Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Global analysis of urinary extracellular vesicle small RNAs in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
- First Published: 25 February 2024
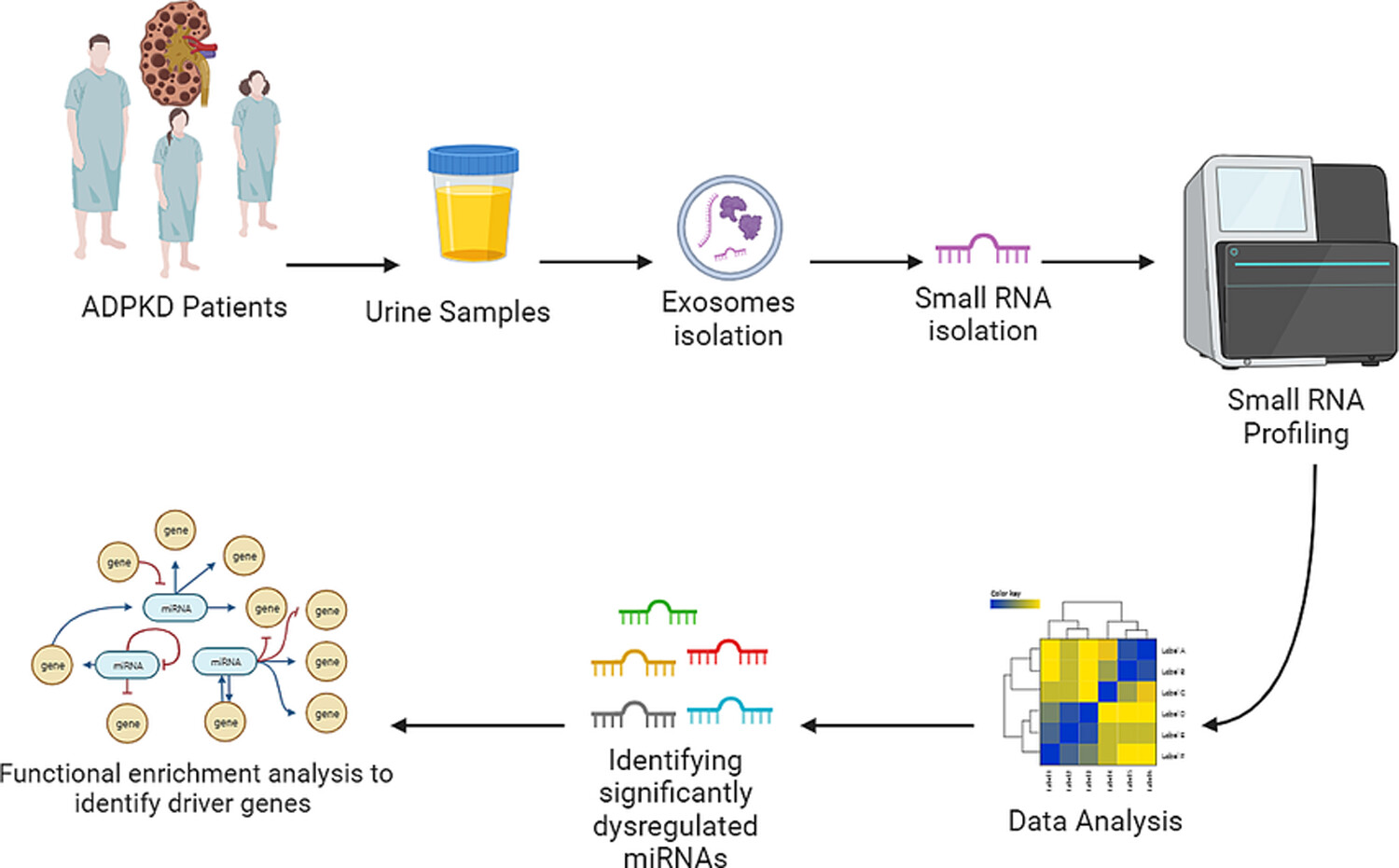
Urine samples were collected from autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) patients and urinary extracellular vesicles were purified. Then, small RNA fraction was sequenced, and data were analyzed and compared to healthy controls. Significantly dysregulated miRNAs were identified, and functional enrichment analysis was performed to identify driver's genes and affected biological pathways. Our findings contribute to the understanding of ADPKD pathogenesis and to the identification of novel biomarkers and potential drug targets aimed at slowing disease progression in ADPKD.
Development of a novel prognostic signature based on single-cell combined bulk RNA analysis in breast cancer
- First Published: 25 February 2024
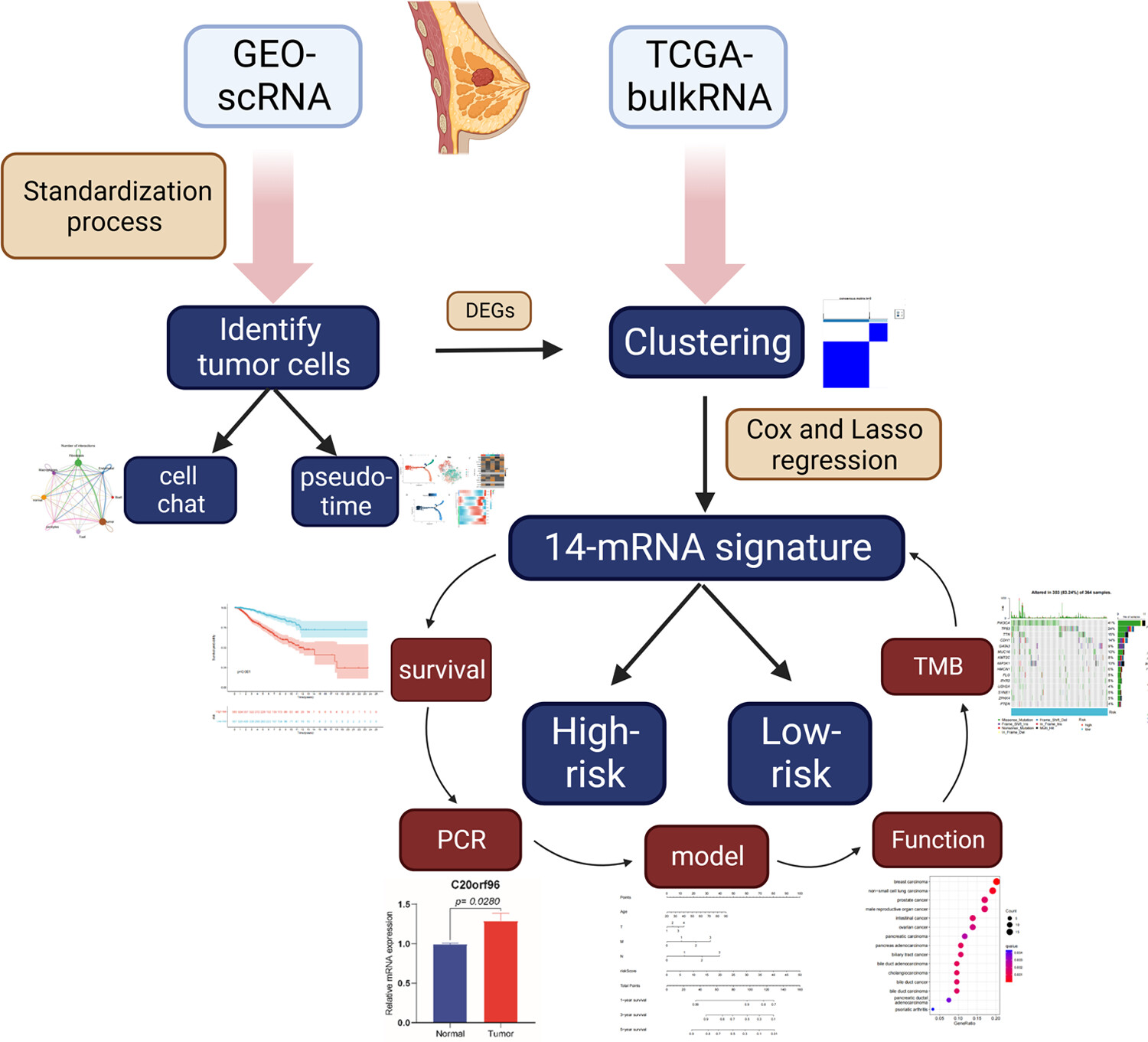
Our study indicated that the 14-gene-related prognostic signature gene could serve as a novel biomarker for predicting breast cancer patients’ prognosis. We found that immunotherapy might play a vital role in therapeutic schedule based on the level and difference of immune-related cells and pathways in different risk groups.
