Editor-in-Chief Yuanlin Song; Executive Editor-in-Chief Bing Li
The Clinical Respiratory Journal (CRJ) is an open access journal providing a forum for clinical research in all areas of respiratory medicine from clinical lung disease to basic research relevant to the clinic. Publishing original research, review articles, case studies, editorials and book reviews in all areas of clinical lung disease.
Journal Metrics
- 3.9CiteScore
- 2.3Journal Impact Factor
- 26%Acceptance rate
- 74 days Submission to first decision
As part of Wiley’s Forward Series, this journal offers a streamlined, faster publication experience with a strong emphasis on integrity. Authors receive practical support to maximize the reach and discoverability of their work.
Themed Collections
Articles
There are no results at this time
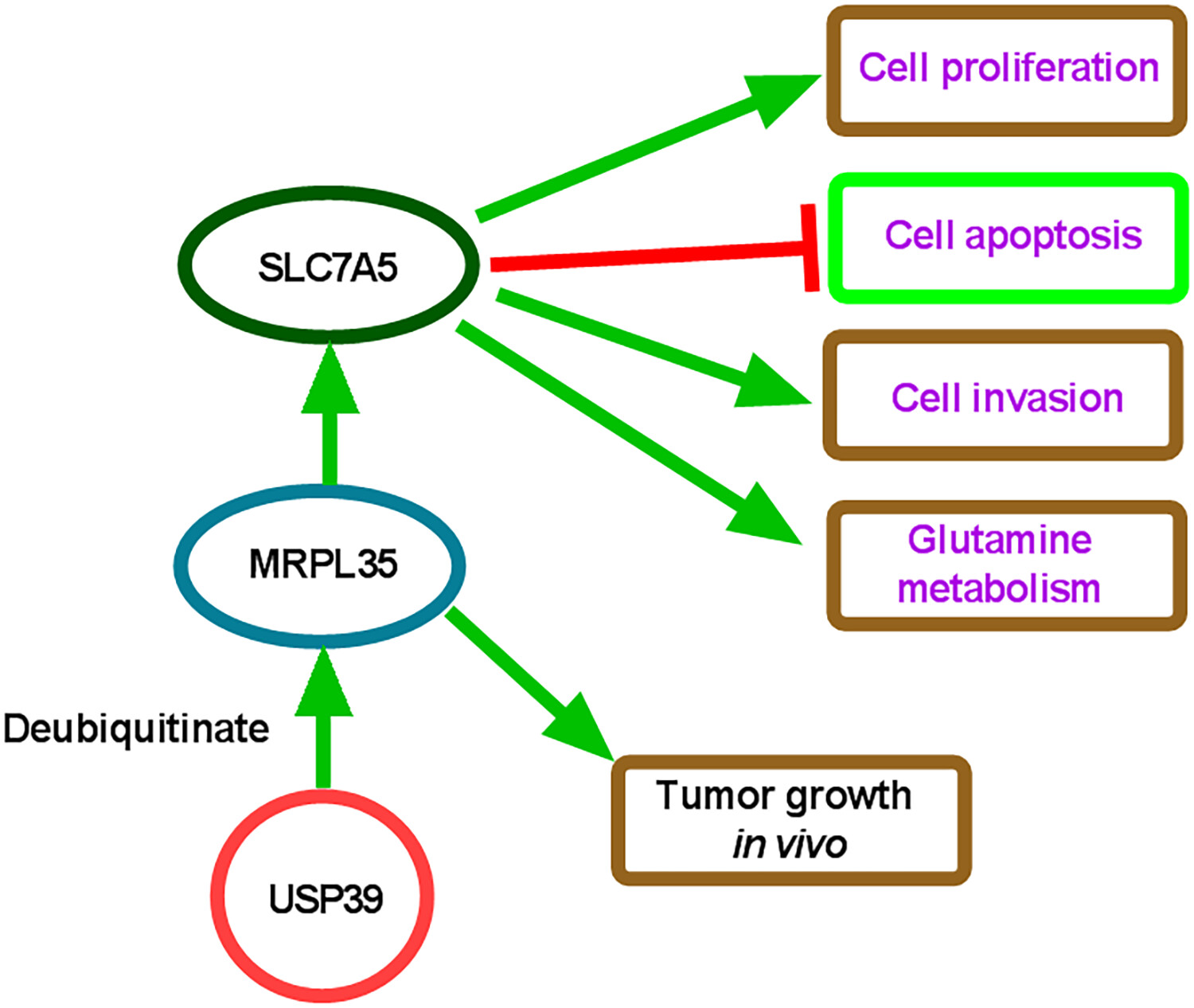
