Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Bottom-up assembly of nano-carbon devices by dielectrophoresis (Phys. Status Solidi B 12/2013)
- First Published: 04 December 2013
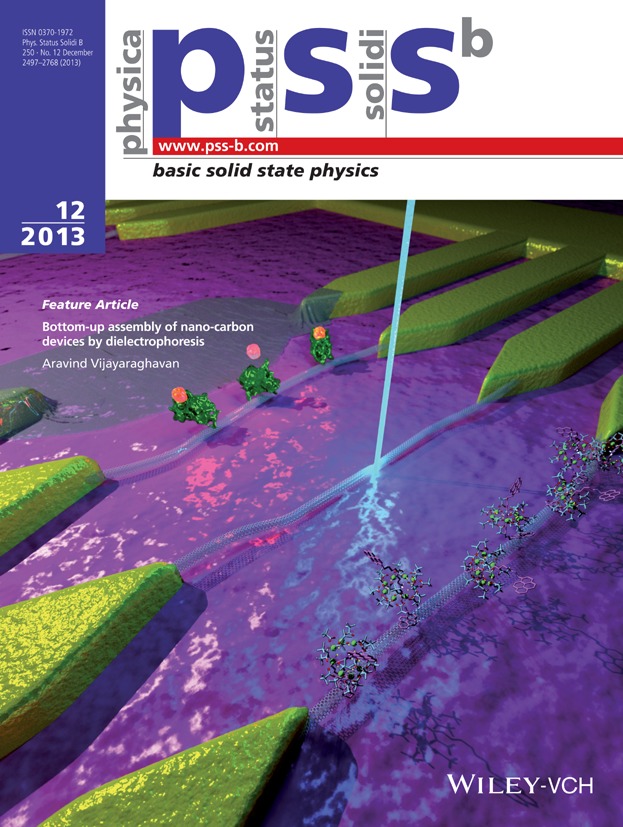
In the past decade, an unconventional approach to large-scale fabrication of carbon-nanotube and graphene devices has emerged, namely, dielectrophoretic (DEP) assembly. This technique has now been demonstrated in wafer-scale assembly of nano-carbon electronic devices, sensors, opto-electronic devices and even suspended structures. It has also served as an enabling tool for a number of experiments which might otherwise not be possible. A detailed review of developments in DEP assembly of nano-carbons is presented as a Feature Article by Aravind Vijayaraghavan (pp. 2505–2517). The cover image is an artist's concept of some typical carbon-nanotube and graphene devices assembled by DEP (image courtesy N. Clark).
Back Cover
Negative frequency tuning of a carbon nanotube nano-electromechanical resonator under tension (Phys. Status Solidi B 12/2013)
- First Published: 04 December 2013
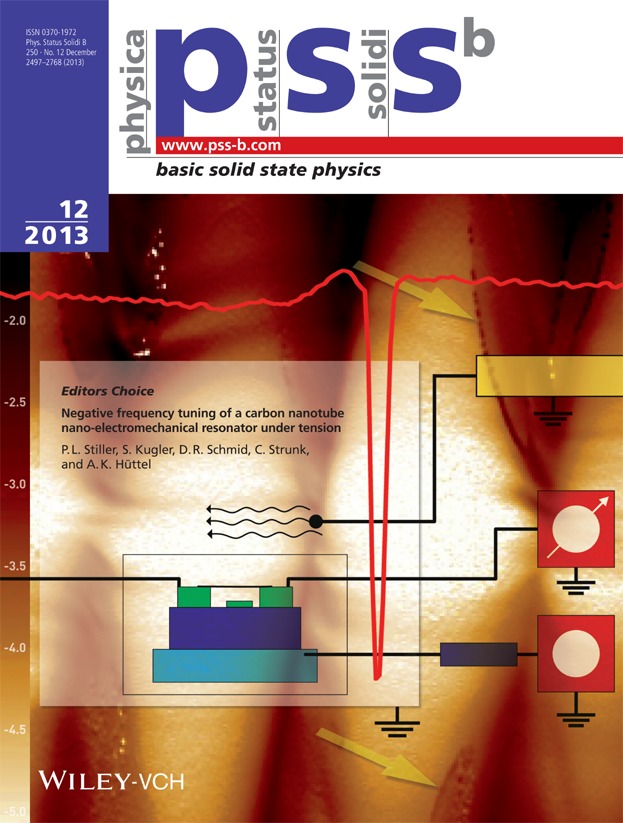
On the back cover, a single wall carbon nanotube is displayed (thin black line in the sketch) that is grown across a trench and contact electrodes (green), cooled to milli-Kelvin temperatures, and then characterized in electronic transport measurements. A quantum dot forms within the suspended segment at these temperatures. The typical Coulomb “diamond” pattern of differential conductance displays distinct signatures of electromechanical feedback and self-excitation (background measurement, yellow arrows). Using a radio-frequency cw source, driven mechanical resonances of the nanotube can be detected in dc transport - as exemplified by the red line, a measurement of time-averaged dc current as a function of the driving frequency. Stiller et al. (pp. 2518–2522) find higher harmonic resonances at integer multiples of the fundamental frequency, indicating that the nanotube is a string under tension. Applying a finite gate voltage to the highly doped chip substrate (light blue), the mechanical resonance strongly shifts to lower frequencies. This can be explained by electrostatic softening of the vibration mode.
