Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Clinical characteristics and serum inflammatory markers of community-acquired mycoplasma pneumonia in children
- Pages: 607-617
- First Published: 04 May 2023
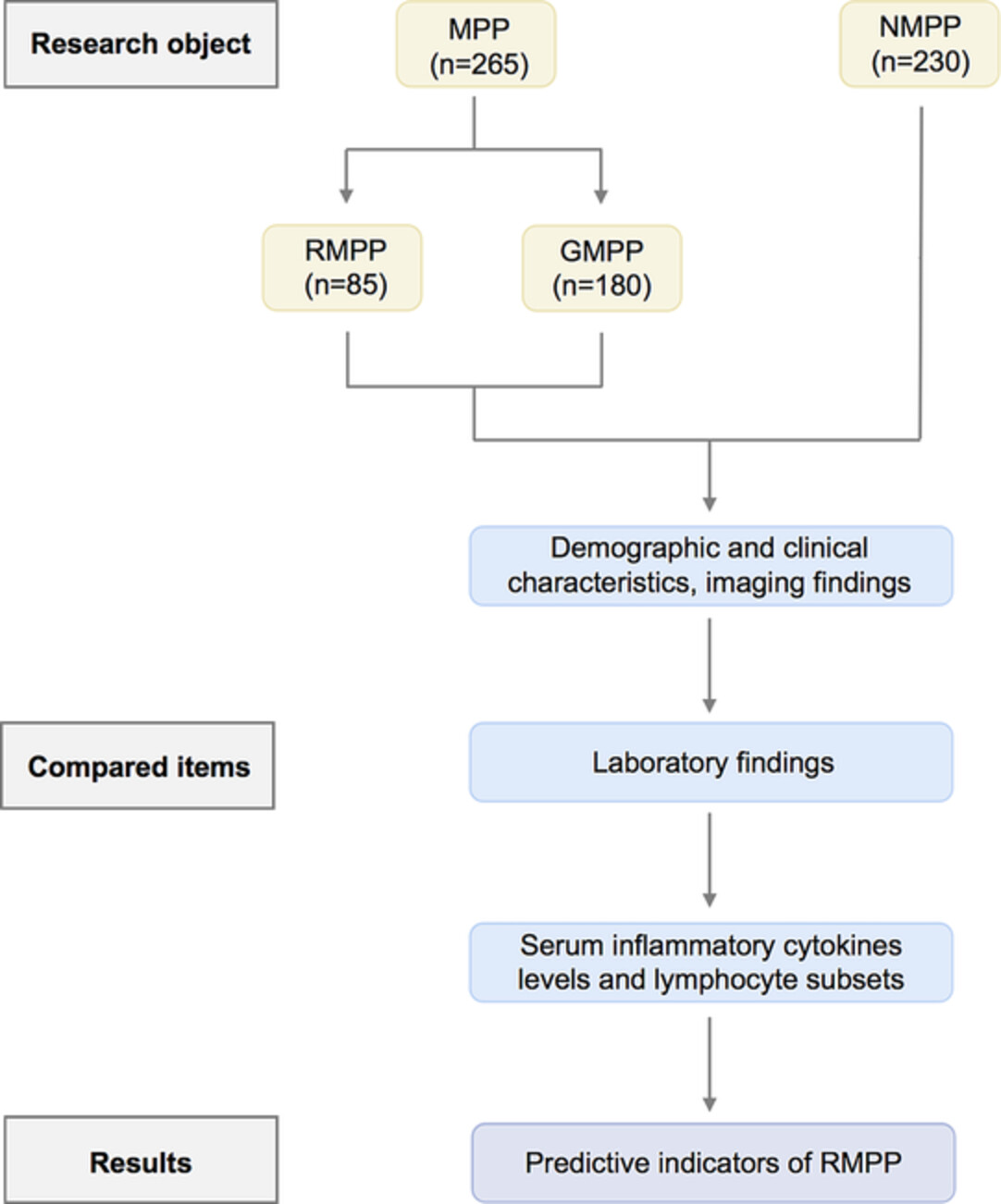
We compare the demographic and clinical features, laboratory and imaging findings in mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia (MPP) children with non-MPP (NMPP) children and general MPP (GMPP) children with refractory MPP (RMPP) children and analysis the relationship with the severity of disease. This study showed that the measurement of IL-6, LDH, IL-10 and D-dimer can be useful predictors for RMPP. There were differences in clinical characteristics and serum inflammatory markers between MPP group and NMPP group, RMPP group and GMPP group.
