Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Electrosprayed Regeneration-Enhancer-Element Microspheres Power Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis Coupling (Small 36/2022)
- First Published: 08 September 2022

Bone Tissue Repair
In article number 2200314, Xin Zhao and co-workers electrospray microspheres encapsulating stem cells and natural tissue metabolites as regeneration-enhancer-element reservoirs to power the inside/outside microsphere cell–cell/cell–material communication for accelerated vascularized bone tissue repair.
Inside Front Cover
Dual Biosignal-Functional Injectable Microspheres for Remodeling Osteogenic Microenvironment (Small 36/2022)
- First Published: 08 September 2022

Bone Defect Treatment
Inspired by the concept of macrophage reprogramming, Wenguo Cui, Youcheng Yu, and co-workers construct immuno-engineering porous microspheres (IL-4/loaded liposomes (Ls)/poly (l-lactic acid) (PLLA)) to realize bone repair through the “physical” porous structure and “molecular” IL-4 chemokines dual signal regulation. The immuno-reprogramming IL-4/Ls/PLLA microspheres achieve the precise immuno-reprogramming of macrophages by driving the activation of the signaling pathways. This immune reengineering strategy paves the way for clinical bone defect treatment.
Inside Back Cover
Adhesive and Injectable Hydrogel Microspheres for Inner Ear Treatment (Small 36/2022)
- First Published: 08 September 2022

Inner Ear Therapy
In article number 2106591, Bin Ye, Wenguo Cui, Mingliang Xiang, and co-workers construct a mussel-inspired injectable hydrogel microsphere loading Ebselen liposomes that adheres to the cochlea round windows membrane (RWM). The positively charged primary amine groups through electrostatic interaction and the catechol groups through high-strength coordination bonds and hydrogen bonds adhere to the RWM. This adhesion can prolong the retention of the middle ear cavity for more than 7 days and helps with inner ear therapy.
Back Cover
Drawn-on-Skin Sensors from Fully Biocompatible Inks toward High-Quality Electrophysiology (Small 36/2022)
- First Published: 08 September 2022
Biocompatible Conductive Inks
In article number 2107099, Cunjiang Yu and co-workers report the recent development of a conductive ink that is fully biocompatible at the cell, tissue, and organ levels. It also allows for conformal interfacing with human skin for high-fidelity electrophysiological measurements. This cover illustrates the conformal contact of the ink film with skin.
Masthead
Guest Editorial
Reviews
Smart Film Actuators for Biomedical Applications
- First Published: 17 January 2022
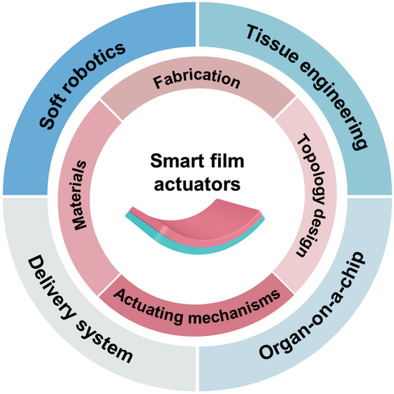
In this review, the authors summarize the latest achievements of smart film actuators applied in biomedical fields. They start by introducing the fabrication techniques of smart film actuators, then shift to their topology design, material selections and distinct actuating mechanisms. After that, they categorize their biomedical applications in practical aspects. The challenges and prospects of this field are finally discussed.
Microfluidic Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery
- First Published: 09 April 2022
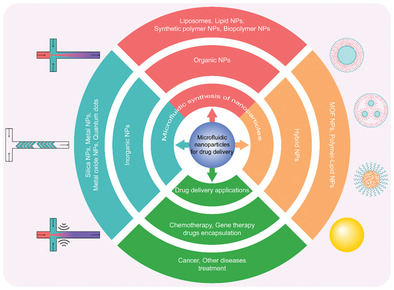
Microfluidics offers a promising strategy for making nanoparticles for drug delivery due to its capability in precisely controlling nanoparticle properties. This article provides a critical review of recent progress in microfluidic nanoparticles for drug delivery. Different microfluidic synthesis technologies and mechanisms of organic, inorganic, and hybrid nanoparticles, as well as their various drug delivery applications are summarized.