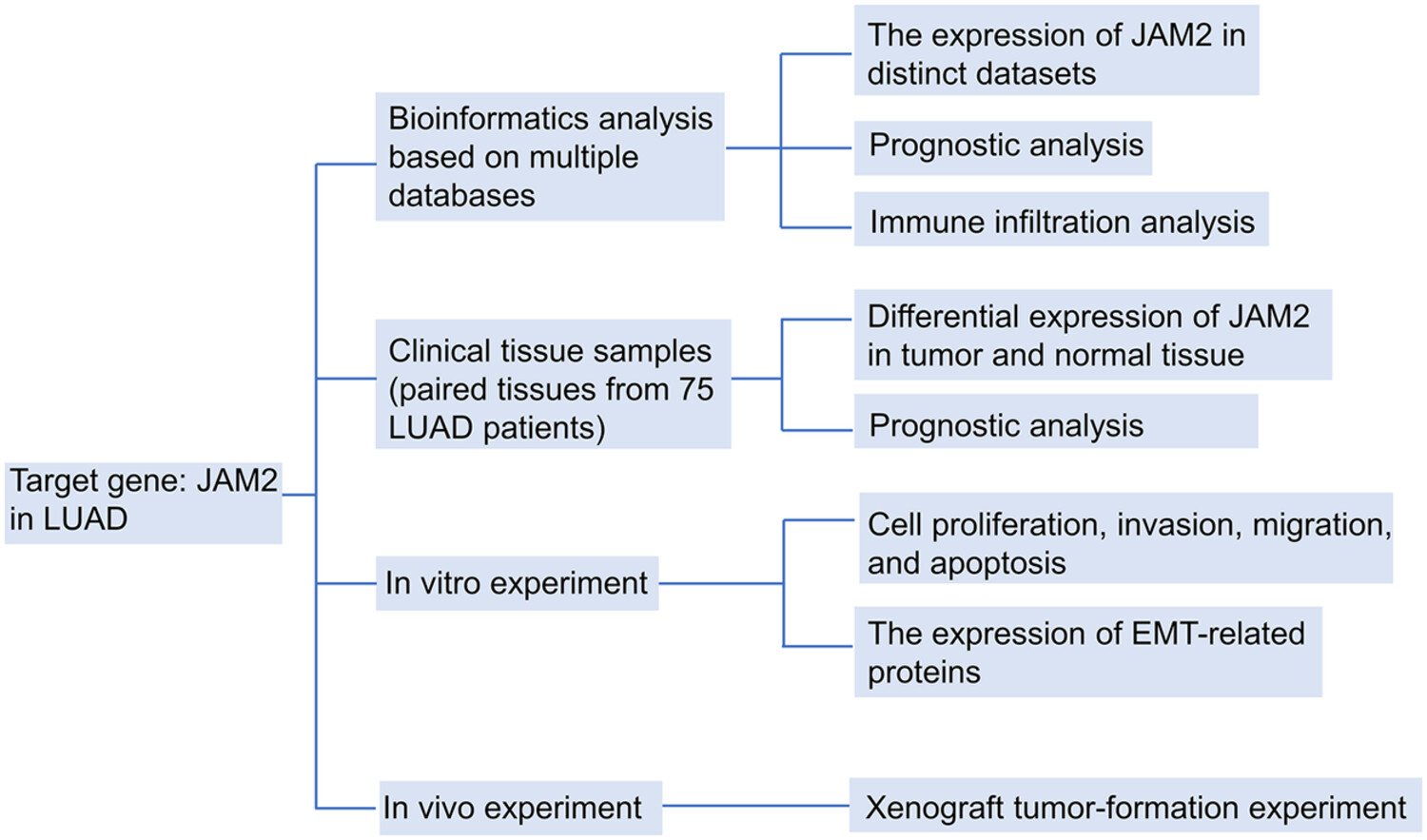
JAM2 is a prognostic biomarker and inhibits proliferation, metastasis and epithelial–mesenchymal transition in lung adenocarcinoma
- First Published: 25 February 2024
Circulating microvesicles miR139-3p from bronchopulmonary dysplasia aggravates pulmonary vascular simplification by targeting 4E binding protein 1
- First Published: 22 February 2024
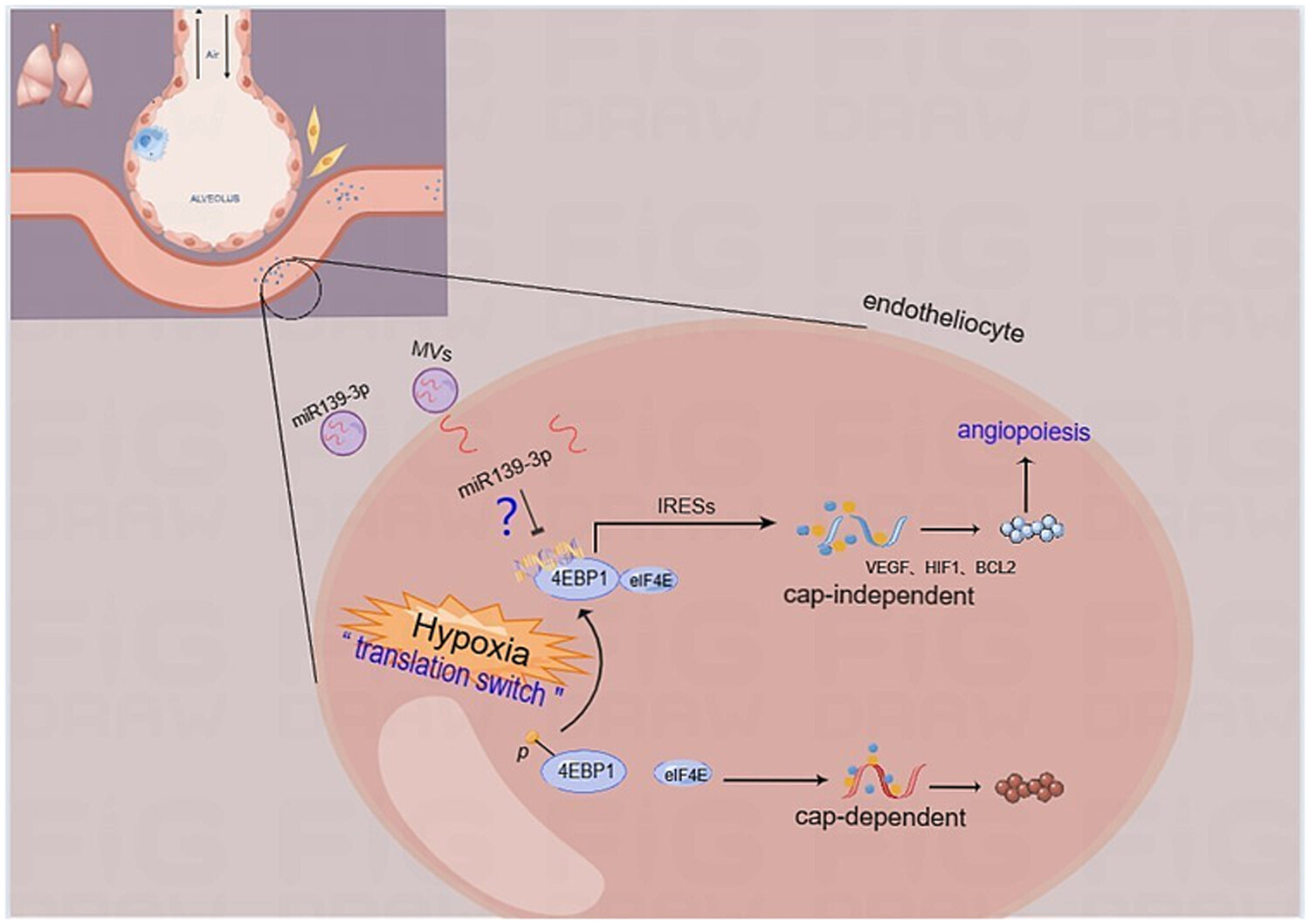
Microvesicles (MVs) derived from bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) show a negative lung simplification role through complex gene networks, and miR139-3p, miR6125 and miR193b-3p are significantly enriched in MVs. Among them, miR139-3p may be the most critical molecule in MVs affecting lung simplification. These