Competitive Effects of Stereocomplexation and Hyper-Conjugation of Triethoxysilyl-Terminated Poly(d-lactide) in Poly(l-lactide) matrices
Abstract
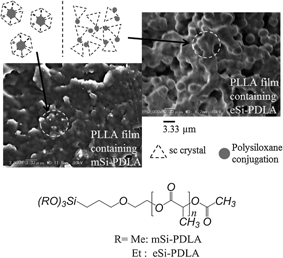
Triethoxysilyl-terminated poly(d-lactide)s (eSi-PDLA) were successfully prepared by hydrosilylation of allyl-terminated PDLAs (A-PDLA-ac) which were readily prepared by ring-opening polymerization of d-lactide and the following terminal protection by acetylation. Their acid-catalyzed hydrolysis produced hyper-conjugated PDLAs with terminal silanol coupling. Blend PLLA films containing eSi-PDLA (Mn = 2.1 kDa) in 5-25 wt.% were successfully prepared by the solution casting method. The blend films were found to take a nano-porous or micro-phase separation structure, being different from that of the blend PLLA films containing trimethoxysilyl-terminated poly(d-lactide) (mSi-PDLA) which exhibited particle distribution structure. This difference was reasonably attributed to the different rate of hydrolytic polycondensation of the trimethoxy- and triethoxy-silyl terminals. These results revealed that the competing sterecomplexation/ hyper-conjugation/phase separation can afford specific morphologies, allowing fine control of properties.