Programmable DNA Hydrogels as Artificial Extracellular Matrix
- First Published: 04 February 2022
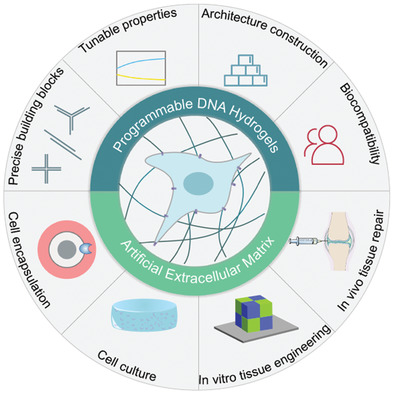
Extracellular matrix plays a crucial role in regulating cell behavior and fate. This review focuses on recent advances in programmable DNA hydrogels as artificial extracellular matrix. It introduces the classification, design, and assembly of DNA hydrogels, and summarizes the state-of-the-art achievements in cell encapsulation, cell culture, and tissue engineering. The challenges for cellular applications of DNA hydrogels are also delivered.
Functional Extracellular Vesicles for Regenerative Medicine
- First Published: 23 March 2022
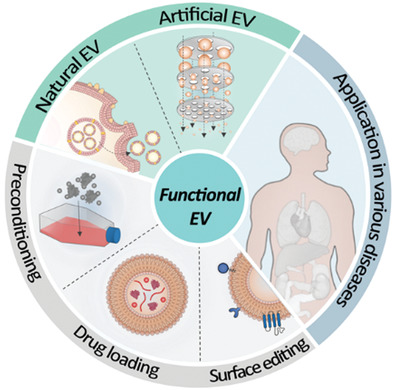
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) have made a meteoric rise as a safer and more efficacious alternative to cell therapy in the last decade. This review provides an updated overview of current techniques for the functionalization of natural EVs and recent advances in artificial EVs, particularly in the scope of regenerative medicine.
Progress in Stimuli-Responsive Biomaterials for Treating Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases
- First Published: 20 March 2022
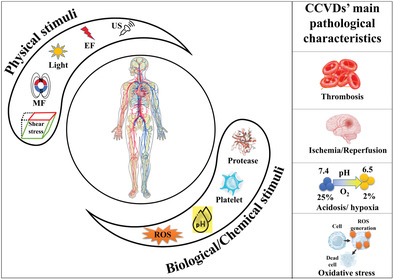
Stimuli-responsive biomaterials are robustly used for the treatment of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. This review thoroughly discusses the recent advances (last 5 years) in the preclinical and clinical stage of these smart materials offering a view of their strengths and weaknesses and a glimpse of their future perspective.
Reciprocity of Cell Mechanics with Extracellular Stimuli: Emerging Opportunities for Translational Medicine
- First Published: 23 March 2022
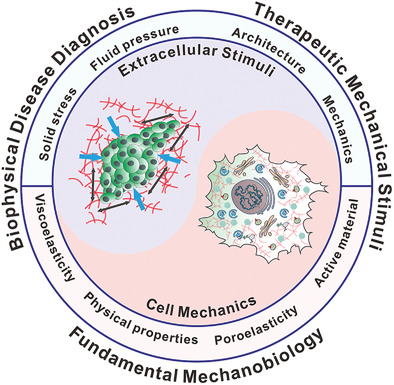
The dynamic interplay of cell mechanics with extracellular stimuli drives new opportunities for potential translational applications. This review focuses on the most recent advances in the fundamental understanding of mechanobiology, and emphasizes on its application including diagnosis of disease based on mechanical measurements and therapeutic treatments that utilize mechanical stimuli and perturbations.
Non-Invasive Thermal Therapy for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine
- First Published: 27 April 2022
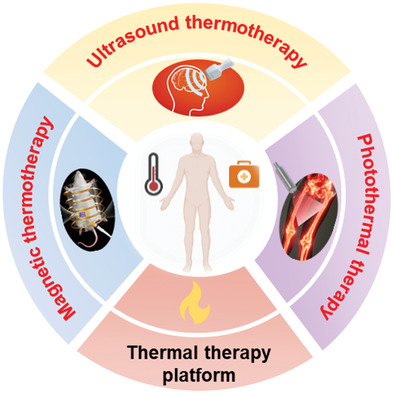
Owing to the development of nanotechnology and non-invasive treatment, thermal therapy in combination with external stimuli has been applied for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, which has attracted more and more attention in recent years. Among them, photothermal therapy, magnetic thermotherapy, and ultrasound thermotherapy show attractive charm due to their convenient regulation and precise thermal positioning.
