Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture: Macromol. Mater. Eng. 11/2015
- Page: 1037
- First Published: 03 November 2015
Front Cover: Triethoxysilyl-terminated poly(D-lactide)s (eSi-PDLA) is incorporated into poly(L-lactide acid) (PLLA) to undergo stereocomplexation followed by terminal hyper-conjugation. Its blend morphology (right) is found to be different from the one (left) formed from the similar blend of PLLA and trimethoxysilyl-terminated PDLA (mSi-PDLA) showing higher hydrolyzability. Further details can be found in the article by Y. Kimura and co-workers on page 1123.
Masthead
Masthead: Macromol. Mater. Eng. 11/2015
- Page: 1038
- First Published: 03 November 2015
Contents
Contents: Macromol. Mater. Eng. 11/2015
- Pages: 1039-1042
- First Published: 03 November 2015
Communications
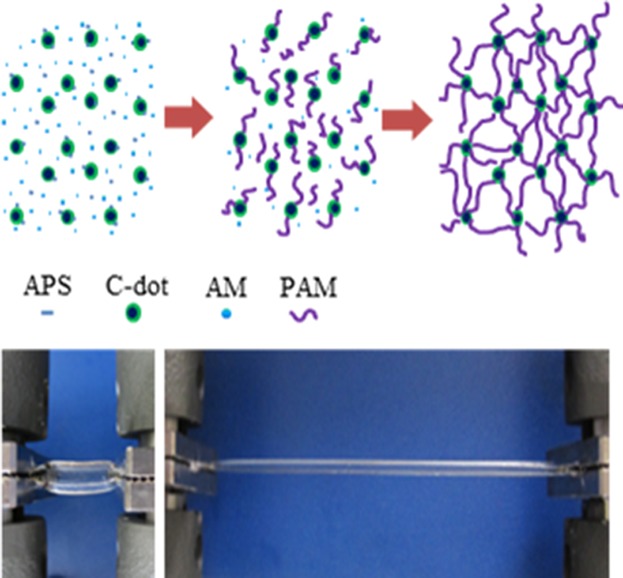
Novel Nanocomposite Hydrogels Consisting of C-Dots with Excellent Mechanical Properties
- Pages: 1043-1048
- First Published: 27 May 2015
Core-Shell Hybrid Particles by Alternating Copolymerization of Ionic Liquid Monomers from Silica as Sorbent for Solid Phase Microextraction
- Pages: 1049-1056
- First Published: 05 June 2015
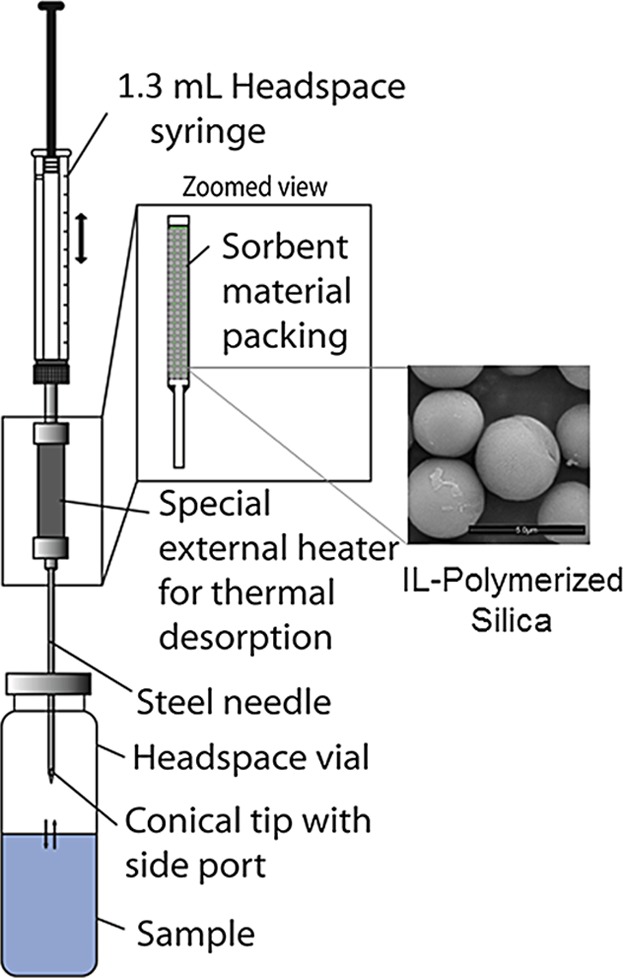
Multifunctional core-shell hybrid particles is prepared by alternating copolymerization of cationic and anionic monomers from silica for solid phase microextraction devices. The material demonstrates excellent extraction efficiency for low molecular weight polar compounds selected as probe compounds (derivatized aldehydes and alcohols).
