Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW ARTICLE
Chinese expert consensus on interventional diagnosis and management of acquired digestive-respiratory tract fistulas (second edition)
- Pages: 343-356
- First Published: 24 April 2023
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
The value of concentration of alveolar nitric oxide in diagnosing small airway dysfunction in patients with stable asthma
- Pages: 357-363
- First Published: 12 December 2022
IRCM-Caps: An X-ray image detection method for COVID-19
- Pages: 364-373
- First Published: 15 March 2023
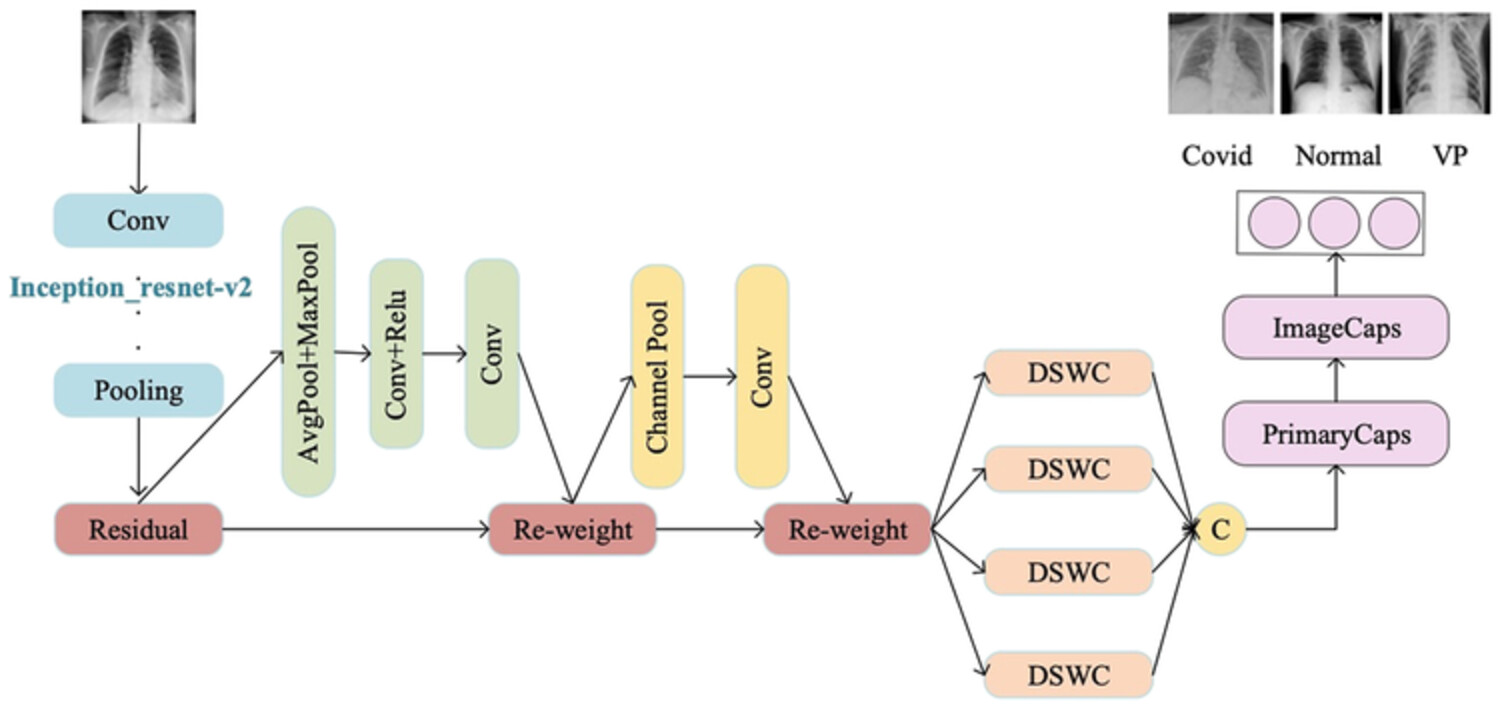
This paper proposes a new model based on CNN and CapsNet, which uses CLAHE algorithm to enhance image contrast, input the preprocessed image into the network for training, and use ReLU as the activation function to adjust the parameters to make it optimal. This method combines the advantages of traditional convolutional neural network and capsule network and has a good classification effect on small COVID-19 X-ray image datasets.