Advances in Translational 3D Printing for Cartilage, Bone, and Osteochondral Tissue Engineering
- First Published: 17 June 2022
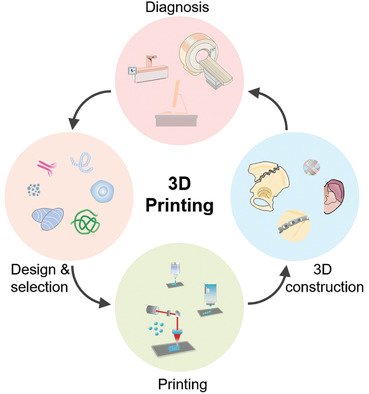
As an emerging additive manufacturing technique, 3D printing can produce personalized scaffolds with desirable architectures, adjustable physicochemical properties, and tunable biological functionalities, which has revolutionized the development of tissue engineering and showed significant potential for clinical transformation, especially in the field of cartilage, bone, and osteochondral tissue regeneration.
Harnessing 4D Printing Bioscaffolds for Advanced Orthopedics
- First Published: 20 January 2022
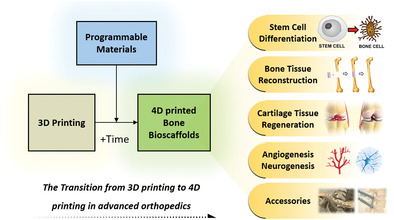
4D printing imparts a new dimension of "time" to 3D printing. Based on stimulus-responsive programmable materials, 4D printed structures could self-transform and self-remodel under prespecified stimuli. Intelligent scaffolds fabricated by the 4D printing technique have been applied in various orthopedic engineering, and are considered as the next generation of bone repair devices.
Research Articles
Drawn-on-Skin Sensors from Fully Biocompatible Inks toward High-Quality Electrophysiology
- First Published: 19 February 2022
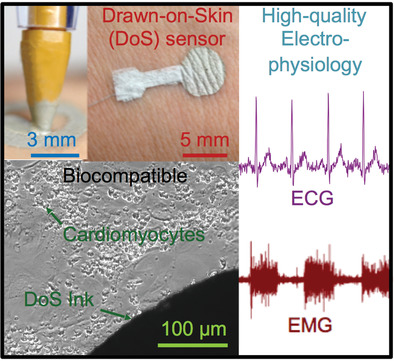
Sensors fabricated directly on the skin are extremely promising for customized, on-demand, and high-quality physiological monitoring. However, the current literature does not thoroughly investigate the biocompatibility of the raw electronic materials deposited on skin. The development of a drawn-on-skin ink that is biocompatible on the cellular, tissue, and organ levels and can be used for multiday, high-fidelity electrophysiology is presented.
Electrosprayed Regeneration-Enhancer-Element Microspheres Power Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis Coupling
- First Published: 08 March 2022
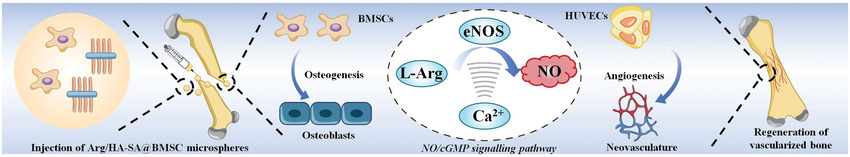
Sodium alginate microspheres encapsulating L-arginine doped hydroxyapatite nanoparticles (Arg/HA NPs) and bone mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) as regeneration-enhancer-element reservoirs (Arg/HA-SA@BMSC) for bone healing are electrosprayed. Such a microsphere system can promote the osteogenesis–angiogenesis coupling at the defect site and realize the internal/external modulation loop of encapsulated cells and native cells during bone healing.
