Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Gene Delivery into T-Cells Using Ternary Complexes of DNA, Lipofectamine, and Carboxy-Terminal Phenylalanine-Modified Dendrimers
- First Published: 05 November 2023
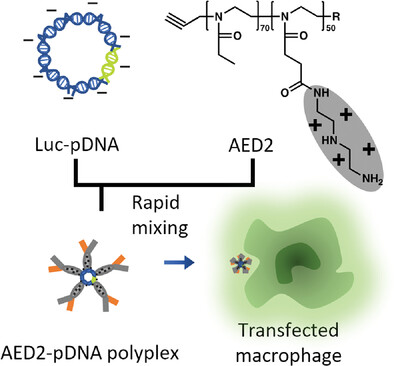
Front Cover: In article 2300139, Chie Kojima, Mei Sawada, Ikuhiko Nakase, and Akikazu Matsumoto construct a non-viral gene delivery system for T cells using a ternary complex composed of plasmid DNA, Lipofectamine, and a polyamidoamine dendrimer of generation 4 modified with 1,2-cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid (CHex) and phenylalanine (Phe).
Back Cover
Polymeric Nanoformulation of Zoledronic Acid Rescues Osteoblasts from the Harmful Effect of its Native Form: An In Vitro Investigation of Cytotoxic Potential on Osteoblasts and Osteosarcoma Cells
- First Published: 05 November 2023
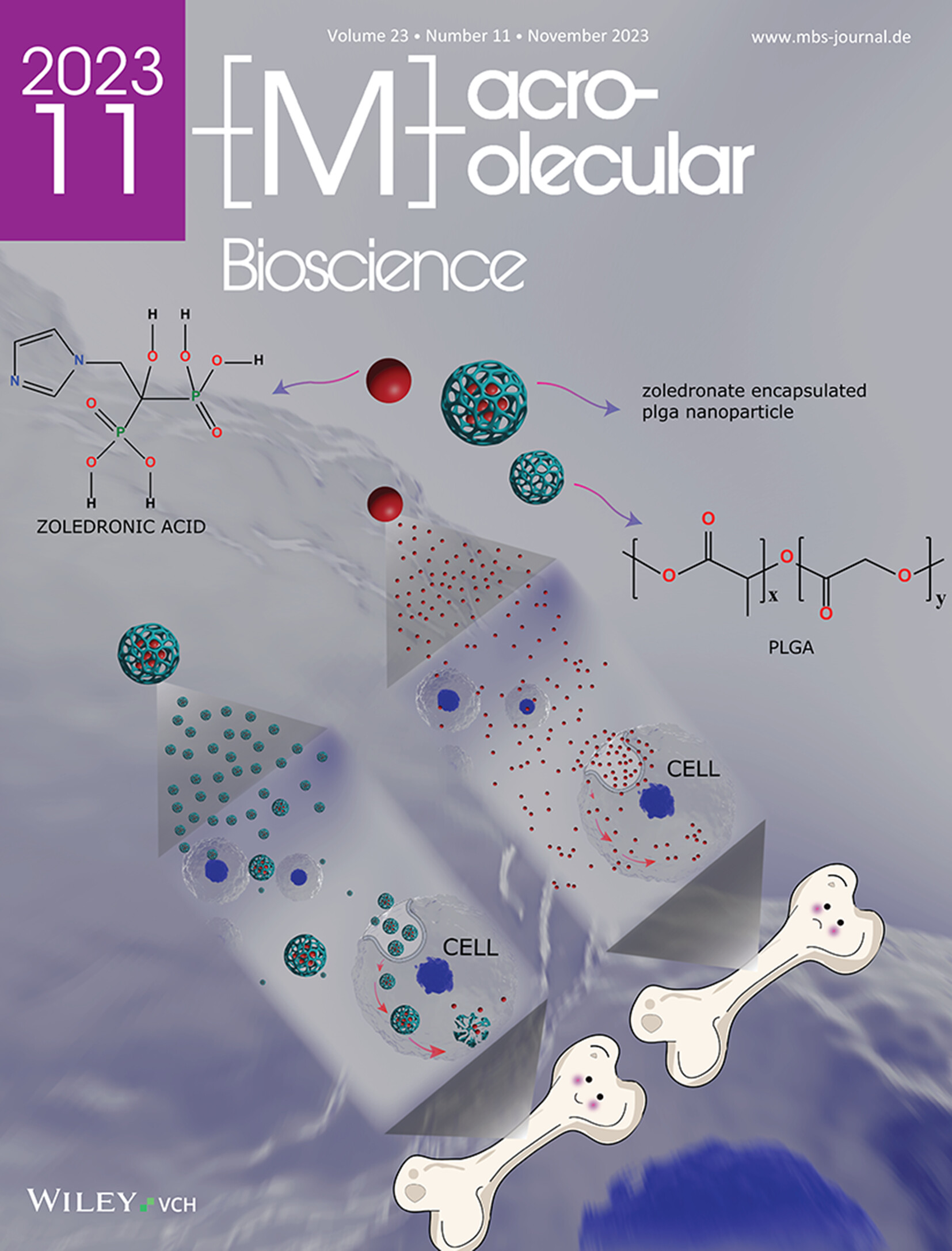
Back Cover: Zoledronic acid in its native form is cytotoxic to both normal healthy pre-osteoblast cells and osteosarcoma cells. The nanoencapsulation of zoledronic acid in a polymeric matrix releases the drug sustained manner, reducing the cytotoxic effect of the drug and supporting the differentiation and mineralization abilities of pre-osteoblast cells while passively targeting osteosarcoma. This is reported by Pratigyan Dash, Sasmita Samal, Gyanendra Prasad Panda, Anna Maria Piras, and Mamoni Dash in article 2300211.
Masthead
Reviews
Polyphenol-Based Nanosystems for Next-Generation Cancer Therapy: Multifunctionality, Design, and Challenges
