Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
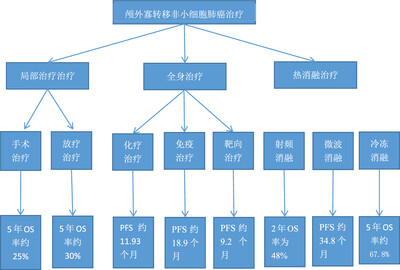
Local thermal ablative therapies for extracranial oligometastatic disease of non-small-cell lung cancer
- Pages: 3-8
- First Published: 22 May 2022
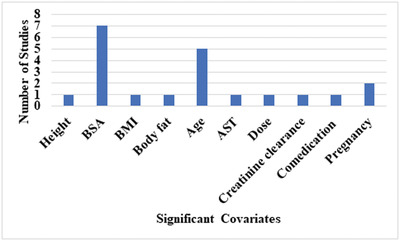
Population pharmacokinetics of doxorubicin: A systematic review
- Pages: 9-26
- First Published: 12 April 2022
The pathophysiology and current treatments for the subcutaneous panniculitis-like T cell lymphoma: An updated review
- Pages: 27-34
- First Published: 04 May 2022
Safety and potential increased risk of toxicity of radiotherapy combined immunotherapy strategy
- Pages: 35-50
- First Published: 10 May 2022
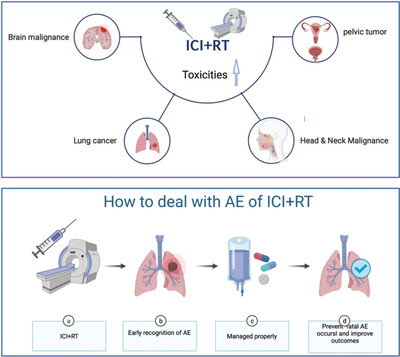
Representative evidence relevant to RT combined with ICI in the brain, lung, head and neck and pelvic malignance suggest that RT+ICI combination therapy might augment toxicities without augmenting sAE. Early recognition and proper management is essential to prevent sAE and indicate a good prognosis.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Real-world evidence of cisplatin versus carboplatin in patients with locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma receiving concurrent chemoradiotherapy: A multicenter analysis
- Pages: 51-61
- First Published: 08 April 2022
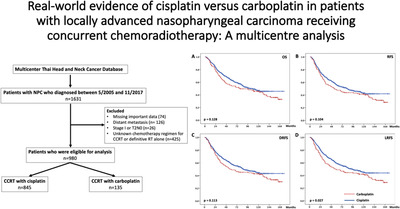
We report a large multicenter study of 980 locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated with either cisplatin or carboplatin concurrently with radiotherapy. The results represent real-world evidence with extensive details of patient characteristics, treatment modalities, tolerability, and survival outcomes. Carboplatin should be considered as an alternative regimen, particularly in cisplatin-ineligible patients.
Pretreatment frailty is an independent prognostic factor among elderly patients with B-cell lymphoma undergoing immunochemotherapy: A prospective observational cohort study in Taiwan
- Pages: 62-70
- First Published: 10 April 2022
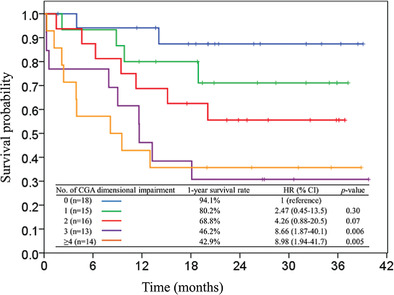
Frailty is a common clinical syndrome among the elderly; however, it is frequently neglected in patients with hematological malignancies, especially among the Asian population. This is the first study to evaluate the prevalence rate and effect of frailty on survival outcome in elderly patients undergoing immunochemotherapy for the treatment of B-cell lymphoma in Taiwan. This study found a negative association between the numbers of geriatric dimensional impairment and survival outcome. Pretreatment frailty assessment is essential to assist clinicians and patients with B-cell lymphoma with prognosis prediction and counseling on an appropriate treatment goal.
A multi-institutional retrospective study of open versus laparoscopic nephroureterectomy focused on the intravesical recurrence
- Pages: 71-78
- First Published: 11 April 2022
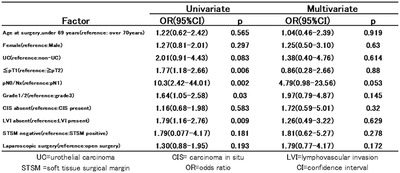
We conducted a A multi-institutional retrospective study of intravesical recurrence (IVR) after nephroureterectomy. Contrary to our expectations, IVR risk factors were ≦pT1, pN0/pNx, G1/2, and absence of LVI. These findings provide insight into IVR, which may help with the development of personalized prevention and treatment strategies.
