Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture: Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2∕2015
- First Published: 06 February 2015

Biobased aromatic polyamines were synthesized by thiol-ene coupling with cysteamine on cardanol, a non-edible by-product of cashew nutshell liquid. The cardanol-derived amines were used as hardeners in biobased epoxy networks. Mechanical and thermal properties of the obtained materials showed that these amines could lead to binders for composite applications. Indeed, this biobased amine reactant bears aromatic rings for interesting properties in formulations and has the advantage to use the unsaturations of the aliphatic chain which prevents the plasticization effect.
Editorial Board
Editorial Board: Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2∕2015
- First Published: 06 February 2015
In this Issue
Contents
Editorial
Fats and oils as renewable feedstock for the chemical industry
- Pages: 133-134
- First Published: 06 February 2015
Dedication
Frank D. Gunstone – Teacher, researcher, and writer
- Pages: 135-140
- First Published: 17 November 2014
Minireview
Microbial oils: A customizable feedstock through metabolic engineering
- Pages: 141-144
- First Published: 08 October 2014
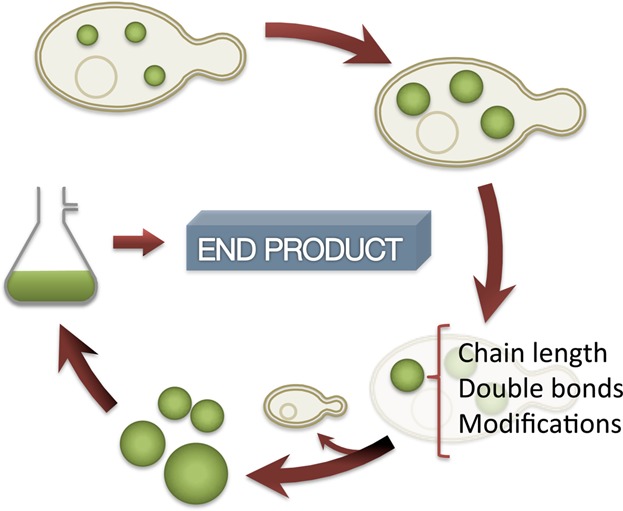
Microbial oils are considered promising alternatives to fossil fuels as feedstock for the chemical industry. Additionally they present advantages over vegetable oils and animal fats since microorganisms can be easily engineered: i) to accumulate high amount of lipids; ii) to be enriched in a desired kind of lipid; and iii) to facilitate the extraction of the oil from the cells. This short article is intended to present the concept of microbial oils to the general reader, taking into special consideration the malleability of microbial oils by metabolic engineering.
Review Article
Enzymatic synthesis and modification of surface-active glycolipids
- Pages: 145-155
- First Published: 20 January 2015
Short Communications
Ethyl rhamnolipids as a renewable source to produce biopolyurethanes
- Pages: 156-160
- First Published: 23 July 2014
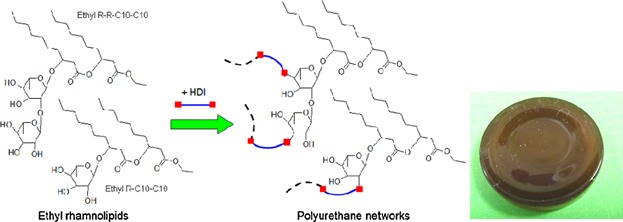
Bio-based polyurethanes were prepared from ethyl rhamnolipids, by reaction with 1,6-hexane diisocyanate (HDI). Rhamnolipids, obtained from fermentation, are an alternative renewable source of reactants for polyurethane production. The unique structure of rhamnolipids may also inspire future synthesis of novel lipid-based polyols.
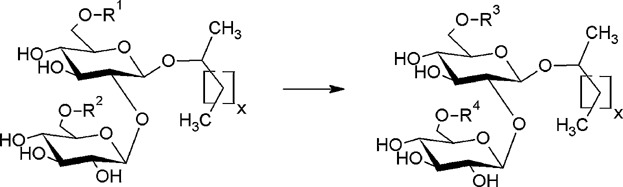
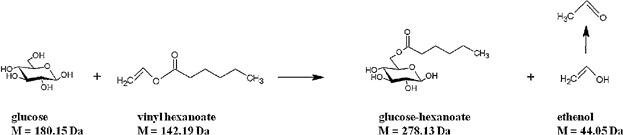
Lipase-catalyzed synthesis of glucose-6-O-hexanoate in deep eutectic solvents
- Pages: 161-166
- First Published: 18 November 2014
Research Articles
Native lipase dissolved in hydrophilic green solvents: A versatile 2-phase reaction system for high yield ester synthesis
- Pages: 167-177
- First Published: 10 December 2014
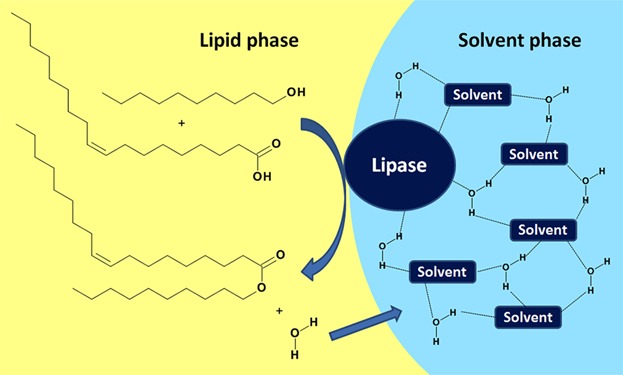
Lipase CalB is dissolved in the hydrophilic phase consisting of a hydrogen bonding network of solvent and water molecules. Lipase catalysis takes place at the solvent/lipid interface and water is adsorbed into the solvent phase, thus shifting the equilibrium towards ester formation in the water-depleted lipid phase.
