Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Macromol. Chem. Phys. 15/2013
- Page: 1653
- First Published: 02 August 2013

Front Cover: 2D ordered trees-like self-assemblies with sizes of over 500 μm and branch widths of 3 to 5 μm are obtained by surface self-assembly of an amido-ended hydrophilic hyperbranched polyester/copper complex, showing intriguing crystal and fractal behaviors. The selfassembly mechanism is explained by diffusion-limited aggregation (DLA) theory. Further details can be found in the article by J. Li, D. Zhang,* S. Li, Z. Xu, S. Chen,* T. Li, J. Zhang, S. Chen, A. Zhang on page 1724.
Masthead
Contents
Talents & Trends
Self-Assembly of Globular-Protein-Containing Block Copolymers
- Pages: 1659-1668
- First Published: 25 July 2013
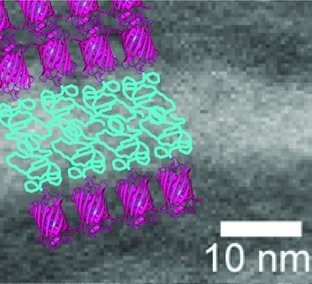
The direct self-assembly of globular-protein-containing block copolymers provides an attractive method for the fabrication of biofunctional nanostructures; a variety of different solid state and block copolymer gel nanostructures may be formed. The thermodynamics and processing of these systems are heavily influenced by the folded, biofunctional structure of the protein.
Full Papers
Photopolymerizable Monomer Miniemulsions: Why Does Droplet Size Matter?
- Pages: 1669-1676
- First Published: 23 July 2013
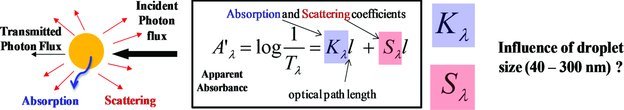
A rational approach to relate the optical properties of monomer miniemulsions with their photopolymerizability is performed. Our starting point is to prepare a series of acrylate miniemulsions ranging from 40 to 300 nm in average diameter. Three independent spectrophotometric studies using an integration sphere are then conducted in dilute conditions that enable the evolution of the scattering and absorption coefficients with droplet size to be determined.
Facile Synthesis of Amphiphilic Heterografted Copolymers with Crystalline and Amorphous Side Chains
- Pages: 1677-1687
- First Published: 23 July 2013
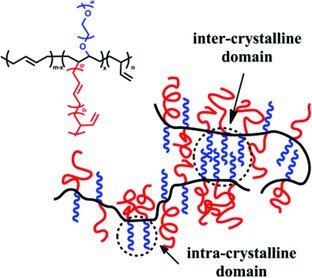
A novel type of prototype polymer with heterografts is designed and synthesized using a facile grafting strategy. This heterografted copolymer with crystalline and amorphous chains exhibits multiple crystallization temperatures due to the different PEO domains. Due to its hydrophilic PEO chains and the lyophobic PB chains, the copolymer possesses amphiphilic nature.
Polymerization Mechanism of MMA in the Presence of 1,1-Diphenylethylene
- Pages: 1688-1698
- First Published: 04 July 2013
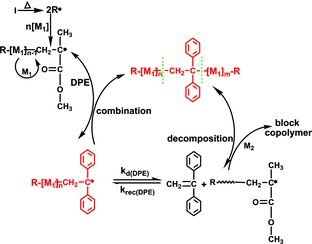
A suitable controlled mechanism based on the reversible reaction between active propagation radicals with 1,1-diphenylethylene (DPE) and with DPE-ended radicals is proposed in this research; the accurate structure of the PMMA precursor is identified by electrospray-ionization quadrupolar time-of-flight mass spectrometry (ESI-Q-TOF-MS). The block copolymers can be prepared by simply heating the obtained PMMA precursor in the presence of a second monomer.