Machine learning-based identification of cuproptosis-related markers and immune infiltration in severe community-acquired pneumonia
- Pages: 618-628
- First Published: 06 June 2023
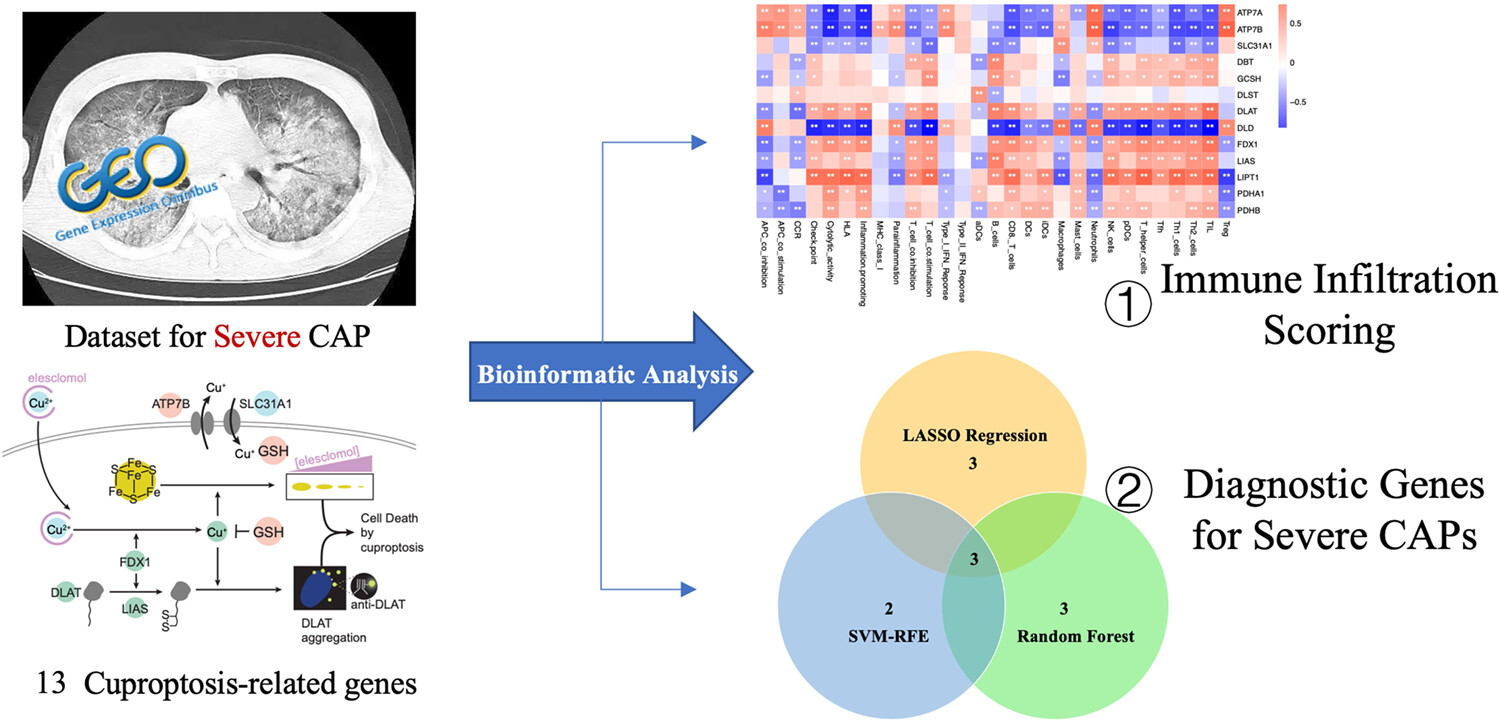
Cuproptosis is a novel form of copper-induced mitochondrial cell death. Researchers for the first time used three machine learning algorithms to identify cuproptosis-related genes (CRGs) in severe community-acquired pneumonia (SCAP), a major cause of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). This article found that CRGs were involved in immune cell infiltration and constructed a three-gene model to predict SCAP onset.
