Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Hernia repair: are we looking through a ‘keyhole’ with rose-coloured glasses?
- Pages: 2155-2157
- First Published: 16 November 2020
PERSPECTIVES
National survey of inguinal hernia mesh repair practices
- Pages: 2158-2159
- First Published: 16 November 2020
Inguinal hernia repair as day-case surgery: a potentially underutilized practice
- Pages: 2159-2161
- First Published: 16 November 2020
The Promise of viral phage therapy in hernia mesh infection, is this the biological ‘silver bullet’ of the future?
- Pages: 2161-2164
- First Published: 16 November 2020
Role of private practice in general surgical training in Australia
- Pages: 2164-2165
- First Published: 16 November 2020
Surgical Outpatient Study: characterizing the educational experience of outpatient clinics for surgical trainees
- Pages: 2166-2167
- First Published: 16 November 2020
Lessons learnt from COVID-19 pandemic: a surgical resident's perspective
- Pages: 2167-2169
- First Published: 17 September 2020
SPECIAL ARTICLES
Changing landscape of surgical research: a trainee perspective
- Pages: 2173-2174
- First Published: 16 November 2020
Trainee-led collaboratives, clinical trials and new opportunities in the COVID-19 era
- Pages: 2175-2176
- First Published: 08 July 2020
Trainee- and student-led research networks: promoting research skills and competency through collaboration
- Pages: 2177-2179
- First Published: 16 November 2020
REVIEW ARTICLES
Another type of diaphragmatic hernia to remember: parahiatal hernia
- Pages: 2180-2186
- First Published: 01 May 2020
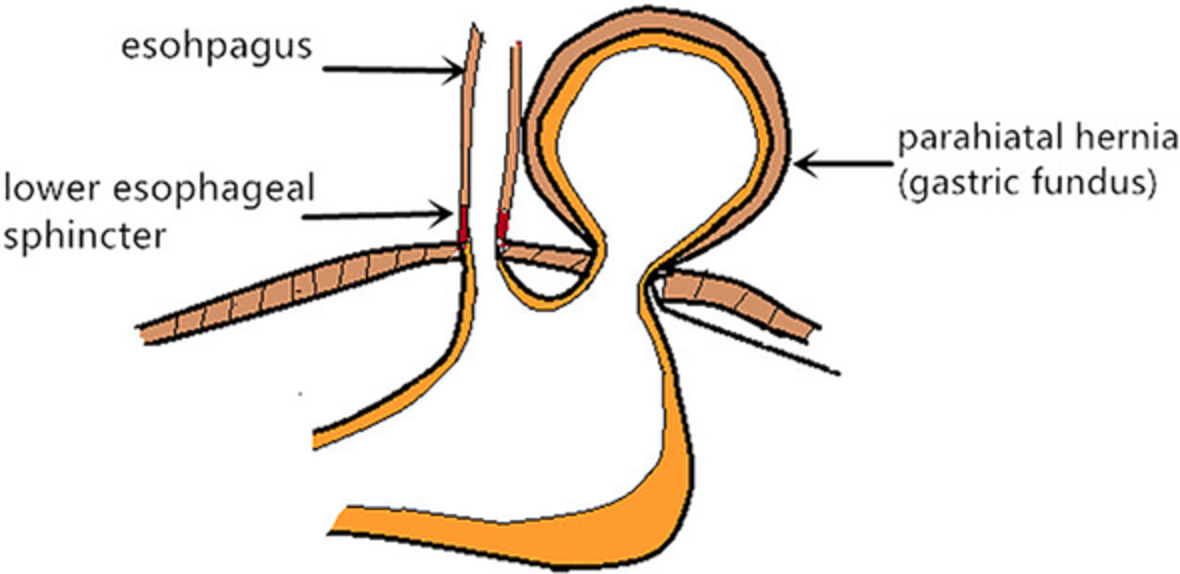
Parahiatal hernias are uncommon diaphragmatic hernias and not familiar to the general surgeons. Laparoscopic treatment of parahiatal hernia is feasible and safe in the majority cases. Surgeons should be aware of this disease when performing paraoesophageal hernia repair, as it may occur with or without previous diaphragmatic surgery.