More articlesMRPL35 Induces Proliferation, Invasion, and Glutamine Metabolism in NSCLC Cells by Upregulating SLC7A5 Expression
- The Clinical Respiratory Journal
- 10 July 2024
Clinical comparison of HMPV and RSV infections in hospitalised Malaysian children: A propensity score matched study
- The Clinical Respiratory Journal
- 26 March 2024
Graphical Abstract
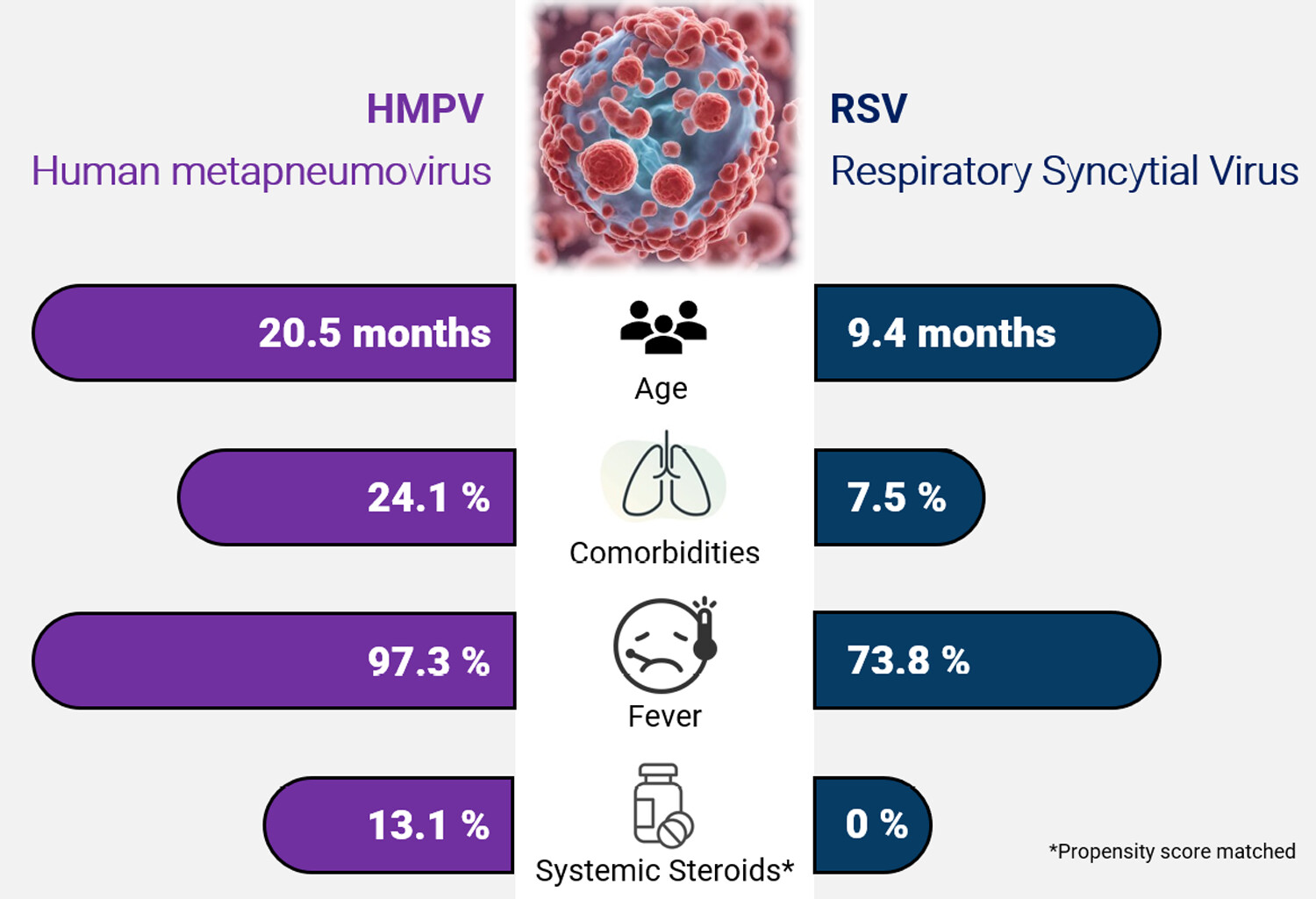
In this study comparing human metapneumovirus (hMPV) and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infections in hospitalised children, hMPV patients were older and exhibited more comorbidities and fever compared with RSV patients. Propensity score matching analysis indicated higher corticosteroid usage in hMPV cases. However, hospital resource utilisation and clinical outcomes were similar between both groups, underscoring the need for equal clinical vigilance for both viruses.