Prediction of response to radiotherapy in locally advanced carcinoma cervix using multiparametric MRI: A prospective, single-center, longitudinal study
- Pages: 79-86
- First Published: 18 April 2022
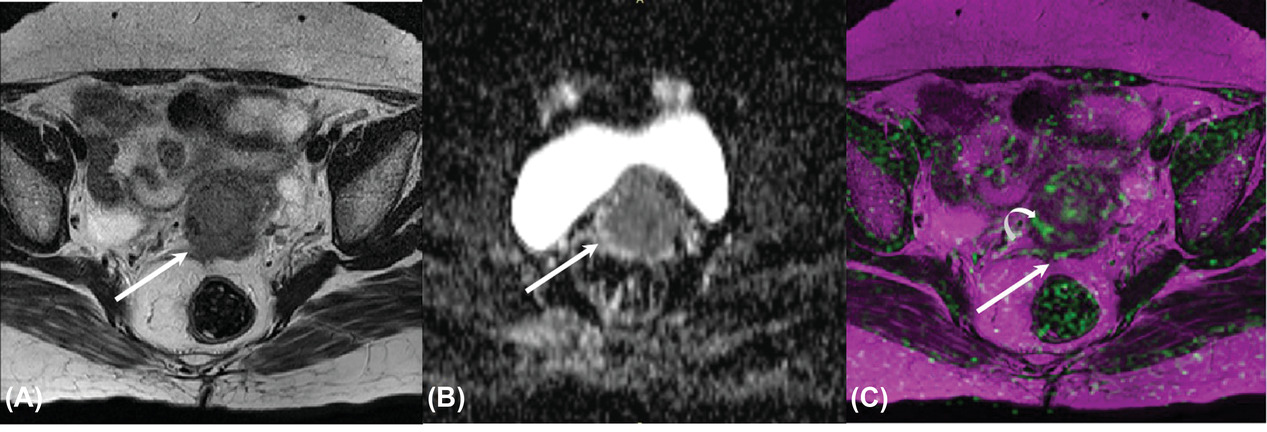
In this study we demonstrate the utility of multiparametric MRI in prediction of response to radiotherapy in cases of locally advanced carcinoma cervix. Pre-treatment apparent diffusion coefficient of the tumor was the most accurate measure for predicting response to treatment as well as for treatment induced fractional volume reduction.
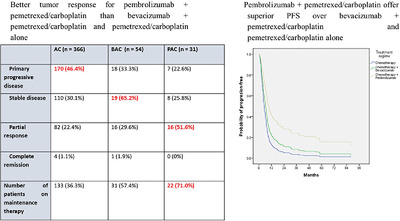
Clinical efficacy and safety of pemetrexed with or without either Bevacizumab or Pembrolizumab in patients with metastatic nonsquamous non–small cell carcinoma
- Pages: 87-95
- First Published: 20 April 2022
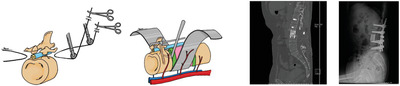
Clinical results of total en bloc spondylectomy using a single posterior approach in spinal metastasis patients: Experiences from Thailand
- Pages: 96-103
- First Published: 19 May 2022
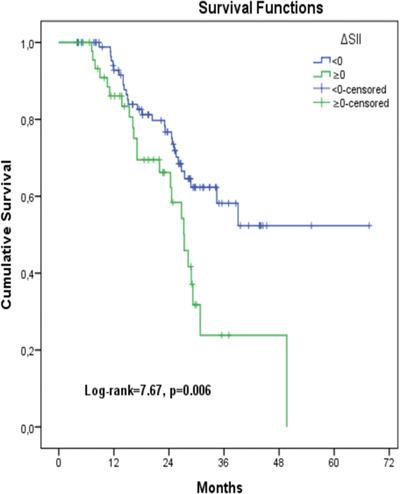
Dynamic changes in systemic immune-inflammation index predict pathological tumor response and overall survival in patients with gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy
- Pages: 104-112
- First Published: 10 May 2022
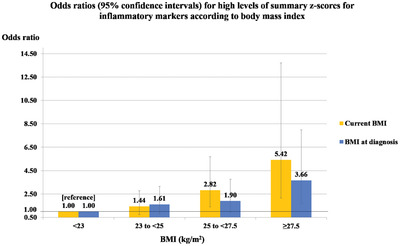
Associations of body mass index and weight change with circulating levels of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, proinflammatory cytokines, and adiponectin among breast cancer survivors
- Pages: 113-125
- First Published: 19 May 2022
Opinions and strategies of Australian health professionals on tackling cancer-related financial toxicity: A nationwide survey
- Pages: 126-135
- First Published: 19 May 2022

Many health professionals caring for patients with cancer often discuss the financial concerns of their patients and have increasing awareness of these issues but are limited by time and practical supports. Resources supporting financial-related discussions for all health professionals are urgently needed to advance action in this field.