- First Published: 02 June 2023
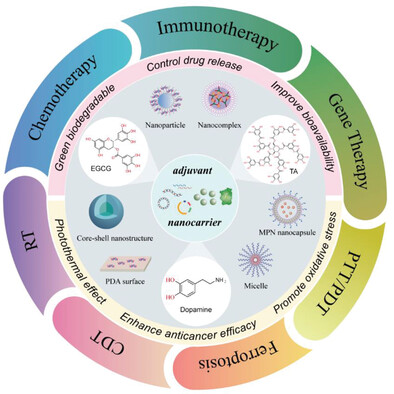
Precision medicine has increased the need for advanced drug delivery systems beyond drug delivery. Scientists are currently investigating polyphenols as efficient and multifaceted drug delivery vehicles for their innate anticarcinogenic properties. In this context, recent advances in polyphenol-based versatilenanosystems for cancer therapy are reviewed. Additionally, the challenges encountered during translating polyphenols for clinical use are explicated.
Amyloid-Like Assembly to Form Film at Interfaces: Structural Transformation and Application
- First Published: 31 May 2023
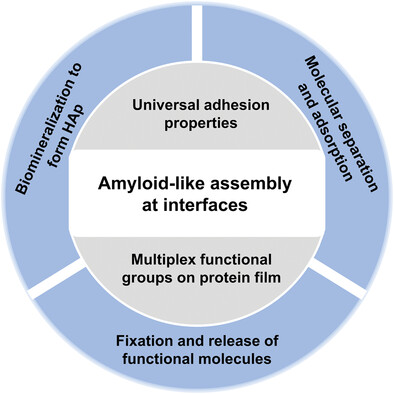
Amyloid-like assembly to form large-scale protein film at interfaces has the features of excellent adhesion and multicomplex functional groups. It can provide an effective strategy to realize surface modification and functionalization, which is required in the interdisciplinary field, such as biomineralization, molecule separation, adsorption, fixation, and release.
Hyperbranched Polymer-Based Vaccines for Cancer Immunotherapy
- First Published: 10 June 2023
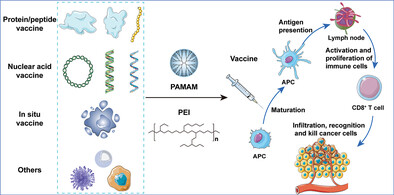
Hyperbranched polymer-based cancer vaccines are constructed using dendrimers or branched polyethylenimine (PEI) to incorporate different antigens and immune adjuvant systems. This review updates the recent advances on the design of dendrimer/branched PEI-based cancer vaccines in aspects of polymer functionalization and design strategies for effective cancer immunotherapy.