The value of folate receptor-positive circulating tumor cells in the diagnosis of lung cancer and its correlation with clinical characteristics
- Pages: 374-383
- First Published: 28 March 2023
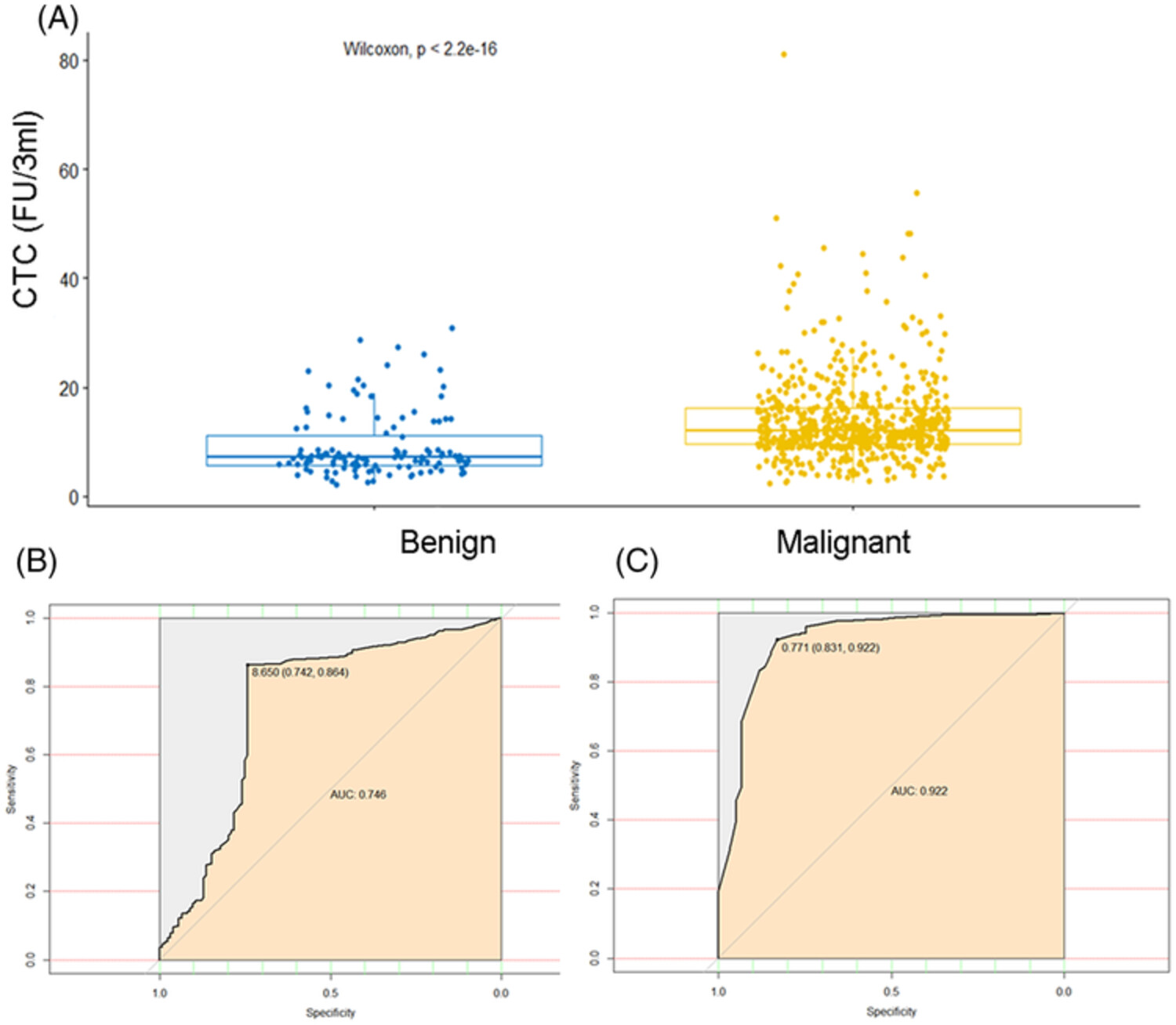
FR+CTC is an effective and reliable biomarker for the diagnosis of lung cancer. Combining conventional serum tumor biomarkers, including CA125, CEA, CYFRA21-1, CA153, and NSE, could improve diagnostic efficiency. Furthermore, FR+CTC level is correlated with tumor staging, degree of invasion, pathological subtypes, and tumor size.