Supravesical hernias: a systematic review of the literature
- Pages: 2187-2192
- First Published: 17 August 2020
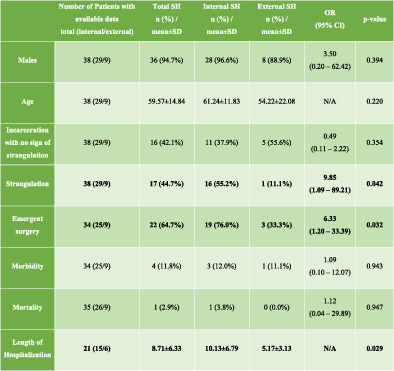
A supravesical hernia is a rare abdominal wall hernia that is defined by the protrusion of abdominal viscera through the supravesical fossa, between the remnants of urachus and foetal umbilical arteries. It mainly concerns males and is usually presented as an internal hernia. The majority of patients refer to healthcare facilities with symptoms and signs of bowel obstruction.
Intraoperative indocyanine green fluorescence angiography to prevent anastomotic leak after low anterior resection for rectal cancer: a meta-analysis
- Pages: 2193-2200
- First Published: 11 March 2020
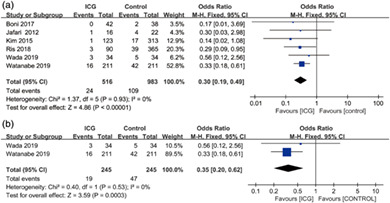
In this study, we analysed 1499 patients undergoing low anterior resection for rectal cancer, proving that intraoperative indocyanine green imaging has a positive significance in reducing the incidence of anastomotic leakage after rectal cancer resection, secondary surgery and post-operative complications. The importance of this report is providing further evidence supporting the intraoperative use of indocyanine green imaging technique in rectal cancer surgery.
Impact of neoadjuvant therapy on post-operative pancreatic fistula: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 2201-2210
- First Published: 17 May 2020
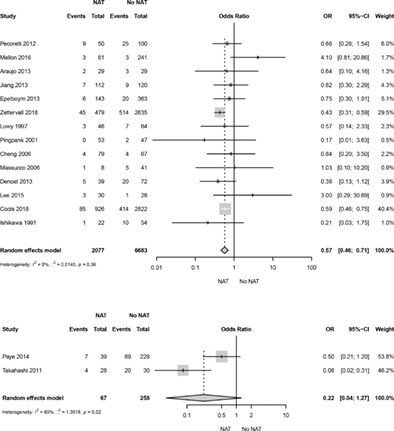
Neoadjuvant therapy is associated with significantly lower rates of post-operative pancreatic fistula after pancreatoduodenectomy but not after distal pancreatectomy. Further studies are required to determine whether neoadjuvant therapy should be added to post-operative pancreatic fistula risk calculators.
Diagnostic approaches for pancreatic cystic lesions
- Pages: 2211-2218
- First Published: 19 August 2020
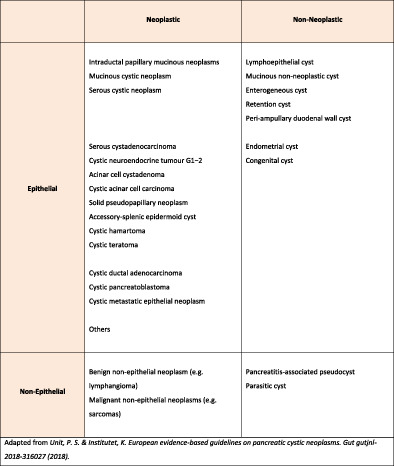
Cystic lesions of the pancreas (PCLs) may be inflammatory or proliferative and making an accurate and timely pre-operative diagnosis remains a significant clinical challenge. This narrative review examines the current diagnostic benchmarks and identifies novel diagnostic techniques that warrant further consideration, a number of which are beginning to be included in routine clinical practice when these PCLs are being investigated. We have highlighted the need for a comprehensive and standardised algorithm for the diagnosis and management of PCLs and we are confident that this can be achieved with the presently available and emerging technologies.
