Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Pictures
Front Cover: Material Design Concept of Lithium-Excess Electrode Materials with Rocksalt-Related Structures for Rechargeable Non-Aqueous Batteries (Chem. Rec. 4/2019)
- Page: 687
- First Published: 05 April 2019

The cover picture, for this special issue on Next Generation Li and Na Rechargeable Batteries, shows the development of a new series of lithium-excess metal oxides for rechargeable battery applications. See the Personal Account by N. Yabuuchi (DOI: 10.1002/tcr.201800089).
Inside Front Cover: Polyanionic Compounds for Potassium-Ion Batteries (Chem. Rec. 4/2019)
- Page: 688
- First Published: 05 April 2019

The cover picture shows a schematic illustration of a potassium-ion battery where K+ ions are reversibly extracted from the polyanionic compounds and intercalated into the graphite. See the Personal Account by T. Hosaka, T. Shimamura, K. Kubota, and S. Komaba (DOI: 10.1002/tcr.201800143).
Editorial
Special Issue: Next Generation Li and Na Rechargeable Batteries
- Page: 689
- First Published: 28 December 2018
Personal Accounts
Material Design Concept of Lithium-Excess Electrode Materials with Rocksalt-Related Structures for Rechargeable Non-Aqueous Batteries
- Pages: 690-707
- First Published: 12 October 2018
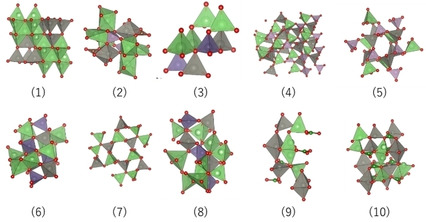
Material design strategies of lithium-excess high-capacity electrode materials with rocksalt-related structures are described. These oxides deliver large reversible capacities with cationic/anionic redox and percolative lithium migration in the oxide/oxyfluoride framework structures, and are possibly used for high-energy non-aqueous batteries.
Solvate Ionic Liquids for Li, Na, K, and Mg Batteries
- Pages: 708-722
- First Published: 09 October 2018
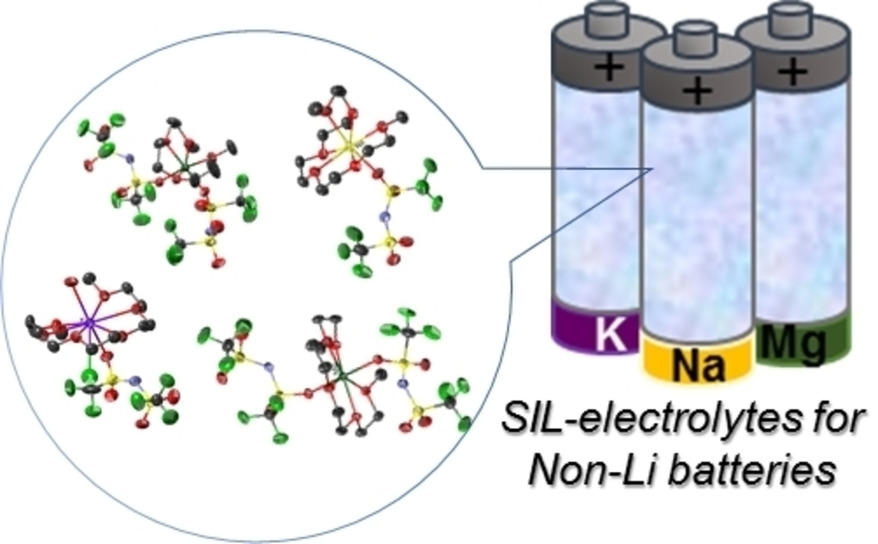
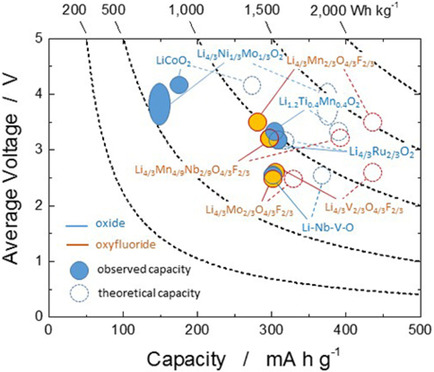
Solvate ionic liquids particularly those incorporating cost-effective earth-abundant non-Li metal ions such as Na+, K+, and Mg2+, are promising electrolytes to realize safe and highly efficient large-scale electrochemical energy storage systems. In this account, the fundamental aspects and characteristics for electrolyte applications of SILs consisting of glymes and non-Li salts are reported. The balance of competitive interactions of anions and ligands with metal ions was found to predominate the stability of the solvate cations. Suitable combinations of salts, ligands, and diluents resulted in electrolytes showing excellent stability and remarkable battery performance.