Dual Biosignal-Functional Injectable Microspheres for Remodeling Osteogenic Microenvironment
- First Published: 14 April 2022
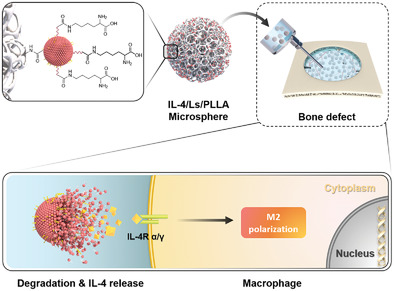
Immunoengineered porous microspheres (interleukin-4 (IL-4)/liposomes (Ls)/poly (l-lactic acid) (PLLA)) are constructed to realize bone repair through the “physical” porous structure and “molecular” IL-4 chemokines dual signal regulation. The immunoreprogrammed IL-4/Ls/PLLA microspheres achieve the precise immuno-reprogramming of macrophages by driving the activation of the signaling pathways. This immune reengineering strategy paves a method for clinical bone defect treatment.
Adhesive and Injectable Hydrogel Microspheres for Inner Ear Treatment
- First Published: 01 February 2022
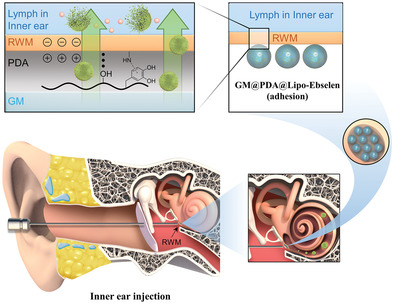
A mussel-inspired injectable hydrogel microsphere loading Ebselen liposomes which adheres to cochlea round windows membrane (RWM) is constructed. The positively charged primary amine groups through electrostatic interaction and the catechol groups through high-strength coordination bonds and hydrogen bonds adhere to the RWM. This adhesion can prolong the retention of the middle ear cavity and helps with inner ear therapy.
Frontispiece
pH Stimuli-Responsive, Rapidly Self-healable Coatings Enhanced the Corrosion Resistance and Osteogenic Differentiation of Mg-1Ca Osteoimplant (Small 36/2022)
- First Published: 08 September 2022
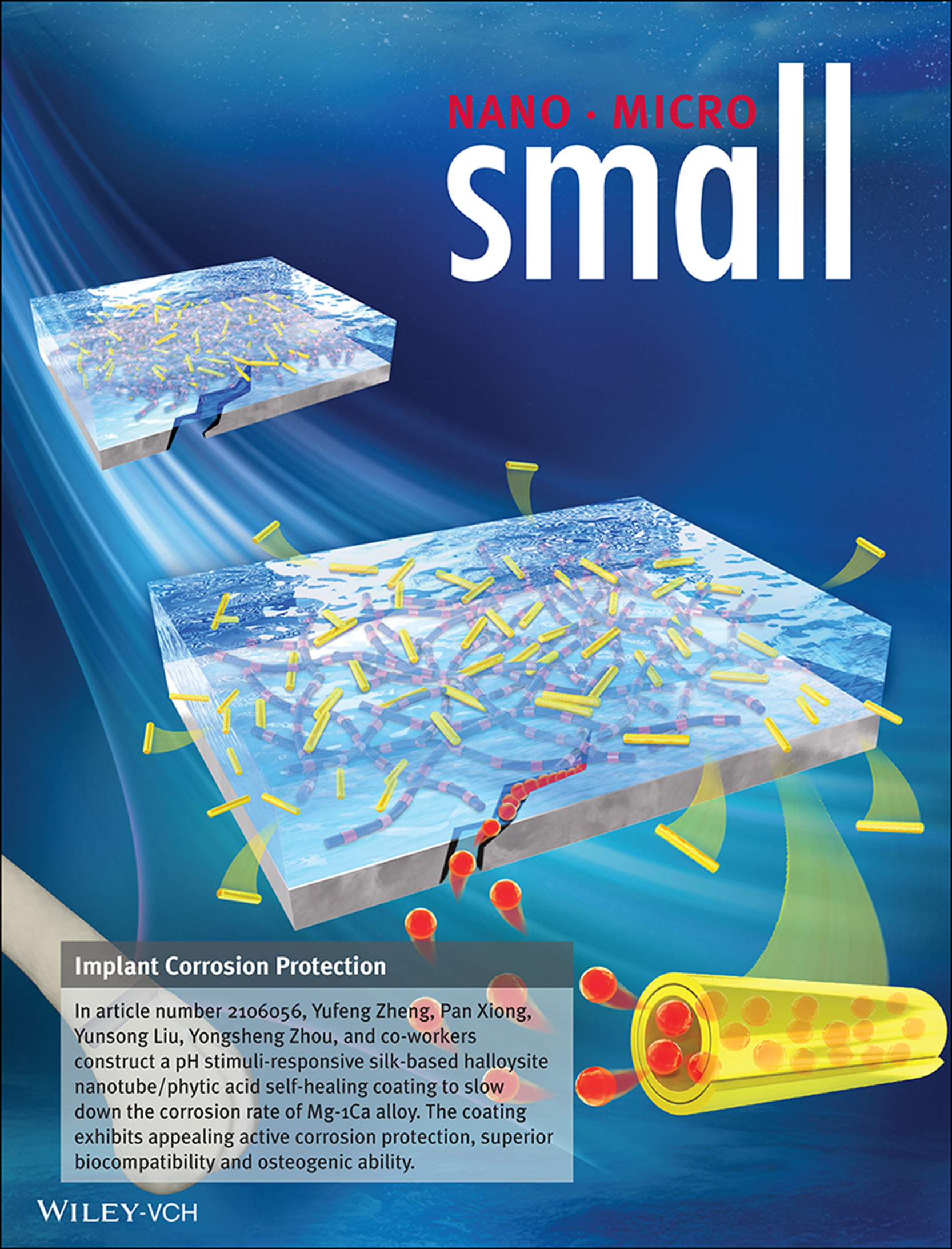
Implant Corrosion Protection
In article number 2106056, Yufeng Zheng, Pan Xiong, Yunsong Liu, Yongsheng Zhou, and co-workers construct a pH stimuli-responsive silk-based halloysite nanotube/phytic acid self-healing coating to slow down the corrosion rate of Mg-1Ca alloy. The coating exhibits appealing active corrosion protection, superior biocompatibility and osteogenic ability.
