Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Evaluation of the effect of marination in different seasoning recipes on the flavor profile of roasted beef meat via chemical and sensory analysis
- First Published: 07 October 2021
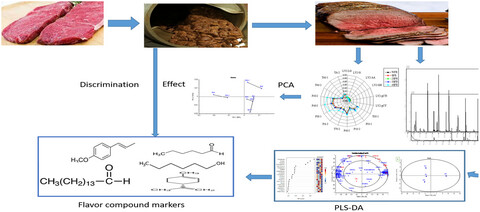
The influence of different seasoning recipes on flavors of roasted beef was studied. HS-SPME-GC-MS and E-nose were used to characterize flavors of marinated roasted beef. A total of 82 flavor compounds were identified in the marinated beef meat samples. Adding seasonings to the beef meat through the tumbling process enhances its flavor. PLS-DA screened 16 flavor markers to distinguish four marinated samples.
Taste compounds generation and variation of broth in pork meat braised processing by chemical analysis and an electronic tongue system
- First Published: 31 May 2021
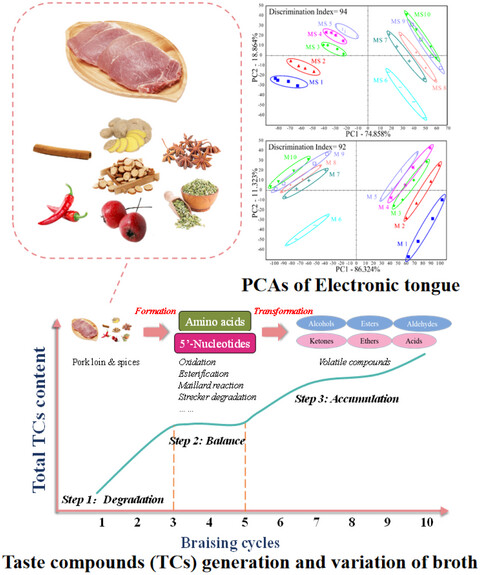
- The generation and variation rule of the main taste components in braised broth for ten quantitative repeated braising cycles was unveiled.
- A significant discrimination of taste in MS and M was revealed by electronic tongue evaluation during the process.
- A hypothesis was proposed to illustrate the whole variation of taste compounds in the process integrally that the ratio of FR/TR dividing the process into three stages, Degradation, Balance and Accumulation.
Identification of changes in volatile organic compounds in Ophiopogonis Radix containing spoiled products in different proportions by headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry
- First Published: 26 May 2021
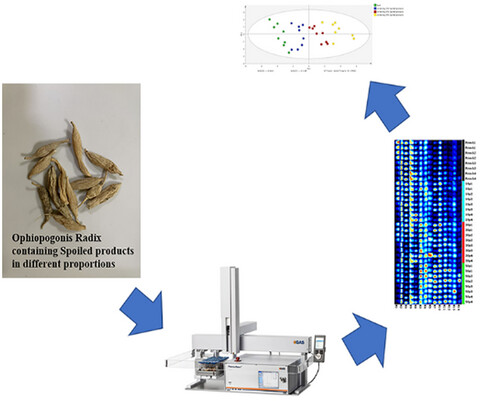
Through the analysis of GC-IMS, 14 VOCs were choosing to established characteristic fingerprints of Ophiopogonis Radix, which involves spoiled products in different proportions. The result of PCA shows that the fresh Ophiopogonis Radix and the spoiled Ophiopogonis Radix could be clearly differentiated. The larger the proportion of spoiled products, the greater the difference between the sample and fresh Ophiopogonis Radix.
Identification and characterization of volatile compounds in Lentinula edodes during vacuum freeze-drying
- First Published: 04 June 2021
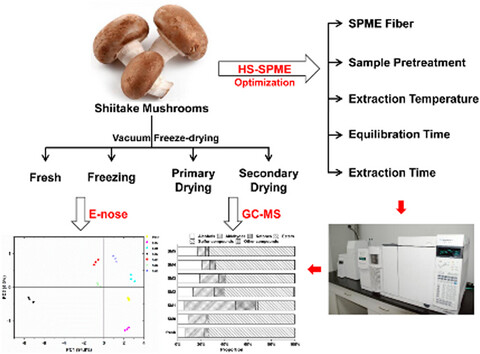
A total of 50 volatiles were identified in Lentinula edodes from different VFD stages by GC-MS, including 20 key odorants. Alcohols, aldehydes, and VSCs were the main flavor constituents of fresh L. edodes, frozen L. edodes, and secondary dried L. edodes. Aldehydes, ketones, and VSCs were the main aroma groups in L. edodes after primary drying.
