Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Perioperative thromboprophylaxis: inconsistent guidelines and evidence gaps lead to variable practice
- Pages: 2391-2392
- First Published: 17 December 2020
PERSPECTIVES
Cultural competency in otolaryngology-head and neck surgery training in Aotearoa, New Zealand
- Pages: 2393-2395
- First Published: 17 December 2020
Time to harness ear, nose and throat surgeons' overwhelming support for increasing Aboriginal Torres Strait Islander outreach services
- Pages: 2395-2396
- First Published: 17 December 2020
Protecting Indigenous Māori in surgical research: a collective stance
- Pages: 2396-2399
- First Published: 17 December 2020
Conducting clinical surgical examinations in Timor-Leste during the COVID-19 global pandemic
- Pages: 2399-2401
- First Published: 17 December 2020
Perioperative thromboprophylaxis is highly variable in general surgery: results from a multicentre survey
- Pages: 2401-2403
- First Published: 17 December 2020
SPECIAL ARTICLES
Artificial intelligence for Australian and New Zealand surgeons: is it time for us to get more involved?
- Pages: 2407-2408
- First Published: 17 December 2020
Part 1: Artificial intelligence technology in surgery
- Pages: 2409-2414
- First Published: 30 September 2020
Artificial intelligence technology in surgery.
Part 2: Blockchain technology in health care
- Pages: 2415-2419
- First Published: 24 November 2020
Blockchain technology in health care.
REVIEW ARTICLES
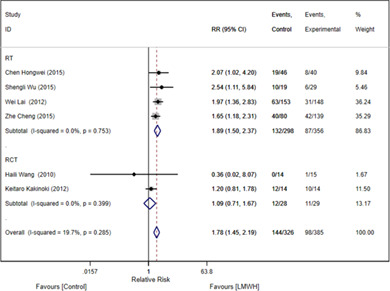
Low-molecular weight heparin prevents portal vein system thrombosis after splenectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 2420-2424
- First Published: 27 April 2020
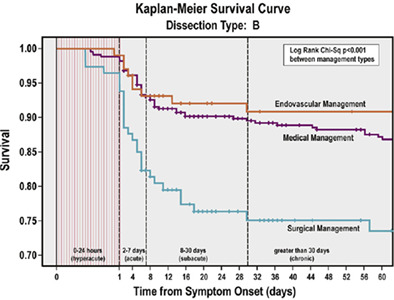
Left heart bypass versus circulatory arrest for open repair of thoracoabdominal aortic pathologies
- Pages: 2434-2440
- First Published: 16 September 2020
Our meta-analysis found equivalent outcomes between left heart bypass and hypothermic circulatory arrest for open repair of thoracic aortic and thoracoabdominal aortic pathologies. Clinical outcomes evaluated were 30-day mortality, post-operative stroke, spinal cord deficit, renal failure and respiratory failure.
GENERAL SURGERY
Variations in practice of thromboprophylaxis across general surgical subspecialties: a multicentre (PROTECTinG) study of elective major surgeries
- Pages: 2441-2448
- First Published: 30 October 2020
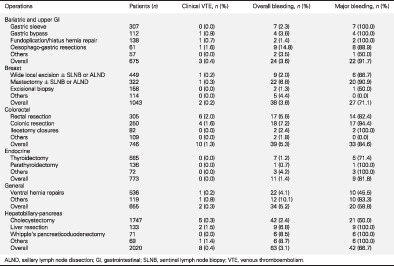
This multicentre study analysed 6628 elective major procedures across all general surgical specialties. Significant variations in practice of perioperative thromboprophylaxis were identified. These included: (i) use of chemoprophylaxis, (ii) timing of its initiation, (iii) type of anticoagulant administered and (iv) application of extended chemoprophylaxis. These variations were seen within the same procedure, and between different surgeries and subspecialties. The inherent bleeding and venous thromboembolism risks of common procedures are also described. Our findings enable surgeons to compare their practices, and provide baseline data to inform efforts towards optimizing thromboprophylaxis for general surgical patients.