Adhesion Tuning at Superhydrophobic States: From Petal Effect to Lotus Effect
- Pages: 1057-1062
- First Published: 26 June 2015
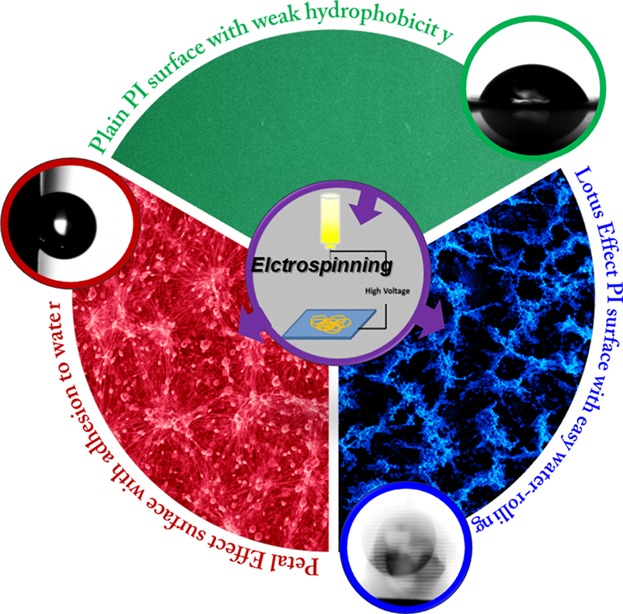
Polyimide with weak hydrophobicity is modified into superhydrophobic surfaces via electrospinning. At superhydrophobic state, high-low adhesions are adjusted by further morphology control and Petal Effect is converted to Lotus Effect. Such non-chemically involved wetting conversion is achieved for the first time.
Full Papers
Aging and Degradation of LDPE by Compact NMR
- Pages: 1063-1070
- First Published: 07 July 2015
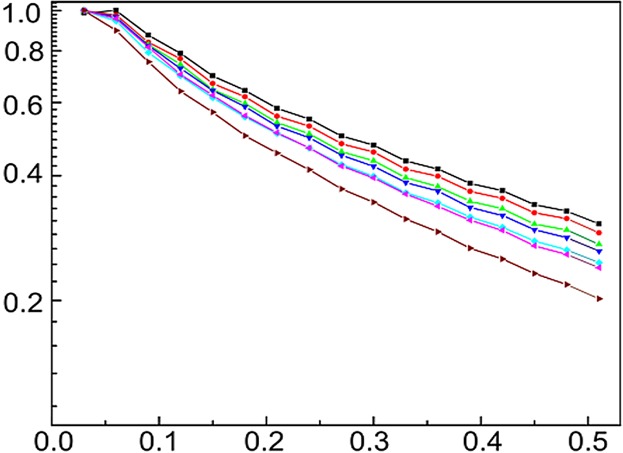
Compact NMR can be a valuable device to monitor the quality of raw and intermediate products in chemical plants. In this framework, NMR relaxation measurements are employed to follow thermally induced crystallization and chemical degradation of polyethylene pellets in a quantitative manner by measuring variations in chain dynamics of LDPE domains under accelerated aging conditions.
An Exploratory Microfluidic Approach to Photopolymerized Polymer-Inorganic Nanocomposite Films
- Pages: 1071-1078
- First Published: 20 August 2015
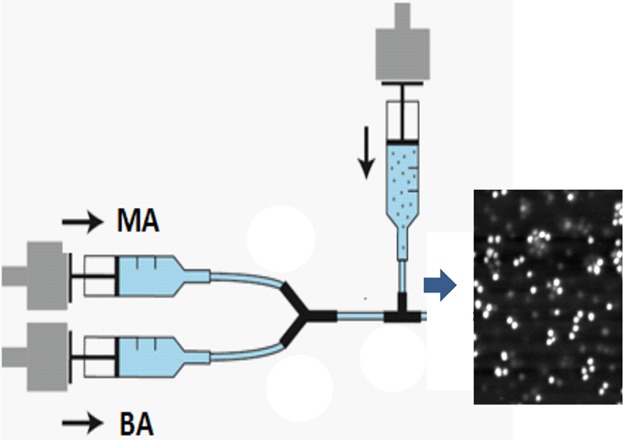
An exploratory microfluidic platform for producing photopolymerized nanocomposite films from dispersions of nanoparticles in monomer mixtures is developed. The platform enables rapid, accurate, and reproducible preparation of films with varying compositions by tuning the flow rates of precursor comonomers and nanoparticle–monomer mixtures. The platform offers a very efficient way to study composition-dependent structure–property relationships in multicomponent multiphase materials.