findings may facilitate the identification of the role of MVs in the pathological of BPD and the treatment of BPD based on MVs’ strategies.
Natural killer cell-based signature: Prognostic analysis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- First Published: 21 February 2024
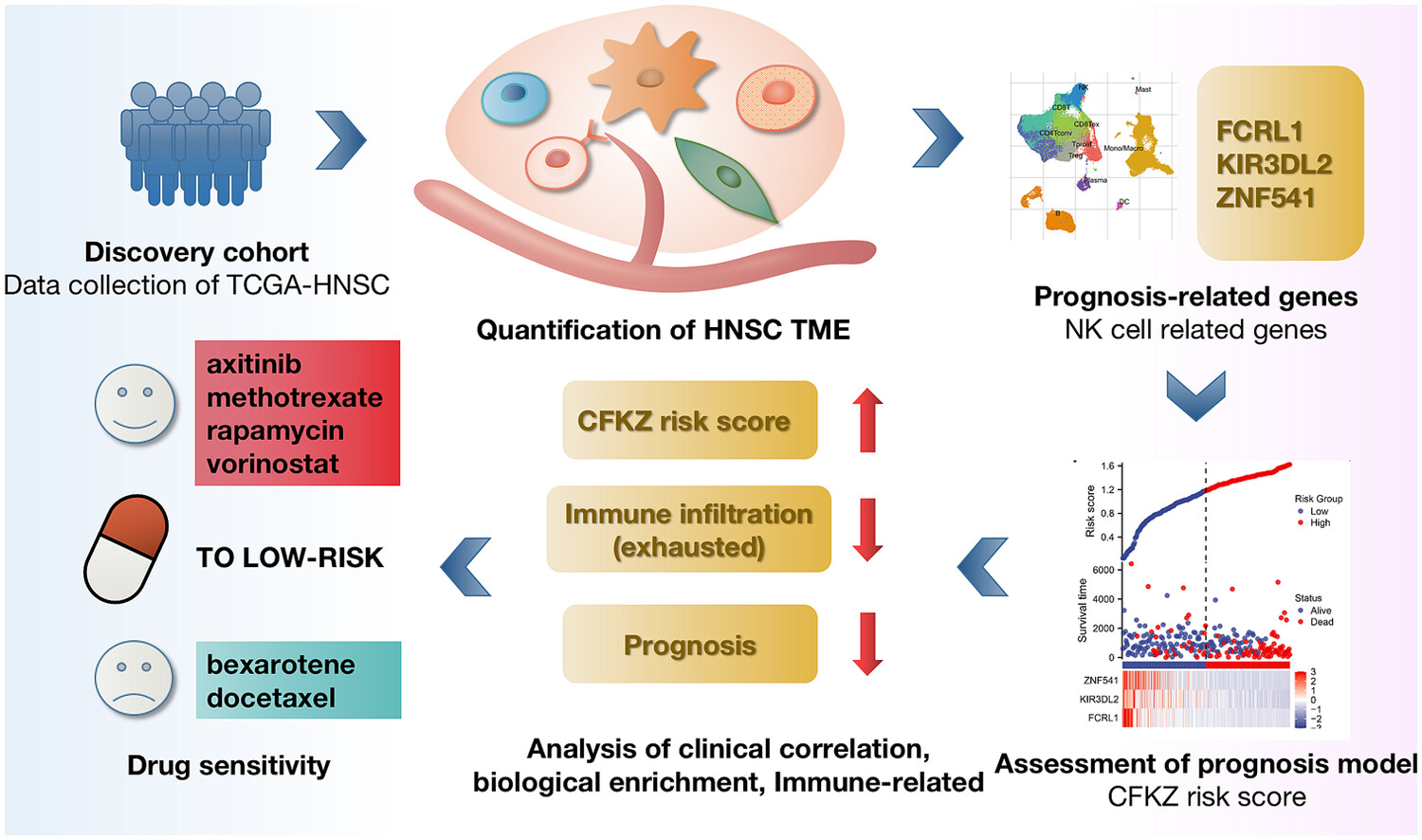
Integrated scRNA-sequencing and bulk RNA-sequencing analysis reveals a natural killer (NK) cell-based gene signature (CFKZ score) as a potential prognostic biomarker and predictor of chemotherapy response in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. This study highlights the significance of NK cells and offers insights for personalized treatment strategies in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSC).