Identification and comparison of Chlamydia psittaci, Legionella and Mycoplasma pneumonia infection
- Pages: 384-393
- First Published: 17 March 2023
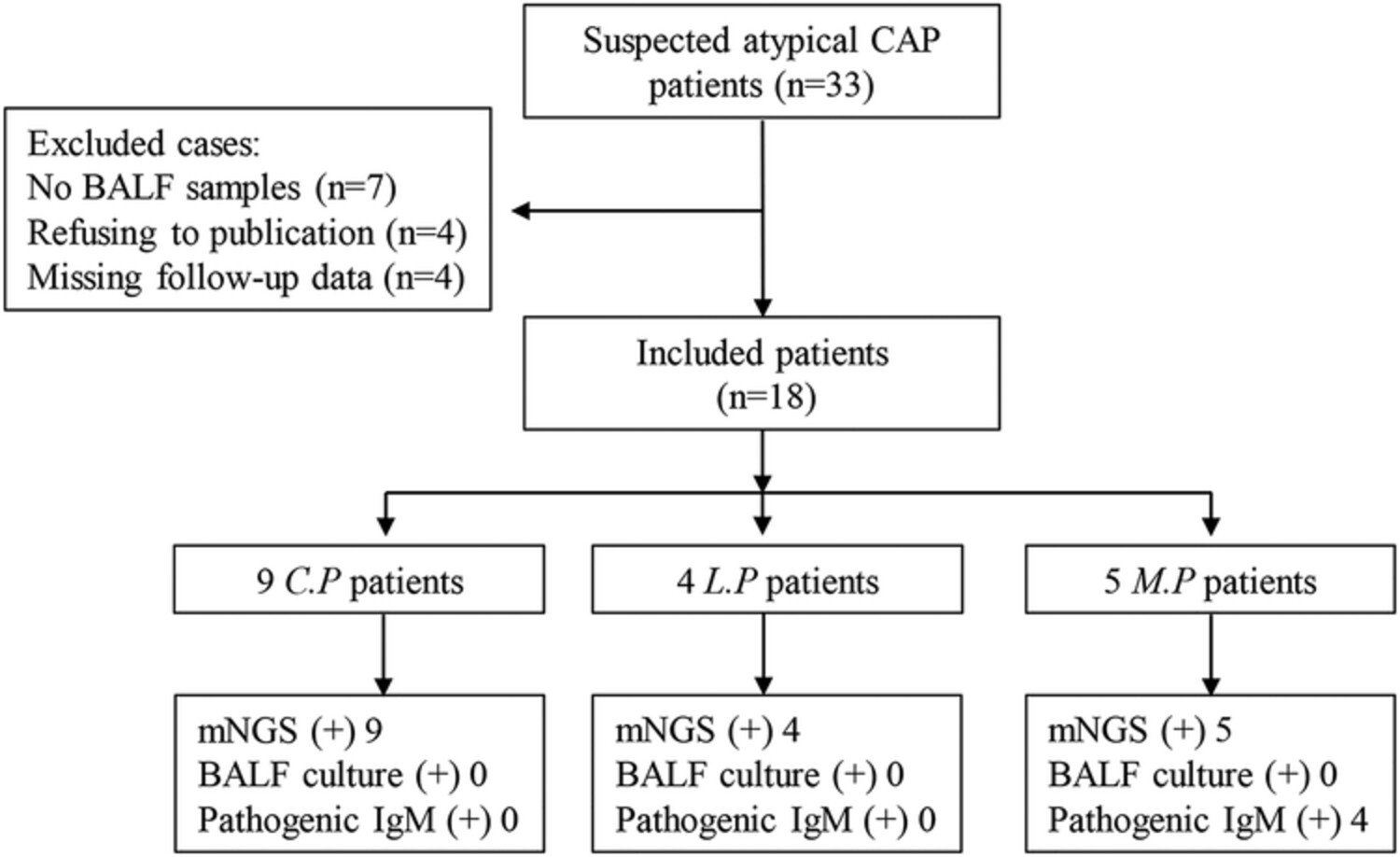
In this retrospective study, all the atypical pathogens including Chlamydia psittaci, Legionella and Mycoplasma were identified by mNGS. A comparison of clinical characteristics of nine Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia (C. p), four Legionella pneumonia (L. p) and five Mycoplasma pneumonia (M. p) were firstly accessed.