Research Articles
pH Stimuli-Responsive, Rapidly Self-healable Coatings Enhanced the Corrosion Resistance and Osteogenic Differentiation of Mg-1Ca Osteoimplant
- First Published: 16 May 2022
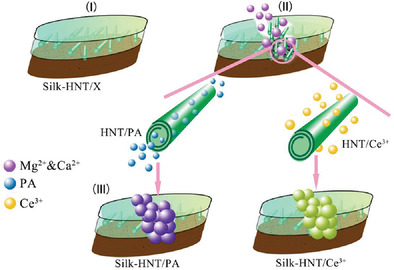
A pH stimuli-responsive silk-halloysite (HNT)/phytic acid (PA) self-healing coating (Silk-HNT/PA) is fabricated on Mg-1Ca alloy. Halloysite (HNT) significantly improves the loading efficiency and shortens the self-healing time of Silk-PA coating. The Silk-HNT/PA coating improves the corrosion resistance and osteogenic differentiation of Mg-1Ca alloy.
NIR/MRI-Guided Oxygen-Independent Carrier-Free Anti-Tumor Nano-Theranostics
- First Published: 02 December 2021
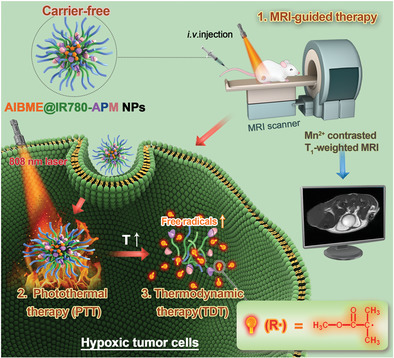
Carrier-free nano-theranostic agents (AIBME@IR780-APM NPs) chelating Mn2+ are developed by self-assembly of two IR780 derivatives and thermally decomposable radical initiators AIBME, for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-guided synergistic photothermal therapy/thermodynamic therapy. The sequentially generated heat and alkyl radicals upon 808-nm laser irradiation synergistically induce cell death, ignoring tumor hypoxia. Mn2+-contrasted T1-weighted MRI further promotes the “precise strike” of hypoxic tumors.
Enzyme-Photocatalyst Tandem Microrobot Powered by Urea for Escherichia coli Biofilm Eradication
- First Published: 05 February 2022

Biohybrid enzyme/photocatalyst-based microrobot structure for the efficient removal of a bacterial biofilm is presented. TiO2 nanotube bundles are decorated with CdS nanoparticles and enzyme urease. This design provides a strategy for developing advanced photoresponsive microrobots with improved catalytic activity, offering great potential for the future applications of micromachines.