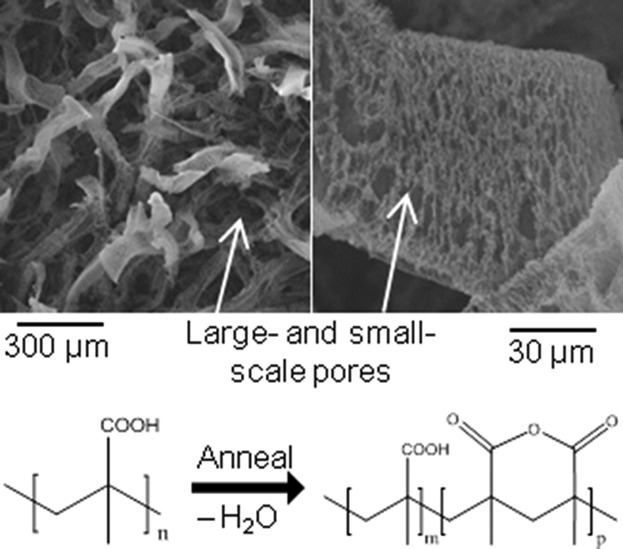
All-Dry Fabrication of Poly(methacrylic acid)-Based Membranes with Controlled Dissolution Behavior
- Pages: 1079-1084
- First Published: 15 May 2015
Electrospun Fibers Containing Bio-Based Ricinoleic Acid: Effect of Amount and Distribution of Ricinoleic Acid Unit on Antibacterial Properties
- Pages: 1085-1095
- First Published: 16 June 2015
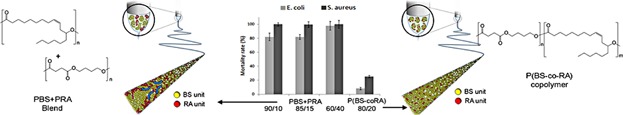
Blends of poly(ricinoleic acid) (PRA) and poly(butylene succinate) (PBS) and a random copolymer of RA and BS units are processed through electrospinning to obtain new bio-based, biodegradable and antibacterial membranes. Phase separation, induced by electrospinning in the blends, enriches the fiber surface with biocidal RA units and the blend exhibits higher antibacterial activity with respect to the copolymer having the same composition.
Preparation of High Performance Copolyimide Fibers via Increasing Draw Ratios
- Pages: 1096-1107
- First Published: 13 June 2015
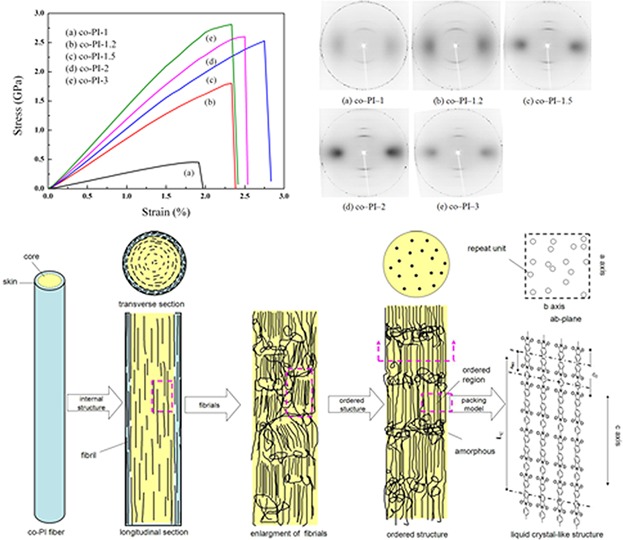
Two-dimensional wide-angle X-ray diffraction (2D WAXD) results show that the molecular orientation of the co-PI fibers along the fiber direction is developed as the draw ratio increased. When the fibers are treated at high draw ratios, the molecule chain is stretched and aligned closely, just as the “smectic A liquid crystal-like” structure, which is orientationally and positionally ordered.