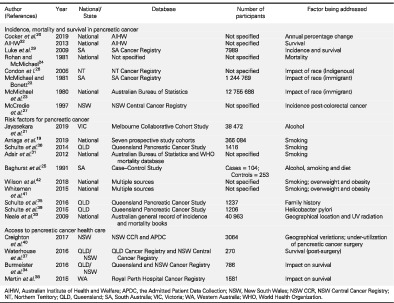
Pancreatic cancer in the Australian population: identifying opportunities for intervention
- Pages: 2219-2226
- First Published: 31 August 2020
TRAUMA AND FRACTURE MANAGEMENT
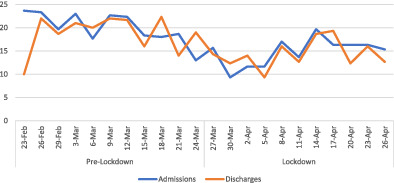
Impact of societal restrictions and lockdown on trauma admissions during the COVID-19 pandemic: a single-centre cross-sectional observational study
- Pages: 2227-2231
- First Published: 07 September 2020
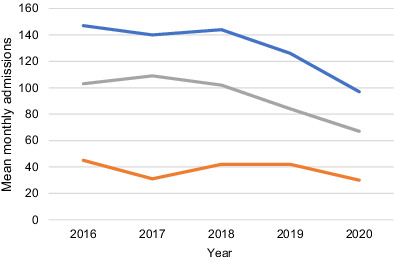
Mean monthly trauma admissions for March/April by year: We aimed to evaluate the impact of societal restrictions and lockdown on trauma admissions during the coronavirus pandemic. There was a decreased number of minor trauma admissions; however the number of major traumas and in-hospital interventions required was unchanged. There was a decrease in trauma admissions from road traffic collisions and falls, but the number of admissions due to assault and self-harm was unchanged.
Closed reduction of paediatric forearm fractures: nitrous oxide versus general anaesthetic
- Pages: 2232-2236
- First Published: 11 September 2020
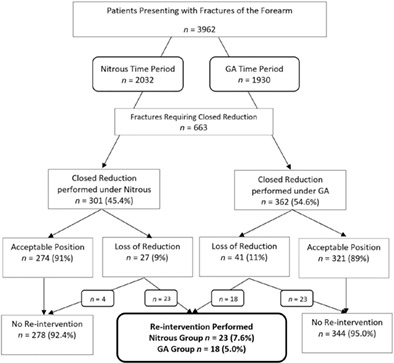
This study compares 663 patients undergoing closed reduction of paediatric forearm fractures in the emergency department under sedation to those performed in the operating theatre under general anaesthetic. We found comparable results between the two groups in regards to both re-intervention rates and adverse events.
Safe and rapid implementation of telemedicine fracture clinics: the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic
- Pages: 2237-2241
- First Published: 17 September 2020

Telemedicine is an innovative way to overcome geographical and infrastructural barriers in health systems, particularly in rural and remote settings. During the COVID-19 pandemic, telemedicine has become a necessary avenue for provision of safe patient care. This study demonstrates that rapid implementation of telehealth for orthopaedic fracture clinics does not seem to increase complication rates. Our experience can be used to implement a rapid telehealth plan if a similar scenario occurs in the future and to support increased uptake of telehealth for patients with geographical barriers to access to healthcare.
GENERAL SURGERY
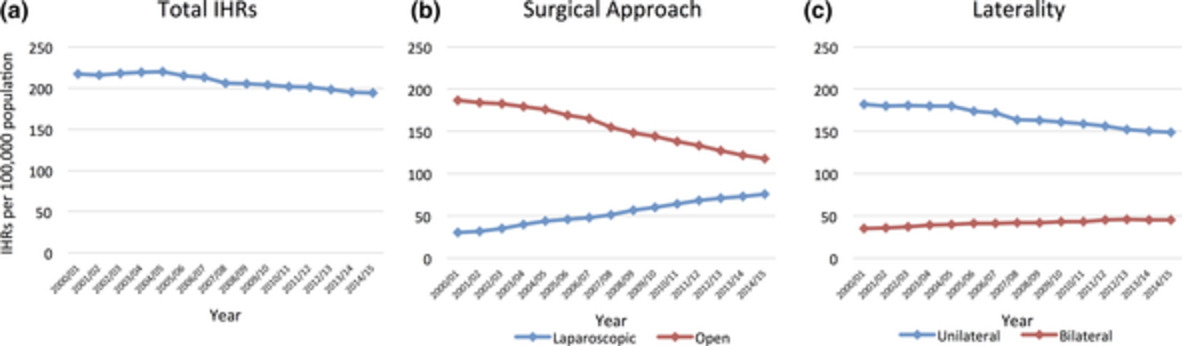
Trends in Australian inguinal hernia repair rates: a 15-year population study
- Pages: 2242-2247
- First Published: 31 July 2020
Operative outcome of hernia repair with synthetic mesh in immunocompromised patients
- Pages: 2248-2253
- First Published: 11 August 2020
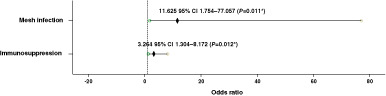
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of immunosuppression on wound complications after hernia repair with synthetic mesh. Our results do not show an association between immunosuppression and mesh infection or surgical site infection, but suggest that immunosuppression and mesh infection increase the odds for hernia recurrence.