Application of gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry (GC-IMS) and ultrafast gas chromatography electronic-nose (uf-GC E-nose) to distinguish four Chinese freshwater fishes at both raw and cooked status
- First Published: 30 June 2021
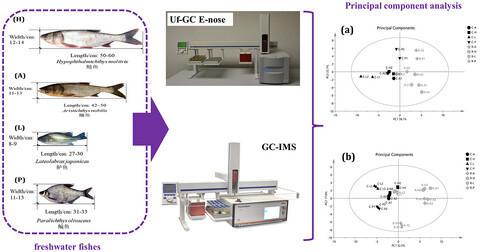
Gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry (GC-IMS) and ultrafast gas chromatography electronic-nose (uf-GC E-nose) were used to separate and analyze the volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in four Chinese freshwater fishes at raw and cooked status. The two techniques can quickly distinguish freshwater fishes based on headspace VOC data using Principal component analysis. GC-MS and fast GC E-nose provide an alternative approaches to differentiate freshwater fishes with fast response, high sensitivity, and qualitative accuracy.
Identification of Ophiopogonis Radix from different producing areas by headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry analysis
- First Published: 05 July 2021
Through the analysis of GC-IMS, 14 VOCs were choosing to established characteristic fingerprints of ZMD and CMD, 12 VOCs were choosing to established characteristic fingerprints of ZMD from Cixi and Sanmen. The result of PCA shows that the ZMD and CMD as well as ZMD from Cixi and Sanmen could be clearly differentiated. PLS-DA method was used to verify the unknown samples, and the accuracy of the verification results was 100%.
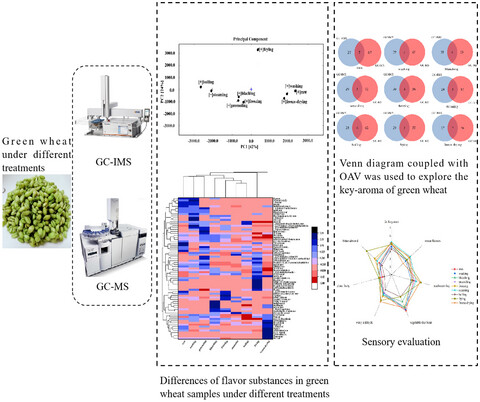
Analysis of volatile flavor compounds of green wheat under different treatments by GC-MS and GC-IMS
- First Published: 27 July 2021
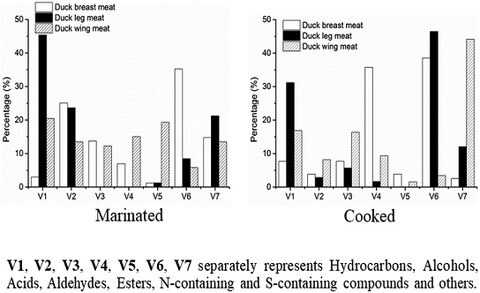
Determination of volatile flavor compounds in raw and treated duck meats of different body parts
- First Published: 23 August 2021
The changes of physicochemical properties, antioxidants, organic, and key volatile compounds associated with the flavor of peach (Prunus cerasus L. Batsch) vinegar during the fermentation process
- First Published: 25 October 2021
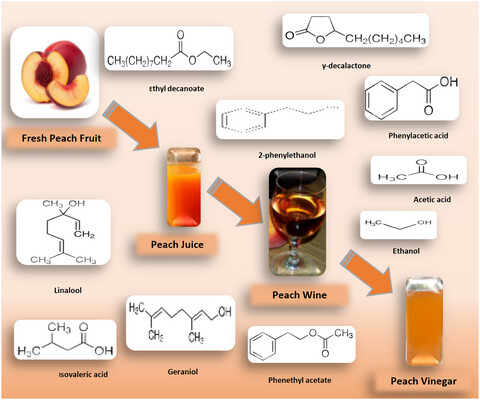
- Peach vinegar is an innovative and alternative product.
- Peach fruit is appropriate for production of vinegar with healthy and desired.
- The important volatile compounds of peach vinegar are ɣ-decalactone phenylacetic and acetic acids.