Issue Information
Contents
Recent and forthcoming publications in pss
Recent and forthcoming publications in pss
- Page: 2504
- First Published: 04 December 2013
Feature Article
Bottom-up assembly of nano-carbon devices by dielectrophoresis
- Pages: 2505-2517
- First Published: 22 November 2013

This Feature Article reviews the development and applications of dielectrophoresis (DEP) towards carbon nanotube (CNT) and graphene devices. DEP was first used to separate metallic and semiconducting CNTs, but has since then emerged as a leading route to large-scale directed assembly of nano-carbons. In addition to field-effect transistors, DEP-assembled devices have been demonstrated for sensors, optoelectronics and resonators. DEP is a bottom-up assembly route, and could pose a challenge to conventional top-down fabrication for nano-carbon electronics.
Editor's Choice
Negative frequency tuning of a carbon nanotube nano-electromechanical resonator under tension
- Pages: 2518-2522
- First Published: 18 October 2013
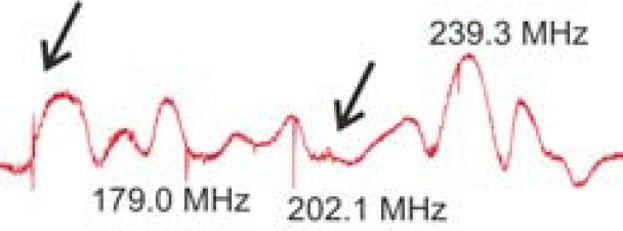
Stiller et al. measured the electronic and mechanical properties of a high-quality factor carbon nanotube vibrational resonator at cryogenic temperatures. Both quantum dot behavior and multiple driven mechanical resonances are observed. A sequence of higher harmonics occurs approximately at multiple integers of a base frequency, indicating that the nanotube resonator is under tension. The gate voltage dependence of the resonance frequency is successfully modelled by electrostatic softening.
First-principles study of H adsorption on graphene/SiC(0001)
- Pages: 2523-2528
- First Published: 20 October 2013
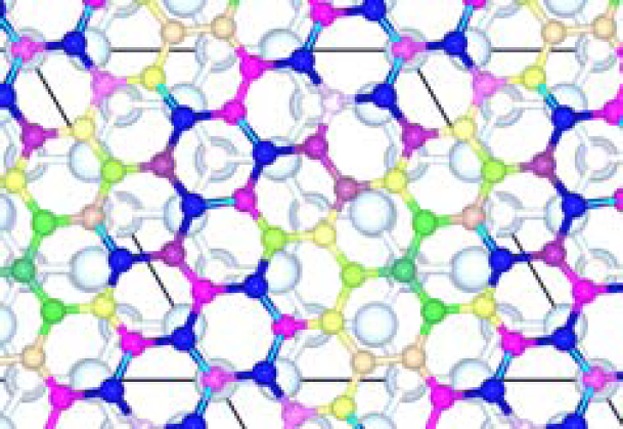
The interaction of atomic hydrogen at the graphene/SiC(0001) interface is addressed here using model interfaces characterized by negligible graphene strains and two different graphene/SiC rotation angles. The threefold coordinated C atoms in the buffer layer display an increased chemical reactivity compared to free-standing graphene, resulting in two--to-four times larger binding energies of hydrogen.