miR-126-5p expression in the plasma of patients with sepsis-induced acute lung injury and its correlation with inflammation and immune function
- Pages: 629-637
- First Published: 29 May 2023
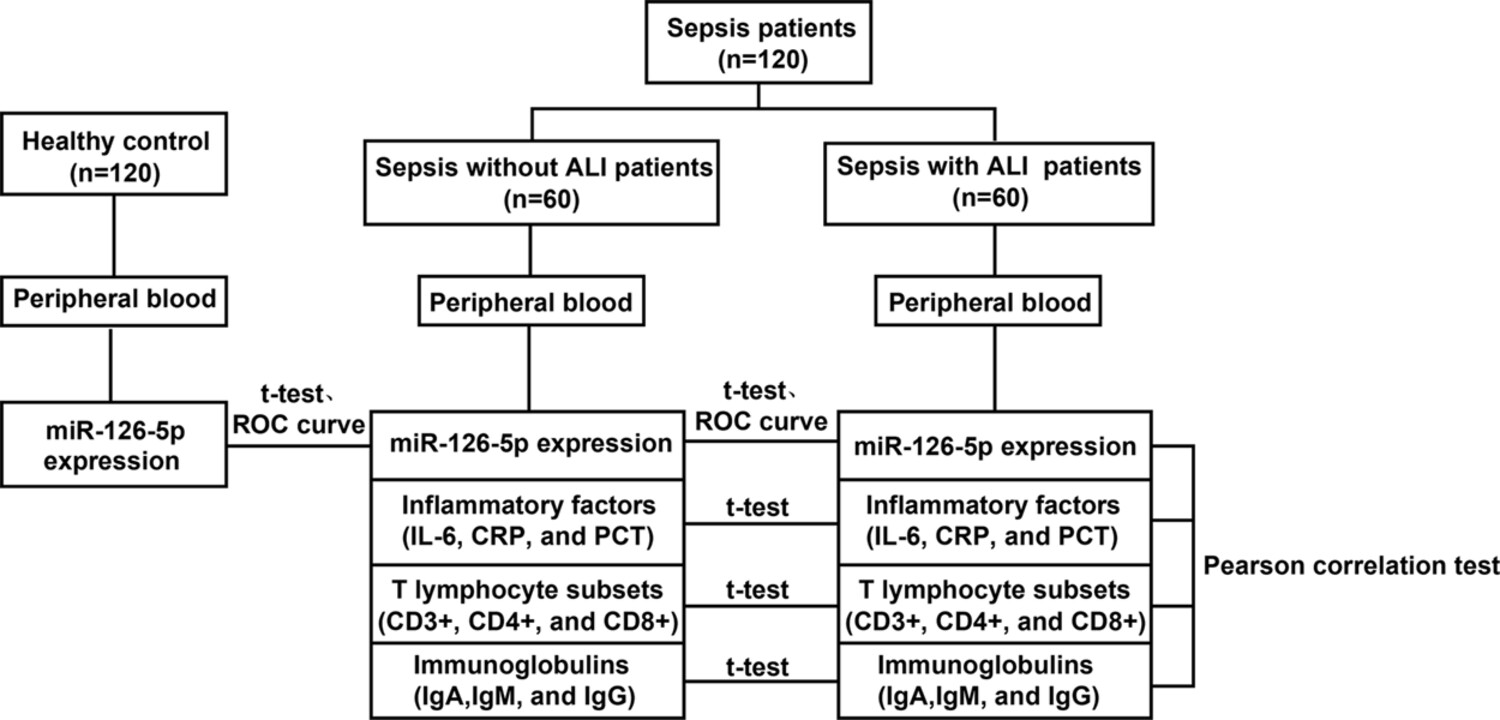
The peripheral blood of patients with sepsis-induced ALI was obtained, and the levels of inflammatory factors (interleukin-6 [IL-6], C-reactive protein [CRP], and procalcitonin [PCT]) were determined. Meanwhile, T lymphocyte subsets (CD3+, CD4+, and CD8+) and immunoglobulins (IgA, IgM, and IgG) were tested. miR-126-5p and TRAF6 mRNA expression in plasma was assessed. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was performed to assess the diagnostic accuracy of miR-126-5p in sepsis without ALI and sepsis with ALI. Correlation between miR-126-5p expression and clinical indicators was analyzed. The targeting relationship between miR-126-5p and TRAF6 was verified.