The Effect of the Nanoparticle Shape on T Cell Activation
- First Published: 16 March 2022
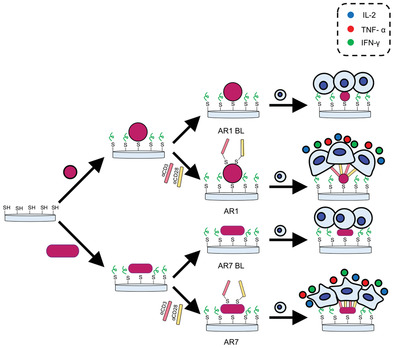
Ex vivo T cell activation efficiency is compared between nanoscale “isotropic” and “anisotropic” presentation of the stimulatory ligands. A large aspect ratio of gold nanorods conjugated substrate enhances both murine and human T cell activation promoting T cell expansion and cytokine secretion, high membrane tension driving morphological changes, actin polymerization, and focal adhesion assembly and phenotype differentiation.
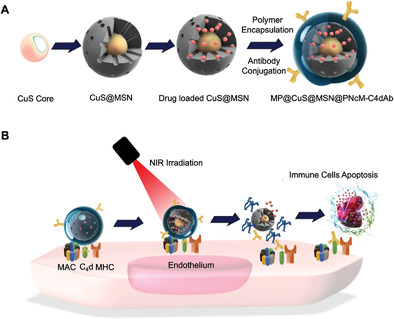
In Vivo Kidney Allograft Endothelial Specific Scavengers for On-Site Inflammation Reduction under Antibody-Mediated Rejection
- First Published: 02 March 2022
Vascular Derived ECM Improves Therapeutic Index of BMP-2 and Drives Vascularized Bone Regeneration
- First Published: 26 February 2022
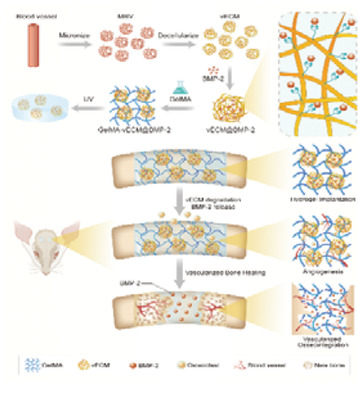
In this study, harnessing the intrinsic angiogenic potential of vascular derived extracellular matrix (vECM) and its specific affinity to growth factors, a vECM/GelMA based hybrid hydrogel delivery system is constructed to achieve optimized bone morphogenetic protein-2 therapeutic index and provide intrinsic angiogenic induction during bone healing.
Secretory Fluid-Aggregated Janus Electrospun Short Fiber Scaffold for Wound Healing
- First Published: 10 March 2022
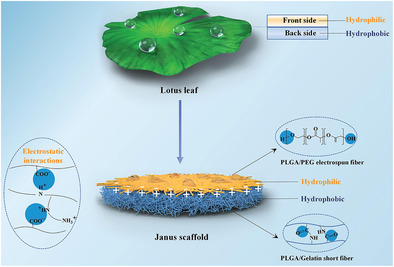
A Janus electrospun short fiber scaffold is fabricated via a combination of electrospinning and short fiber modeling technologies. It can aggregate the wound exudate through pumping from the hydrophobic layer to the hydrophilic and simultaneously trigger the cascade release of curcumin in the upper membrane, thus promoting neovascularization and collagen deposition to accelerate wound healing.
Hydrolytically Degradable Microgels with Tunable Mechanical Properties Modulate the Host Immune Response
- First Published: 10 March 2022
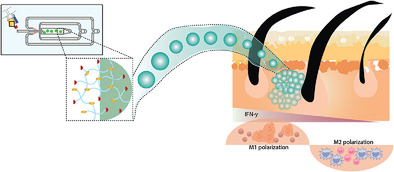
Hydrolytically susceptible ethylene linkers are used for microparticle crosslinking to fabricate degradable droplet microfluidic based microgels for therapeutic delivery. The tunability and degradability conferred by the ester-based degradation in vivo regulate the infiltration of immune cells to the implant site and the host immune polarization.