New aromatic amine based on cardanol giving new biobased epoxy networks with cardanol
- Pages: 178-189
- First Published: 15 September 2014

Biobased aromatic polyamine was synthesized by thiol-ene coupling with cysteamine on cardanol, coming from cashew nut shell liquid (CNSL). Cardanol-derived amine was used as hardener in biobased epoxy networks. Mechanical and thermal properties of obtained materials showed that cardanol-derived amine material could lead to binders for composite application.
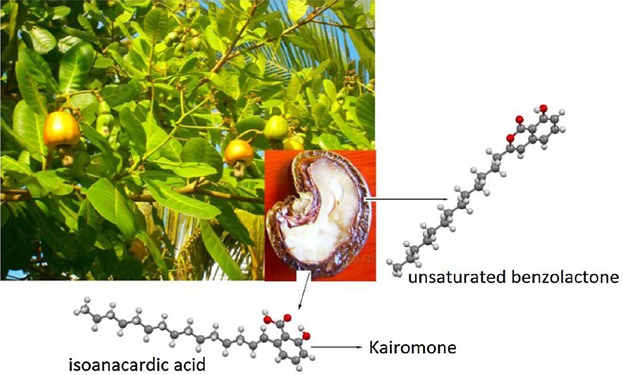
Isomerization of anacardic acid: A possible route to the synthesis of an unsaturated benzolactone and a kairomone
- Pages: 190-199
- First Published: 16 September 2014
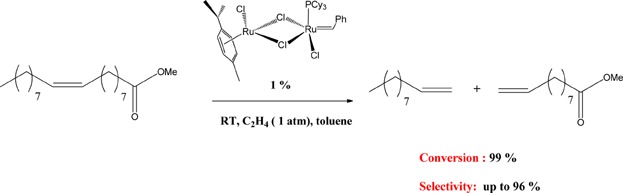
Metathesis reactions of rapeseed oil-derived fatty acid methyl esters induced by monometallic and homobimetallic ruthenium complexes
- Pages: 200-208
- First Published: 03 October 2014
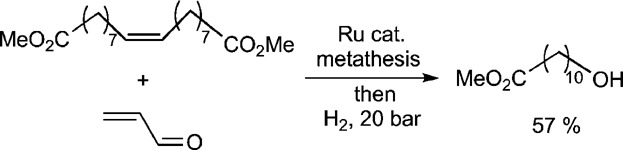
Cross-metathesis of fatty acid methyl esters with acrolein: An entry to a variety of bifunctional compounds
- Pages: 209-216
- First Published: 28 October 2014
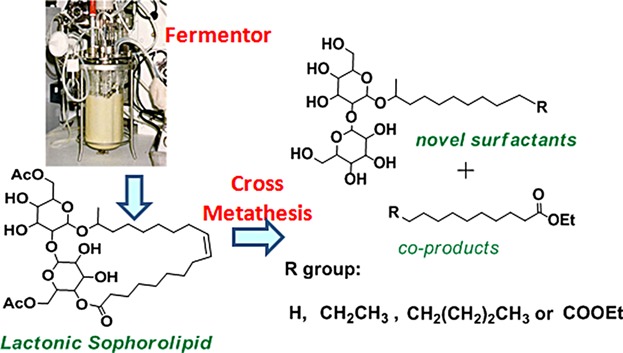
Sophorolipids: Expanding structural diversity by ring-opening cross-metathesis