Effect of PRDX6 gene polymorphism on susceptibility to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in the Chinese Han population
- Pages: 638-646
- First Published: 17 June 2023
Rapid vision improvement by using icotinib in a patient with bilateral choroidal metastases symmetrically from lung cancer
- Pages: 647-653
- First Published: 14 June 2023
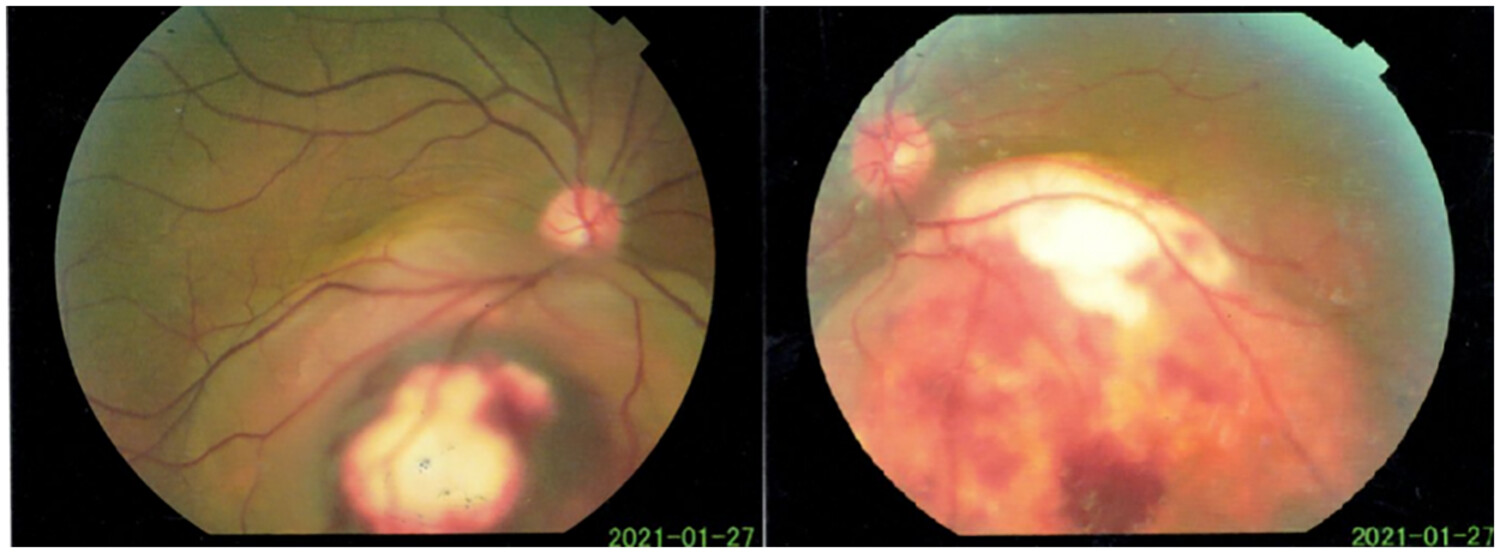
A man presented with vision losing as an initial presentation and ophthalmofundoscopy with PET/CT confirmed the bilateral choroidal metastases from lung cancer. His visions were rapidly improved after 5 days of icotinib treatment with progression-free survival for up to 17 months. Icotinib following by almonertinib was an alternative therapy for choroidal metastasis of lung cancer.
Evaluation of the prognostic value of lncRNA UCA1 combined with extravascular lung water index and lung ultrasound score in patients with acute lung injury
- Pages: 654-662
- First Published: 15 June 2023
Patients with ALI were cataloged into the survival group and death group according to the prognosis. The relative expression of lncRNA UCA1, the scores of EVLWI, and the LUS score were detected in patients with ALI. The ROC curve and the logistic regression analysis showed that highly expressed UCA1 was a biomarker in forecasting the outcome of patients with ALI. It had high accuracy in predicting the endpoint of patients with ALI when combined with LUS and EVLWI.