Recent Advances in Dual-Function Superhydrophobic Antibacterial Surfaces
- First Published: 02 June 2023
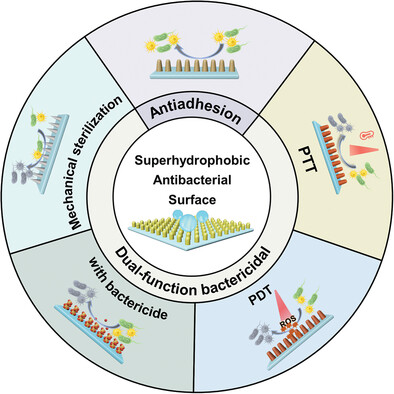
This review focuses on the recent development of dual-function superhydrophobic antibacterial surfaces that exhibit both bacteria-repelling and bacteria-killing properties. These surfaces are classified into three types based on the bacteria-killing mechanism and the representative examples are introduced.
Cellular Membrane Components-Mediated Cancer Immunotherapeutic Platforms
- First Published: 15 June 2023
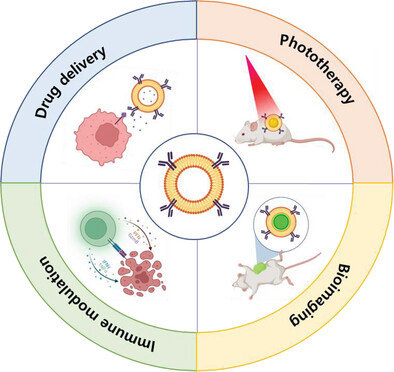
This review focuses on cell membrane-mediated biomimetic techniques of cell membrane coating and artificial nanovesicles. The aim is to offer a comprehensive overview of the specific advantages it offers for a wide range of applications, with a particular emphasis on those that benefit from the incorporation of biological membranes.
Phosphorus and Silicon-Based Macromolecules as Degradable Biomedical Polymers
- First Published: 16 June 2023
Hydrogels as Scaffolds in Bone-Related Tissue Engineering and Regeneration
- First Published: 05 June 2023
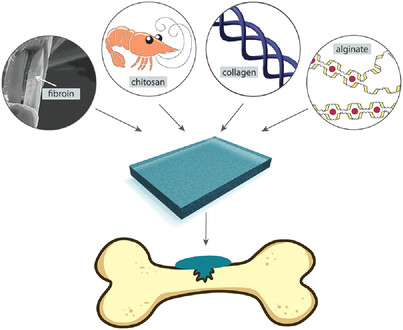
Several years have passed since the medical and scientific communities leaned toward tissue engineering as the most promising field to aid defects resulting from degenerative conditions or trauma. The aim of this review is to bring the reader closer to the subject of hydrogel scaffolds and present the potential of these materials, applied in bone and cartilage tissue engineering.
Biocompatible Polymer-Modified Nanoplatform for Ferroptosis-Enhanced Combination Cancer Therapy
- First Published: 26 June 2023
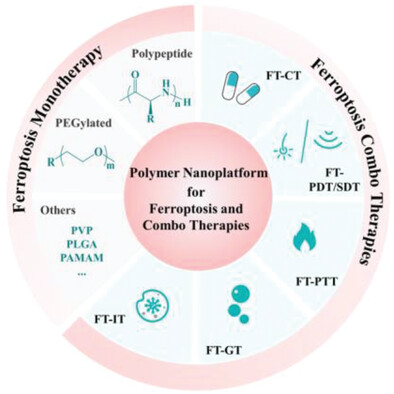
Owing to iron-dependent non-apoptotic anticancer mechanisms including causing lipid peroxide accumulation, sensitizing drug-resistant cancers, priming immunity by immunogenic cell death, and cooperatively acting with other anticancer modalities, the ferroptosis and combo treatments based on various biocompatible polymer-modified nanoplatforms are summarized, and the challenges and perspectives are discussed to move forward potential clinical transitions.