Pre-operative and intra-operative chemical thromboprophylaxis increases bleeding risk following elective cholecystectomy: a multicentre (PROTECTinG) study
- Pages: 2449-2455
- First Published: 09 June 2020
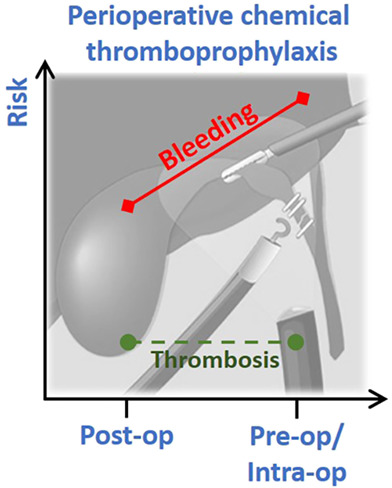
PROTECTinG (Perioperative Timing of Elective Chemical Thromboprophylaxis in General surgery) is a multicentre cohort study which has demonstrated that perioperative chemical thromboprophylaxis usage is variable among patients undergoing elective cholecystectomy. The rate of clinical venous thromboembolism post-cholecystectomy is low. Early chemoprophylaxis increases bleeding risk without an appreciable additional protection from venous thromboembolism.
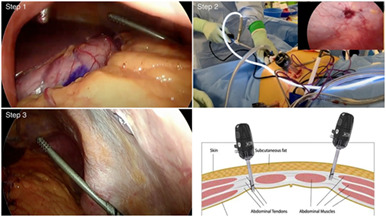
The Abdominal Re-Approximation Anchor device (ABRA®) has the potential to be useful in both emergency and elective dynamic temporary fascial closure
- Pages: 2456-2462
- First Published: 05 October 2020
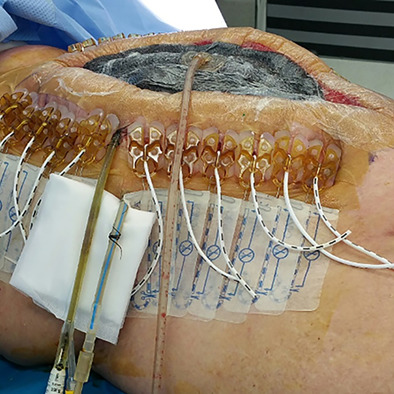
The management of an open abdomen in critically ill patients remains an evolving field because of its relative rarity. We describe our experience with the Abdominal Re-approximation Anchor device in the emergency and elective setting at a tertiary hospital in Queensland, Australia. Primary fascial closure was achieved in 100% of patients demonstrating that the Abdominal Re-approximation Anchor device is an important tool for the general surgeon in managing these complex cases.
Peritonitis-associated hyperlactatemia for evaluating mortality in secondary peritonitis
- Pages: 2463-2466
- First Published: 09 September 2020
HEPATOPANCREATICOBILIARY SURGERY
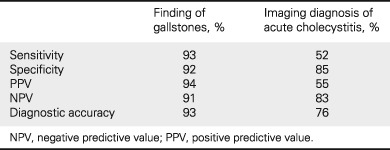
Bedside ultrasonography for acute gallstone disease: a diagnostic accuracy study of surgical registrars and emergency medicine physicians
- Pages: 2467-2471
- First Published: 31 July 2020
Retrorenal fat predicts grade C pancreatic fistula after pancreaticoduodenectomy
- Pages: 2472-2477
- First Published: 20 July 2020
Prediction of the most severe form of postoperative pancreatic fistula is crucial for successful management of patients who are to undergo cephalic pancreatoduodenectomy. Measurement of retrorenal fat tissue thickness is a simple measure that may help to predict the most severe grade of pancreatic fistula after pancreaticoduodenectomy.
COLORECTAL SURGERY
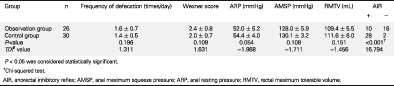
Study of anorectal dynamics in patients undergoing laparoscopic ultra-low resection and transanal intersphincteric resection for rectal cancer
- Pages: 2478-2483
- First Published: 21 June 2020
Increasing rate of colorectal cancer in younger patients: a review of colonoscopy findings in patients under 50 at a tertiary institution
- Pages: 2484-2489
- First Published: 08 June 2020
In Australia, colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most common cancer and the second leading cause of cancer death. Recent Australian and International studies have shown an increase in CRC incidence in patients under 50 years of age. The main aim of this study was to analyse the incidence of CRC in patients under 50 in our facility and in doing so, determine if CRC screening would have been beneficial in this population.
