Facile Synthesis of Amphiphilic Heterografted Copolymers with Crystalline and Amorphous Side Chains
Qing Gao
State Key Laboratory of Fine Chemicals, Department of Polymer Science and Engineering, School of Chemical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, Liaoning, China
Search for more papers by this authorYanshai Wang
State Key Laboratory of Fine Chemicals, Department of Polymer Science and Engineering, School of Chemical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, Liaoning, China
Search for more papers by this authorYingying Ren
State Key Laboratory of Fine Chemicals, Department of Polymer Science and Engineering, School of Chemical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, Liaoning, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yang Li
State Key Laboratory of Fine Chemicals, Department of Polymer Science and Engineering, School of Chemical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, Liaoning, China
State Key Laboratory of Fine Chemicals, Department of Polymer Science and Engineering, School of Chemical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, Liaoning, China.Search for more papers by this authorQing Gao
State Key Laboratory of Fine Chemicals, Department of Polymer Science and Engineering, School of Chemical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, Liaoning, China
Search for more papers by this authorYanshai Wang
State Key Laboratory of Fine Chemicals, Department of Polymer Science and Engineering, School of Chemical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, Liaoning, China
Search for more papers by this authorYingying Ren
State Key Laboratory of Fine Chemicals, Department of Polymer Science and Engineering, School of Chemical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, Liaoning, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yang Li
State Key Laboratory of Fine Chemicals, Department of Polymer Science and Engineering, School of Chemical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, Liaoning, China
State Key Laboratory of Fine Chemicals, Department of Polymer Science and Engineering, School of Chemical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, Liaoning, China.Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
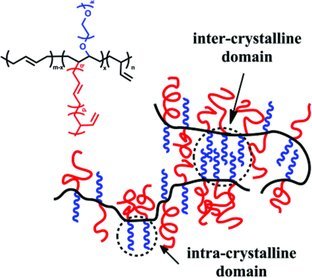
An amphiphilic polymer brush with PB and PEO side chains is prepared by combined “grafting-onto” and “grafting-from”. The linear and star-shaped heterografted copolymer synthesized is of controlled molecular weight and has a narrow molecular weight distribution (Mw/Mn < 1.2). A DSC study of this heterografted copolymer containing crystalline and amorphous chains shows that it displays “fractionated crystallization” behavior. The study on isothermal crystallization kinetics of the copolymer is carried out in isothermal step crystallization (ISC) experiments, in which two crystallization exothermic peaks at low temperatures are observed. The critical micelle concentration (cmc) of the amphiphilic brush polymer in an aqueous solution is determined by a fluorescence technique. The results show that this amphiphilic brush forms aggregates in the system.
References
- 1 D. Zehm, A. Laschewsky, M. Gradzielski, S. Prevost, H. Liang, J. P. Rabe, R. Schweins, J. Gummel, Langmuir 2010, 26, 3145.
- 2 C. Cheng, E. Khoshdel, K. L. Wooley, Macromolecules 2007, 40, 2289.
- 3 Y. Chen, Macromolecules 2012, 45, 2619.
- 4 J. Z. Du, L. Y. Tang, W. J. Song, Y. Shi, J. Wang, Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 2169.
- 5 K. Huang, J. Rzayev, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6880.
- 6 Z. Cheng, X. Zhu, G. D. Fu, E. T. Kang, K. G. Neoh, Macromolecules 2005, 38, 7187.
- 7 D. Lanson, M. Schappacher, R. Borsali, A. Deffieux, Macromolecules 2007, 40, 9503.
- 8 Q. Fu, C. Liu, W. Lin, J. Huang, J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem. 2008, 46, 6770.
- 9 Y. Y. Yuan, Q. Du, Y. C. Wang, J. Wang, Macromolecules 2010, 43, 1739.
- 10 H. Zhu, G. Deng, Y. Chen, Polymer 2008, 49, 405.
- 11 P. Xu, H. Tang, S. Li, J. Ren, E. V. Kirk, W. J. Murdoch, M. Radosz, Y. Shen, Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 1736.
- 12 Y. Zhang, X. Li, G. Deng, Y. Chen, Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2006, 207, 1394.
- 13 D. Wu, Y. Yang, X. Cheng, L. Liu, J. Tian, H. Zhao, Macromolecules 2006, 39, 7513.
- 14 J. Wu, C. Gao, Macromolecules 2010, 43, 7139.
- 15 A. Z. Samuel, S. Ramakrishnan, Macromolecules 2012, 45, 2348.
- 16 K. Ishizu, H. Yamada, Macromolecules 2007, 40, 3056.
- 17 S. S. Sheiko, B. S. Sumerlin, K. Matyjaszewski, Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 759.
- 18 G. Cheng, A. Böker, M. Zhang, G. Krausch, A. H. E. Müller, Macromolecules 2001, 34, 6883.
- 19 M. Zhang, T. Breiner, H. Mori, A. H. E. Müller, Polymer 2003, 44, 1449.
- 20 T. Stephan, S. Muth, M. Schmidt, Macromolecules 2002, 35, 9857.
- 21 M. D. Mihaylova, V. P. Krestev, M. N. Kresteva, A. Amzil, I. V. Berlinova, Eur. Polym. J. 2001, 37, 233.
- 22 P. C. Ashman, C. Booth, Polymer 1972, 13, 459.
- 23 D. R. Beech, C. Booth, D.V. Dodgson, R. R. Sharpe, J. R. S. Waring, Polymer 1972, 13, 73.
- 24 A. J. Muller, V. Balsamo, M. L. Arnal, Adv. Polym. Sci. 2005, 190, 1.