Stimuli-Responsive Delivery of Antimicrobial Peptides Using Polyelectrolyte Complexes
- First Published: 14 July 2023
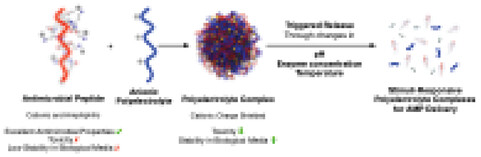
The delivery of antimicrobial peptides from polyelectrolyte complexes in response to bacteria-mediated stimuli such as pH, enzymes, or temperature is reviewed. Specially, an overview of the state-of-the-art in the field, and the challenges and potential of approaches employed is presented. This review is anticipated to stimulate the development of stimuli-responsive polyelectrolyte complexes in addressing current limitations in translating antimicrobial peptides.
Advanced Silk Fibroin Biomaterials-Based Microneedles for Healthcare
- First Published: 06 July 2023
Functional Microneedle Patch for Wound Healing and Biological Diagnosis and Treatment
- First Published: 26 August 2023
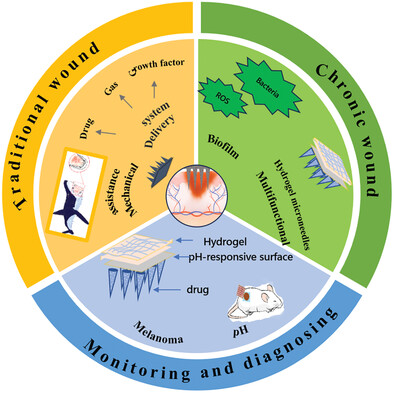
This article mainly classifies the functions of microneedles in the treatment of different types of wounds, and comprehensively summarizes the characteristics of different categories of microneedles, discusses the current challenges in the transformation of microneedle technology toward clinical applications, and finally look forward to the future design and development directions of microneedles in this field.
Research Articles
Gene Delivery into T-Cells Using Ternary Complexes of DNA, Lipofectamine, and Carboxy-Terminal Phenylalanine-Modified Dendrimers
- First Published: 07 June 2023
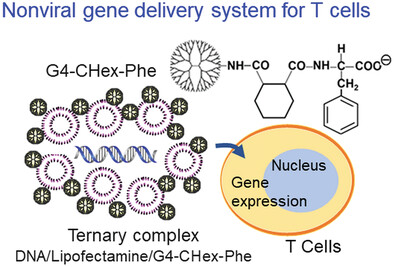
In this study, an efficient non-viral gene delivery system is constructed for T-cells using a ternary complex composed of plasmid DNA, Lipofectamine, and a polyamidoamine dendrimer of generation 4 (G4) modified with 1,2-cyclohexanedicarboxylic anhydride (CHex) and phenylalanine (Phe) (G4-CHex-Phe), which can enhance cellular uptake into T-cells and show no cytotoxicity.
Polymeric Nanoformulation of Zoledronic Acid Rescues Osteoblasts from the Harmful Effect of its Native Form: An In Vitro Investigation of Cytotoxic Potential on Osteoblasts and Osteosarcoma Cells
- First Published: 29 June 2023
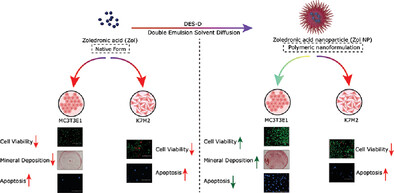
Zoledronic acid (Zol) in its native form is harmful to normal pre-osteoblast cells and osteosarcoma(OS) cells. Zol hampers viability, mineralization, and differentiation. Upon nanoencapsulation in a polymeric matrix (Zol NP), the drug is released slowly thus overcoming the existing lacuna of Zol. Zol NP can be used to passively target OS with less side effects on normal bone cells.