Factors influencing recurrence of stage I–III rectal cancer in regional Australia
- Pages: 2490-2495
- First Published: 30 July 2020
VASCULAR SURGERY
Reconstruction of the aorto-iliac segment in occlusive disease using the AFX unibody graft
- Pages: 2496-2501
- First Published: 23 August 2020
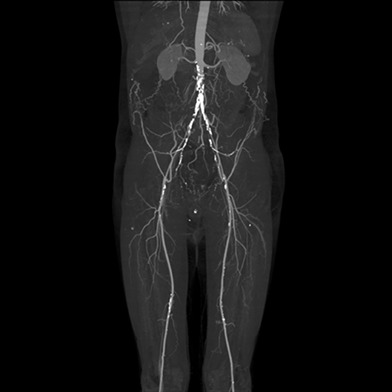
This article describes a novel technique using the AFX stent to treat the aortic bifurcation with occlusive atherosclerotic disease. It is the largest single-centre case series published to date. The minimally invasive technique preserves a future cross-over approach and is a safe and durable method for the treatment of aorto-iliac occlusive disease.
Ureteric complications and left retroperitoneal abdominal aortic surgery
- Pages: 2502-2505
- First Published: 09 September 2020
Patterns of arterial involvement and feasibility of revascularization in thromboangiitis obliterans: a tertiary care centre experience
- Pages: 2506-2509
- First Published: 11 November 2020

Thromboangiitis obliterans typically affects the medium- and small-sized extremity vessels, making arterial revascularization difficult. However, in this study involving 83 patients with thromboangiitis obliterans who underwent angiography, 79.5% of patients had at least one or more target artery feasible for revascularization. The patients who underwent revascularization had a patency rate of 64.8% and limb salvage rate of 80.9%.
BREAST SURGERY
Sentinel node occult lesion localization technique for impalpable breast cancer
- Pages: 2510-2515
- First Published: 30 October 2020

This study demonstrates the performance characteristics and efficiency of the sentinel node and occult lesion localization technique in localizing non-palpable breast cancer and successful identification and removal of sentinel nodes. The results are compared to the literature for wire-guided localization techniques, the most common form of lesion localization.
Breast cancer subtypes in Australian Chinese women
- Pages: 2516-2520
- First Published: 15 September 2020
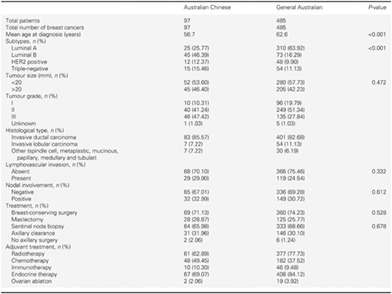
It has been suggested that Chinese patients with breast cancer present at a younger age compared to the general Australian population, with tumour pathological characteristics that carry less favourable outcomes. This study was aimed to investigate if a substantial difference in breast cancer subtypes exists between the Australian Chinese population and the general Australian population.
B3 lesion upgrade rates in a tertiary Australian breast centre: a 8-year experience (2012–2019)
- Pages: 2521-2526
- First Published: 23 September 2020
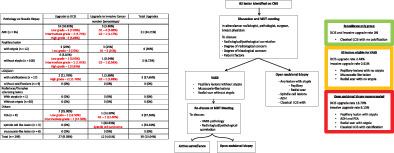
Vacuum-assisted excisional biopsy may be appropriate for low malignant risk lesions, such as papillary lesion without atypia, mucocoele-like lesion and radial scar lesion without atypia. Open-surgical-excisional biopsy remains essential for high upgrade lesions such as flat epithelial atypia, atypical ductal hyperplasia, papillary lesion with atypia and classical lobular carcinoma in situ with calcification.