Oleic Acid Inhibits SDC4 and Promotes Ferroptosis in Lung Cancer Through GPX4/ACSL4
- The Clinical Respiratory Journal
- 13 October 2024
Graphical Abstract
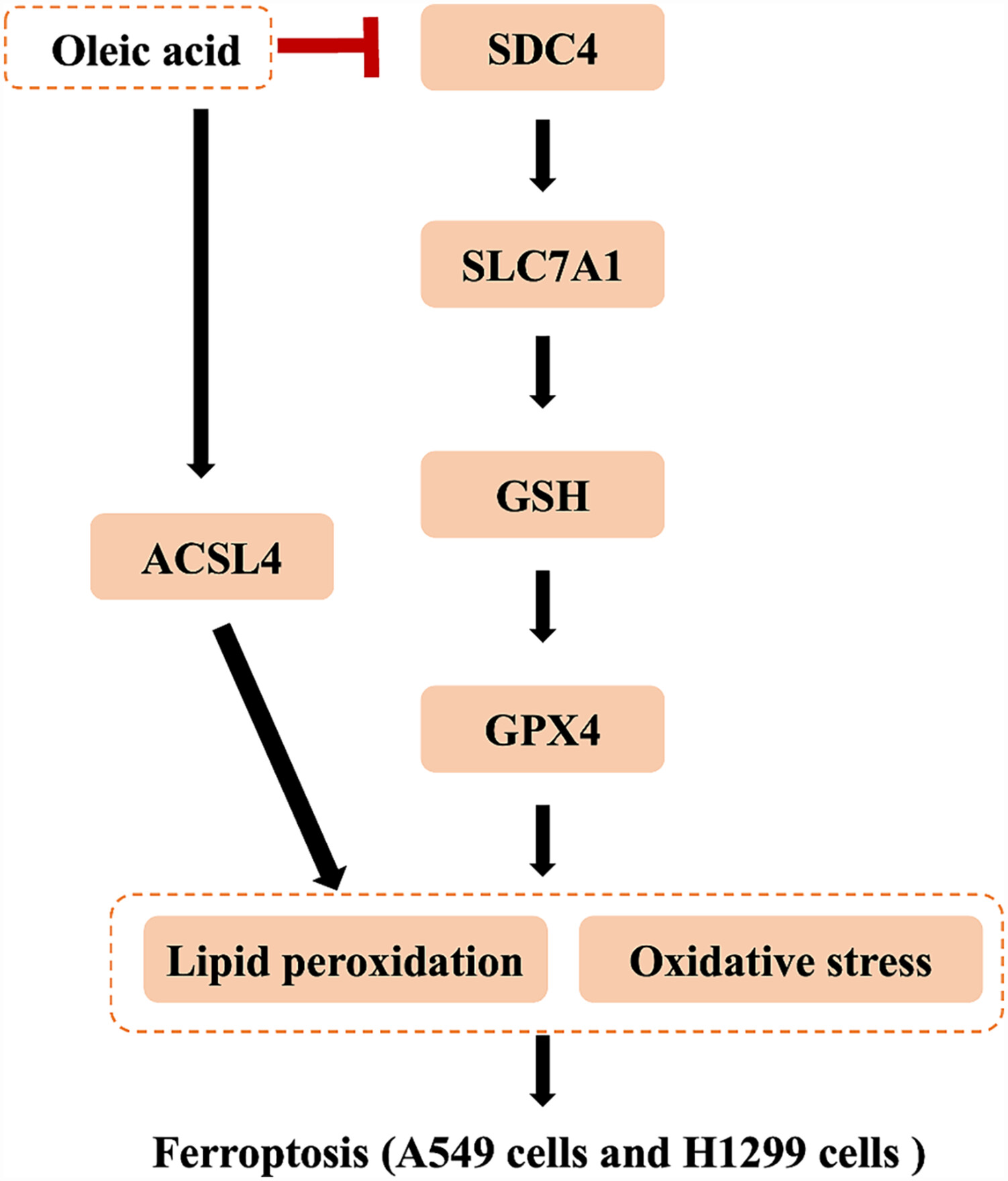
In this study, in vitro experiments on A549 cells and H1299 cells confirmed that oleic acid can inhibit the expression of SDC4, promote the occurrence of ferroptosis in A549 cells and H1299 cells through the GPX4/ACSL4 pathway, and provide an effective basis for the clinical application of targeted ferroptosis drugs in the effective treatment of lung cancer.
