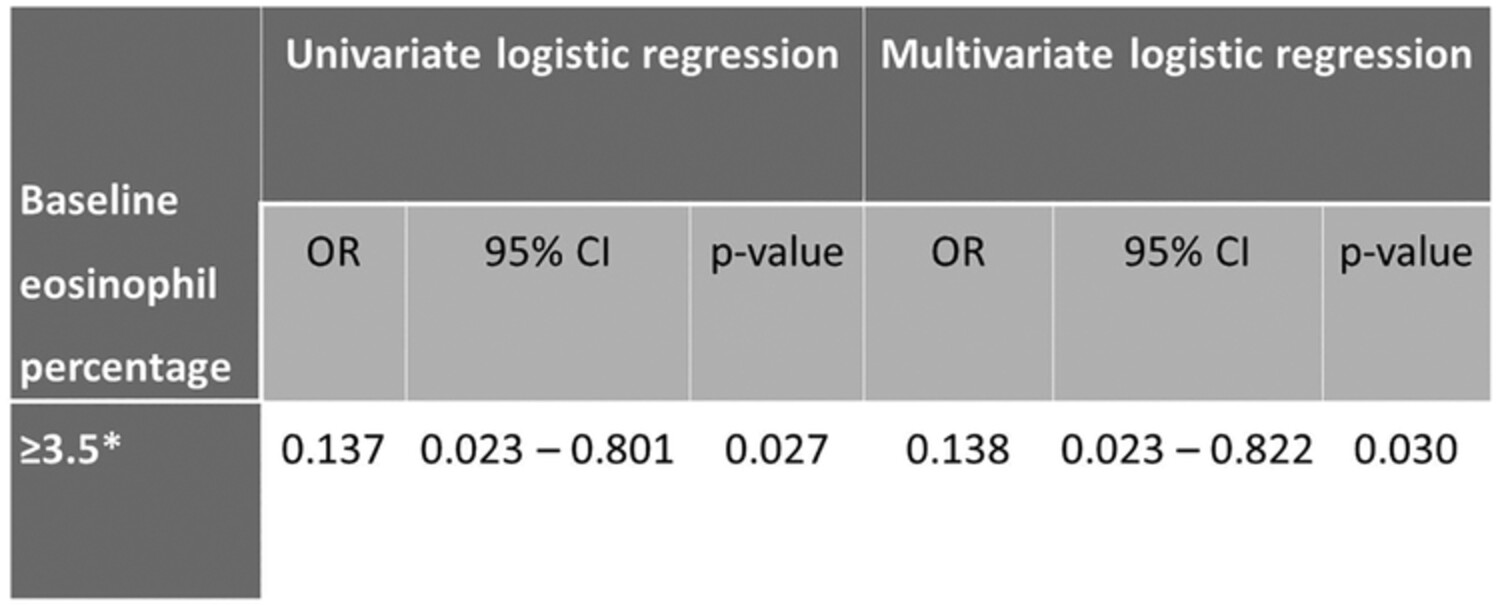
Blood eosinophil percentage as a predictor of response to inhaled corticosteroid in bronchiectasis
- Pages: 548-555
- First Published: 26 April 2023
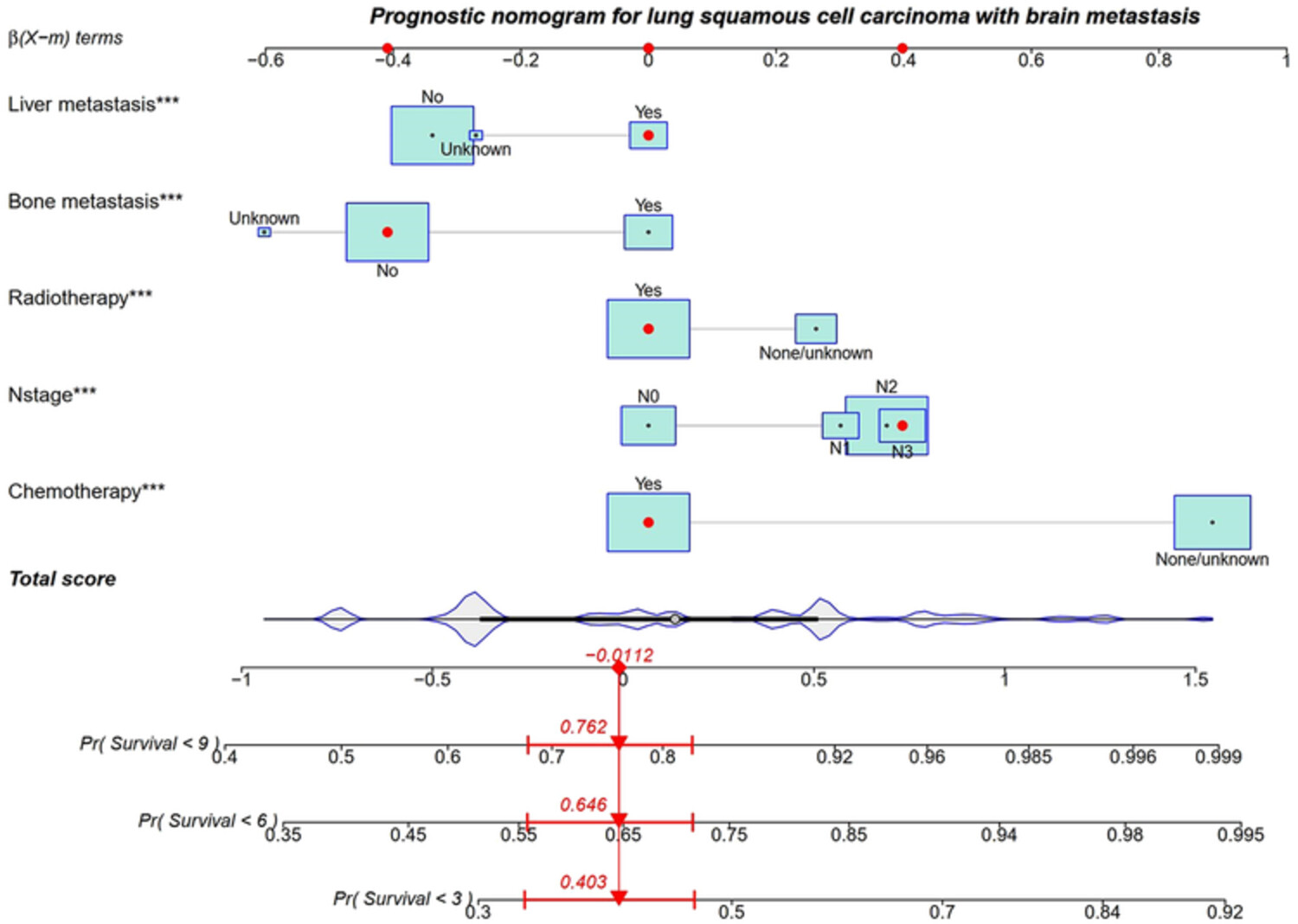
A visualized dynamic prediction model for overall survival in patients diagnosed with brain metastases from lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 556-567
- First Published: 29 April 2023
The GLCCI1 rs37973 variant and the efficacy of inhaled corticosteroids in the treatment of asthma: A meta-analysis
- Pages: 568-579
- First Published: 08 May 2023
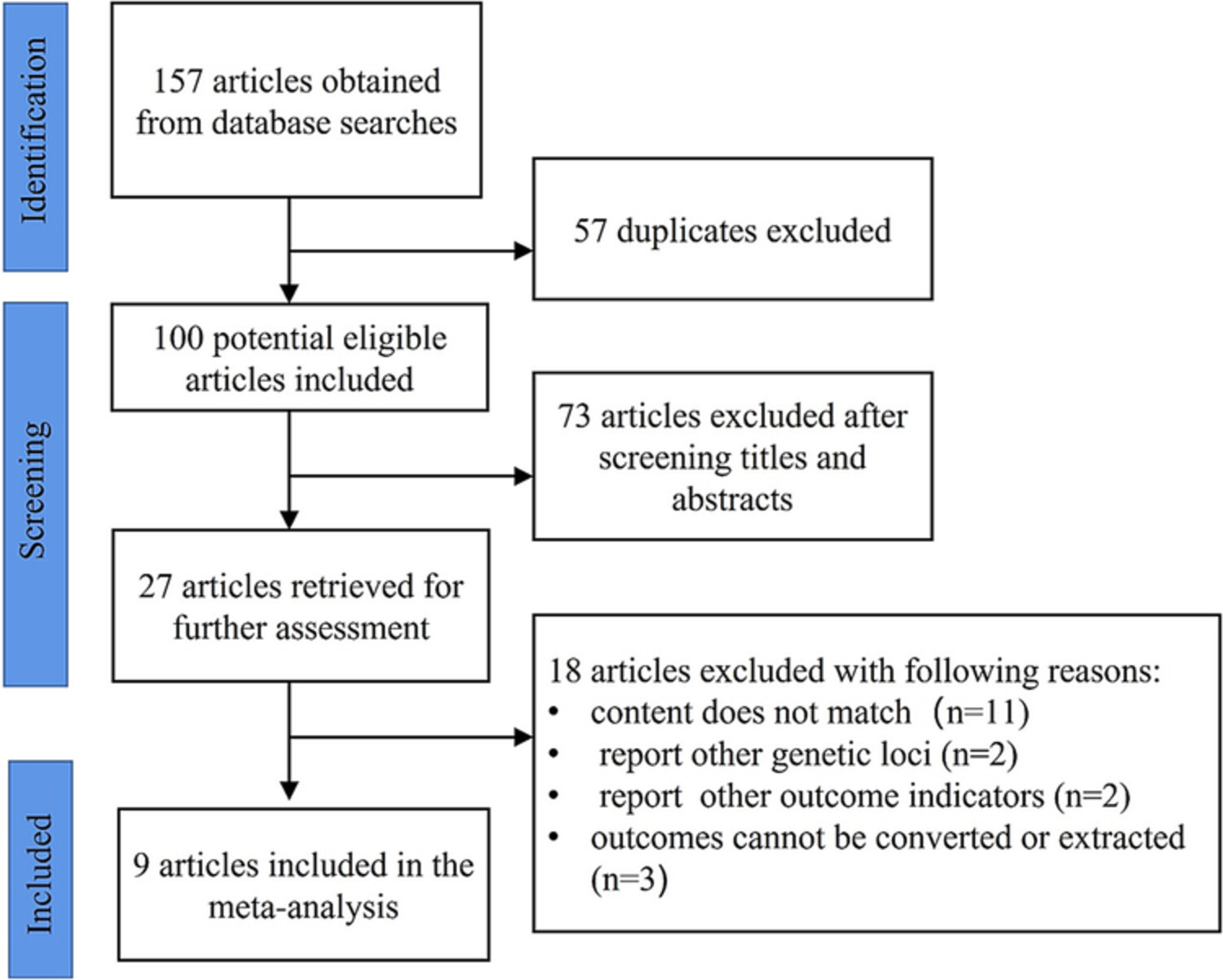
This meta-analysis suggests that the GLCCI1 rs37973 variant had significant influence on ICS therapy in patients with asthma. Compared with the AA and AG group, the GG group had smaller improvement in lung function with ICS. Our meta-analysis could provide evidence for the optimisation of ICS therapy by GLCCI1 rs37973 genotyping in clinical practice.