Preparation and characterization of expanded graphite polymer composite films for thermoelectric applications
- Pages: 2529-2534
- First Published: 12 November 2013

Piao et al. explored a more economical source of thermopower by investigating expanded graphite (ExG) composite thin films. They demonstrate that ExG can be sufficiently dispersed in polymer solution to form stable suspensions. Thin composite films were prepared by casting and drying the suspension. Electrically and thermally insulating polymers, PC and PVA, and an intrinsically conductive polymer PEDOT:PSS served as a matrix material in this study. The authors also demonstrate that the thermoelectric properties of ExG in polymers can be easily modified by chemical functionalization.
Original Papers
Carbon nanotubes
Anisotropy of thermal expansion of helically coiled carbon nanotubes
- Pages: 2535-2538
- First Published: 15 October 2013
Carbon nanotubes quench singlet oxygen generated by photosynthetic reaction centers
- Pages: 2539-2543
- First Published: 18 October 2013
Growth and characterization of bamboo-like carbon nanotubes synthesized on Fe–Co–Cu catalysts prepared by high-energy ball milling
- Pages: 2544-2548
- First Published: 14 November 2013
Preparation of SnO2–TiO2/MWCNT nanocomposite photocatalysts with different synthesis parameters
- Pages: 2549-2553
- First Published: 04 October 2013
Preparation and characterization of multiwalled carbon nanotube/WO3 composite materials
- Pages: 2554-2558
- First Published: 04 October 2013
Sensing hydrogen peroxide by carbon nanotube/horseradish peroxidase bio-nanocomposite
- Pages: 2559-2563
- First Published: 18 October 2013
Sorting of CVD-grown single-walled carbon nanotubes by means of gel column chromatography
- Pages: 2564-2568
- First Published: 15 November 2013
Synthesis and characterization of Pt/MWCNTs nanocomposites
- Pages: 2569-2574
- First Published: 12 November 2013
Inner tube growth properties and electronic structure of ferrocene-filled large diameter single-walled carbon nanotubes
- Pages: 2575-2580
- First Published: 15 November 2013
Chemisorbed nickel catalyst for the production of SWCNTs with a very narrow size distribution
- Pages: 2581-2585
- First Published: 27 November 2013
Supercapacitor performance of nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube arrays
- Pages: 2586-2591
- First Published: 12 November 2013
Tuning the adsorption of perylene-based surfactants on the surface of single-walled carbon nanotubes
- Pages: 2592-2598
- First Published: 15 November 2013
Environmental stability of ferrocene filled in purely metallic single-walled carbon nanotubes
- Pages: 2599-2604
- First Published: 13 November 2013
Evaluation of bimetallic catalysts for the growth of carbon nanotube forests
- Pages: 2605-2610
- First Published: 14 November 2013
Carbon nanotubes from enhanced direct injection pyrolytic synthesis as templates for long linear carbon chain formation
- Pages: 2611-2615
- First Published: 15 November 2013
Role of the pressure transmitting medium on the pressure effects in DWCNTs
- Pages: 2616-2621
- First Published: 20 October 2013
Effect of contact geometry on magnetoresistance in CoPd-contacted carbon nanotubes
- Pages: 2622-2626
- First Published: 07 October 2013
Structural model of semi-metallic carbon nanotubes
- Pages: 2627-2630
- First Published: 15 November 2013
Length scales in orientational order of vertically aligned single walled carbon nanotubes
- Pages: 2631-2634
- First Published: 13 November 2013
Environmental effects on the Raman spectra of single walled carbon nanotubes
- Pages: 2635-2638
- First Published: 18 October 2013
Raman spectra of metallic carbon nanotubes in solution and on substrates
- Pages: 2639-2642
- First Published: 25 November 2013
Invited Articles
Graphene
Application of graphene-based nanostructures in dye-sensitized solar cells
- Pages: 2643-2648
- First Published: 04 October 2013
Kavan et al. review recent advances in the application of graphene and related materials, viz. graphene nanoplatelets, functionalized graphene sheets, graphene oxide, and reduced graphene oxide as electrode building materials in dye sensitized solar cells. Graphene promises multifaceted use as prospective sensitizer, photoanode additive, current collector, and electrocatalyst for the redox-shuttle turnover. Of particular significance is the use of graphene as cathode catalyst in state-of-the-art cobalt-mediated solar cells, where it can successfully replace platinum.