Clinical Management in NSCLC Patients With EGFR Mutation After Osimertinib Progression With Unknown Resistance Mechanisms
- The Clinical Respiratory Journal
- 15 October 2024
Analysis of Depression and Anxiety Scores Following Initiation of Elexacaftor/Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor in Adults With Cystic Fibrosis
- The Clinical Respiratory Journal
- 29 August 2024
Pyopneumothorax with bronchopleural fistula due to pulmonary infection caused by Porphyromonas gingivalis in a patient with periodontitis
- The Clinical Respiratory Journal
- 962-965
- 13 August 2023
Graphical Abstract
Pyopneumothorax with bronchopleural fistula is a rare complication of lung infection. We herein report a case of pyopneumothorax with bronchopleural fistula caused by Porphyromonas gingivalis infection, a common pathogenic pathogen of periodontitis, in a 49-year-old man with periodontitis. The patient was admitted with respiratory failure. Pleural puncture yielded a lot of gas continually and foul-smelling light brown pus, which was found to be caused due to infection with P. gingivalis by the next generation sequencing (NGS) and anaerobic culture.
A systematic review of psychological interventions in adults with pulmonary hypertension: Is the evidence‐base disproportionate to the problem?
- The Clinical Respiratory Journal
- 966-972
- 15 August 2023
Graphical Abstract
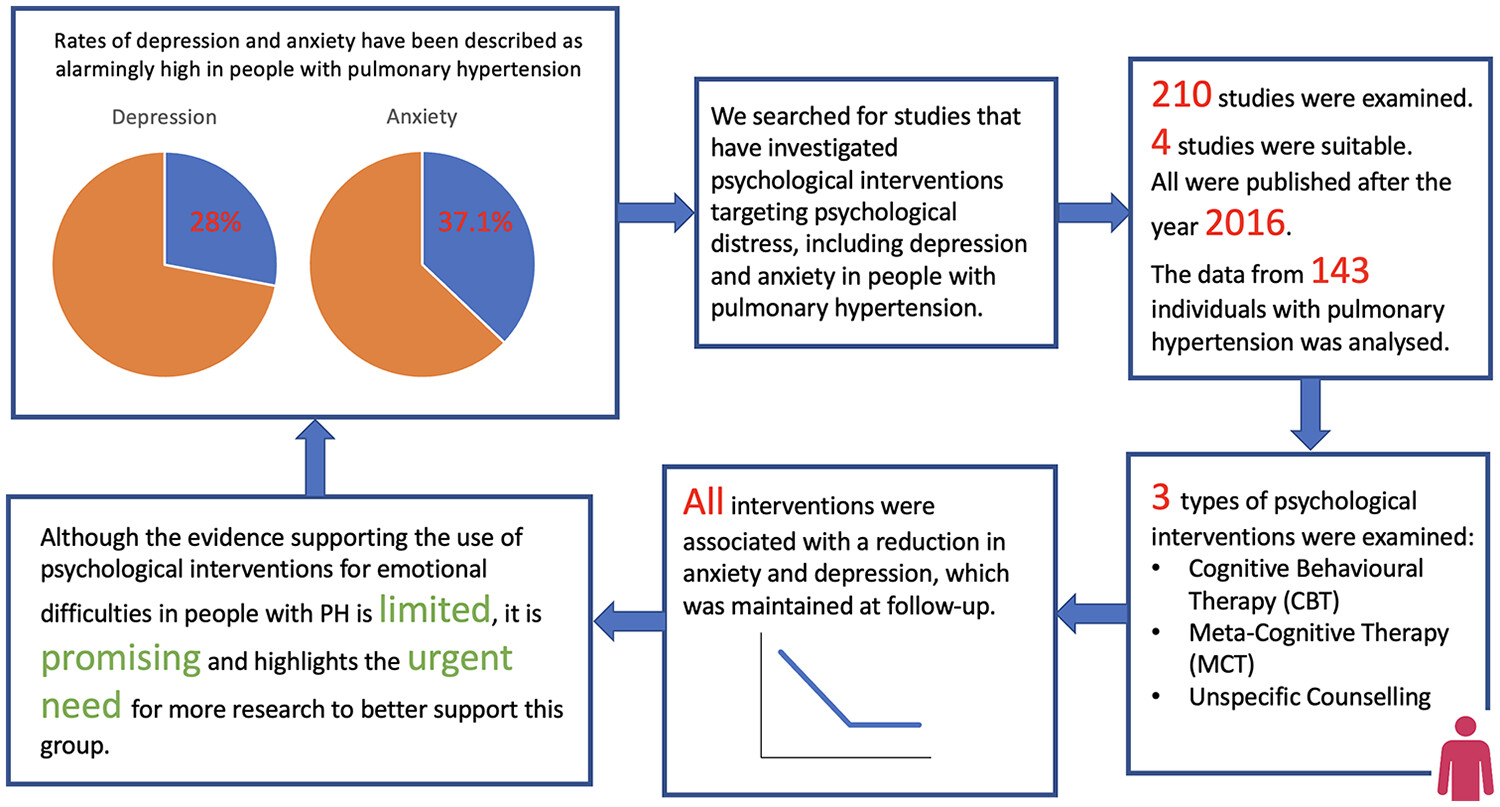