Synthesis, Characterization, and Anticancer Potency of Branched Poly (p-Hydroxy Styrene) Schiff-Bases
- First Published: 27 June 2023
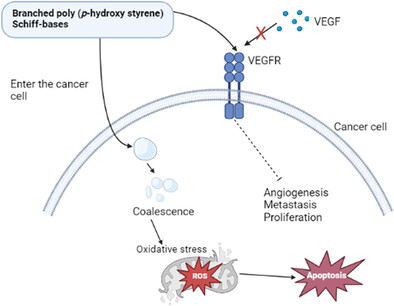
Schiff bases based on branched poly (p-hydroxy styrene) show anti-cancer potency against different types of cancer. The newly prepared Schiff bases slow down breast cancer cells viability and trigger apoptosis through ROS generation, which significantly hinders the cells growth and proliferation. They inhibit angiogenesis and metastasis through inhibition of the vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway.
Self-Assembled Amino Acid Microstructures as Biocompatible Physically Unclonable Functions (BPUFs) for Authentication of Therapeutically Relevant Hydrogels
- First Published: 26 June 2023
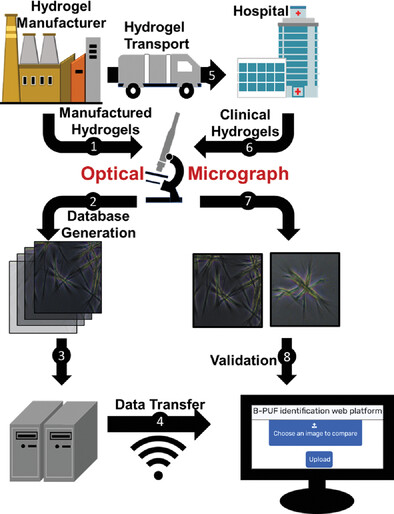
Physically unclonable functions based on tyrosine self-assembly have been developed to authenticate and detect tampering of hydrogels. Each hydrogel has its own specific code generated from the unique optical micrographs produced by the self-assembled structures. The technology, with its simple fabrication, ease of operation, biocompatibility, and cost-effectiveness, makes it a promising anti-counterfeiting tool for hydrogels.
Photodynamic Therapy Minimally Affects HEMA-DMAEMA Hydrogel Viscoelasticity
- First Published: 21 June 2023
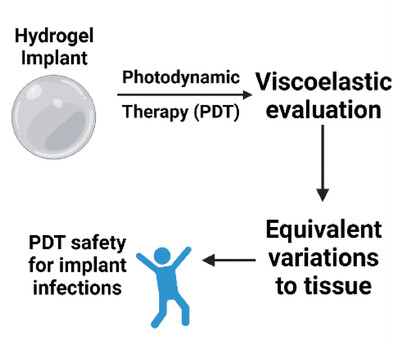
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is an effective method for microbial elimination. High-dose PDT is applied in a hydrogel model to assess the mechanical damage for relevance to medical applications. Moderate changes are observed in PDT and component controls (photosensitizer and light). These changes remain within biological mechanical variation limits, suggesting feasibility at medically relevant doses.
A New Strong-Acid Free Route to Produce Xanthan Gum-PANI Composite Scaffold Supporting Bioelectricity
- First Published: 03 July 2023
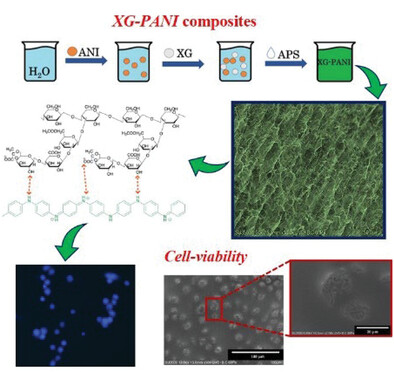
A new strong acidic-free route is used to synthetize biocompatible xanthan gum (XG)–polyaniline (PANI) composite with a porous 3D architecture able to respond to electric stimuli with electron and ion exchanges in physiological-like environment. The hybrid biomaterial exhibits bioelectricity potentially utilizable for producing scaffold that requires electrical stimulations for inducing cell growth and communication or for monitoring biological signals.