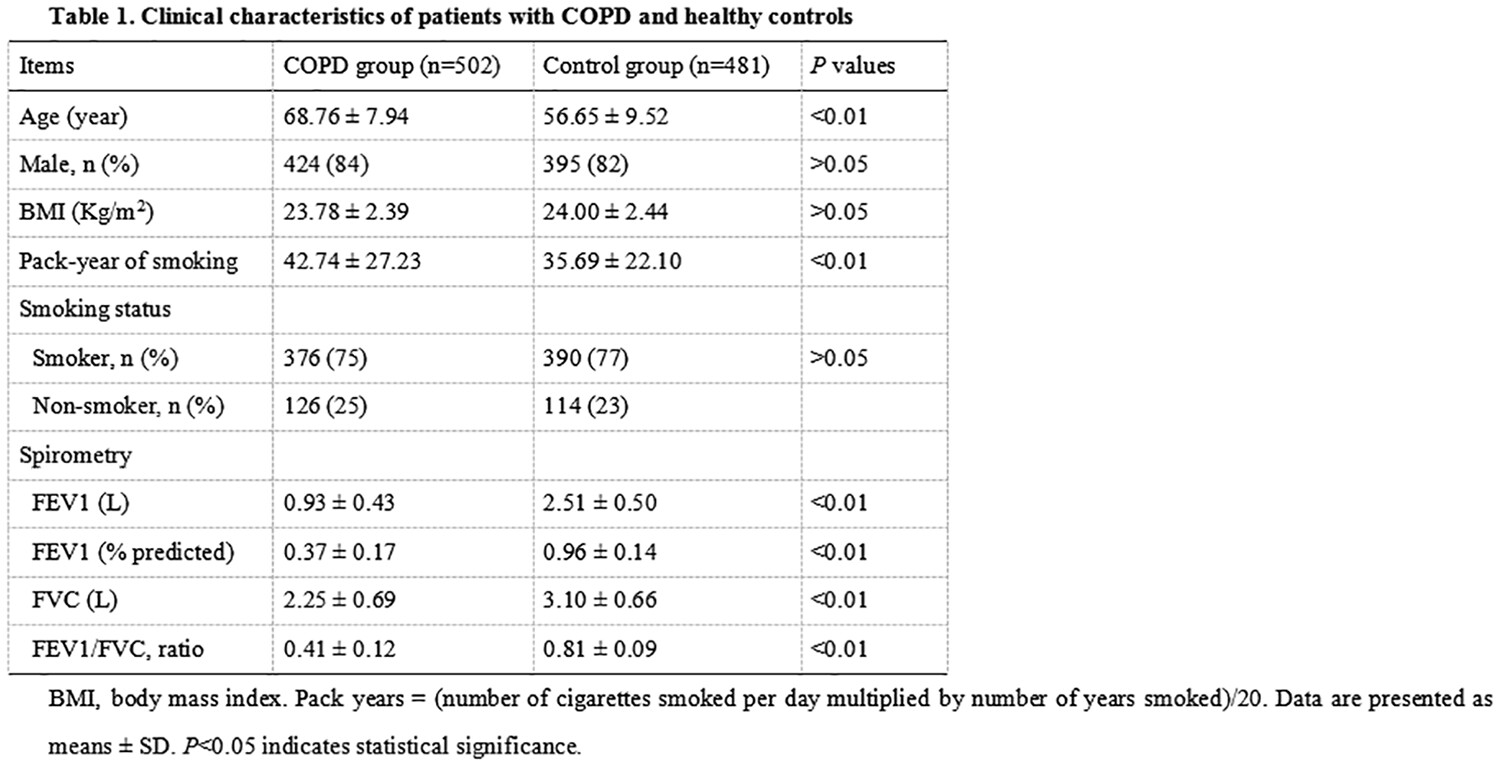
Risk factors for the recurrence in pulmonary tuberculosis patients with massive hemoptysis
- Pages: 663-671
- First Published: 05 July 2023
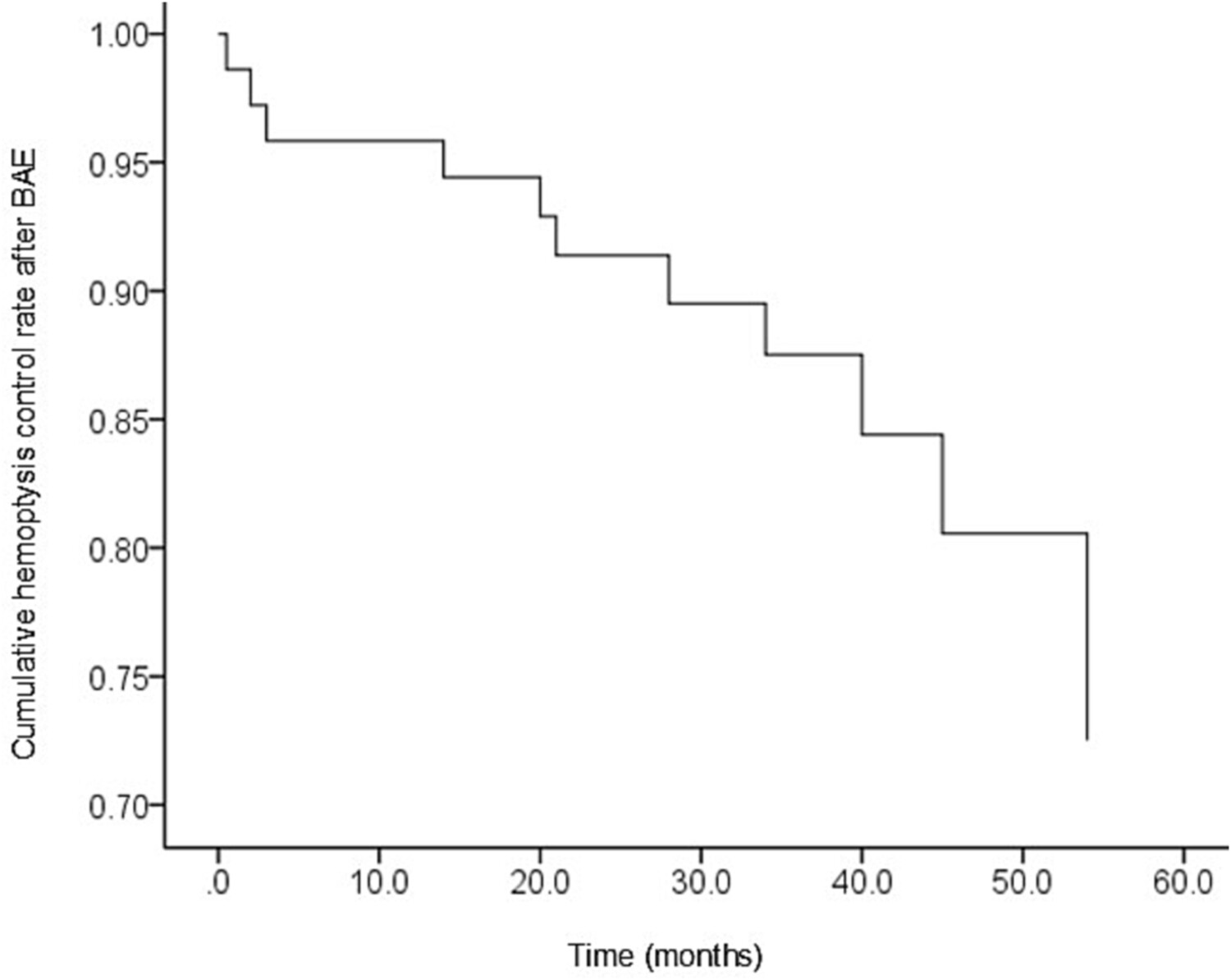
Long-term effects of air pollution on hospital admissions and mortality for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Beijing, China
- Pages: 672-683
- First Published: 01 July 2023
Efficient clinical data analysis for prediction of coal workers' pneumoconiosis using machine learning algorithms
- Pages: 684-693
- First Published: 28 June 2023
After close data analysis and careful evaluation of machine learning algorithms, clinical indicators belonged to significant predictors of pulmonary disease diagnosis. We chose the embedded method using three feature selection approaches to perform the prediction analysis, then performed machine learning algorithms as the model backbones, and combined them with three feature selection methods, respectively, to determine the optimal predictive model.