Our understanding of the psychological impact of living with pulmonary hypertension (PH) is growing. Evidence exists for the use of psychological interventions in chronic lung conditions; however, trials involving adults with PH have not been subject to a systematic review. We show that although the evidence is limited, the findings are promising and there is a need for more research.
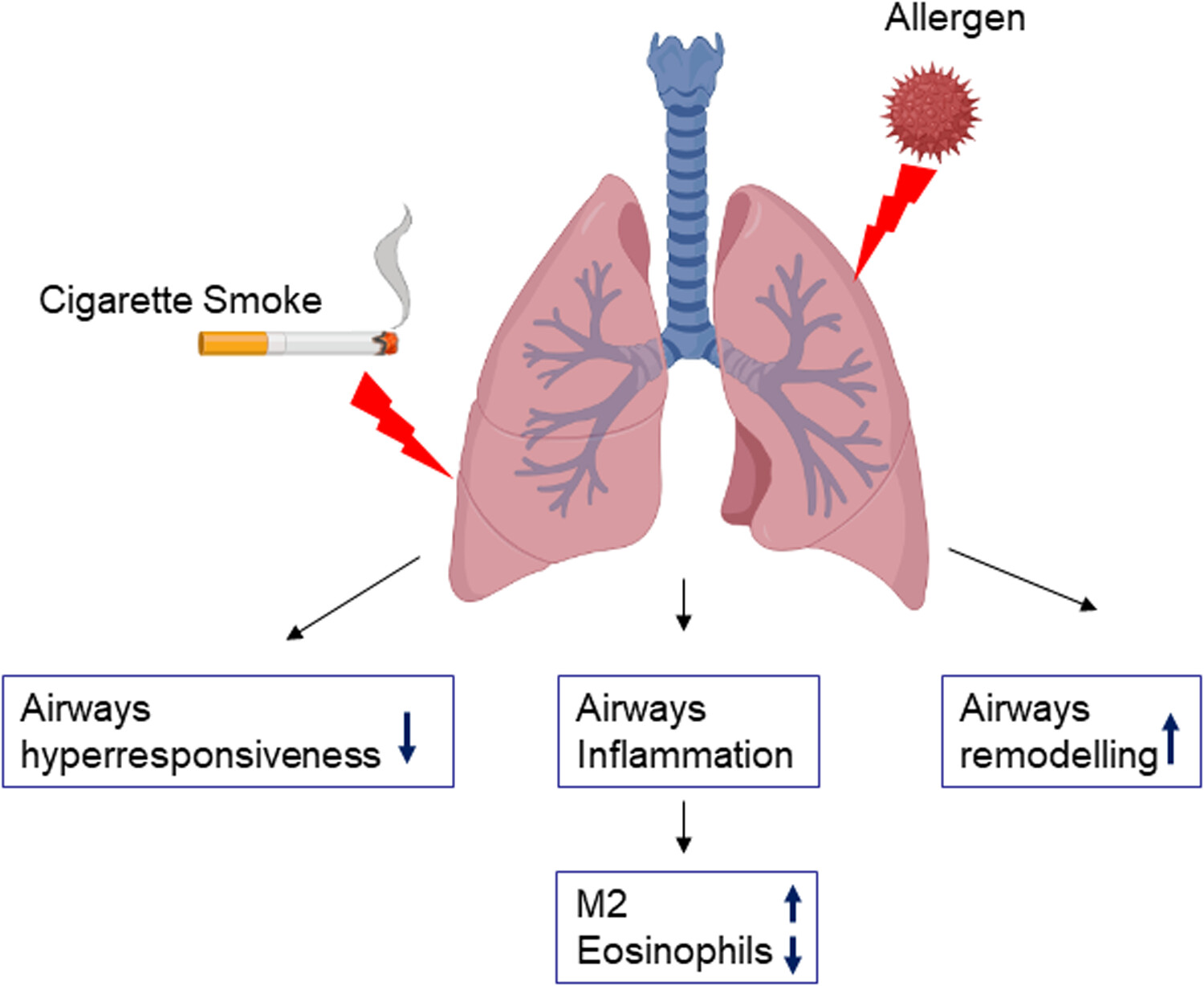
Cigarette smoke aggravates asthma via altering airways inflammation phenotypes and remodelling
- The Clinical Respiratory Journal
- 1316-1327
- 14 November 2023
Pleural fluid characteristics of patients with COVID‐19 infection
- The Clinical Respiratory Journal
- 26 March 2024
Graphical Abstract