Potential predictive value of CT radiomics features for treatment response in patients with COVID-19
- Pages: 394-404
- First Published: 21 March 2023
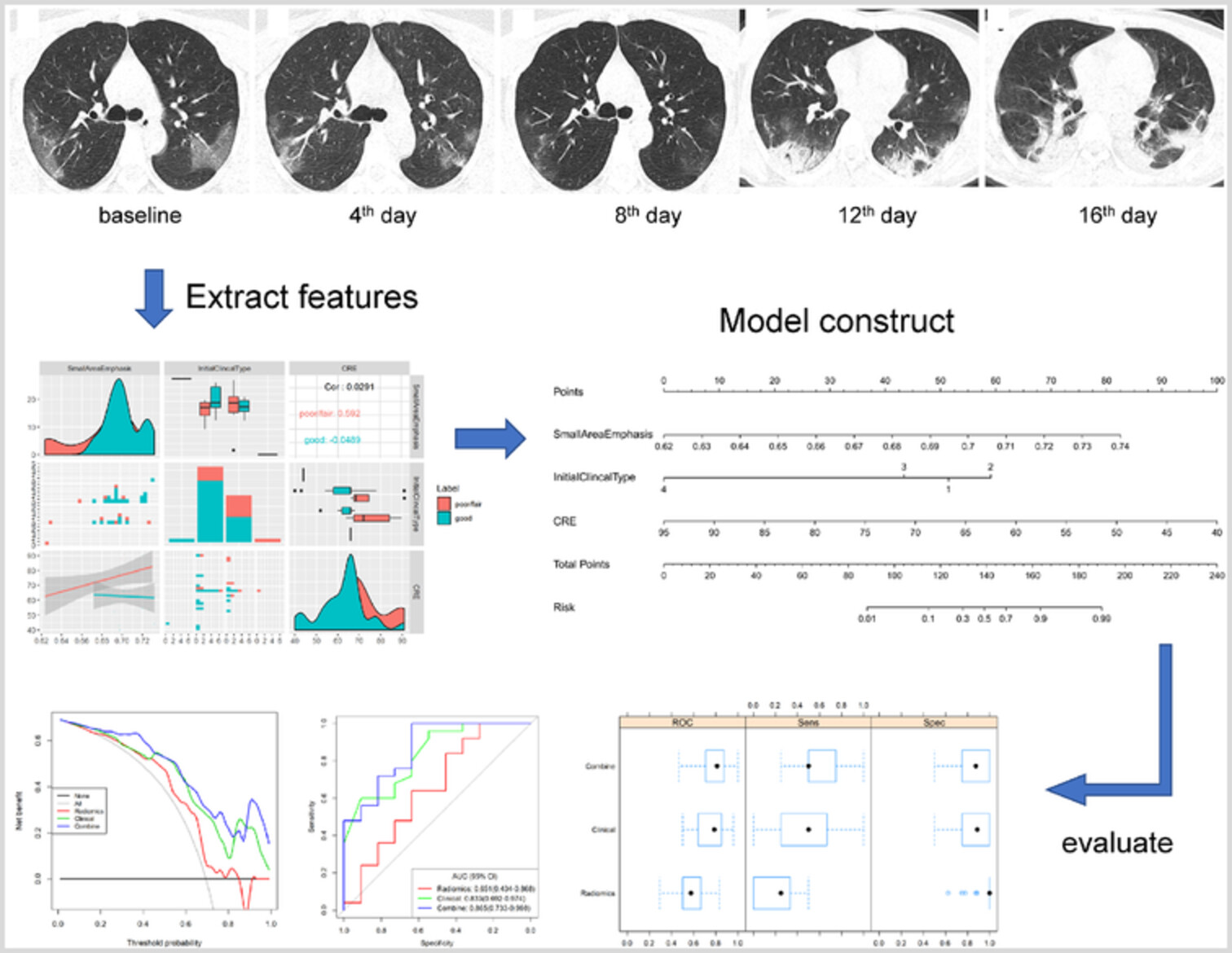
Can radiomic and clinical characteristics method improve the prediction of treatment response in COVID-19 patients? This study found that small area emphasis and serum creatinine levels have significance in different treatment response groups. It is suggested that the combined model can improve the prognostic prediction and dynamic clinical process analysis finding more potential valuable indicators.