A Treg-related riskscore model may improve the prognosis evaluation of colorectal cancer
- First Published: 11 February 2024
This study investigates a gene signature related to regulatory T cells (Tregs) and evaluates its prognostic value in colorectal cancer (CRC). Using data from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database, 7 key Treg-related genes were identified to construct the riskscore model. This model proved effective in evaluating patient survival and was corroborated by an external dataset. The model, reflecting riskscore and clinical factors, may facilitate the prognosis evaluation, guide precise treatment, and potentially improve the clinical outcomes of CRC patients.
Interaction of BANCR in the relationship between Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and papillary thyroid carcinoma expression patterns and possible molecular mechanisms
- First Published: 11 February 2024
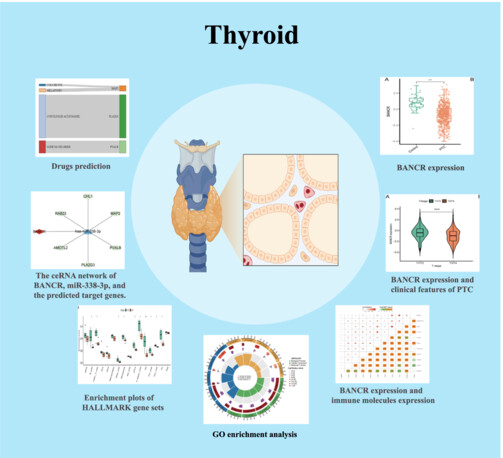
This study explored the role of BRAF-activated non-coding RNA (BANCR) in Hashimoto's thyroiditis (HT) and papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC). Results showed BANCR is downregulated in PTC but slightly upregulated in HT. In PTC with HT, BANCR levels further decreased. The study suggests BANCR's oncogenic role in PTC, affecting cancer pathways, and its potential as a therapeutic target. However, no significant link was found between BANCR expression and lymph node metastasis in PTC. These findings provide insights into HT and PTC's molecular mechanisms and new diagnostic and therapeutic opportunities.
Characterization of the m6A/m1A/m5C/m7G-related regulators on the prognosis and immune microenvironment of glioma by integrated analysis of scRNA-seq and bulk RNA-seq data
- First Published: 06 February 2024
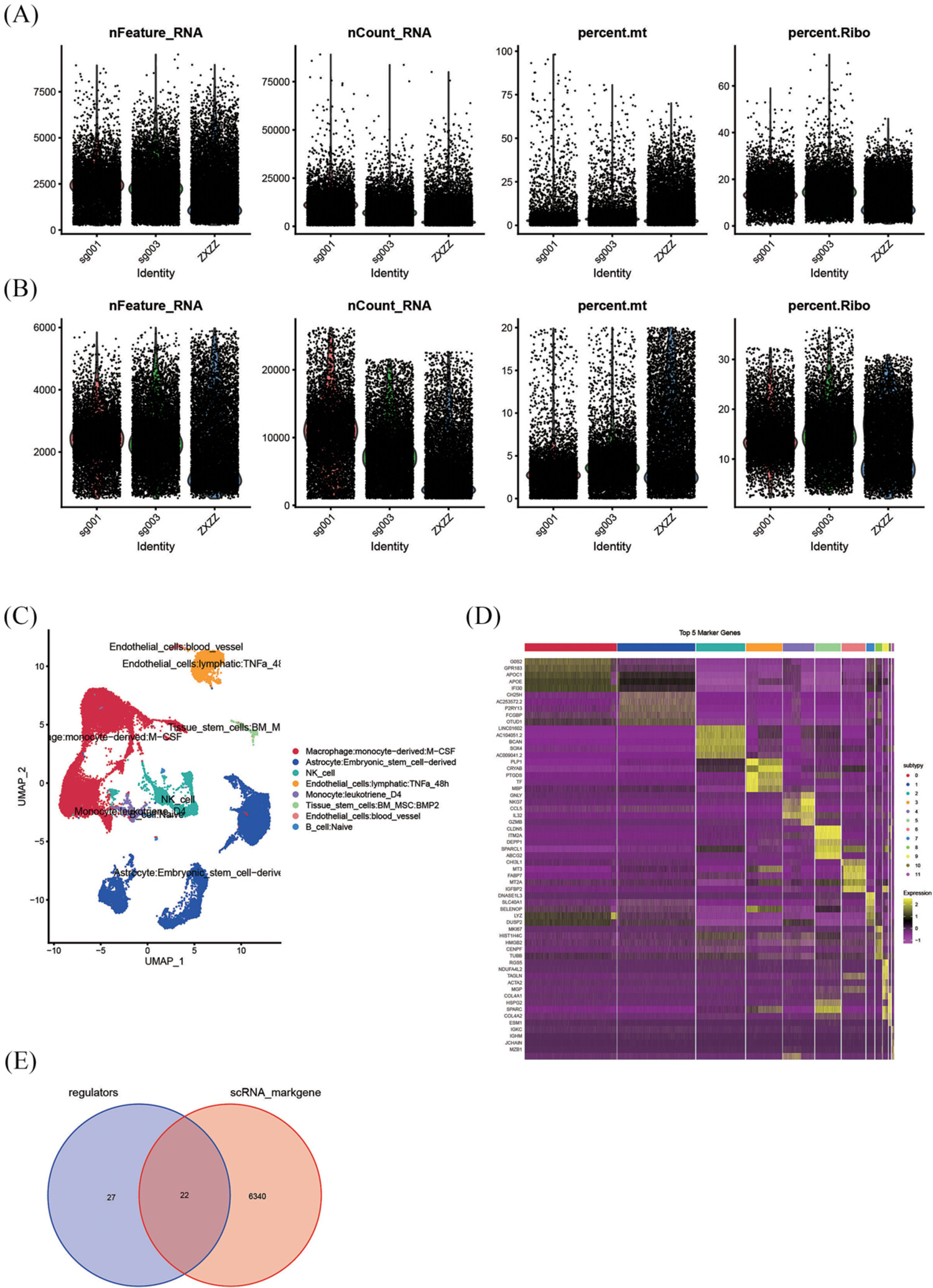
This study developed an m6A/m1A/m5C/m7G-related risk model by integrating scRNA-seq and bulk mRNA sequencing data, contributed to further understand role of m6A/m1A/m5C/m7G-related regulators in the intratumoral heterogeneity of gliomas, and provided novel and reliable prognostic markers for gliomas.