Spatial-Decomposition Analysis of Electrical Conductivity
- Pages: 723-734
- First Published: 30 October 2018
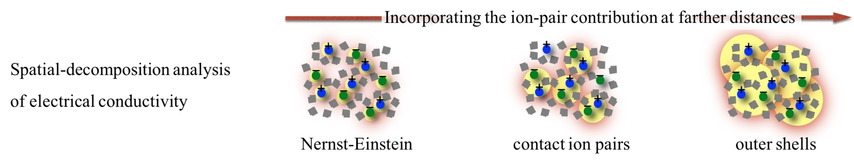
The electrical conductivity is spatially decomposed. It is expressed as an integral over the ion-pair distance by identifying the contribution of a pair at a certain distance. The spatial-decomposition formula is applied to NaCl aqueous solution and an ionic liquid, and the extent of spatial localization of the cross-correlation effect on the conductivity is analyzed by employing a cutoff in the integral expression and examining the convergence with respect to the variation in the cutoff.
Polyanionic Compounds for Potassium-Ion Batteries
- Pages: 735-745
- First Published: 30 October 2018
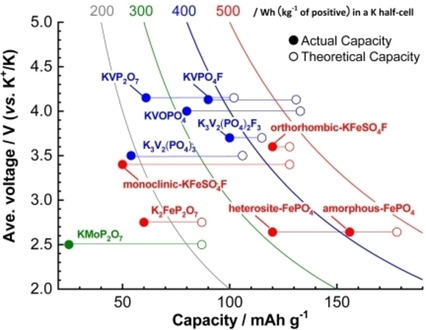
In recent years, the development of K-ion batteries based on abundant elements has attracted attention. This article offers a review of polyanionic compounds as cathode materials for K-ion batteries. Furthermore, we deliver our new results to partially compensate for lack of studies and provide a future perspective.
Development of Divide-and-Conquer Density-Functional Tight-Binding Method for Theoretical Research on Li-Ion Battery
- Pages: 746-757
- First Published: 21 November 2018
The diffusion constants of common electrolyte molecules and LiTFSA salt in solution have been estimated using the divide-and-conquer density-functional tight-binding molecular dynamics simulation with refined and newly created extension of the popular 3ob DFTB parameters. The resulting diffusion constants of the electrolyte molecules and lithium ions have good agreement to the experimental diffusion constants.
Sodium Ion Batteries using Ionic Liquids as Electrolytes
- Pages: 758-770
- First Published: 27 November 2018

The present review focuses on sodium ion batteries using binary systems of sodium and quaternary ammonium salts as electrolytes. A series of electrode materials were prepared, and examined to be combined with ionic liquid electrolytes. Sodium ion batteries using ionic liquids exhibited great performance and improved the safety of the batteries remarkably in a wide temperature range.
Data-Driven Materials Exploration for Li-Ion Conductive Ceramics by Exhaustive and Informatics-Aided Computations
- Pages: 771-778
- First Published: 30 November 2018
Theoretical Analysis of Materials, used in Energy Storage Applications: the Quest for Robust and Accurate Computational Methodologies
- Pages: 779-791
- First Published: 27 December 2018
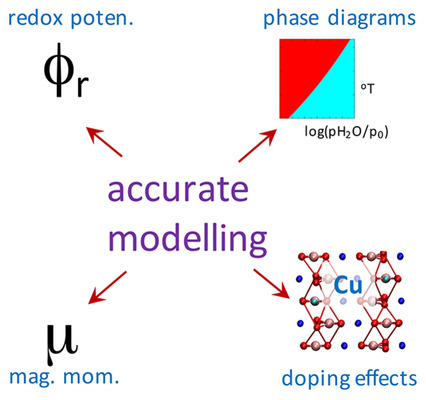
Computational accuracy is essential for reliable prediction of various properties of transition metal compounds, used as cathode materials in Li- and Na-ion batteries. In this account we discuss our efforts in formulating accurate and computationally robust methodologies, that can be used for this purpose. The examples of evaluation of redox potentials, construction of phase diagrams and description of the effects of dopants in good agreement with experiments are demonstrated.