OTOLARYNGOLOGY HEAD AND NECK SURGERY
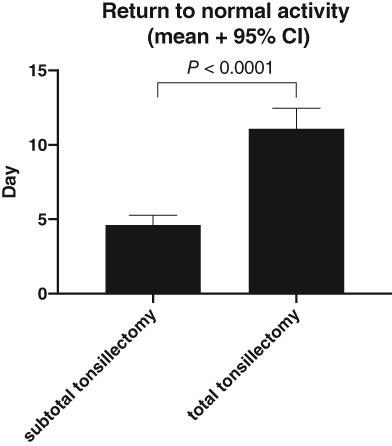
Paediatric patient bleeding and pain outcomes following subtotal (tonsillotomy) and total tonsillectomy: a 10-year consecutive, single surgeon series
- Pages: 2532-2536
- First Published: 23 September 2020
Nodal metastasis size predicts disease-free survival in cutaneous head and neck squamous cell carcinoma involving the parotid but not cervical nodes
- Pages: 2537-2542
- First Published: 11 November 2020
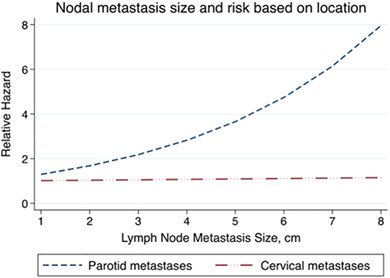
Nodal metastatic size significantly predicts disease-free survival on multivariate analysis, with the prognostic impact predominantly occurring in parotid metastases. Each 1 cm increase in the size of nodal metastasis increased the risk of recurrence or death by 27%. Parotid nodal metastasis size thresholds of <3, 3–4.5 and > 4.5 cm optimized prognostic discrimination.
ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY
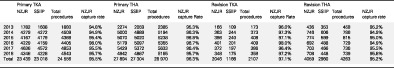
Completeness and capture rate of publicly funded arthroplasty procedures in the New Zealand Joint Registry
- Pages: 2543-2548
- First Published: 02 November 2020
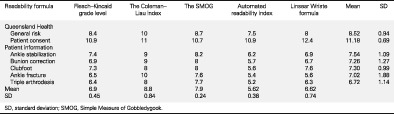
Readability of foot and ankle consent forms in Queensland
- Pages: 2549-2552
- First Published: 05 October 2020
Clinical, radiological and pathological outcomes following treatment of primary giant cell tumour of bone with Denosumab
- Pages: 2553-2558
- First Published: 06 August 2020
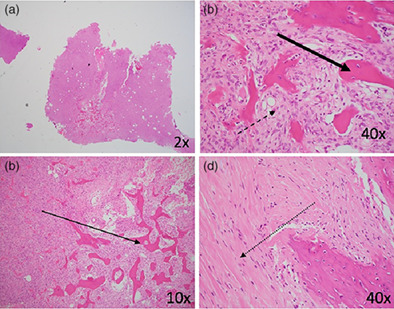
We investigated the use of Denosumab in the treatment of primary giant cell tumour of bone. Denosumab has been an increasingly utilized treatment option in managing giant cell tumour of bone. However, much is still unknown about its current indications, long-term effects and the potential risk for rapid relapse and sarcomatous transformation. In this manuscript, we highlight the clinical, radiological and pathological outcomes following treatment with Denosumab and of concern we noted a trend towards increasing recurrence rates with the potential risk for rapid relapse and sarcomatous transformation.
HOW TO DO IT
How to minimize airborne droplet contamination while performing laparoscopy in the COVID-19 era
- Pages: 2559-2560
- First Published: 06 October 2020
How to do safe intracorporeal marking of structures during minimally invasive surgery by simple modification of a skin marking pen
- Pages: 2561-2562
- First Published: 22 September 2020
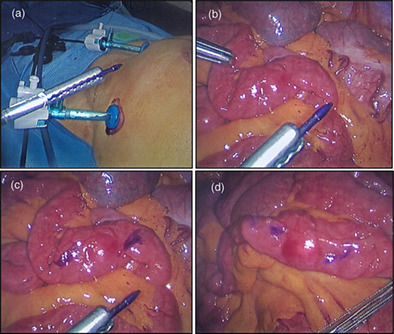
This study describes how to do safe intracorporeal marking of structures during minimally invasive surgery by simple modification of a skin marking pen. We wish to publicize the use of a skin marking pen tip held within laparoscopic graspers as an effective, simple and cheap method to mark intracorporeal structures, avoiding tissue damage.