- Pages: 217-228
- First Published: 19 December 2014
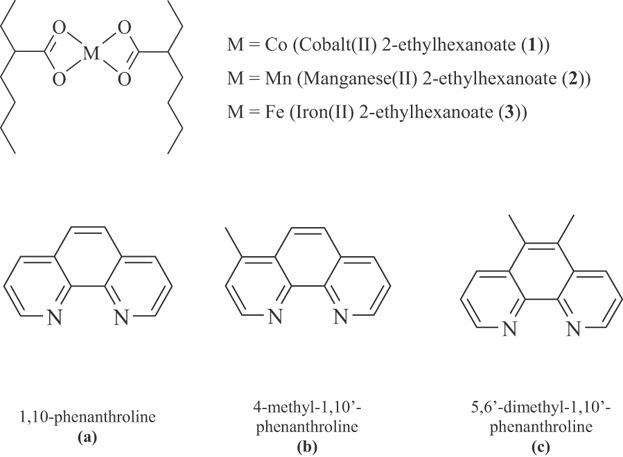
Systematic investigation of the oxidative polymerization of linseed oil catalyzed by Co(II), Mn(II), and Fe(II) complexes with chelating nitrogen ligands
- Pages: 229-234
- First Published: 09 July 2014
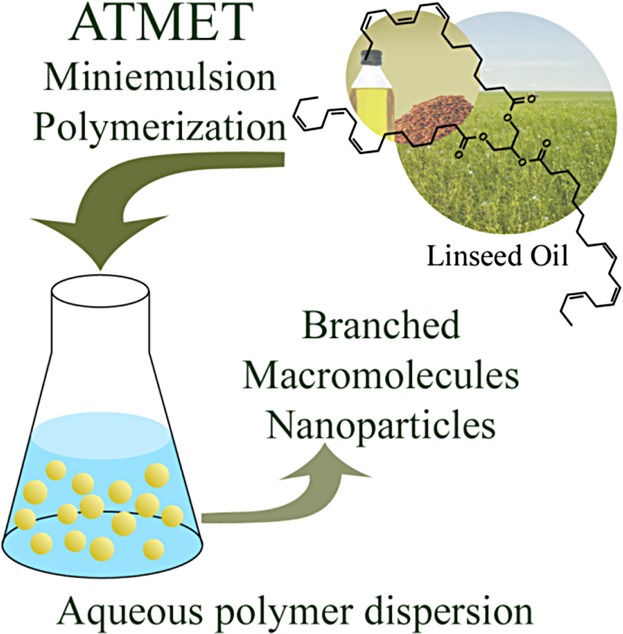
Acyclic triene metathesis (ATMET) miniemulsion polymerization of linseed oil produces polymer nanoparticles with comparable molecular weight to that of bulk reactions
- Pages: 235-241
- First Published: 01 December 2014
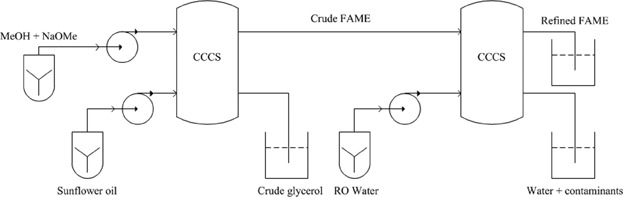
Synthesis and refining of sunflower biodiesel in a cascade of continuous centrifugal contactor separators
- Pages: 242-254
- First Published: 05 August 2014
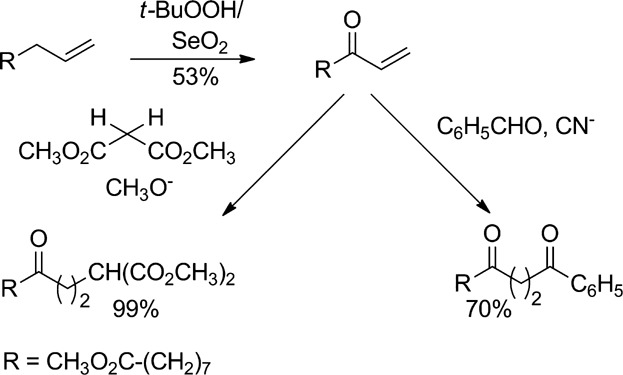
Allylic oxidation of methyl 10-undecenoate and nucleophilic additions to methyl 9-oxo-10-undecenoate
- Pages: 255-265
- First Published: 22 December 2014
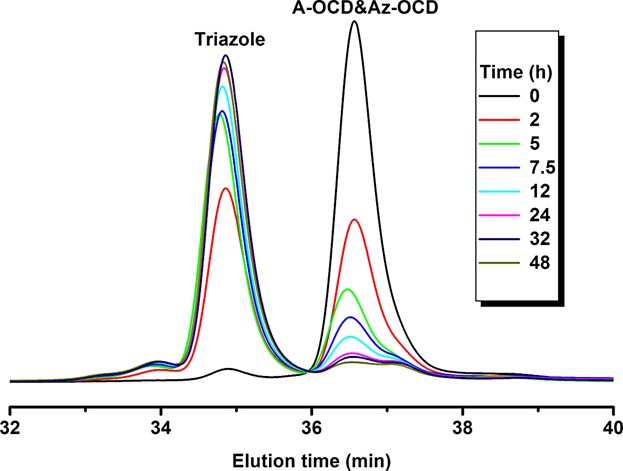
Alkynated and azidated octadecane as model compounds for kinetic studies of Huisgen 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition in vegetable oils
- Pages: 266-270
- First Published: 21 January 2015