Impact of the COVID-19 national lockdown on emergency general surgery: Auckland City Hospital's experience
- Pages: 2254-2258
- First Published: 17 September 2020
Reducing length of stay for patients presenting to general surgery with acute non-surgical abdominal pain
- Pages: 2259-2263
- First Published: 28 August 2020
HEPATOPANCREATICOBILIARY SURGERY
The incidence of symptomatic remnant gall bladder: a population study
- Pages: 2264-2268
- First Published: 03 June 2020
Long-term outcomes of oesophagogastric devascularization and splenectomy in patients with portal hypertension and liver cirrhosis
- Pages: 2269-2273
- First Published: 14 May 2020
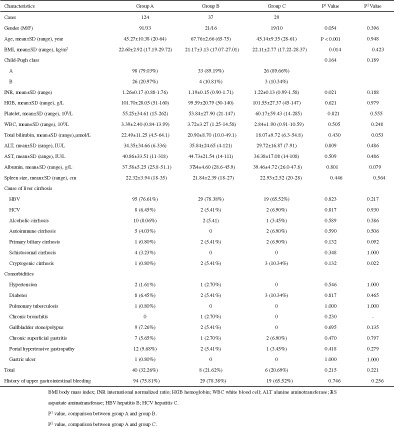
Research about the long-term outcomes of oesophagogastric devascularization and splenectomy (OGDS) to treat portal hypertension is scarce. The aim of this study was to evaluate the safety and the long-term treatment efficacy of OGDS, especially in elderly patients. OGDS remains safe and effective to treat portal hypertension secondary to liver cirrhosis and it can be performed successfully in elderly patients and achieve a curative effect that is not inferior to young patients.
Management of pyogenic liver abscess: a South Australian experience
- Pages: 2274-2278
- First Published: 26 May 2020
This retrospective study of patients with pyogenic liver abscess demonstrates continued preference for percutaneous drainage techniques over surgical drainage. The mortality rate attributable to pyogenic liver abscess was low; however, the risk of complications appeared to concentrate in patients who did not undergo abscess drainage.
Unsuspected choledocholithiasis found by routine intra-operative cholangiography during laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Pages: 2279-2284
- First Published: 13 June 2020
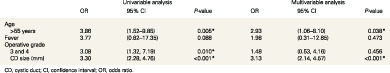
This study determined the incidence of unsuspected choledocholithiasis in a population deemed to be low risk undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy with routine intra-operative cholangiography. In addition to this, the management of these patients was reported along with predictive factors for an abnormal intra-operative cholangiogram were determined. Risk factors independently associated with unsuspected choledocholithiasis included patients over the age of 55 years of age (odds ratio 2.93, P = 0.038) and a large cystic duct size (odds ratio 3.13, P < 0.001) on multivariable analysis.
COLORECTAL SURGERY
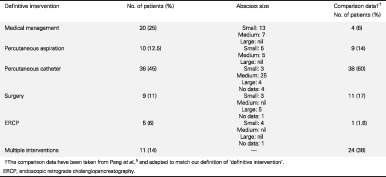
Laparoscopic-assisted colectomy with Duhamel procedure for idiopathic megacolon in adults: a retrospective study
- Pages: 2285-2289
- First Published: 08 April 2020
Due to the lack of understanding of definite aetiology and the rarity of idiopathic megacolon in adults, preoperative examination and diagnosis must be comprehensive. Laparoscopic-assisted colectomy with Duhamel procedure is a safe and effective technique for idiopathic megacolon in adults. The scope of colon resection and the anastomosis pattern should be individually selected.