Thoroughly Hydrophilized Electrospun Poly(L-Lactide)/ Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Sponges for Tissue Engineering Application
- First Published: 26 June 2023
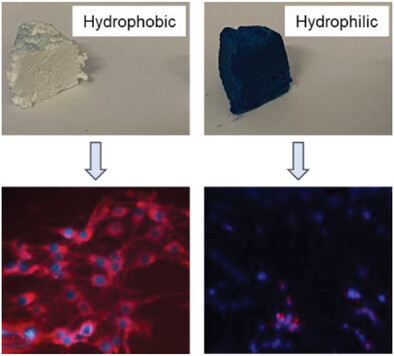
Polymer fiber-based sponges with porous structure are prepared by self-assembly of electrospun PLLA/PCL short fibers. The hydrophilicity of sponge is improved significantly by dip-coating the hydrophobic sponge in surfactant solution. The hydrophilic dye coating test indicates the thorough hydrophilization of the sponge. The MG63 and HDF cell culture tests on the sponges show hydrophilic sponge is preferable for cell growth, proliferation, and infiltration.
Mitochondria Targeted Nanoparticles Potentiate Tumor Chemo-Phototherapy by Toxic Oxidative Stress Mediated Oxeiptosis
- First Published: 09 June 2023
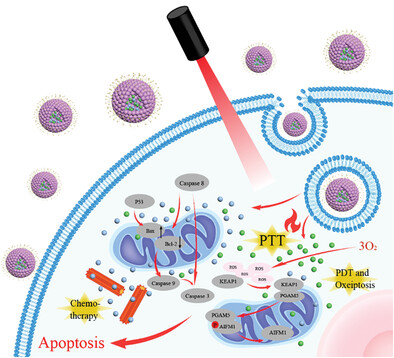
Mitochondria targeting nanomedicine (M-ICG-PTX NPs) are reported for mitochondria-targeted photo-chemotherapy of malignant breast cancers. The systematic study revealed that M-ICG-PTX NPs exhibited improved mitochondria distribution and mitochondria membrane potential damage, which promoting cell apoptosis, and significantly inhibiting tumor growth and metastasis under photo-chemotherapy. This research suggests that sub-cellular targeted photo-chemotherapy provide opportunities for regulating cellular oxeiptosis pathway apoptosis to potentiate synergistic cancer treatment.
Bioactive Phenylboronic Acid-Functionalized Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels Induce Chondro-Aggregates and Promote Chondrocyte Phenotype
- First Published: 03 July 2023
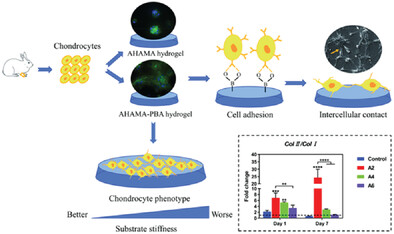
Phenylboronic acid-functionalized hyaluronic acid hydrogels are prepared for the two-dimensional culture of rabbit articular chondrocytes. Those hydrogels can enhance cell-material interactions by forming phenylborate ester bonds with glycans on cell membranes. The formation of filopodia promotes cell adhesion and intercellular contact. In addition, soft hydrogel substrates with low stiffness exhibit the best effect on promoting the chondrocyte phenotype.
Organic Functional Group on Carbon Nanotube Modulates the Maturation of SH-SY5Y Neuronal Models
- First Published: 01 July 2023
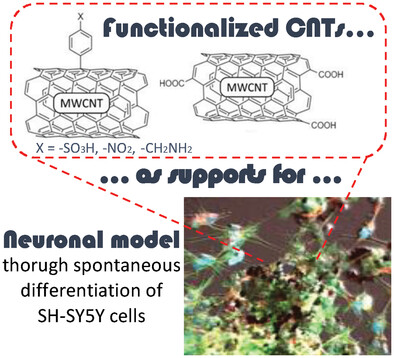
Functionalized carbon nanotubes (f-CNTs) have been used as substrates to modulate the maturation properties of neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y neuronal cell model. It is demonstrated that, even though in all types of functionalizations studied intricate cell-CNT networks are formed, sulfonic groups show selectively better differentiation and, thus, maturation. A possible correlation is also found between conductivity of f-CNTs and cell-processes lengths.