A Natural Hydrogel with Prohealing Properties Enhances Tendon Regeneration
- First Published: 18 March 2022
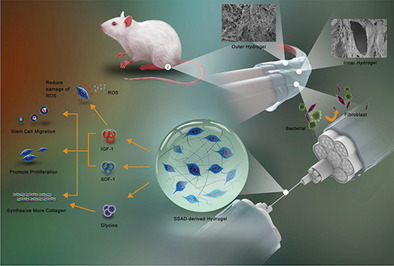
A dual-layered skin secretion of Andrias davidianus (SSAD)-derived hydrogel to promote tendon regeneration and antiadhesion is reported. The strong adhesiveness allows the SSAD hydrogel to reconnect ruptured tendons. The inner hydrogel with a large pore size allows cells growth and the outer layer of the hydrogel with a small pore size could serve as a barrier to prevent peritendinous adhesion.
Multiscale Engineering of Nanofiber-Aerogel Composite Nanogenerator with Tunable Triboelectric Performance Based on Multifunctional Polysuccinimide
- First Published: 20 March 2022
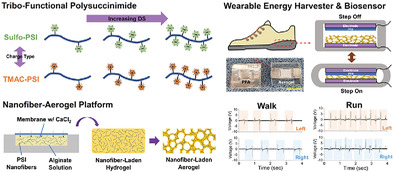
A nanofiber-infused aerogel is developed as a new material platform for triboelectric nanogenerators. Functional polysuccinimide-based nanofibers with tunable triboelectric polarity and mechanically conformal and durable aerogel are synergistically combined for optimal triboelectric performance and wearability.
Sticking Together: Injectable Granular Hydrogels with Increased Functionality via Dynamic Covalent Inter-Particle Crosslinking
- First Published: 22 March 2022
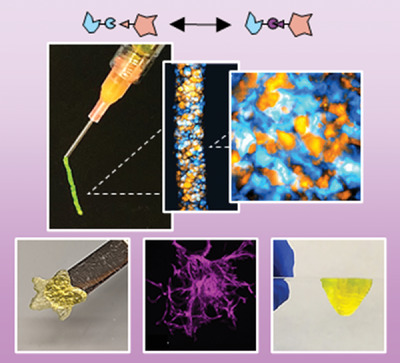
Granular hydrogels are an exciting class of microporous and injectable biomaterials. To further their properties, the authors introduce adhesion between particles via dynamic covalent inter-particle hydrazone crosslinking through the modification of particles with aldehyde and hydrazide chemical groups. This enhances the mechanical integrity and shape stability of granular hydrogels, including when 3D printed, while still allowing for cellular interactions.
Biomimic Trained Immunity-MSCs Delivery Microcarriers for Acute Liver Failure Regeneration
- First Published: 11 April 2022
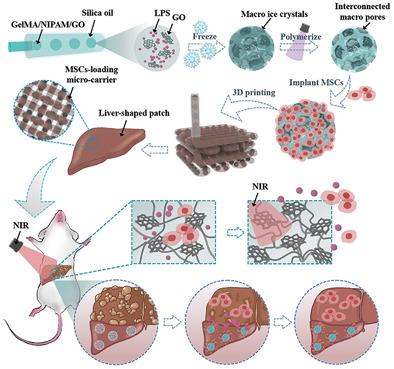
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-loaded photoresponsive porous microparticles (CPMs) release LPS under NIR irradiation, where the delivered mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are imparted with the feature of “trained immunity.” By remodeling the MSCs-laden CPMs patch through bioprinting in treating acute liver failure rats, this photothermal delivery system displays superior anti-inflammatory and regeneration ability.
Development of Biodegradable Osteopromotive Citrate-Based Bone Putty
- First Published: 19 June 2022
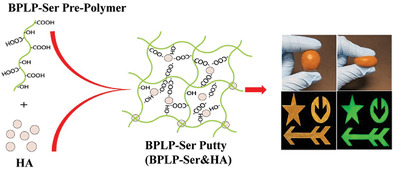
The critical chemical and bioactive properties of citric acid are leveraged into a biodegradable photoluminescent polymer/hydroxyapatite (BPLP-Ser/HA) bone putty as an off-the-shelf replacement for clinically utilized bone waxes. Obtained putty materials combine mechanical stability in physiological conditions, blood vessel sealing, and adhesion with hemostatic, antimicrobial, and osteopromotive properties, culminating in cranial bone regeneration equivalent to autograft.
