Core-Shell Hybrid Particles by Alternating Copolymerization of Ionic Liquid Monomers from Silica as Sorbent for Solid Phase Microextraction
Corresponding Author
Mohammed Mizanur Rahman
Instrumental Analytical Chemistry, University Duisburg-Essen, Essen 45141, Germany
Applied Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, University of Dhaka, Dhaka 1000, Bangladesh
Search for more papers by this authorXochitli L. Osorio Barajas
Instrumental Analytical Chemistry, University Duisburg-Essen, Essen 45141, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorJacobo L. Hermosillo Luján
Instrumental Analytical Chemistry, University Duisburg-Essen, Essen 45141, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorMaik A. Jochmann
Instrumental Analytical Chemistry, University Duisburg-Essen, Essen 45141, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorChristian Mayer
Instrumental Analytical Chemistry, University Duisburg-Essen, Essen 45141, Germany
Department of Chemistry and Center for Nanointegration Duisburg-Essen (CeNIDE), University Duisburg-Essen, Essen 45141, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Torsten C. Schmidt
Instrumental Analytical Chemistry, University Duisburg-Essen, Essen 45141, Germany
Centre for Water and Environmental Research (ZWU), University Duisburg-Essen, Essen 45141, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Mohammed Mizanur Rahman
Instrumental Analytical Chemistry, University Duisburg-Essen, Essen 45141, Germany
Applied Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, University of Dhaka, Dhaka 1000, Bangladesh
Search for more papers by this authorXochitli L. Osorio Barajas
Instrumental Analytical Chemistry, University Duisburg-Essen, Essen 45141, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorJacobo L. Hermosillo Luján
Instrumental Analytical Chemistry, University Duisburg-Essen, Essen 45141, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorMaik A. Jochmann
Instrumental Analytical Chemistry, University Duisburg-Essen, Essen 45141, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorChristian Mayer
Instrumental Analytical Chemistry, University Duisburg-Essen, Essen 45141, Germany
Department of Chemistry and Center for Nanointegration Duisburg-Essen (CeNIDE), University Duisburg-Essen, Essen 45141, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Torsten C. Schmidt
Instrumental Analytical Chemistry, University Duisburg-Essen, Essen 45141, Germany
Centre for Water and Environmental Research (ZWU), University Duisburg-Essen, Essen 45141, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
Multifunctional ionic liquid monomer (1) was synthesized from 1-vinylimidazole and 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulphonic acid (AMPS) and alternately copolymerized from 3-mercaptopropyltrimethoxysilane grafted silica core (2) to obtain hybrid core-shell particles Sil-PIL.1. Elemental analysis and 13C CP/MAS results confirmed that the ionic monomers retained the alternation after grafting on silica surface, which make it a promising candidate as sorbent for trapping analytes from aqueous and other samples for solventless microextraction processes. The material demonstrated excellent extraction efficiency for low molecular weight polar compounds and the peak areas for derivatized aldehydes can be increased up to 200 times in comparison with a commercial polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) sorbent. 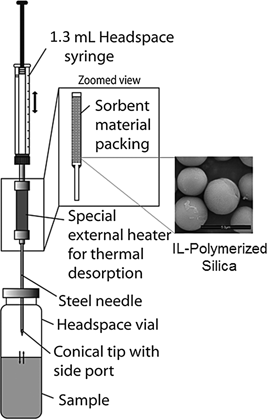
References
- 1 C. L. Arthur, J. Pawliszyn, Anal. Chem. 1990, 62, 2145.
- 2 Z. Zhang, J. Pawliszyn, Anal. Chem. 1993, 65, 1843.
- 3 Z. Zhang, M. J. Yang, J. Pawliszyn, Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 844A.
- 4 J. G. Huddleston, A. E. Visser, W. M. Reichert, H. D. Willauer, G. A. Broker, R. D. Rogers, Green Chem. 2001, 3, 156.
- 5 R. Sheldon, Chem. Commun. 2001, 2399.
- 6 J.-F. Liu, G.-B. Jiang, Y.-G. Chi, Y.-Q. Cai, Q.-X. Zhou, J.-T. Hu, Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 5870.
- 7 L. Vidal, E. Psillakis, C. E. Domini, N. Grané, F. Marken, A. Canals, Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 584, 189.
- 8 V. Pino, J. L. Anderson, J. H. Ayala, V. González, A. M. Afonso, J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1182, 145.
- 9 J.-H. Wang, D.-H. Cheng, X.-W. Chen, Z. Du, Z.-L. Fang, Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 620.
- 10 T. Welton, Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2071.
- 11 Y. Meng, V. Pino, J. L. Anderson, Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 7107.
- 12 J.-F. Liu, N. Li, G.-B. Jiang, J.-M. Liu, J. Ã. k. JÃnsson, M.-J. Wen, J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1066, 27.
- 13 M. A. Jochmann, X. Yuan, B. Schilling, T. C. Schmidt, J. Chromatogr A 2008, 1179, 96.
- 14 J. Laaks, M. A. Jochmann, B. Schilling, T. C. Schmidt, Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 7641.
- 15 J. Laaks, M. A. Jochmann, T. C. Schmidt, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 565.
- 16 C. L. Arthur, L. M. Killam, K. D. Buchholz, J. Pawliszyn, J. R. Berg, Anal. Chem. 1992, 64, 1960.
- 17 K. D. Buchholz, J. Pawliszyn, Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 160.
- 18 H. Qiu, A. K. Mallik, T. Sawada, M. Takafuji, H. Ihara, Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 1299.
- 19 H. Qiu, A. K. Mallik, M. Takafuji, X. Liu, S. Jiang, H. Ihara, Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 738, 95.
- 20 T. Luan, S. Fang, Y. Zhong, L. Lin, S. Chan, C. Lan, N. F. Tam, J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1173, 37.
- 21 Y. Meng, V. Pino, J. L. Anderson, Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 687, 141.
- 22 M. Yoshizawa, W. Ogihara, H. Ohno, Polym. Adv. Technol. 2002, 13, 589.
- 23 B. Cancho, F. Ventura, M. T. Galceran, J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 943, 1.
- 24 M. Sun, J. Feng, S. Liu, X. Wang, X. Liu, S. Jiang, J. Sep. Sci. 2011, 34, 1149.
- 25 M. Sun, H. Qiu, L. Wang, X. Liu, S. Jiang, J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 3904.
- 26 M. Chaimberg, R. Parnas, Y. Cohen, J. App. Polym. Sci. 1989, 37, 2921.
- 27 S. Xiao, X. Lu, Q. Lu, Macromolecules 2007, 40, 7944.
- 28 M. M. Rahman, M. Takafuji, H. Ihara, J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1203, 59.
- 29 A. K. Mallik, T. Sawada, M. Takafuji, H. Ihara, Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 3320.
- 30 M. Hanson, B. Eray, K. Unger, A. V. Neimark, J. Schmid, K. Albert, E. Bayer, Chromatographia 1993, 35, 403.
- 31 M. Pursch, L. C. Sander, K. Albert, Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 4107.