Down-expression of Foxj1 on airway epithelium with impaired cilia architecture in non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis implies disease severity
- Pages: 405-413
- First Published: 16 March 2023
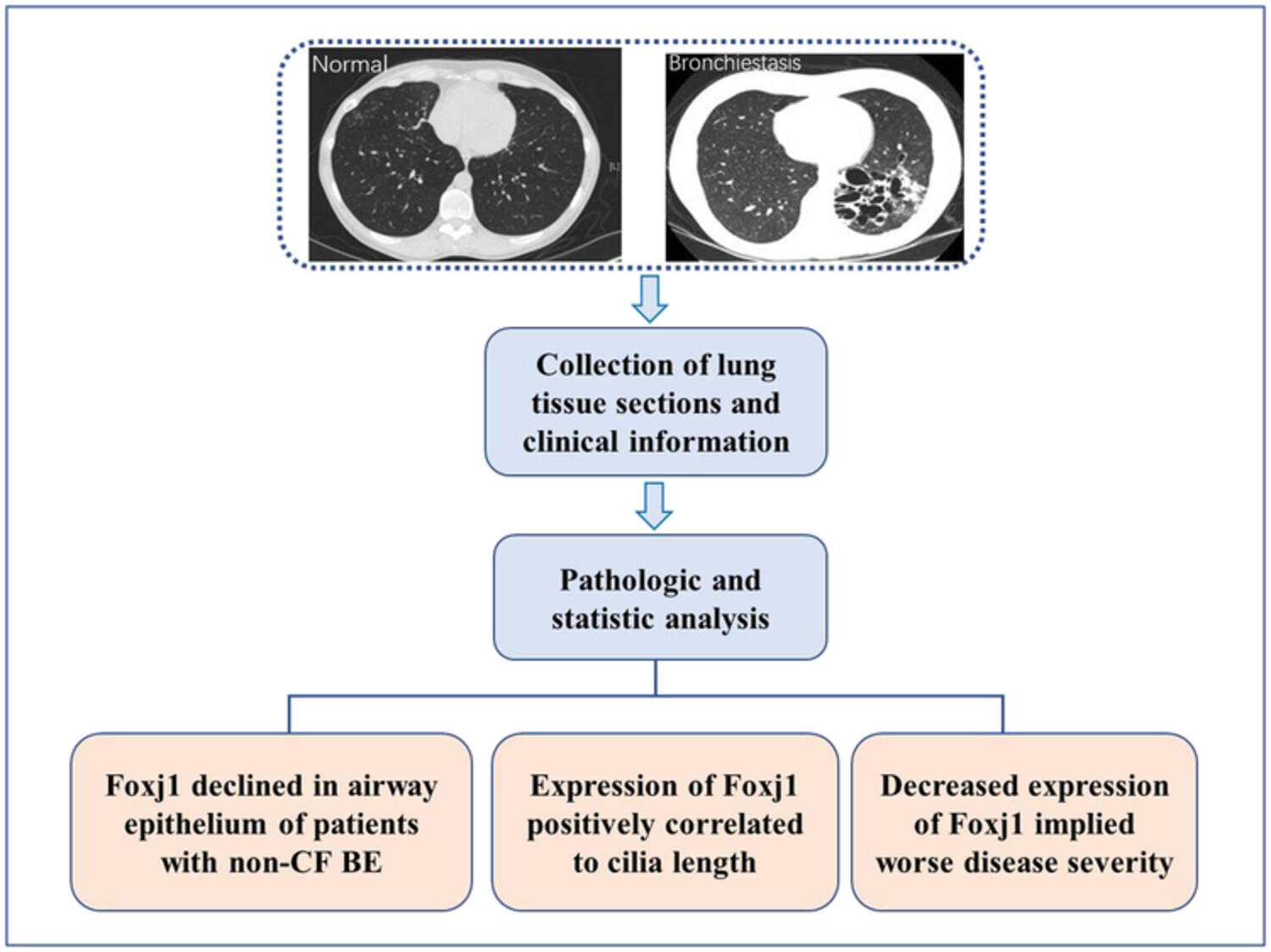
The present study found that expression of forkhead box protein j1 (Foxj1) declined in the airway epithelium of patients with non-CF BE and was related to cilia length and disease severity. It indicated that downregulation of Foxj1 might play an important role in pathogenesis and development of non-CF BE by modulating airway cilia function.