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS FOR SURGEONS
Surgeons and cultural safety and cultural competency: the road to transformation
- Pages: 2563-2566
- First Published: 08 October 2020
IMAGES FOR SURGEONS
Spinal subdural, extra-arachnoid hygroma following lumbar decompression: a rare case following cauda equina syndrome
- Pages: 2567-2569
- First Published: 27 April 2020
Isolated thenar muscle wasting secondary to anomalous course of recurrent median nerve branch posterior to flexor pollicis longus tendon
- Pages: 2569-2571
- First Published: 14 May 2020
Case of ureterosciatic hernia managed by laparoscopic repair
- Pages: 2571-2573
- First Published: 30 April 2020
Per-rectal passage of intestinal cast: an unusual complication of pseudomembranous enterocolitis in an immunocompromised patient and literature review
- Pages: 2574-2576
- First Published: 04 May 2020
Intestinal schistosomiasis mimicking caecal malignancy
- Pages: 2576-2577
- First Published: 21 May 2020
Intermittent caecal volvulus: a rare cause of right iliac fossa pain in patients with previous right oophorectomy
- Pages: 2577-2579
- First Published: 30 April 2020
Endoscopic retrieval of an impacted chicken bone in a sigmoid diverticulum
- Pages: 2579-2581
- First Published: 02 May 2020
Synchronous small bowel neuroendocrine tumour and lymphoma in a centenarian
- Pages: 2581-2583
- First Published: 02 May 2020
Sexually transmitted infective vasitis mimicking left inguinal hernia: computed tomography clarifies diagnosis
- Pages: 2583-2584
- First Published: 05 May 2020
Subcutaneous cervicofacial emphysema following thyroid surgery
- Pages: 2584-2586
- First Published: 13 May 2020
Beware of the acute bowel disease in COVID-19 patients
- Pages: 2586-2588
- First Published: 03 October 2020
COVID-19 pandemic consciousness: droplet contamination and aerosolization during pleural decompression
- Pages: 2588-2591
- First Published: 08 October 2020
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
Comparison of three-dimensional and 4K imaging systems in novice surgeons: a cross-over study
- Page: 2592
- First Published: 17 December 2020
Doctor-in-training delivered telehealth consultations, a safe and supported environment for clinical education
- Pages: 2592-2593
- First Published: 29 July 2020
Re: How to deal with complex anal fistula in an immunosuppressed patient
- Page: 2593
- First Published: 17 December 2020
HEPATOPANCREATICOBILIARY SURGERY
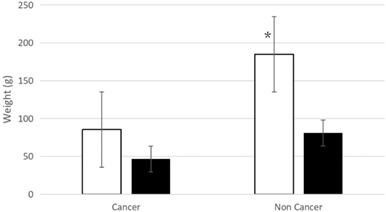
Application of a preoperative image scoring system in laparoscopic spleen-preserving distal pancreatectomy
- Pages: E143-E147
- First Published: 28 September 2020
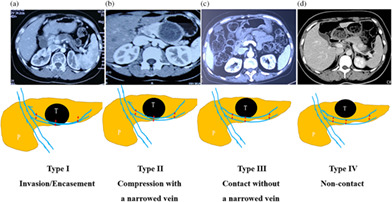
The article proposes an image classification with four types according to the relationship between a tumor and the splenic vein. We establish a scoring system by combining two parameters (that are the image classification and tumor size), which are helpful in making a spleen-preservation strategy during laparoscopic spleen preserving distal pancreatectomy.
Clinical features and outcomes of endovascular treatment of latent pseudoaneurysmal bleeding after pancreaticoduodenectomy
- Pages: E148-E153
- First Published: 06 August 2020
This study aimed to evaluate the clinical features and outcomes of patients who experienced PA bleeding after pancreaticoduodenectomy. In patients with suspected PA, urgent angiography should be considered immediately for diagnosis and treatment. The stent-graft placement can be performed first if it is technically feasible in PA bleeding. However, TAE is also a safe and effective treatment in patient intact portal flow, as well as those who do not have disrupted collateral pathways because of previous surgery, such as hepatectomy.
COLORECTAL SURGERY
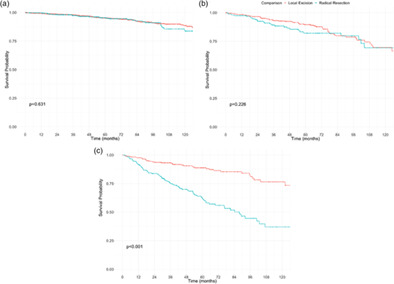
Local excision versus radical resection in patients with rectal neuroendocrine tumours: a propensity score match analysis
- Pages: E154-E162
- First Published: 17 August 2020
Random colonic biopsies in macroscopically normal colonoscopies: is there any benefit? A two-centre audit of current practice
- Pages: E163-E167
- First Published: 28 August 2020
Routine performance of random colonic biopsies should be questioned. These should be performed in selected patients only with a high degree of suspicion of an organic cause of their chronic non-bloody watery diarrhoea as they otherwise have low yield and are of significant cost. All random colonic biopsies should be placed in one specimen pot when submitted for histopathology analysis as a cost saving measure.