Effect of platelet-rich plasma on colon anastomosis in rats in which hyperthermic intra-peritoneal chemotherapy was performed using 5-fluorouracil
- Pages: 2290-2297
- First Published: 21 May 2020
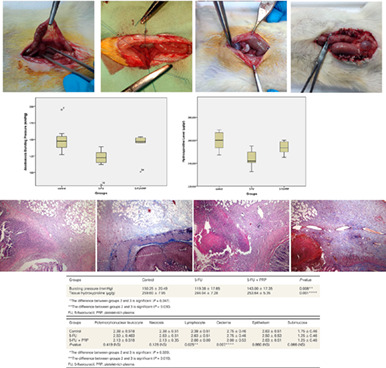
This experimental study aims to investigate the effect of platelet-rich plasma gel on colon anastomosis in rats treated with hyperthermic intra-peritoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) using 5-fluorouracil. The HIPEC procedure significantly reduces anastomotic bursting pressure through its negative effects on anastomotic healing. This paper suggests that the negative effect of HIPEC on anastomotic healing can be reversed by the application of platelet-rich plasma gel.
Opportunistic use of radiological measures of visceral adiposity for assessment of risk of colorectal adenoma
- Pages: 2298-2303
- First Published: 05 June 2020
OTOLARYNGOLOGY HEAD AND NECK SURGERY
Normative data for the Nasal Obstruction Symptom Evaluation Scale in the general Australian population
- Pages: 2304-2309
- First Published: 17 May 2020
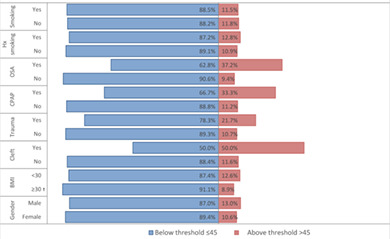
Recent changes to the Australian Medicare Benefits Scheme funding for rhinoplasty on November 2018 have included a Nasal Obstruction Symptom Evaluation (NOSE) Scale threshold of >45 as a criteria for surgical intervention. The NOSE Scale is a patient-reported outcome measure of nasal obstruction which is well validated for use in rhinoplasty and septorhinoplasty patients. Up until now, however, there has been minimal normative data for the NOSE Scale in the general population and no normative data from the general Australian population published in the literature. This article provides that context, presenting the first normative NOSE Scale data for the general Australian population.
Colonization rates of tracheostomy tubes associated with the frequency of tube changes
- Pages: 2310-2314
- First Published: 17 May 2020
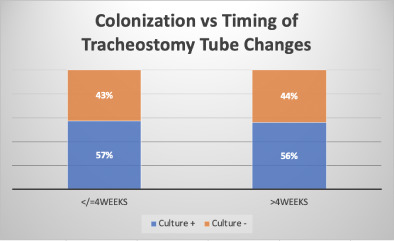
Tracheostomy-tube change protocols are implemented primarily due to concern regarding infections. However, currently no evidence-based guidelines exist to justify these protocols. In this prospective cohort study, no statistically significant difference in colonisation in patients undergoing tube changes more than every 4 weeks to those less than every 4 weeks was found. The timing of tracheostomy-tube changes may not affect colonisation and infection rates.
Reducing the morbidity of parotidectomy for benign pathology
- Pages: 2315-2321
- First Published: 02 June 2020
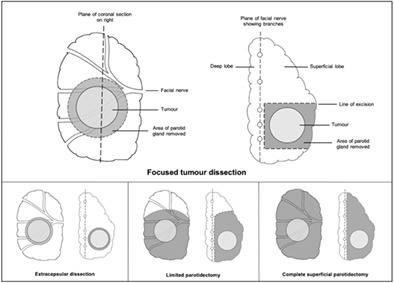
The aim of this study was to determine the surgeon-modifiable factors which impact the rates of post-operative complications following parotidectomy for benign pathology. Focused tumour dissection, nerve integrity monitoring and dermofat grafting are surgeon-modifiable variables associated with lower rates of post-operative complications following parotidectomy for benign pathology. However, the benefit of these operative techniques relies on their appropriate utilization by performing surgeons.