4D Printing of Extrudable and Degradable Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Microgel Scaffolds for Multidimensional Cell Culture
- First Published: 22 June 2022
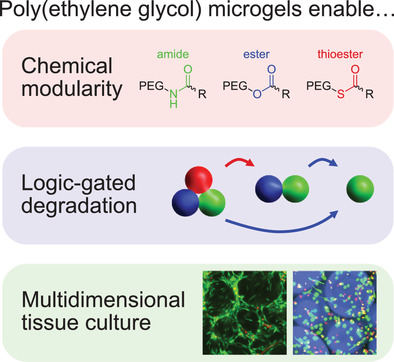
Microgel scaffolds are prepared from chemically modular synthetic polymer precursors, allowing for post-printing tuning of void fraction, logic-gated degradation, and bioprinting of cells encapsulated in 2.5D and 3D culture. Cellularized microgel constructs enable high viability on length scales that are inaccessible by bulk encapsulation, presenting opportunities for additive manufacturing of large format cell-laden biomaterials for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
Polysaccharide-Polyplex Nanofilm Coatings Enhance Nanoneedle-Based Gene Delivery and Transfection Efficiency
- First Published: 30 June 2022
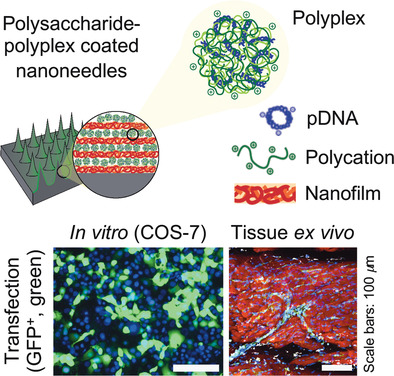
Herein, nanoneedles coated with polysaccharide-nanofilms enhance transfection efficiency of polyplexes, using an order of magnitude lower in gene cargo, compared to existing delivery systems. This enhancement is attributed to the physicochemical properties of the anionic polysaccharides. Nanofilms enable surface-mediated and spatially controlled gene delivery in cells and tissues, which is also applicable to microneedles, devices, and other bioengineered systems.
Biostimulatory Micro-Fragmented Nanofiber-Hydrogel Composite Improves Mesenchymal Stem Cell Delivery and Soft Tissue Remodeling
- First Published: 10 August 2022
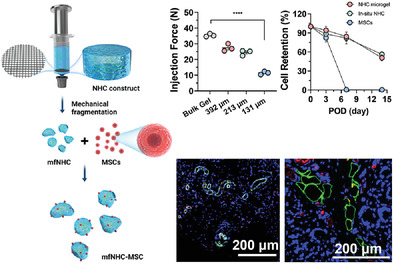
A biostimulatory, micro-fragmented nanofiber-hydrogel composite (mfNHC) is generated by mechanical shear-induced fragmentation of crosslinking a hyaluronic acid hydrogel network covalently bonded with surface-functionalized poly(ε-caprolactone) nanofiber fragments. The granular form of mfNHCs shows strong potential as a stem cell carrier to deliver mesenchymal stem cells for soft tissue remodeling.
4D Cell-Condensate Bioprinting
- First Published: 16 August 2022
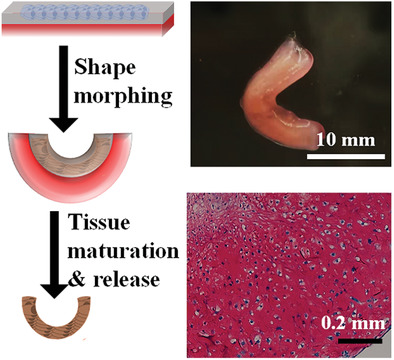
A 4D bioprinting strategy that enables the construction of complex scaffold-free cell condensates through predefined shape transformations is reported. Cell condensates with diverse geometries can be designed to undergo preprogrammed deformations over time. With this system, complex tissues are engineered through controlled shape morphing and tissue maturation. This 4D bioprinting strategy opens an avenue for scaffold-free 4D tissue engineering.