Frequency of delirium and its associated factors among COVID-19 inpatients in Iran
- Pages: 414-428
- First Published: 13 April 2023
The İmportance of tumor markers in patients undergoing resection for lung metastasis of colorectal carcinoma
- Pages: 429-438
- First Published: 17 April 2023
Pseudomonas aeruginosa in tracheal aspirate: Colonization, infection, and recurrence
- Pages: 439-446
- First Published: 27 April 2023
Given the recent change challenge in the treatment of the costs of Pseudomonas infection, the need to understand the risk of recurrence and mortality is important. This study demonstrated, despite of intrinsic limitations of the study design, that monotherapy in a short time (<14 days) is effective, and it is possible to report the susceptibility profile of this pathogen.
Alveolar–arterial oxygen gradient nonlinearly impacts the 28-day mortality of patients with sepsis: Secondary data mining based on the MIMIC-IV database
- Pages: 447-455
- First Published: 19 April 2023
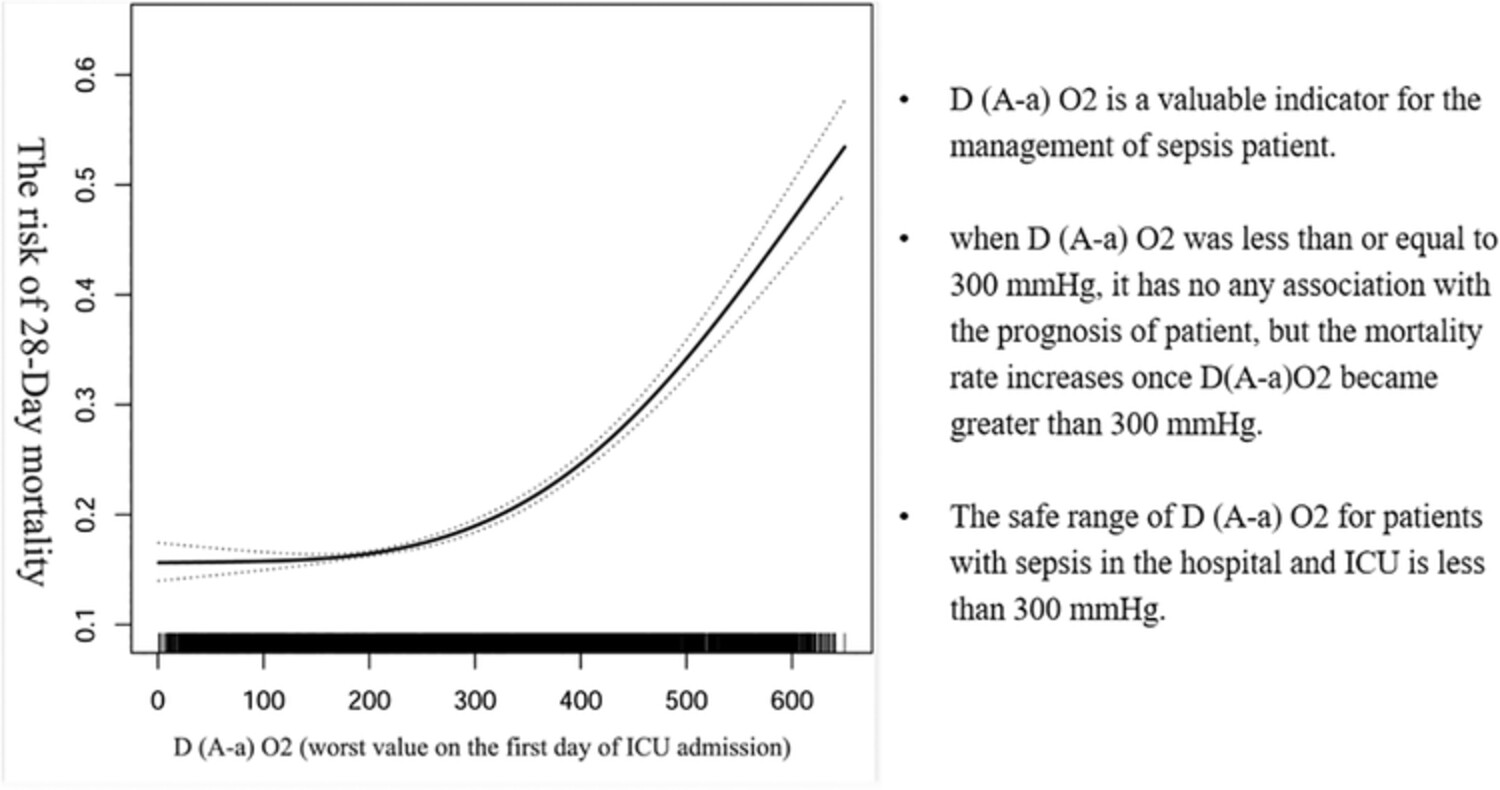
