Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Advanced microscopy technologies enable rapid response to SARS-CoV-2 pandemic
- First Published: 17 February 2021
AFM in cellular and molecular microbiology
- First Published: 12 March 2021
Human stem cell-based models for studying host-pathogen interactions
- First Published: 01 April 2021
Organ-on-chip to investigate host-pathogens interactions
- First Published: 02 April 2021
Advances in host-based screening for compounds with intracellular anti-mycobacterial activity
- First Published: 04 April 2021
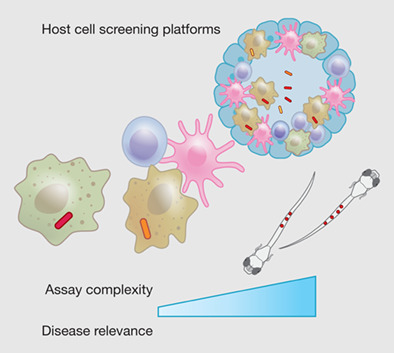
Host based systems are disease relevant platforms for screening anti Mtb compounds. New target and chemical spaces open up for drug discovery in these platforms while recent advances enable sensitive detection and identification of subtle phenotypes. This review provides an overview of these advances and the recent host based chemical screens for identification of anti-Mtb compounds.
New methods to decrypt emerging macropinosome functions during the host–pathogen crosstalk
- First Published: 13 April 2021
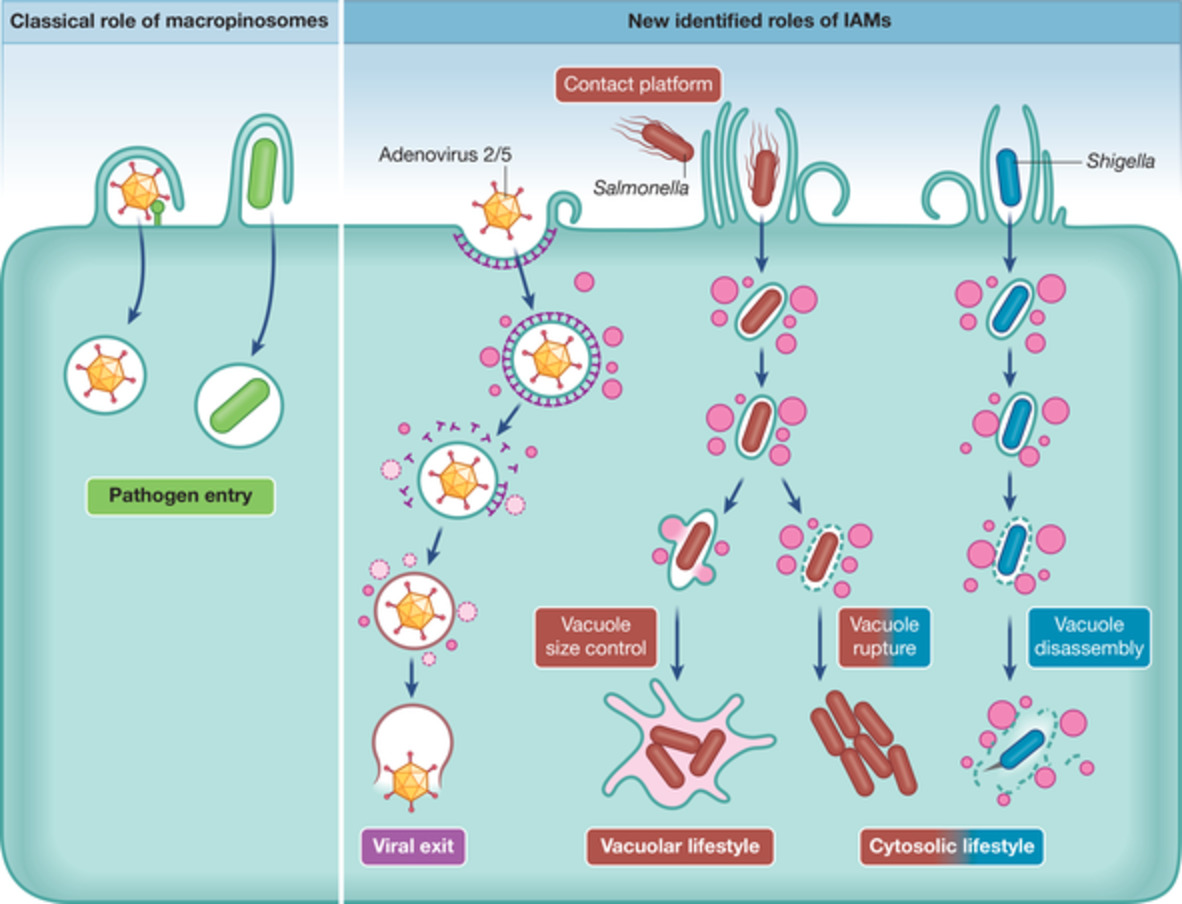
Viruses and intracellular bacteria commonly hijack macropinocytosis to invade host cell. Classically, subversion of macropinocytosis by intracellular pathogens was perceived as purely entry-related. Yet, recent discoveries showed that pathogen-induced ruffling leads to the formation of distinct class of macropinosomes termed infection-associated macropinosomes (IAMs). Thanks to novel method developments, it has emerged that these non-pathogen-containing IAMs contribute to establish pathogen replicative niches; for instance by facilitating cytosolic escape or by promoting the maturation of a permissive pathogen-containing compartment.