PLASTIC AND RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY
Treatment of tendinous mallet finger deformity with a part of the flexor digitorum profundus tendon
- Pages: 2325-2328
- First Published: 02 June 2020
Necrotising fasciitis deaths in Australia: patient characteristics and potential areas for improvement in clinical management
- Pages: 2329-2333
- First Published: 06 September 2020
BREAST SURGERY
Determinants influencing immediate breast reconstruction in an Australian tertiary public hospital
- Pages: 2334-2339
- First Published: 05 October 2020
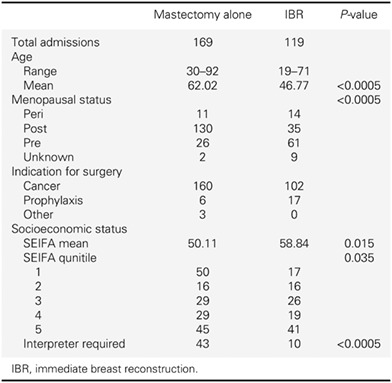
Our research demonstrates a high rate of immediate breast reconstruction following mastectomy that includes a wide range of autologous and alloplastic reconstructions within a diverse patient population. Our study represents a unique opportunity to identify barriers and facilitate patient choice reconstruction rates, particularly in tertiary services with a strong multicultural and multi-linguistic population.
Breast reconstruction in South Western Sydney
- Pages: 2340-2345
- First Published: 05 October 2020
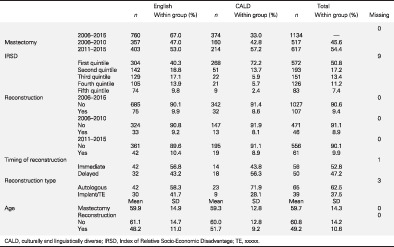
This retrospective study determined the rate of breast reconstruction in women who had mastectomy as treatment for breast cancer at public hospitals in South Western Sydney Local Health District – a culturally diverse health district in New South Wales, Australia – and compared the rate of reconstruction in the culturally and linguistically diverse (CALD) and non-CALD populations. The study found a low breast reconstruction rate in public hospitals in South Western Sydney Local Health District. The reconstruction rate did not differ between CALD or English-speaking patients, or between patients from diverse socio-economic backgrounds.
Achieving margin clearance following oncoplastic breast surgery in comparison with simple wide local excision: a three-dimensional specimen assessment
- Pages: 2346-2352
- First Published: 17 August 2020
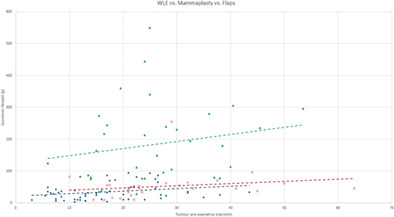
In this paper, we reviewed the three-dimensional interplay between tumour and surgical specimen dimensions in patients undergoing oncoplastic breast surgery compared to simple wide local excision. The relationship between tumour and specimen medio-lateral, supero-inferior and antero-posterior dimensions were explored in both groups. Despite larger tumour dimensions, oncoplastic surgery is not inferior to wide local excision in providing clear surgical margins.
HOW TO DO IT
How to do hernioscopy for incarcerated femoral hernia with laparoscopic O-ring retractor system
- Pages: 2353-2354
- First Published: 10 August 2020
How to repair a small umbilical hernia laparoscopically
- Pages: 2355-2356
- First Published: 01 September 2020
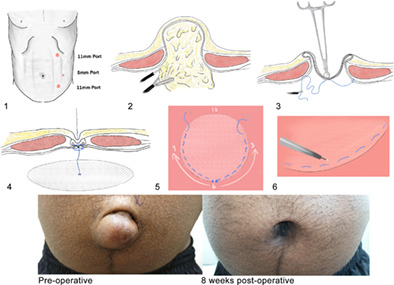
We describe a step by step technique for repair of a small umbilical hernia laparoscopically that aims to provide an excellent technical and cosmetic result without a significant increase in operative time or cost. Patients report good quality of life post-operatively and appear satisfied with the cosmetic result.