D(A-a)O2 is a valuable indicator for the management of sepsis patient. When D(A-a)O2 was less than or equal to 300 mmHg, it has no any association with the prognosis of patient, but the mortality rate increases once D(A-a)O2 became greater than 300 mmHg. The safe range of D(A-a)O2 for patients with sepsis in the hospital and ICU is less than 300 mmHg.
Development and validation of a nomogram for the prediction of brain metastases in small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 456-467
- First Published: 18 April 2023
BRIEF REPORTS
Cytomegalovirus serology in young to mid-adult life and decline of lung function
- Pages: 468-472
- First Published: 16 March 2023
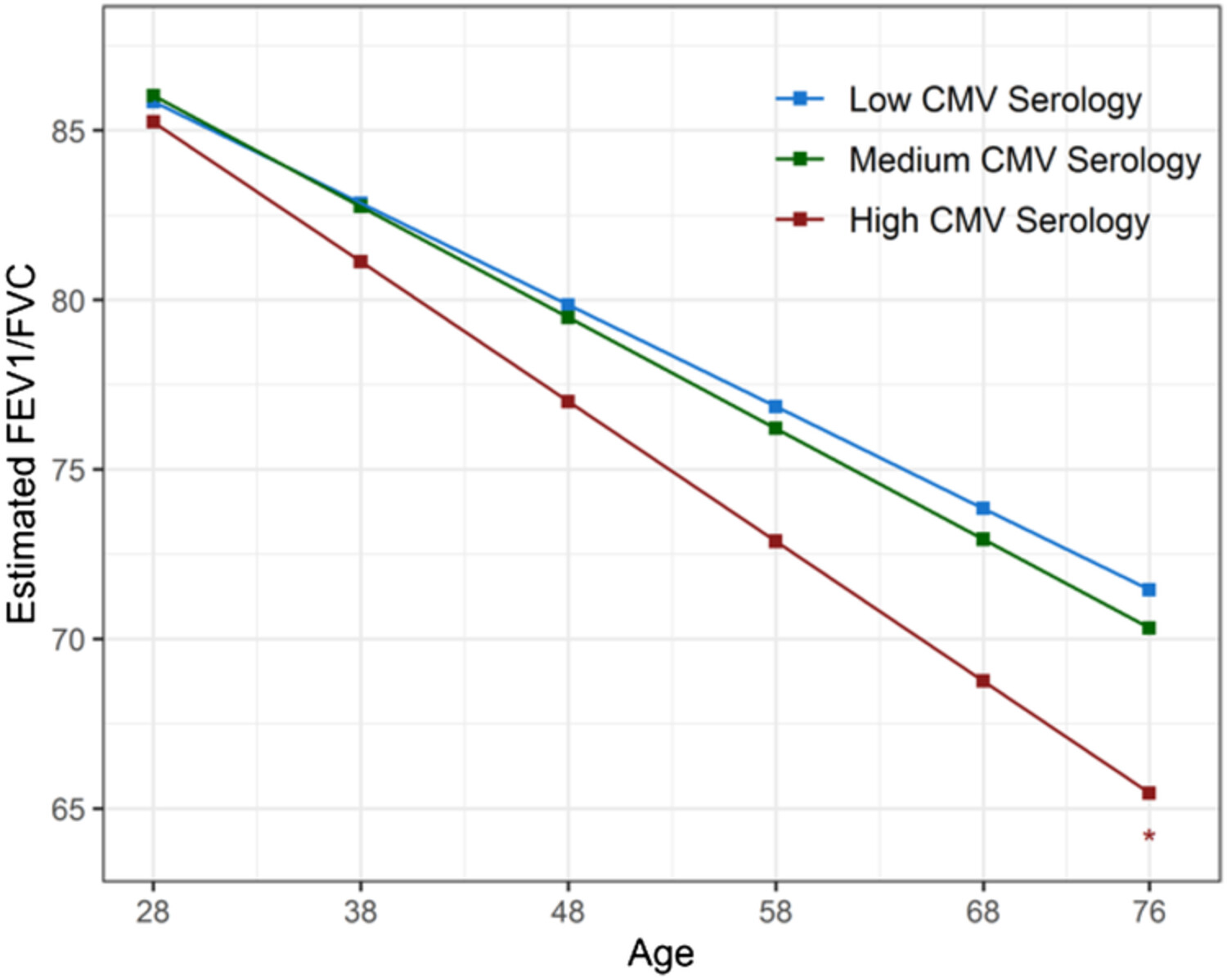
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) seropositivity has been recently linked to severity and progression of obstructive lung diseases. Among 403 participants from the longitudinal, population-based TESAOD study aged 28–55 years at enrollment, we found that, after full adjustment for covariates, high CMV serology at enrollment was associated with accelerated decline of FEV1 and FEV1/FVC (see figure) during follow-up.