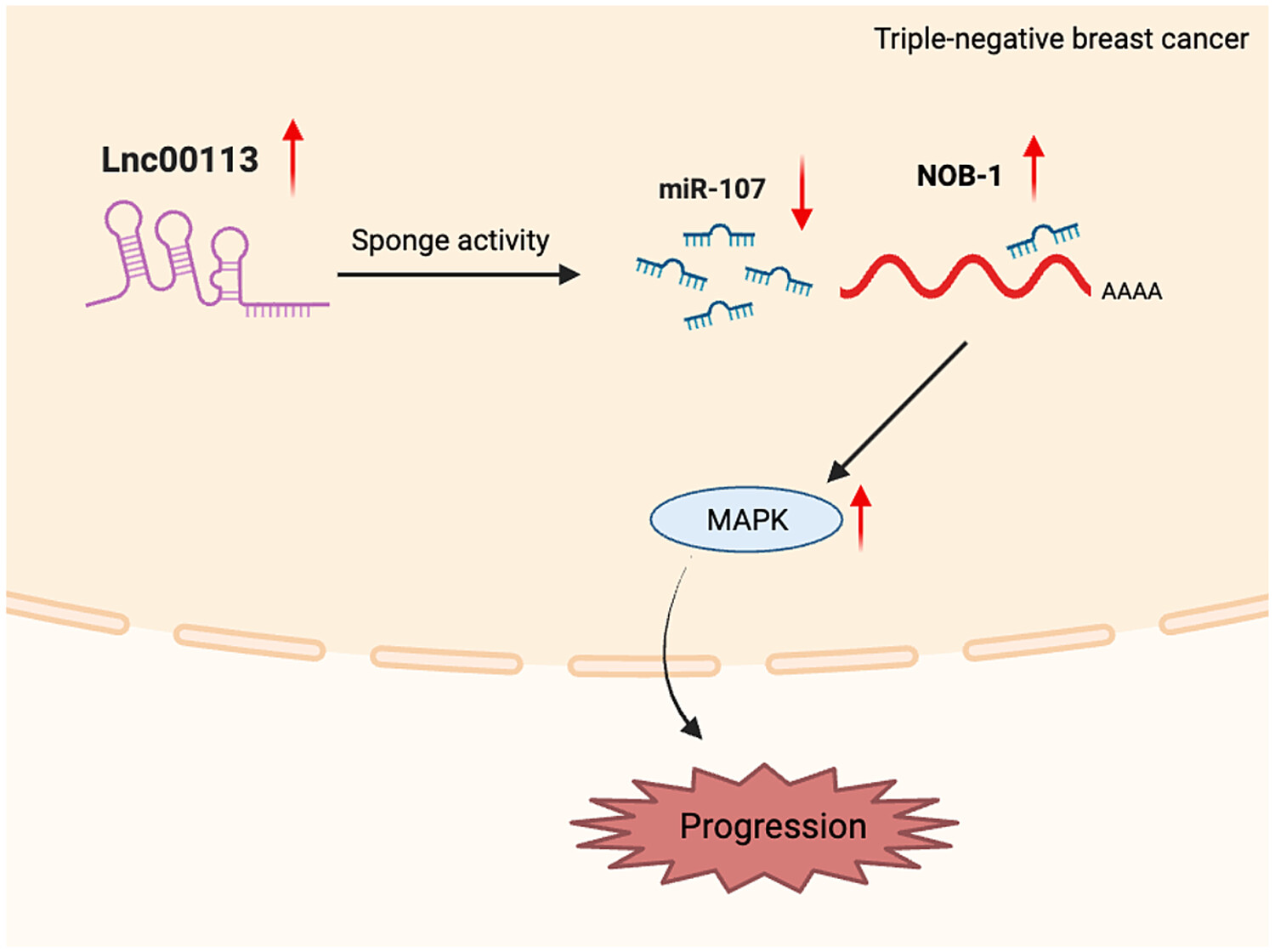
Lnc00113 promotes triple-negative breast cancer progression via the NOB-1/MAPK signaling axis
- First Published: 01 February 2024
Clinical and prognostic significance analysis of glycolysis-related genes in HNSCC
- First Published: 09 February 2024
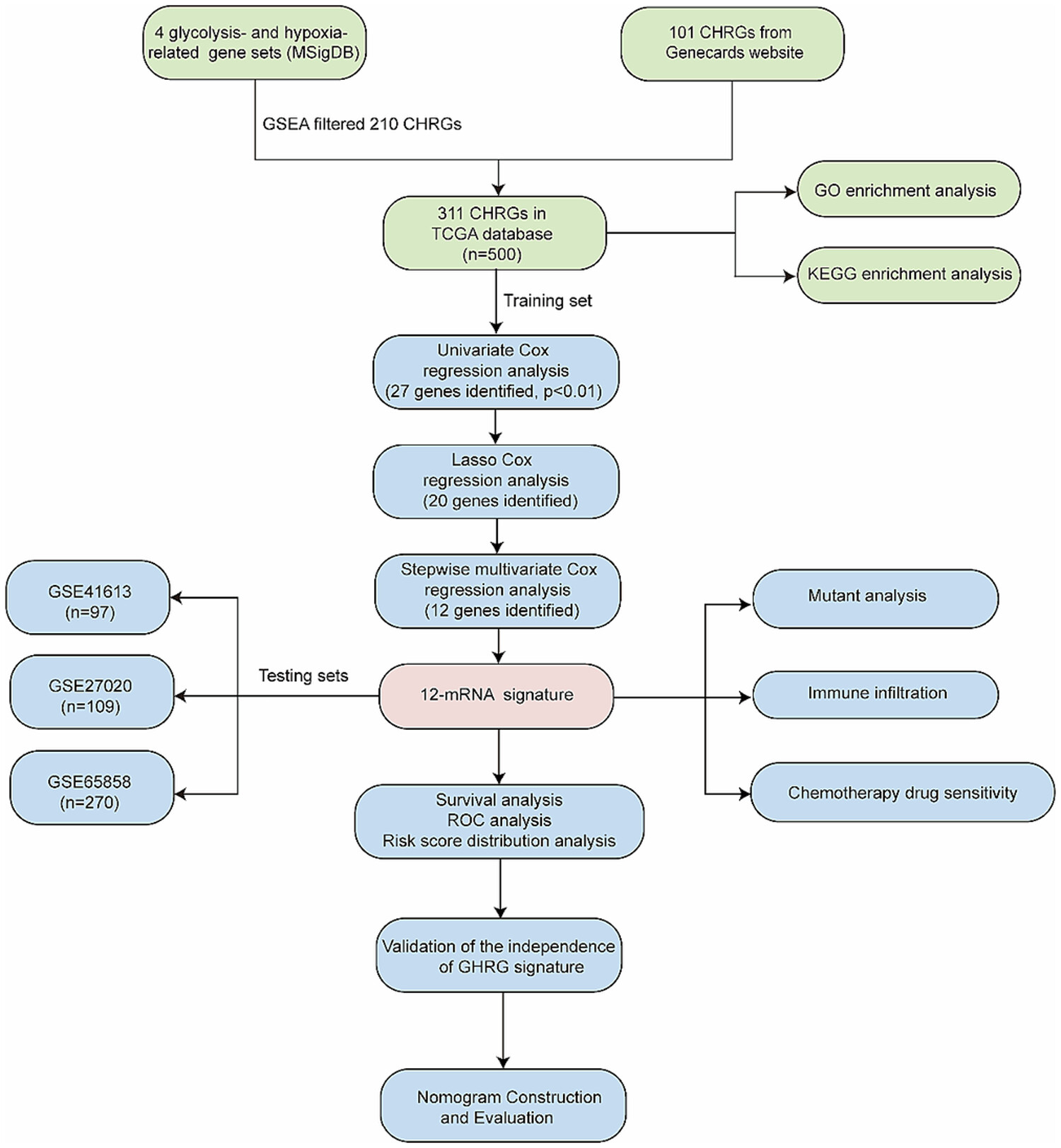
Yuan et al. established and validated a 12-GHRG signature for the prognostic prediction of HNSCC, which has potential for use in clinical settings for convenient prognostic monitoring. Moreover, the GHRG model could predict the immune infiltrate features and chemotherapy drug sensitivities of HNSCC.