- The organic acids of peach vinegar are acetic, lactic, oxalic malic acids
Cinnamon could improve hepatic steatosis caused by a high-fat diet via enhancing hepatic beta-oxidation and inhibiting hepatic lipogenesis, oxidative damage, and inflammation in male rats
- First Published: 04 March 2022
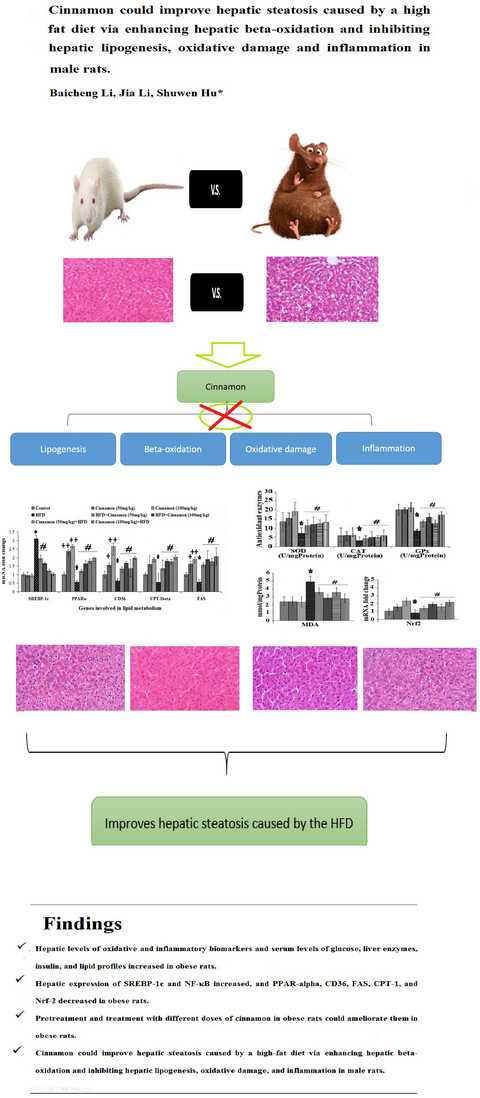
Hepatic levels of oxidative and inflammatory biomarkers and serum levels of glucose, liver enzymes, insulin, and lipid profiles increased in obese rats. Hepatic expression of SREBP-1c and NF-κB increased, and PPAR-alpha, CD36, FAS, CPT-1, and Nrf-2 decreased in obese rats. Pretreatment and treatment with different doses of cinnamon in obese rats could ameliorate them in obese rats. Cinnamon could improve hepatic steatosis caused by a high-fat diet via enhancing hepatic beta-oxidation and inhibiting hepatic lipogenesis, oxidative damage, and inflammation in male rats.
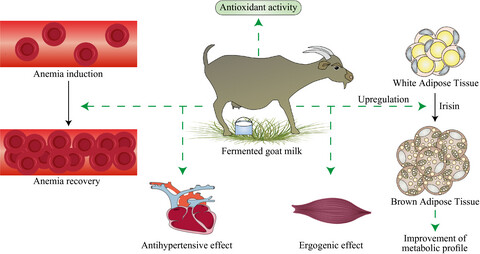
Role of fermented goat milk as a nutritional product to improve anemia
- First Published: 17 October 2021
Potential nutraceuticals from the casein fraction of goat’s milk
- First Published: 30 October 2021
Inhibitory effect of whey protein concentrate on SARS-CoV-2-targeted furin activity and spike protein-ACE2 binding in methotrexate-induced lung damage
- First Published: 03 January 2022
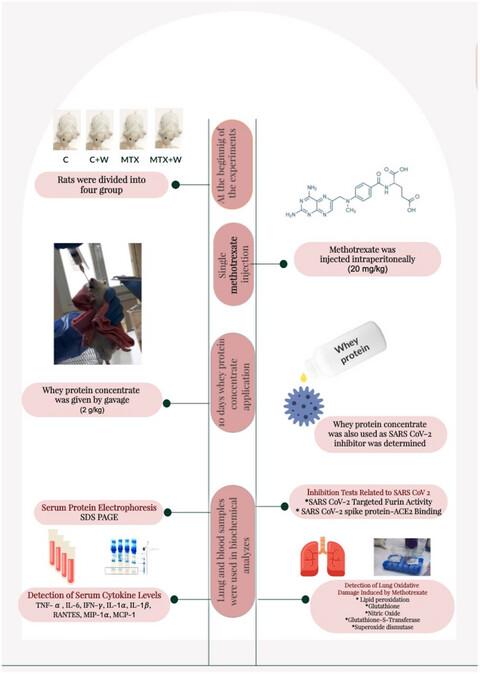
This study reports the effects of whey proteins on SARS CoV-2 in methotrexate-induced lung tissue damage in rats. According to the findings of this study, whey protein concentrate ameliorated methotrexate-induced lung damage and inhibited lung furin activity targeting SARS-CoV-2 S1/S2 site cleavage and SARS CoV-2 spike protein-angiotensin converting enzyme binding. Whey proteins are potential protective candidates that inhibit SARS CoV-2 related interactions, even in methotrexate-induced lung injury.