Doping of bi-layer graphene by gradually polarizing a ferroelectric polymer
- Pages: 2649-2652
- First Published: 04 October 2013
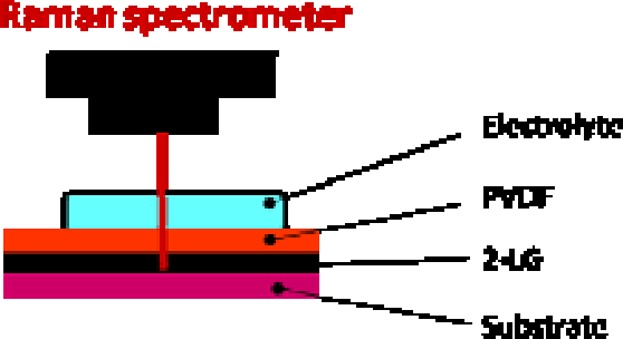
Previous reports on the electrochemical doping of graphene left many open questions; in particular how the electrolyte anions interact with graphene or whether the electrolyte ions penetrate into graphene layers during the doping. To answer these questions, Kalbac et al. probed the Raman spectra of two-layer graphene (2-LG). They studied the 2-LG both in its neutral and doped states, which were realized using the polarization of a ferroelectric polymer.
Original Papers
Graphene
Raman spectroscopy investigation of defect occurrence in graphene grown on copper single crystals
- Pages: 2653-2658
- First Published: 18 October 2013
Raman spectroscopy of strongly doped CVD-graphene
- Pages: 2659-2661
- First Published: 04 October 2013
In situ Raman spectroelectrochemistry of graphene oxide
- Pages: 2662-2667
- First Published: 14 November 2013
Polymer-assisted transfer printing of graphene composite films
- Pages: 2668-2671
- First Published: 18 November 2013
Ultrafast quantitative nanomechanical mapping of suspended graphene
- Pages: 2672-2677
- First Published: 25 November 2013
Probing built-in strain in freestanding graphene monolayers by Raman spectroscopy
- Pages: 2681-2686
- First Published: 15 November 2013
Raman bands of nano-graphene flakes on carbon nanotubes after oxidation
- Pages: 2687-2691
- First Published: 15 November 2013
Etched graphene single electron transistors on hexagonal boron nitride in high magnetic fields
- Pages: 2692-2696
- First Published: 14 November 2013
Influence of the layer number and stacking order on out-of-plane phonons in few-layer graphene
- Pages: 2697-2701
- First Published: 15 November 2013
Graphite, fullerenes, diamonds, silicon and other materials
Fast combustion synthesis and characterization of YAG:Ce3+ garnet nanopowders
- Pages: 2702-2708
- First Published: 04 October 2013
Predicting stabilities of endohedral metallofullerenes Yb@C84
- Pages: 2709-2712
- First Published: 02 December 2013
Toward green chemistry: A new approach to the synthesis of semiconducting SiC nanowires
- Pages: 2713-2716
- First Published: 27 November 2013
Tailoring morphologies of diamond thin films for neural stem cells culturing
- Pages: 2717-2722
- First Published: 14 November 2013
Perspectives of linear antenna microwave system for growth of various carbon nano-forms and its plasma study
- Pages: 2723-2726
- First Published: 12 November 2013
Low pressure chemical vapor deposition synthesis of hexagonal boron nitride on polycrystalline metal foils
- Pages: 2727-2731
- First Published: 04 October 2013
Geometry of nanostructures and eigenvectors of matrices
- Pages: 2732-2736
- First Published: 13 November 2013
Structural properties of mirrored carbon spirals as revealed by scanning electron microscopy and micro-Raman spectroscopy
- Pages: 2737-2740
- First Published: 13 November 2013
H-terminated diamond as optically transparent impedance sensor for real-time monitoring of cell growth
- Pages: 2741-2746
- First Published: 22 November 2013
Functional composition and super-capacitor properties of graphite oxide reduced with hot sulfuric acid
- Pages: 2747-2752
- First Published: 14 November 2013
Enhanced spontaneous nucleation of diamond nuclei in hot and cold microwave plasma systems
- Pages: 2753-2758
- First Published: 14 November 2013
Photoluminescence of CdS nanoparticles grown on carbon nanotubes covered by a dielectric polymer layer
- Pages: 2759-2764
- First Published: 14 November 2013