REVIEW ARTICLES
The role of key biomarkers in lymphatic malformation: An updated review
- First Published: 20 February 2024
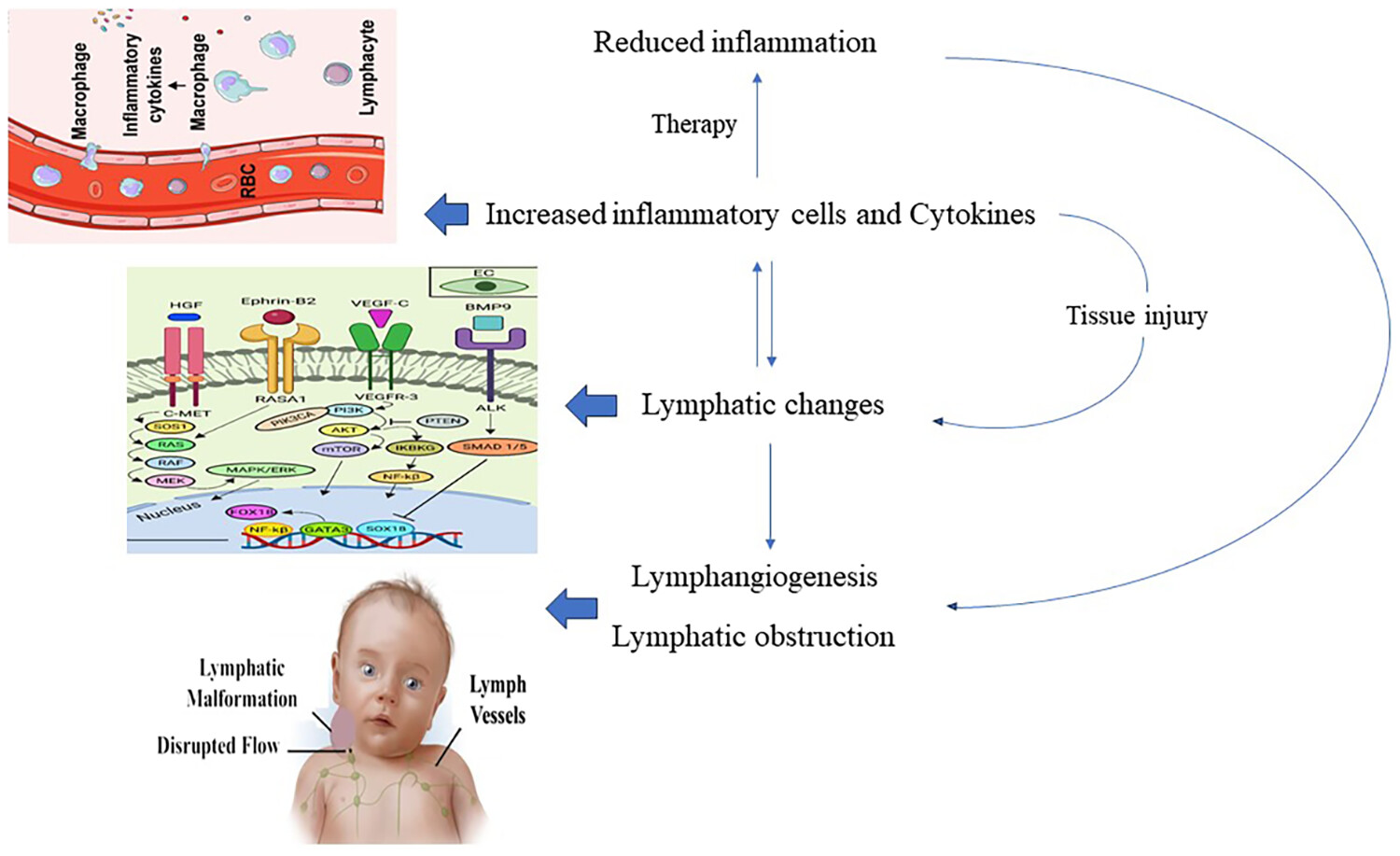
Lymphatic malformations are linked to an elevation in inflammatory cells and cytokines, which aid in the stimulation of lymphatic alterations. Lymphangiogenesis, the process of generating new lymphatic vessels, enhances the movement of immune cells and cytokines from the site of inflammation. This mitigates inflammation and minimizes tissue damage.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Comparison of immune-related gene signatures and immune infiltration features in early- and late-onset preeclampsia
- First Published: 16 February 2024
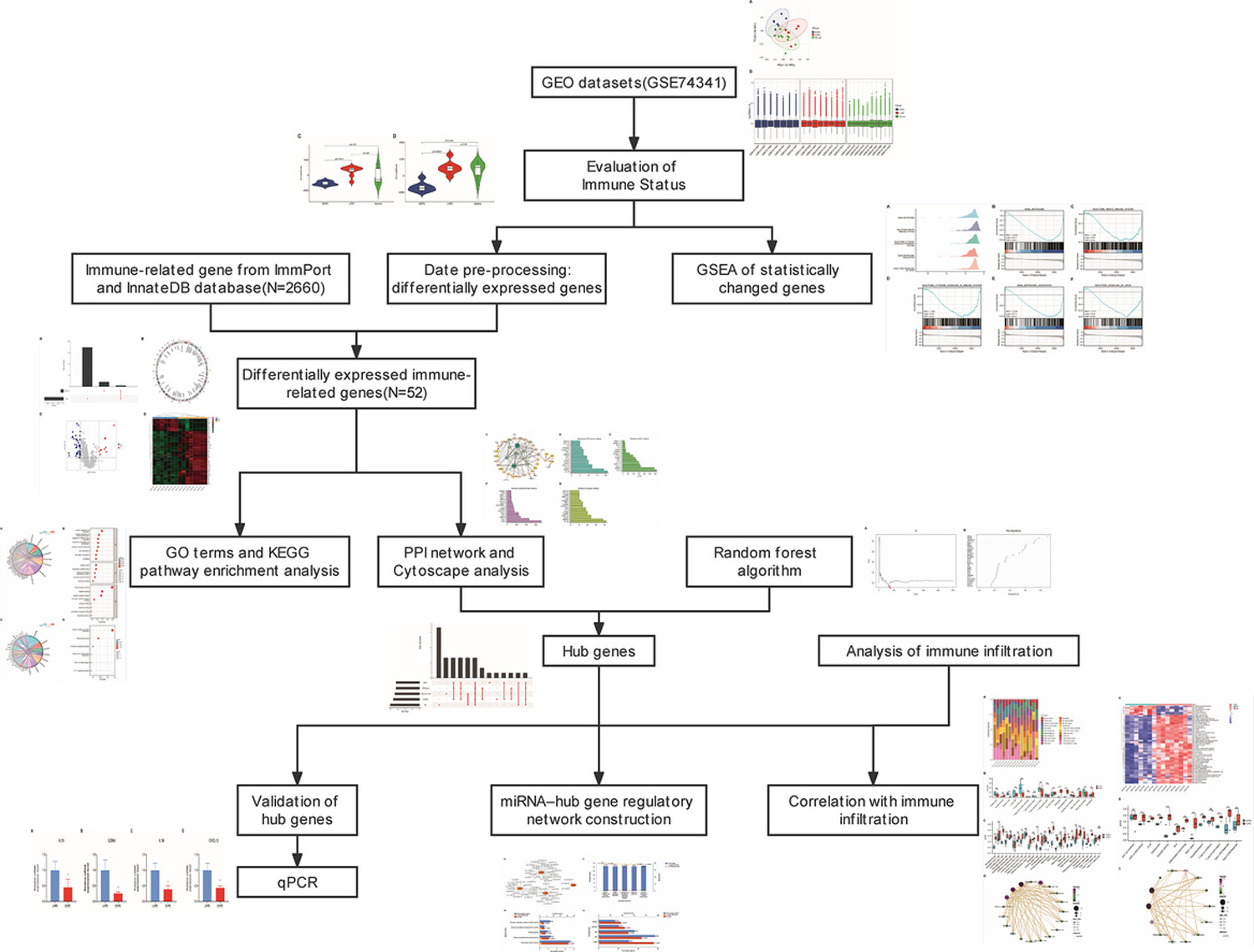
A schematic presentation of the analysis process is shown. Early- and late-onset preeclampsia (EOPE) placentas demonstrate immune dysfunction. IL15, GZMB, IL1B and CXCL12 were hub genes involved in EOPE placental immune-related pathogenesis. The hub immune-related genes related to EOPE were associated with six hsa-miRNAs.