Breaching the phagosome, the case of the tuberculosis agent
- First Published: 15 April 2021
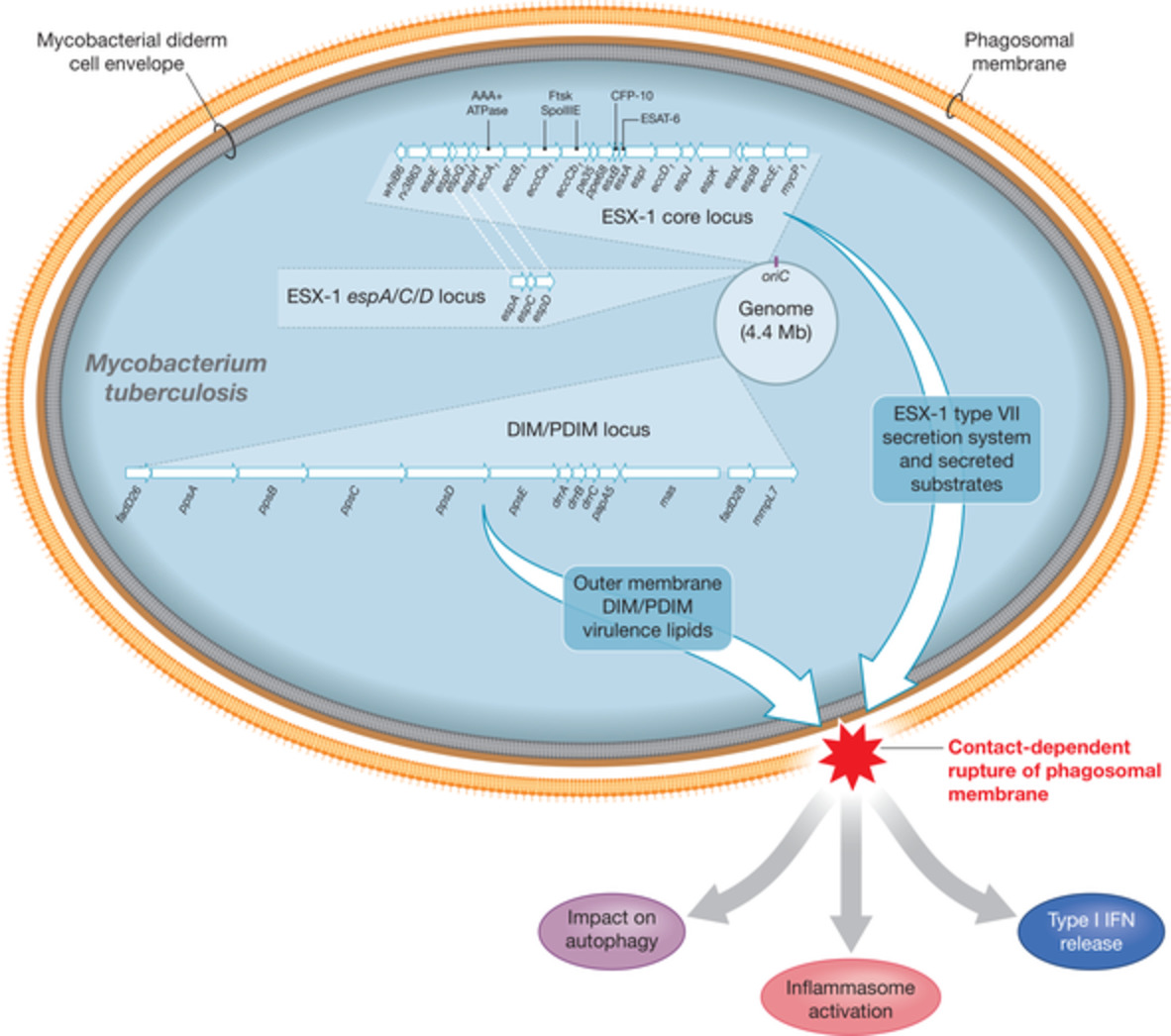
The genome of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the causative agent of human tuberculosis, harbors two loci (ESX-1 and DIM/PDIM), whose gene products are essential for the bacterium's ability to induce phagosomal rupture, when ingested by host phagocytes. The access to the host cytosol leads to important cellular signaling events and immune reactions.
HRMAn 2.0: Next-generation artificial intelligence–driven analysis for broad host–pathogen interactions
- First Published: 30 April 2021
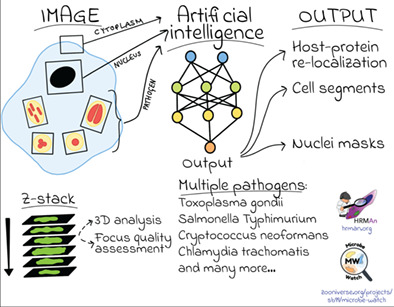
HRMAn 2.0 is an artificial intelligence-driven, high-throughput image analysis tool to study host-pathogen interactions. It uses AI for object detection and phenotypical classification. HRMAn 2.0 has been validated for several different intracellular pathogens and is easily adaptable for new pathogens and experimental questions.