- 25 M. Raimo, Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 597.
- 26 F. Candau, F. Afchar-Taromi, P. Rempp, Polymer 1977, 18, 1253.
- 27 M. D. Shalati, C. G. Overberger, J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem. 1983, 21, 3425.
- 28
H. Q. Xie,
J. Liu,
H. Li,
J. Macromol. Sci., Pure Appl. Chem.
1990,
27,
725.
10.1080/10601329008544802 Google Scholar
- 29 F. Bonaccorsi, A. Lezzi, A. Prevedello, L. Lanzini, A. Roggero, Polym. Int. 1993, 30, 93.
- 30 L. Zhang, H. Zeng, Q. Liu, J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 17554.
- 31 J. R. M. Giles, F. M. Gray, J. R. MacCallum, C. A. Vincent, Polymer 1987, 28, 1977.
- 32 H. Decher, R. Stadler, Polym. Int. 1995, 38, 219.
- 33 F. Shao, X. F. Ni, Z. Q. Shen, Chin. Chem. Lett. 2012, 23, 347.
- 34 J. Rieger, P. Dubois, R. Jérôme, C. Jérôme, Langmuir 2006, 22, 7471.
- 35 H. Q. Xie, M. H. Cui, J. S. Guo, Eur. Polym. J. 1997, 33, 1537.
- 36 H. Q. Xie, Y. Liu, Eur. Polym. J. 1991, 27, 1339.
- 37 D. Hourdet, F. L'Alloret, A. Durand, F. Lafuma, R. Audebert, J.-P. Cotton, Macromolecules 1998, 31, 5323.
- 38 J. Hao, G. Yuan, W. He, H. Cheng, C. C. Han, C. Wu, Macromolecules 2010, 43, 2002.
- 39 C. Liu, K. Zhao, J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 763.
- 40 C. Batis, G. Karanikolopoulos, M. Pitsikalis, N. Hadjichristidis, Macromolecules 2003, 36, 9763.
- 41 W. A. Kuhlman, E. A. Olivetti, L. G. Griffith, A. M. Mayes, Macromolecules 2006, 39, 5122.
- 42 H. Chen, J. Li, Y. Ding, G. Zhang, Q. Zhang, C. Wu, Macromolecules 2005, 38, 4403.
- 43 J. Zhao, H. Schlaad, Macromolecules 2011, 44, 5861.
- 44 F. Hua, E. Ruckenstein, Langmuir 2004, 20, 3954.
- 45 D. Neugebauer, Polymer 2007, 48, 4966.
- 46 M. Xie, J. Dang, H. Han, W. Wang, J. Liu, X. He, Y. Zhang, Macromolecules 2008, 41, 9004.
- 47 L. Gu, Z. Shen, C. Feng, Y. Li, G. Lu, X. Huang, J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem. 2008, 46, 4056.
- 48 R. Venkatesh, L. Yajjou, C. E. Koning, B. Klumperman, Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2004, 205, 2161.
- 49 Y. Li, E. Themistou, J. Zou, B. P. Das, M. Tsianou, C. Cheng, ACS Macro Lett. 2012, 1, 52.
- 50
R. G. Jones,
J. Kahovec,
R. Stepto,
E. S. Wilks,
M. Hess,
T. Kitayama,
W. V. Metanomski, in
Compendium of Polymer Terminology and Nomenclature, IUPAC Recommendations 2008, (Eds:
R. G. Jones,
J. Kahovec,
R. Stepto,
E. S. Wilks,
M. Hess,
T. Kitayama,
W. V. Metanomski), Royal Society of Chemistry,
UK
2009, p.
377.
10.1039/9781847559425 Google Scholar
- 51 H. L. Hsieh, R. P. Quirk, Anionic Polymerization Principles and Practical Applications, Marcel Dekker, New York 1996, p. 371.
- 52 H. Gilman, A. H. Haubein, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1944, 66, 1515.
- 53 M. Gauthier, M. Moeller, Macromolecules 1991, 24, 4548.
- 54 R. V. Castillo, M. L. Arnal, A. J. Muller, I. W. Hamley, V. Castelletto, H. Schmalz, V. Abetz, Macromolecules 2008, 41, 879.
- 55 H. Zhang, Y. Li, C. Zhang, Z. Li, X. Li, Y. Wang, Macromolecules 2009, 42, 5073.
- 56 J. Zhao, G. Mountrichas, G. Zhang, S. Pispas, Macromolecules 2009, 42, 8661.
- 57 D. R. Burfield, K. L. Lim, K. S. Law, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1984, 29, 1661.
- 58 M. Szwarc, Adv. Polym. Sci. 1983, 49, 1.
- 59 D. Attwood, C. Booth, in Colloids and Interface Science Series, (Ed: T. F. Tadros), Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, Germany 2010, p. 61
- 60 I. W. Hamley, Adv. Polym. Sci. 1999, 148, 114.
- 61
Y. L. Loo,
R. A. Register, in
Developments in Block Copolymer Science and Technology, (Ed:
I. W. Hamley), John Wiley & Sons,
New York
2004, p.
213.
10.1002/0470093943.ch6 Google Scholar
- 62
M. L. Arnal,
A. J. Müller,
Macromol. Chem. Phys.
1999,
200,
2559.
10.1002/(SICI)1521-3935(19991101)200:11<2559::AID-MACP2559>3.0.CO;2-O CAS Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 63 A. Manaure, A. J. Müller, Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2000, 201, 958.
- 64 U. W. Gedde, Polymer Physics, Chapman and Hall, London 1995, p. 176.