The risk of venous thromboembolism and blood hyperlactatemia is associated with increased mortality among critically ill patients with Covid-19
- Pages: 580-588
- First Published: 05 May 2023
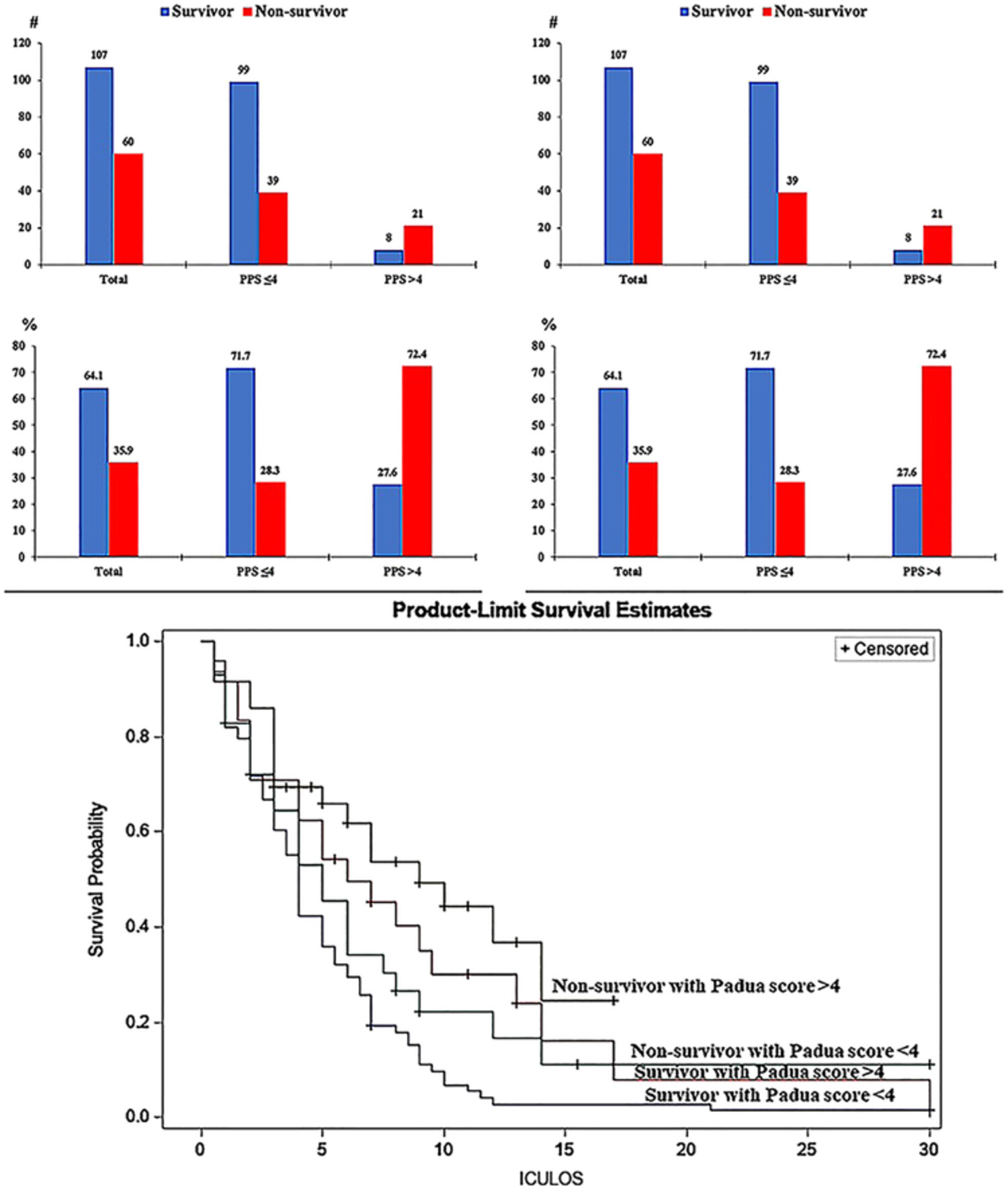
Critically ill Covid-19 patients treated in the ICU in Saudi Arabia had a greater mortality risk when they had VTE risk and blood hyperlactatemia. These findings indicated that these individuals required more efficient VTE preventive methods based on evaluating their bleeding risk and monitoring together glucose and lactate, including in people without diabetes.