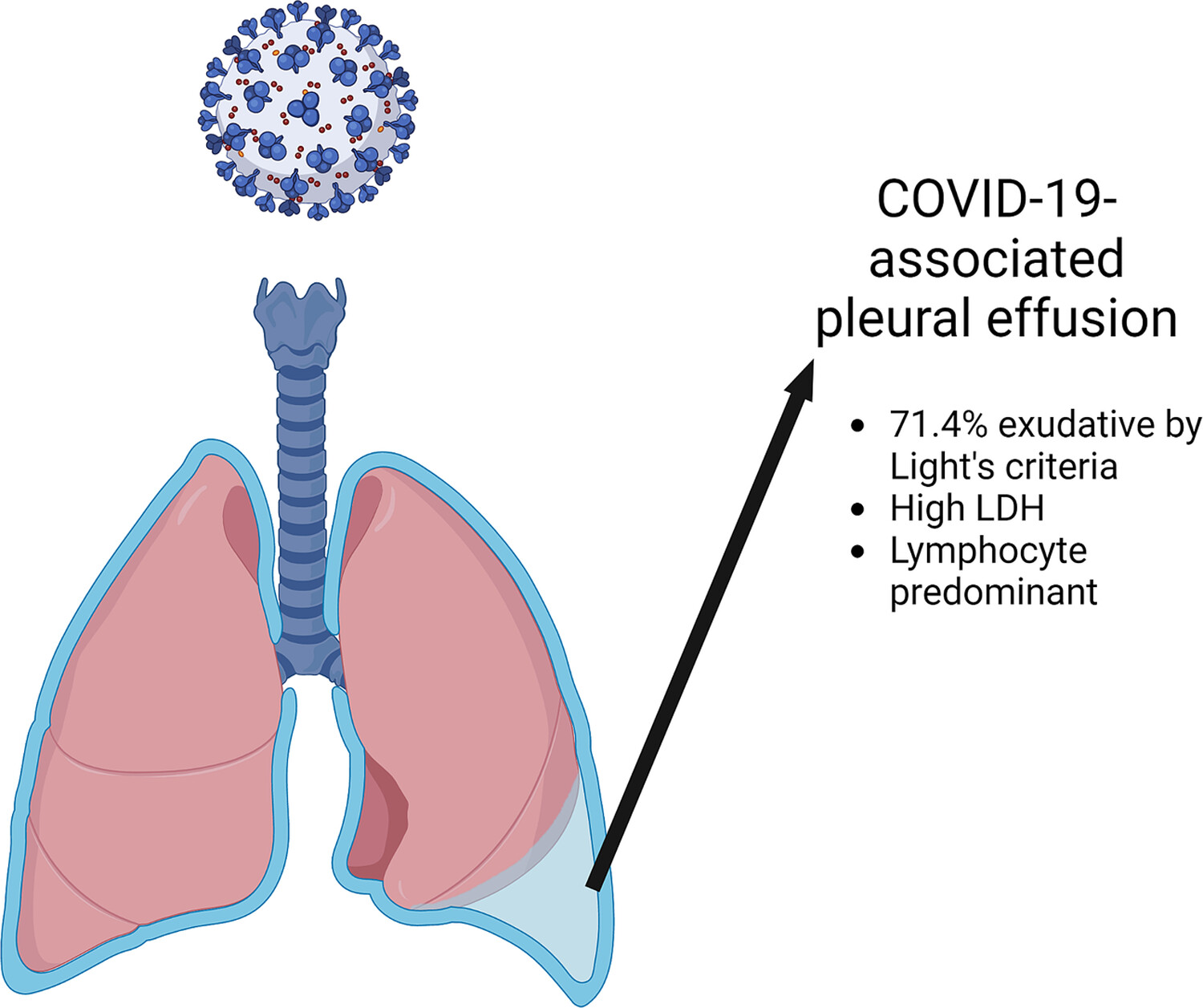
The pleural fluid characteristics associated with COVID-19 infection were assessed in 128 effusions from 106 unique patients; 68.5% of effusions met at least one of the three Light's criteria and therefore were exudative. Elevated LDH was notable. The white blood cell differential was predominantly lymphocytic (in 60.9% of effusions) or neutrophilic (30.5%).
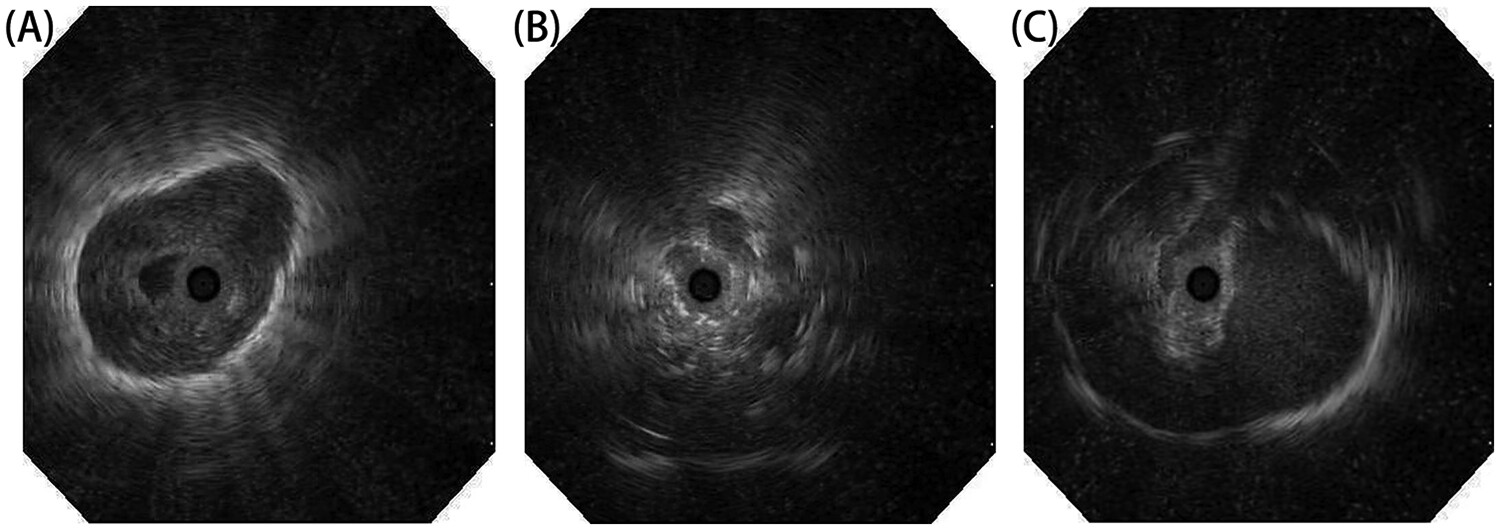
Evaluation of the diagnostic role of radial probe endobronchial ultrasound for peripheral pulmonary lesions
- The Clinical Respiratory Journal
- 28 July 2024
Recent issues
- Volume 19, Issue 7July 2025
- Volume 19, Issue 6June 2025
- Volume 19, Issue 5May 2025
- Volume 19, Issue 4April 2025