Safety and efficacy of high-dose cytarabine MEAM therapy and other treatments for auto-peripheral blood stem cell transplantation: A retrospective comparative study
- Pages: 136-148
- First Published: 22 May 2022
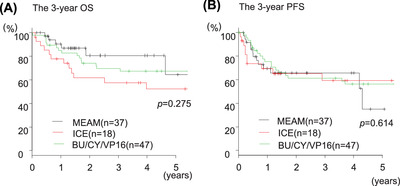
We retrospectively analyzed malignant lymphoma in patients who underwent auto-peripheral blood stem cell transplantation, with high-dose cytarabine MEAM therapy as the conditioning regimen. In all cases, the 3-year overall survival after transplantation was 80.6% and the 3-year progression-free survival after transplantation was 65.7%. There were no cases of treatment-related mortality with this therapy, and this one tended to be more effective than ICE and BU/CY/VP-16 therapies.
Large variation in radiation therapy fractionation for multiple myeloma in Australia
- Pages: 149-157
- First Published: 22 May 2022
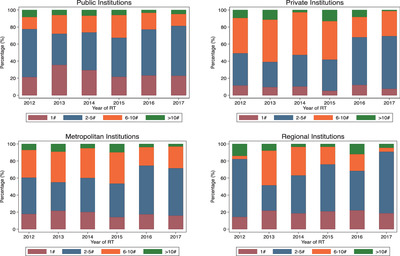
Radiation therapy (RT) is effective treatment for symptomatic multiple myeloma-related bone disease. This population-based study showed increasing use of short course RT of 2-5 fractions. However, the use of single-fraction RT remains low, even at the end of life. There is large institutional variation in practice.
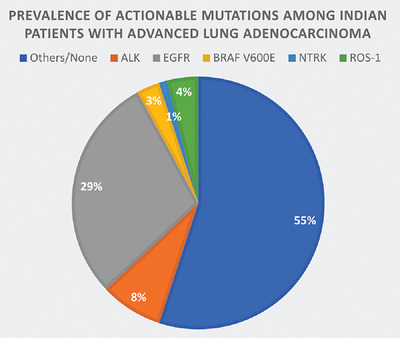
Prevalence of highly actionable mutations among Indian patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 158-171
- First Published: 30 May 2022
Awake craniotomy for brain tumor resection: Patient experience and acceptance in an Asian population
- Pages: 172-178
- First Published: 09 June 2022
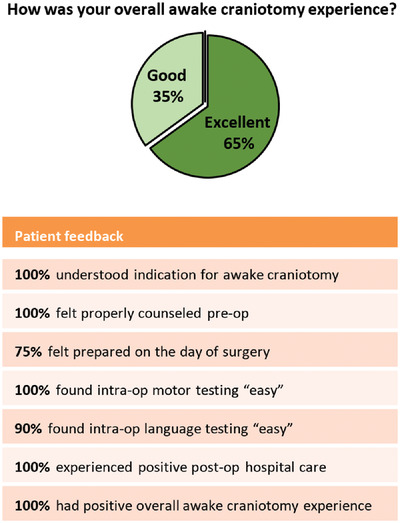
We evaluated the experience of patients from an Asian population who underwent awake craniotomy for brain tumor resection. We showed that there is high level of acceptance for awake craniotomy in this population. Patients generally felt well-prepared before the surgery, tolerated intraoperative procedure and motor/language testing well, and were mostly satisfied with the postoperative care. The overall experience was overwhelmingly positive—100% “good” or “excellent” rating.
New Zealand national retrospective cohort study of survival outcomes of patients with metastatic melanoma receiving immune-checkpoint inhibitors
- Pages: 179-186
- First Published: 10 June 2022
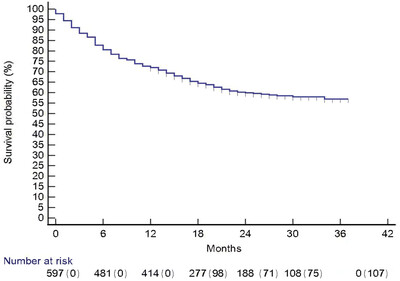
Graphical Abstract: Our study showed overall survival comparable to that reported by pivotal clinical trials and other recent RWD studies. Other survival outcomes were also reassuring and overall, the findings support the achievement of health gains from use of ICI in advanced unresectable and metastatic melanoma in New Zealand.