REVIEW ARTICLES
Trends in the synthetic polymer delivery of RNA
- First Published: 21 February 2024
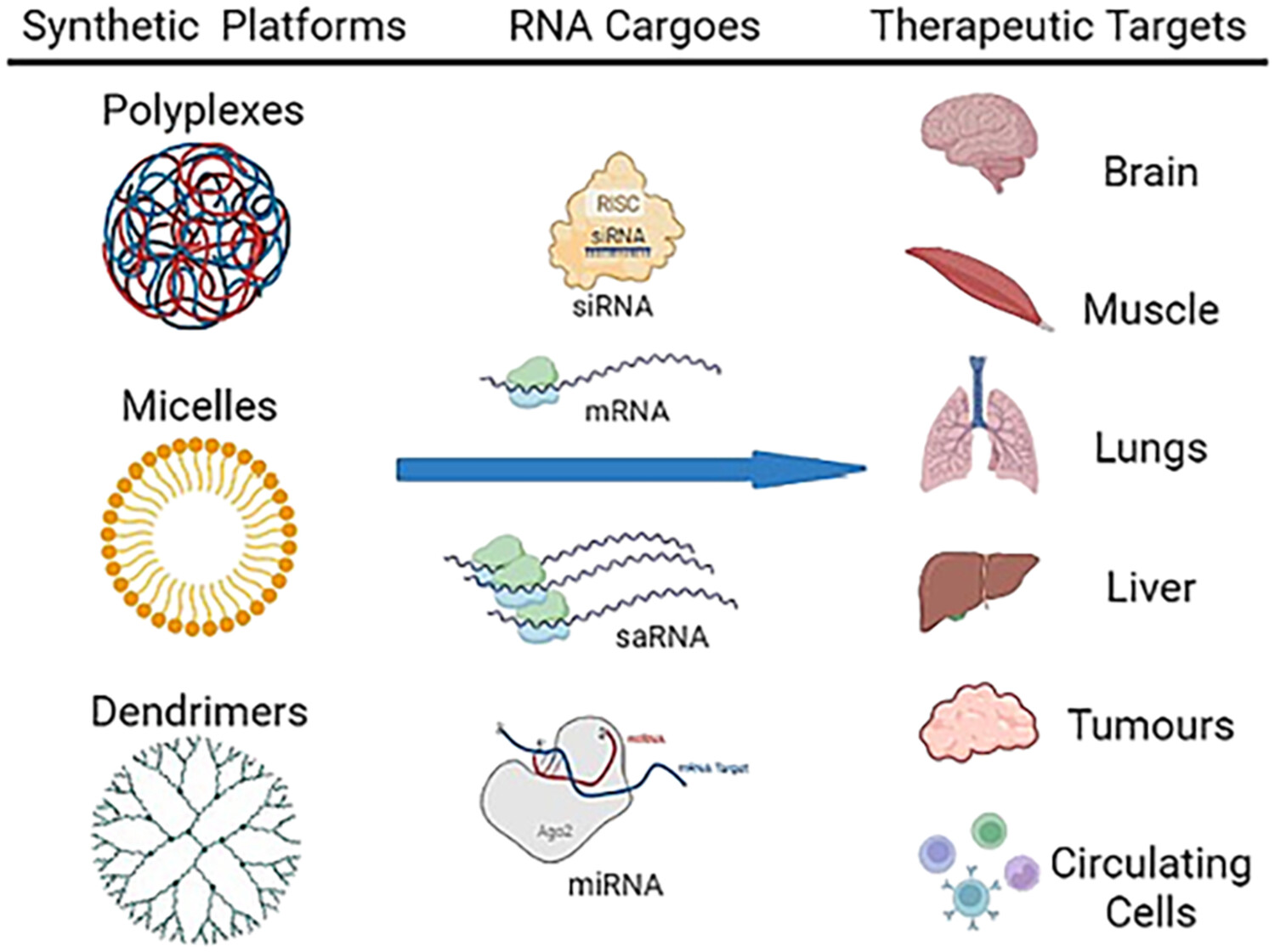
Synthetic polymers are one of the main vehicles used to efficiently deliver RNA therapeutics. They are a complex category of molecules that allow for flexible design of their chemical composition, size, structure, and formulation with RNA. This review aims to summarize the most used synthetic polymers for RNA delivery, highlight their strengths and weaknesses and address what improvements are needed for their advancement.