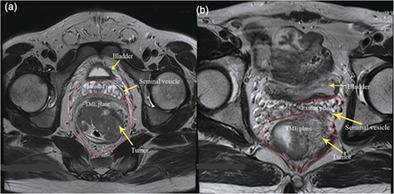
Laparoscopic total mesorectal excision combined with en-bloc seminal vesicle and prostate resection for rectal cancer after chemoradiotherapy
- Pages: E168-E171
- First Published: 28 August 2020
ENDOCRINE SURGERY
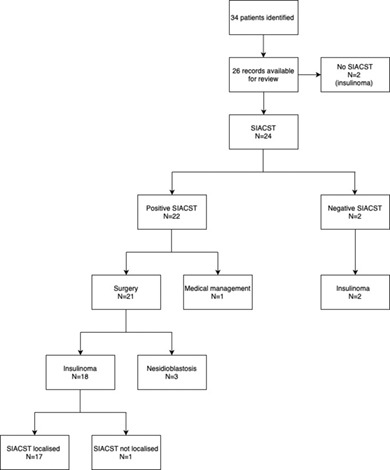
Selective intra-arterial calcium stimulation test for the localization of insulinomas: an Australian hospital experience
- Pages: E172-E176
- First Published: 01 May 2020
How does thyroidectomy for benign thyroid disease impact upon quality of life? A prospective study
- Pages: E177-E182
- First Published: 25 September 2020
IMAGES FOR SURGEONS
Subglottic plasma cell mucositis: a case study highlighting challenge in management
- Pages: E183-E185
- First Published: 17 May 2020
Atypical mesenteroaxial gastric volvulus with wandering spleen as a late complication of vagotomy and pyloromyotomy for peptic duodenal ulcer
- Pages: E186-E187
- First Published: 05 May 2020
Primary cavernous haemangioma of the thyroid: a rare pathology
- Pages: E188-E190
- First Published: 09 May 2020
Avulsive radiocarpal subluxation treated successfully with reduction and percutaneous fixation: a case report
- Pages: E191-E192
- First Published: 21 May 2020
Importance of perioperative planning in an impalement injury of neck highlighted by an aberrant right subclavian artery
- Pages: E193-E195
- First Published: 07 July 2020
Case report: splenic flexure mobilization from the retro-pancreatic space
- Pages: E196-E197
- First Published: 23 May 2020
Toxic megacolon due to Salmonella acute infectious colitis requiring total colectomy following loop ileostomy closure
- Pages: E200-E201
- First Published: 12 May 2020
Unexpected cause of acute abdomen in a young healthy woman: the stercoral perforation
- Pages: E202-E203
- First Published: 21 May 2020
Colon cancer or is it?: a fortunate aetiology for a caecal mass
- Pages: E206-E207
- First Published: 21 May 2020
Intragastric balloon inside a Meckel's diverticulum: a rare cause of small bowel obstruction
- Pages: E210-E211
- First Published: 21 May 2020
Unusual case of extensive leg ulceration following ultrasound-guided foam sclerotherapy
- Pages: E212-E214
- First Published: 12 May 2020
Jumping the gun: traumatic splenosis mimicking 68-gallium-dotatate avid neuroendocrine tumour
- Pages: E217-E218
- First Published: 30 May 2020
Plug mesh repair of rare prevascular femoral hernia: a case report
- Pages: E219-E220
- First Published: 17 May 2020
Splenohepatic sarcoidosis 12 years after breast cancer curative surgery: a diagnostic dilemma in imaging
- Pages: E221-E222
- First Published: 03 June 2020
Case of proximal small bowel obstruction: is it the motility or the chewing?
- Pages: E223-E224
- First Published: 07 June 2020
Lessons learnt from a rare case of splenic ectopic pregnancy
- Pages: E225-E227
- First Published: 17 July 2020