BRIEF REPORT
“It's like a forgotten issue sometimes …”: Qualitative study of individuals living and caring for people with chronic breathlessness
- Pages: 694-700
- First Published: 23 June 2023
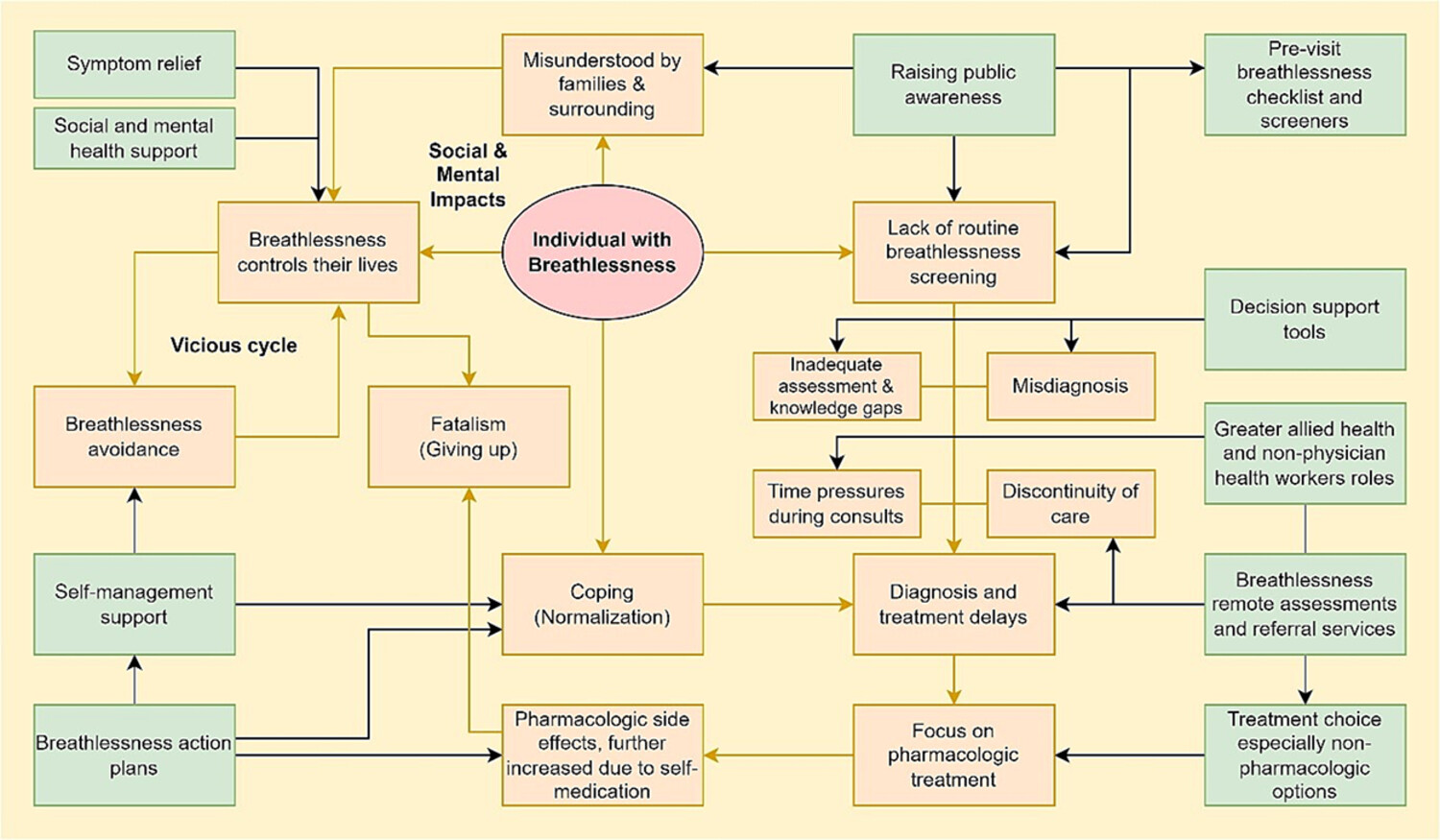
A qualitative study of carers and patients with chronic breathlessness found patients suffer from lack of awareness, discontinuity of care, and too few clinical and self-management options. To improve outcomes, community perspectives, practice, and system changes are required to improve identification, shorten time to diagnosis, provide wider treatment options especially nonpharmacologic support, and to empower patients to self-manage.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Incident changes in the prevalence of influenza type A virus among children before and after COVID-19 pandemic in Hangzhou, China
- Pages: 701-703
- First Published: 29 June 2023