Nanoscale Bumps and Dents on Nanofibers Enabling Sonication-Responsive Wetting and Improved Moisture Collection
- Pages: 1108-1115
- First Published: 18 June 2015
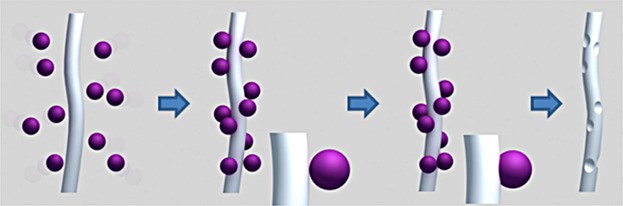
The formation of clinging nanoparticles half-embedded onto the surfaces of nanofibers and the introduction of nano-craters onto the surfaces were developed for the first time. These unique surface nanoengineering techniques offer the possibility to tailor the properties of nanofibers one degree further from conventional electrospun fibers.
One-Pot, One-Step Strategy for the Preparation of Clickable Melamine Based Microporous Organic Polymer Network
- Pages: 1116-1122
- First Published: 17 June 2015

A clickable MOP with high surface area is synthesized in one-pot and one-step polymerization process using melamine and independently prepared propargyl anthracene selecting as nitrogen source and carbonyl monomer, respectively. As a model reaction, the feasibility of the click coupling on the acetylene containing MOP is demonstrated using independently prepared fluorescent azido-pyrene.
Competitive Effects of Stereocomplexation and Hyper-Conjugation of Triethoxysilyl-Terminated Poly(d-lactide) in Poly(l-lactide) matrices
- Pages: 1123-1132
- First Published: 29 June 2015

Triethoxysilyl-terminated PDLA (eSi-PDLA) is blended with PLLA to undergo terminal hyper-conjugation through hydrolytic polycondensation of the silyl functionalities and stereo complexation with the matrix. The morphology is found to be different from the one formed from the similar blend of PLLA and trimethoxysilyl-terminated PDLA (mSi-PDLA).
Quantitative Correlation Between Cross-Linking Degrees and Mechanical Properties of Protein Films Modified With Polycarboxylic Acids
- Pages: 1133-1140
- First Published: 03 August 2015
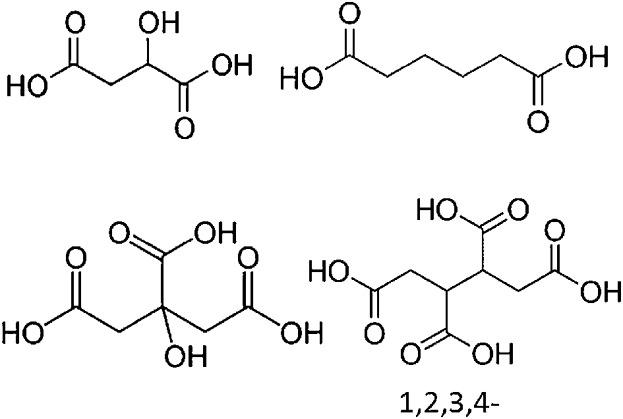
Cross-linking reaction between gliadin, a wheat protein, and polycarboxylic acids is verified via quantification of changes in amine and carboxylic groups in gliadin before and after cross-linking. For the first time, mechanical properties of cross-linked proteinous products are quantitatively correlated with cross-linking degrees and molecular structures of polycarboxylic acids.
A New High Sensitivity System to Detect Instabilities During the Extrusion of Polymer Melts
- Pages: 1141-1152
- First Published: 20 August 2015

A novel high sensitivity instability detection die for a laboratory size extruder is presented. The high sensitivity detection system consists of piezoelectric transducers placed along the die length to monitor local pressure fluctuations, having remarkable temporal and pressure resolutions. The system is tested on short chain branched polyethylenes, namely on the detection and characterization of the sharkskin instability.
Structure–Properties Relationships in Thermoplastic Polyurethane Elastomer Nanocomposites: Interactions between Polymer Phases and Nanofillers
- Pages: 1153-1162
- First Published: 19 August 2015
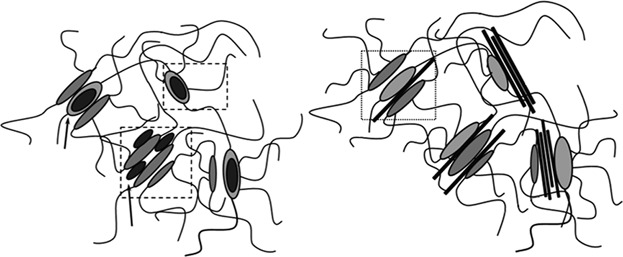
Well-dispersed nanofillers led to enhanced TPU properties. Enhanced modulus, sustained stress levels and deformation capabilities. The nanofiller particles influence the polymer chain mobility and crystallization behavior upon cooling, mainly at the HS rich phase. The developed polymer morphology plays a key role in final assessed properties.