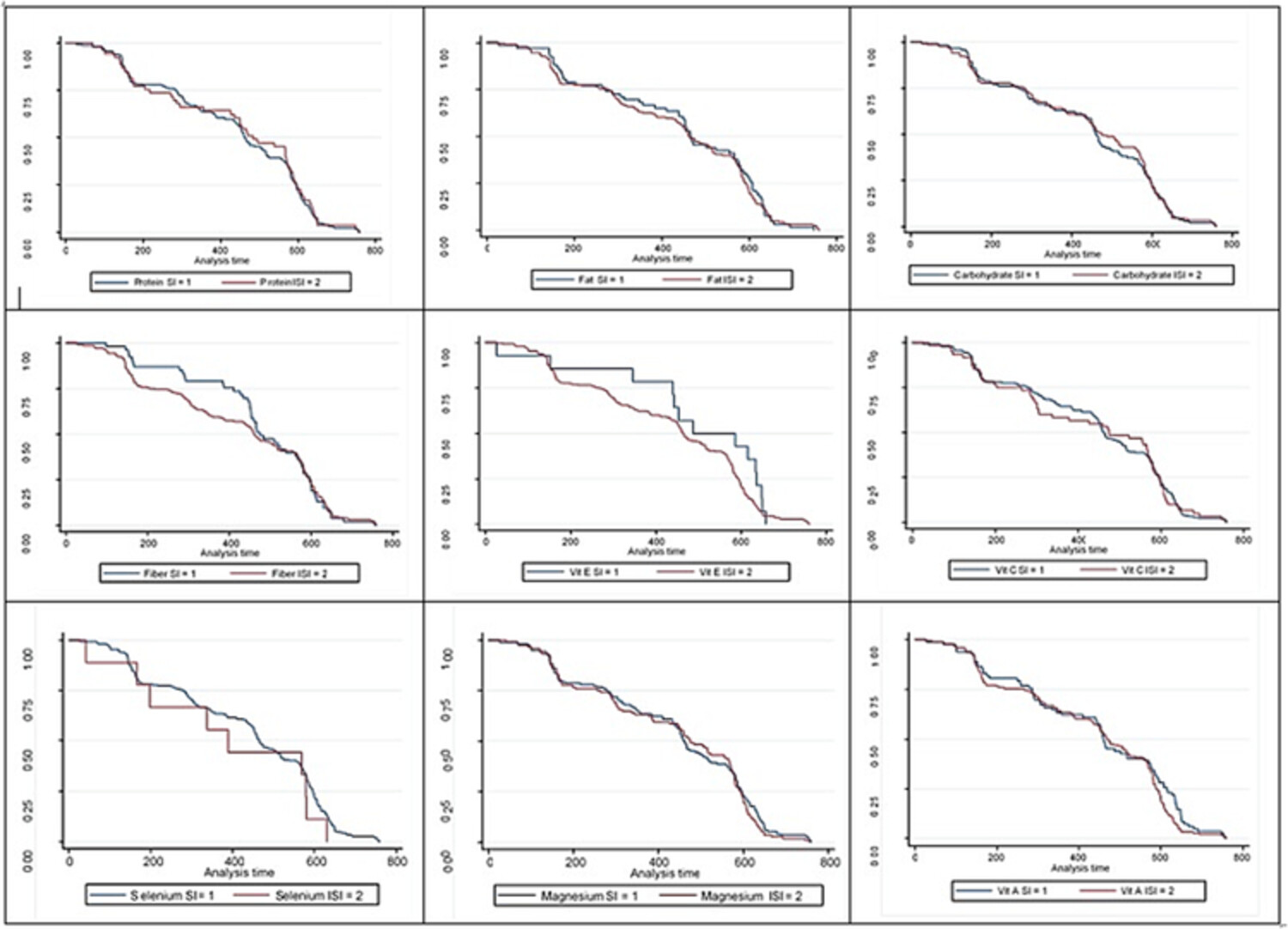
The association between nutrients and occurrence of COVID-19 outcomes in the population of Western Iran: A cohort study
- Pages: 589-602
- First Published: 11 May 2023
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Reply to the letter to the editor regarding the study “The effectiveness of gabapentin and gabapentin/montelukast combination compared with dextromethorphan in the improvement of COVID-19-related cough: A randomized, controlled clinical trial”
- Pages: 603-604
- First Published: 26 April 2023