Fabrication of Insoluble Elastin by Enzyme-Free Cross-Linking
- First Published: 13 July 2023
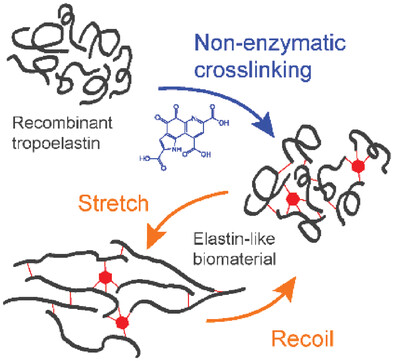
A technique involving recombinant tropoelastin polymerization, coacervation, and allysine-mediated cross-linking with pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) creates artificial elastin with native characteristics. PQQ, covalently attached to magnetic Sepharose beads, enables its repeated use in protein cross-linking. The resulting material closely resembles natural elastin in molecular, biochemical, and mechanical properties. This approach enables the development of resilient elastin-like materials for biomedical applications.
pH-temperature Responsive Hydrogel-Mediated Delivery of Exendin-4 Encapsulated Chitosan Nanospheres for Sustained Therapeutic Efficacy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- First Published: 26 June 2023
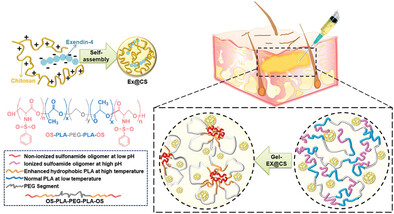
A pH-temperature responsive hydrogel system is developed for sustained release of exendin-4 (EX) in type 2 diabetes (T2D) treatment. EX@CS nanospheres, prepared using the electrospray technique, are dispersed in the hydrogel. Upon injection, the hydrogel gradually degrades, releasing EX@CS nanospheres for over 72 h and maintaining therapeutic levels. This biocompatible system offers a promising approach for addressing the limitations of EX's short half-life and improving T2D treatment.
Aminosilane Functionalized Aligned Fiber PCL Scaffolds for Peripheral Nerve Repair
- First Published: 26 June 2023
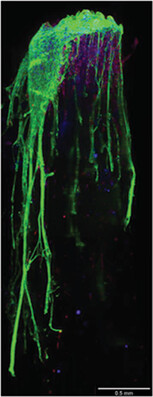
Modifying biomaterials with functional groups can significantly control and influence cell adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation at the sub-micron scale. The smallest changes in surface chemistry and topography can drive neuronal cell differentiation and guide axonal growth from the dorsal root ganglia. Silanization is a simple, scalable, and cost-effective tool for tissue engineering applications.
Poly(2-oxazoline)-Based Polyplexes as a PEG-Free Plasmid DNA Delivery Platform
- First Published: 19 July 2023
Dermatan Sulfate/Chitosan Nanoparticles Loaded with an Anti-Inflammatory Peptide Increase the Response of Human Colorectal Cancer Cells to 5-Fluorouracil
- First Published: 19 July 2023
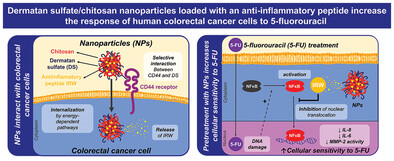
New therapeutic strategies are required to reverse resistance to the 5-FU in CRC This work reports nanoparticles (NPs) loaded with the anti-inflammatory egg-derived tripeptide IRW, able to selectively interact with human cancer cells through the CD44 receptor and increase their sensitivity to 5-FU by inhibiting nuclear translocation of NFκB pathway.
Electrospun Polymeric Fibers Decorated with Silk Microcapsules via Encapsulation and Surface Immobilization for Drug Delivery
- First Published: 22 July 2023
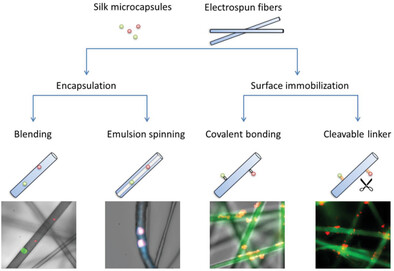
Hollow polymer microcapsules as drug carriers have the advantages of drug protection, storage, and controlled release. To enhance the in situ drug delivery, the silk microcapsules with electrospinning technology to construct the fiber-microcapsule composite scaffolds are combined, including direct blending and emulsion electrospinning for encapsulation, as well as covalent and cleavable disulfide-linkage for surface immobilization for different drug delivery requirements.