Zebrafish in understanding molecular pathophysiology, disease modeling, and developing effective treatments for Rett syndrome
- First Published: 21 February 2024
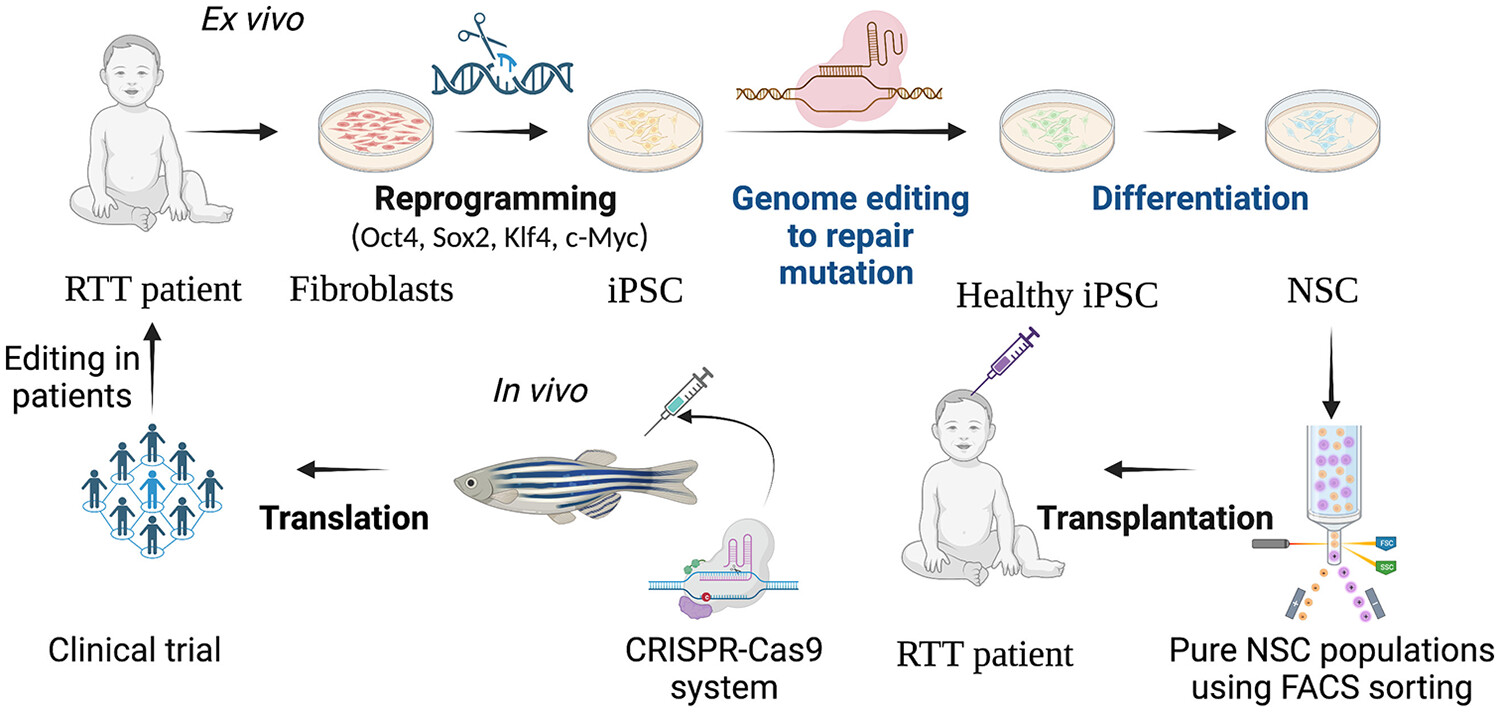
Zebrafish contribute to our understanding of the pathogenesis of Rett syndrome (RTT) and propose a stem cell therapy strategy with respect to treating RTT. RTT is an X-linked dominant genetic neurological disease that affects young girls. In the proposed therapeutic approach, patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) could be corrected using the clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)/CRISPR-associated protein 9 (Cas9) system to produce healthy iPSC, which could be differentiated into neural stem cells for the transplantation of healthy. In an in vivo study, the designed CRISPR-Cas9 system could be texted in the zebrafish model, which could be translated into clinical trials upon successful therapeutic and toxicity evaluations.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Baicalin induces ferroptosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma by suppressing the activity of FTH1
- First Published: 21 February 2024
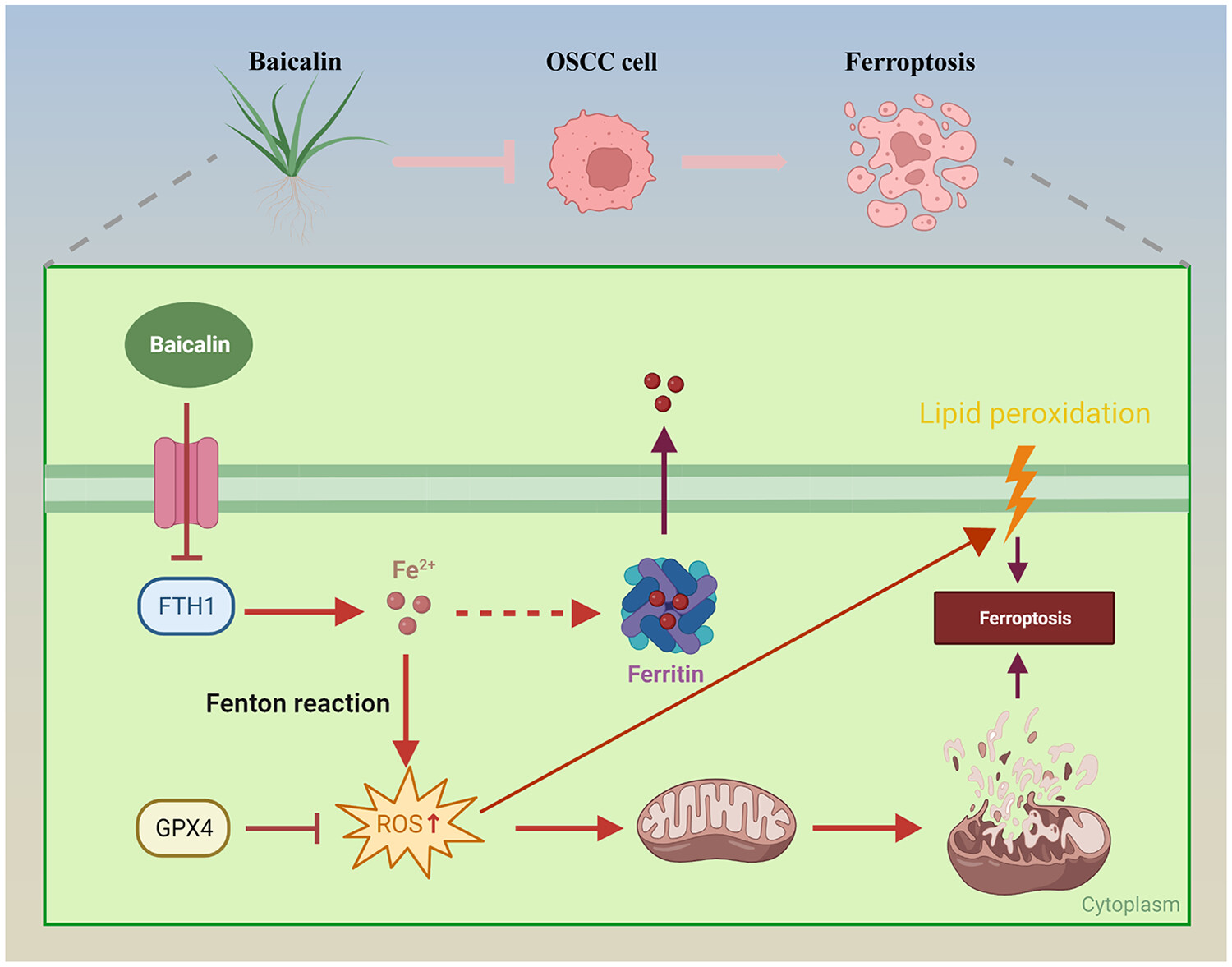
In oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), the ferroptosis-related gene FTH1 is overexpressed, promoting cell proliferation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), while concurrently suppressing ferroptosis. Baicalin, by down-regulating FTH1, mitigates these effects, reducing EMT and proliferation and facilitating ferroptosis in OSCC cells. (Created by Biorender)