Combined Theoretical and Experimental Studies of Sodium Battery Materials
- Pages: 792-798
- First Published: 29 January 2019
Owing to developments in theoretical chemistry and computer power, the combination of calculations and experiments is now standard practice in understanding and developing new materials for battery systems. Here, we briefly review our recent combined studies based on density functional theory and molecular dynamics calculations for electrode and electrolyte materials for sodium-ion batteries. These findings represent case studies of successful combinations of experimental and theoretical methods.
Microscopic Elucidation of Solid-Electrolyte Interphase (SEI) Film Formation via Atomistic Reaction Simulations: Importance of Functional Groups of Electrolyte and Intact Additive Molecules
- Pages: 799-810
- First Published: 21 March 2019
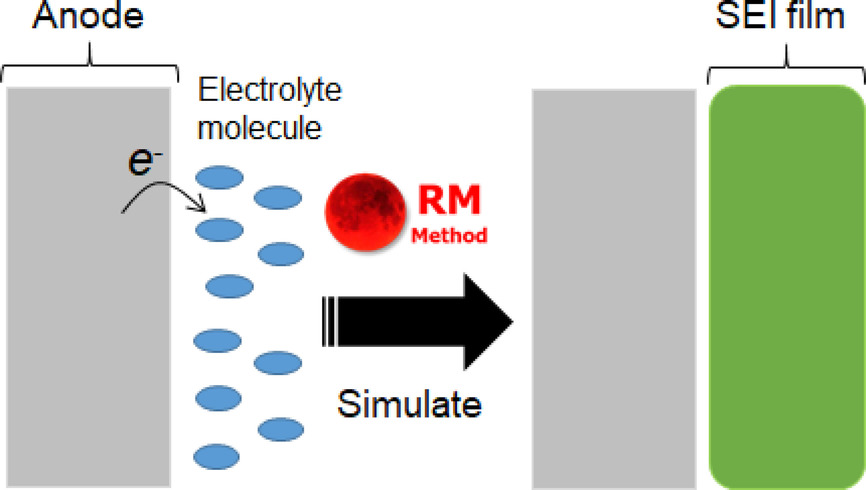
Solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) is a key factor to improve lifetime and safety of secondary batteries. Here, we review our recent theoretical studies which have analyzed the SEI film formation mechanism by using Red Moon method. The microscopic insights obtained must provide an important guiding principle to design the electrolytes for the high performance secondary batteries.
First-Principles Study of Na-Ion Battery Performance and Reaction Mechanism of Tin Sulfide as Negative Electrode
- Pages: 811-816
- First Published: 01 April 2019
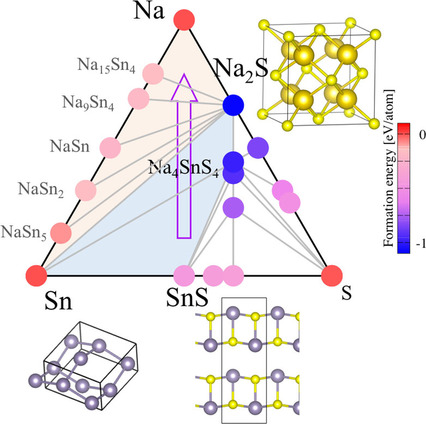
By using the first-principles calculations, we investigate discharge reaction mechanisms in a negative electrode of tin sulfide SnS for sodium-ion batteries. Possible reaction formulae in Na/SnS during the discharge processes are theoretically shown based on the ternary Na−Sn−S phase diagrams. Theoretical voltage-capacity curves and x-ray absorption spectra show reasonable agreements with experiments.