Efficacy evaluation of different measurement methods for target lesions after neoadjuvant chemotherapy and radical radiotherapy in locally advanced hypopharyngeal carcinoma
- Pages: 187-195
- First Published: 12 June 2022
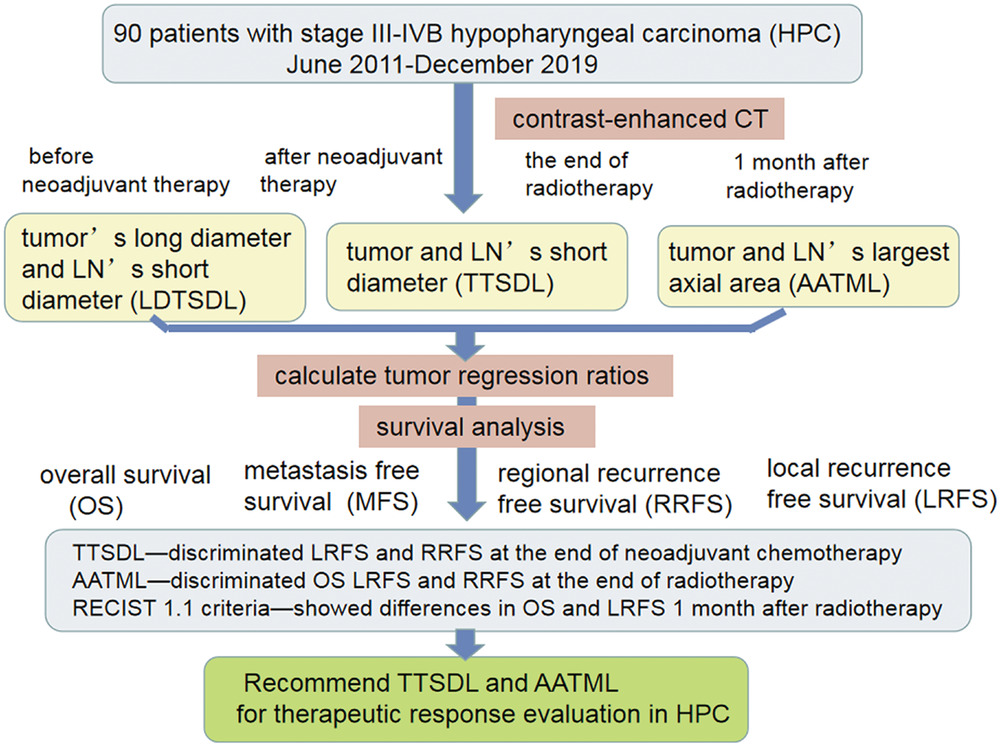
Diagnostic efficacy in therapeutic response by different imaging measurement of hypopharyngeal carcinoma with evaluated and proved diagnostic performance in different time point. The thickness and axial area distinguish prognosis better than RECIST 1.1. The thickness is the best for therapeutic response evaluation.
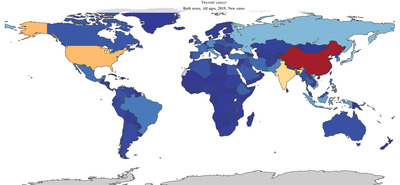
Current status and temporal trend of disease burden of thyroid cancer in China from 1990 to 2019
- Pages: 196-205
- First Published: 12 June 2022
A prospective study of diagnostic accuracy of multidisciplinary team and radiology reporting of preoperative colorectal cancer local staging
- Pages: 206-213
- First Published: 17 June 2022
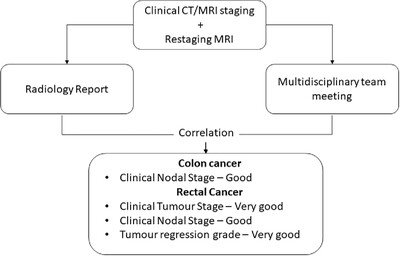
Graphical Abstract: Colorectal cancer local staging using preoperative imaging may differ between the multidisciplinary team (MDT) opinion and original radiology report. This is the first prospective study to compare diagnostic agreement between a specialised colorectal cancer MDT and the radiology report in this setting, demonstrating consistent local staging between the two modalities.