Fluorene/Carbazole Alternating Copolymers Tethered with Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxanes: Synthesis, Characterization, and Electroluminescent Properties
- Pages: 1710-1723
- First Published: 05 July 2013
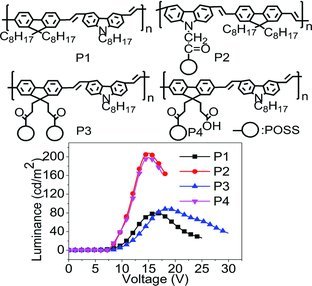
Four novel fluorene/carbazole alternating copolymers that possess similar polymerization degrees and good thermal stability are synthesized. The morphologies of the copolymers and the effects of POSS on their photophysical and electroluminescent properties are investigated. The results indicate that controlling the content and the linked position of POSS have an important influence on constructing outstanding electroluminescent materials.
2D Self-Assembly of an Amido-Ended Hydrophilic Hyperbranched Polyester by Copper Ion Induction
- Pages: 1724-1733
- First Published: 05 July 2013

2D ordered tree-like self-assemblies with sizes of over 500 μm and branch widths of about 3–5 μm are obtained by surface self-assembly of an amido-ended hydrophilic hyperbranched polyester/copper complex, showing intriguing crystal and fractal behaviors. The self-assembly process and mechanism are explained by the synergistic action of cupric ion coordination induction, hydrogen bonds, and diffusion-limited aggregation (DLA) of micelles.
Investigation of the Physical Properties of Poly(ortho- and para-trifluoromethoxy styrenes)
- Pages: 1734-1737
- First Published: 03 July 2013
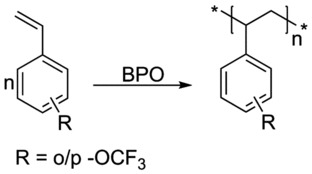
The synthesis and free-radical polymerization of ortho- and para-trifluoromethoxystyrenes is reported. The glass-transition temperature (Tg) values of the polymers are rather lower than that of polystyrene. Compared with poly(2-trifluoromethylstyrene), the Tg of ortho-trifluoromethoxy-substituted styrene polymer is lower. This unexpected result inspires the investigation of the physical properties of the ortho- and para-trifluoromethoxy-substituted styrene polymers.
Kinetics of Dithiobenzoate-Mediated Methyl Methacrylate Polymerization
- Pages: 1738-1748
- First Published: 11 July 2013
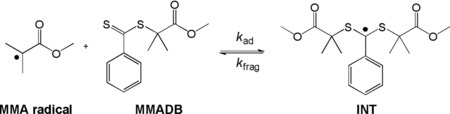
RAFT equilibrium constants (Keq = kad/kfrag) for MMA polymerization mediated by methyl methacryl dithiobenzoate (MMADB) and for the associated monomer-free model system are measured via electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. Low Keq, due to slow kad and fast kfrag, as well as “missing step” reactions of cross-termination products with radicals are responsible for rate retardation being absent in dithiobenzoate-mediated MMA polymerization.
Keggin-Type Polyoxometalate ([PMo12O40]3−) in Radical Initiating Systems: Application to Radical and Cationic Photopolymerization Reactions
- Pages: 1749-1755
- First Published: 11 July 2013
![Keggin-Type Polyoxometalate ([PMo12O40]3−) in Radical Initiating Systems: Application to Radical and Cationic Photopolymerization Reactions](/cms/asset/e928aae6-513d-428f-8eda-be509bd28445/mcontent.jpg)
Phosphomolybdic acid in combination with silane, iodonium salt, or germane can be used to generate silyl, phenyl, or germyl radicals as well as silylium cations under light irradiation. The generated radicals and cations can initiate the radical photopolymerization of acrylates and the cationic photopolymerization of epoxides, respectively.
Counter-Anion Effect on the Properties of Anion-Conducting Polymer Electrolyte Membranes Prepared by Radiation-Induced Graft Polymerization
- Pages: 1756-1762
- First Published: 08 July 2013
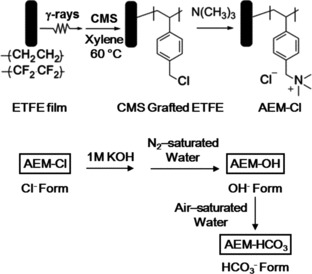
Graft-type anion-conducting polymer electrolyte membranes are prepared to evaluate the counter-anion effects on fuel cell properties. The hydroxide form shows conductivity and water uptake four and two times higher than the chloride and bicarbonate forms. The hydroxide form is thermally and chemically less stable, resulting in the tendency to absorb water and to convert to the bicarbonate form.