Ivacaftor: Five-year outcomes in the West of Scotland cystic fibrosis population
- Pages: 473-477
- First Published: 20 March 2023
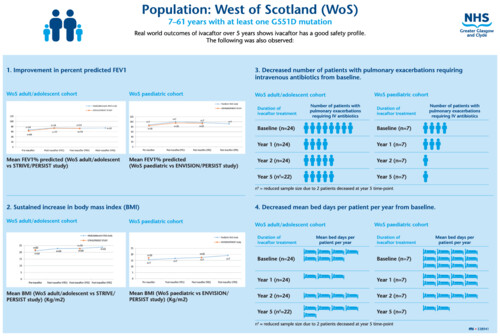
Ivacaftor's effectiveness and safety was evaluated in the real world, over 5 years, in patients with at least one G551D mutation within the West of Scotland. Findings include the following: Improvement in mean per cent predicted forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV1), sustained increase in body mass index, decreased intravenous antibiotic use from baseline, reduced hospital bed occupancy from baseline, and good safety profile.
Effects of steroid stewardship on glycemic control in acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients
- Pages: 478-484
- First Published: 13 April 2023
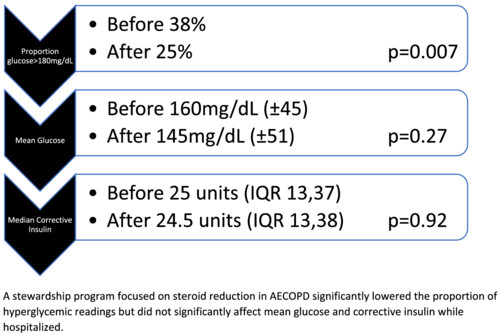
A post-hoc analysis of a steroid stewardship program evaluated the effect of this intervention on glycemic control in AECOPD patients. Steroid stewardship decreased the proportion of glucose readings >180 mg/dL in hospitalized patients. Mean glucose readings were lower but did not reach statistical significance.