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS FOR SURGEONS
Sharing the helm: medical co-management for the older surgical patient
- Pages: 2357-2361
- First Published: 30 September 2020
IMAGES FOR SURGEONS
Traumatic lung herniation managed by rib fixation alone
- Pages: 2362-2364
- First Published: 20 February 2020
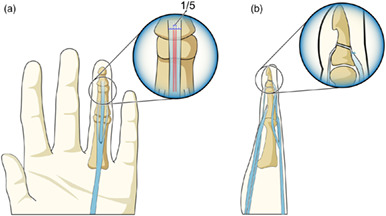
Brachydactyly-anonychia with congenital absent phalanges of the hand
- Pages: 2364-2366
- First Published: 18 February 2020
Delayed presentation of a semicentennial gossypiboma in the soft palate and posterior nasopharyngeal wall
- Pages: 2366-2368
- First Published: 17 February 2020
Lateral lymph node dissection after endoscopic submucosal dissection for T1 rectal cancer: a case report
- Pages: 2369-2370
- First Published: 25 February 2020
Large bowel obstruction from a full-thickness resection device clip: rare complication of a novel technique
- Pages: 2370-2372
- First Published: 22 March 2020
Silicone cast of the colon: management of an unusual colorectal foreign body
- Pages: 2372-2374
- First Published: 03 March 2020
Aortoduodenal fistula 2 years after elective endovascular repair of an abdominal aortic aneurysm
- Pages: 2374-2376
- First Published: 20 February 2020
Mucin-containing pancreatic lymphoepithelial cyst: a potential surgical pitfall
- Pages: 2376-2378
- First Published: 17 February 2020
Metastatic de-differentiated melanoma resembling synovial sarcoma diagnosed by synchronous NRAS genetic mutation
- Pages: 2378-2380
- First Published: 06 March 2020
Congenital transverse colon mesenteric defect in an adult patient leading to acute large bowel obstruction
- Pages: 2380-2382
- First Published: 06 March 2020
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
Re: Hidden blood loss and the influencing factors after laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Page: 2383
- First Published: 16 November 2020
Response to Re: Hidden blood loss and the influencing factors after laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Pages: 2383-2384
- First Published: 16 November 2020
IMAGES FOR SURGEONS
Durable complete response to immunotherapy in treatment-resistant metastatic colorectal cancer with thyroid transcription factor 1 expression
- Pages: E97-E99
- First Published: 06 March 2020
Perforated descending colon adenocarcinoma manifesting as necrotizing fasciitis
- Pages: E100-E102
- First Published: 10 March 2020
Surgical tetralogy: simultaneous perforated gastric ulcer and appendicular perforation with liver and cerebral abscesses
- Pages: E103-E105
- First Published: 18 March 2020
Unusual presentation of a symptomatic large pelvic lipoma in a middle-aged woman
- Pages: E106-E107
- First Published: 15 May 2020
Recalcitrant plunging ranulas: a new approach to salivary tissue localization using prostate-specific membrane antigen positron emission tomography
- Pages: E108-E109
- First Published: 21 March 2020
Chylous cyst of the mesentery: an unexpected diagnosis for an abdominal mass
- Pages: E110-E111
- First Published: 30 March 2020
Close encounter of the right-sided Zenker's diverticulum masquerading as a thyroid nodule
- Pages: E112-E113
- First Published: 04 April 2020
Repair of a paraumbilical hernia containing an incarcerated urachal remnant
- Pages: E114-E115
- First Published: 30 March 2020
Endovascular aortic aneurysm repair to facilitate computed tomography-guided biopsy and aid diagnosis in a case of presumed immunoglobulin G4 aortitis
- Pages: E116-E118
- First Published: 08 April 2020
Partial inferior vena cava resection without reconstruction
- Pages: E119-E120
- First Published: 04 April 2020
Recurrent acute limb ischaemia and thoracic outlet syndrome secondary to a clavicle fracture malunion
- Pages: E121-E122
- First Published: 08 April 2020
Rare presentation of infected duplication cyst in an adult
- Pages: E123-E124
- First Published: 01 May 2020
Rare case of intra-articular lymphoma of the knee arising from the Hoffa fat pad
- Pages: E132-E134
- First Published: 25 April 2020
Perianal extramammary Paget's disease: a diagnosis worth considering
- Pages: E135-E136
- First Published: 30 April 2020
Endometriosis as a rare cause of small bowel obstruction
- Pages: E137-E138
- First Published: 27 April 2020
Clinical diagnosis of a double primary sigmoid colon cancer and metastatic tumour using a gene-targeted panel test: a case report
- Pages: E139-E140
- First Published: 25 April 2020
Colonic obstruction: a rare complication of acute pancreatitis
- Pages: E141-E142
- First Published: 25 April 2020