Use and outcomes from neoadjuvant chemotherapy in borderline resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in an Australasian population
- Pages: 214-225
- First Published: 13 July 2022
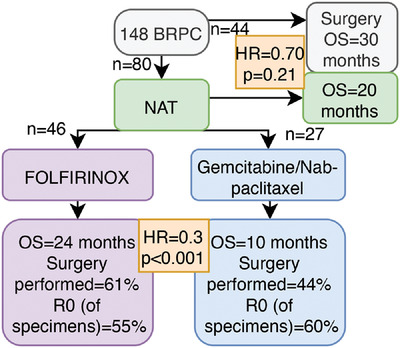
This study aimed to describe the current practice in Australasia in managing potentially resectable pancreatic cancer. Description of neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAT), surgical and survival outcomes in borderline resectable pancreatic cancer (BRPC) using real-world data was extracted from PURPLE (Pancreatic cancer: Understanding Routine Practice and Lifting End results).
Prognostic markers including immune and inflammatory factors predict outcomes in patients receiving postoperative radiation therapy for cholangiocarcinoma
- Pages: 226-233
- First Published: 13 July 2022
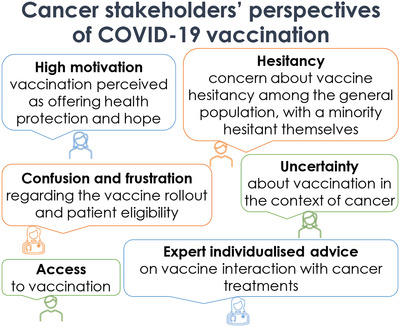
Experiences and perspectives of cancer stakeholders regarding COVID-19 vaccination
- Pages: 234-242
- First Published: 18 July 2022
Physical activity behaviors in cancer survivors treated with neurotoxic chemotherapy
- Pages: 243-249
- First Published: 25 July 2022

• One in five participants with CIPN reported their symptoms interfered with their ability to exercise.
• Participants aged ≥60, with grade ≥1 CIPN or BMI ≥30, were less likely to meet physical activity guidelines.
• Tailored interventions are needed to increase physical activity post treatment to improve physical function and quality of life.
Novel color fluorescence imaging for sentinel lymph node detection in oral and oropharyngeal cancer
- Pages: 250-256
- First Published: 24 July 2022
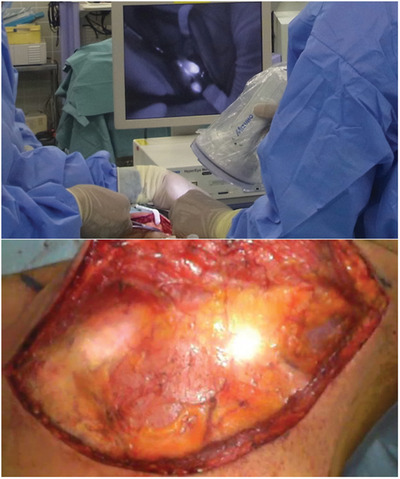
Color fluorescence imaging using indocyanine green would allow for the accurate and safe harvest of sentinel lymph nodes by the improvement of visibility in head and neck cancer. However, it would be currently preferable that this method is used complementally in combination with the conventional methods due to low sensitivity.
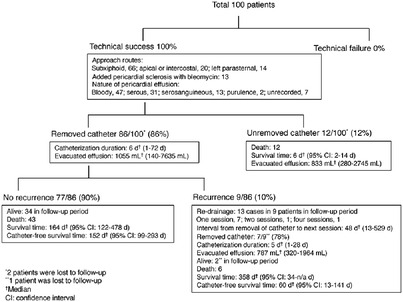
Clinical outcomes of image-guided percutaneous drainage of pericardial effusion in cancer patients: A single-center retrospective analysis
- Pages: 257-262
- First Published: 13 July 2022
GUIDELINES
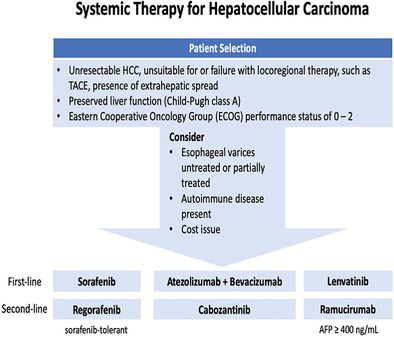
Indonesian consensus on systemic therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pages: 263-274
- First Published: 22 May 2022
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
The implications of rising alcohol-associated cancer burden: Considerations for the Indian context
- Pages: 275-276
- First Published: 30 January 2022