A Mucin-Based Bio-Ink for 3D Printing of Objects with Anti-Biofouling Properties
- First Published: 19 July 2023
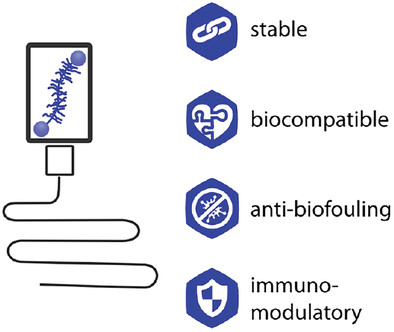
Mucin glycoproteins—the functional key component of mammalian mucus—combine several biomedically beneficial properties. However, as mucin-based hydrogels typically lack mechanical stability, they are never used for 3D printing. In this study, a highly functional mucin-based bio-ink with tailored rheological properties is developed, enabling the printing of objects with mechanical properties similar to soft tissue, anti-biofouling behavior, good biocompatibility, tunable cell adhesion, and immunomodulating behavior.
Self-Assembly Nanochaperone with Tunable Hydrophilic–Hydrophobic Surface for Controlled Protein Refolding
- First Published: 18 July 2023
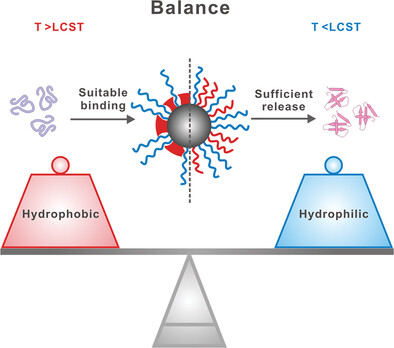
A series of nanochaperones is demonstrated with tunable hydrophilic–hydrophobic surfaces to control the denatured protein refolding. The appropriate hydrophilic–hydrophobic balance is important for enhancing protein renaturation because it can simultaneously guarantee the suitable capture and sufficient release of client proteins, providing new ideas for the design of nanochaperones in the future.
Zn2+@Polyvinylpyrrolidone and Urushiol Preparation of Nanofibrous Membranes and Their Synergistic Effect
- First Published: 22 July 2023
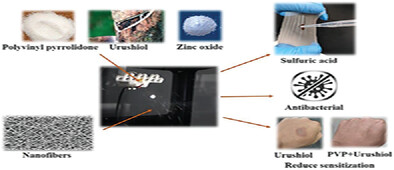
This study finds that polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) has a synergistic effect with urushiol, which is acid-resistant and sticky after contact with water, so a PVP wound dressing can effectively protect the wound. Adding nano-zinc oxide can increase the antibacterial effect by more than 95%, forming an organic/inorganic material for biomedical fields.
Incorporation of Cell-Adhesive Proteins in 3D-Printed Lipoic Acid-Maleic Acid-Poly(Propylene Glycol)-Based Tough Gel Ink for Cell-Supportive Microenvironment
- First Published: 15 September 2023
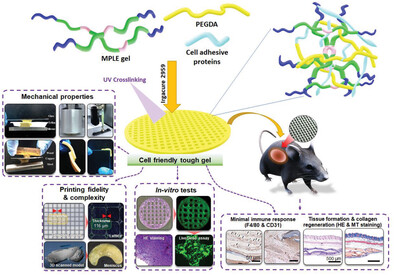
Cell-adhesive proteins like gelatin and albumin within the poly(maleate-propylene oxide)-lipoate-poly(ethylene oxide) gel allows printing of biofunctional 3D scaffolds with high cell proliferation compared to pure gel. The addition of proteins supports the formation of interconnected cell clusters and spreading of cells in the printed scaffolds without additional growth factors. The protein-loaded scaffolds showed excellent biocompatibility and increased angiogenesis without inflammatory response in mice.