Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
Clinical management among individuals with variant of uncertain significance in hereditary cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 119-131
- First Published: 12 April 2021
The genetic underpinnings of anthracycline-induced cardiomyopathy predisposition
- Pages: 132-143
- First Published: 19 April 2021
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
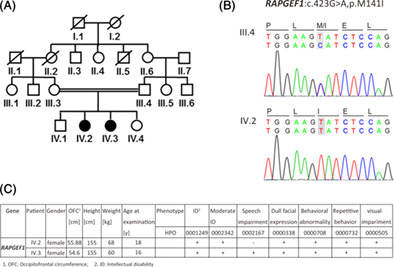
Zebrafish modeling mimics developmental phenotype of patients with RAPGEF1 mutation
- Pages: 144-155
- First Published: 09 April 2021
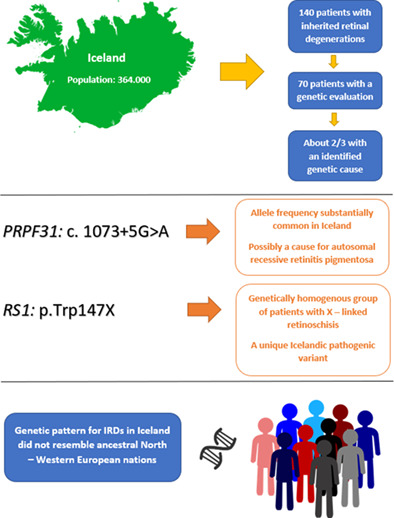
Molecular genetics of inherited retinal degenerations in Icelandic patients
- Pages: 156-167
- First Published: 14 April 2021
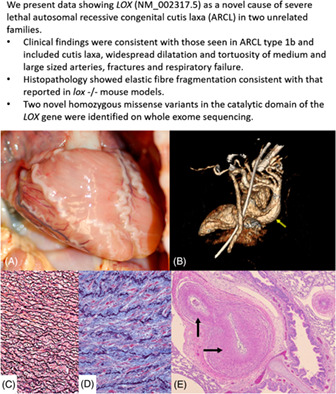
Severe congenital cutis laxa: Identification of novel homozygous LOX gene variants in two families
- Pages: 168-175
- First Published: 18 April 2021
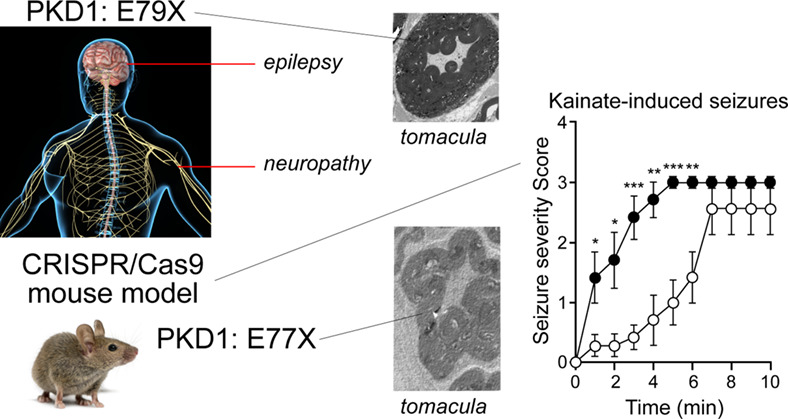
Protein kinase D1 variant associated with human epilepsy and peripheral nerve hypermyelination
- Pages: 176-186
- First Published: 27 April 2021
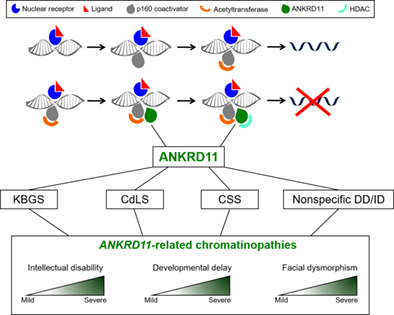
ANKRD11 variants: KBG syndrome and beyond
- Pages: 187-200
- First Published: 05 May 2021
SHORT REPORTS
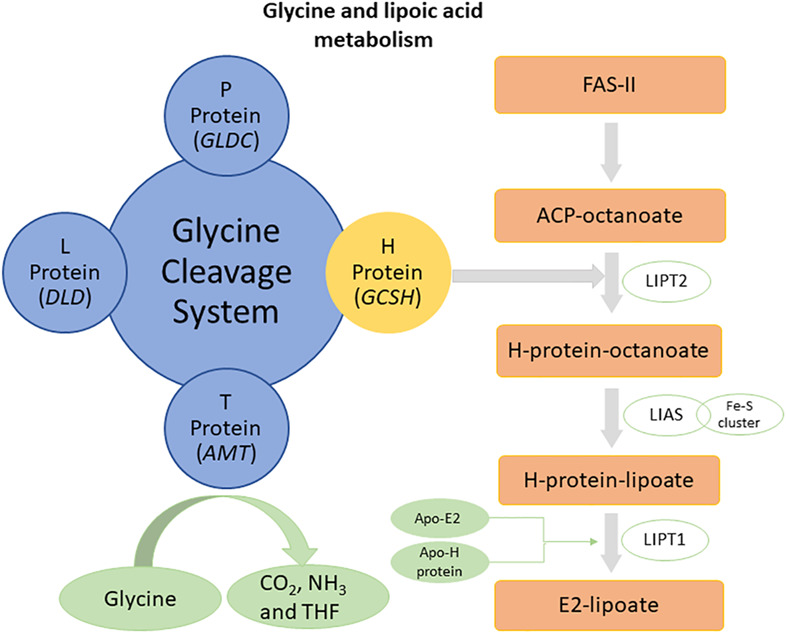
Biallelic start loss variant, c.1A > G in GCSH is associated with variant nonketotic hyperglycinemia
- Pages: 201-205
- First Published: 23 April 2021
Periodontal (formerly type VIII) Ehlers–Danlos syndrome: Description of 13 novel cases and expansion of the clinical phenotype
- Pages: 206-212
- First Published: 23 April 2021

Periodontal Ehlers–Danlos syndrome (pEDS) is a rare condition caused by autosomal dominant pathogenic variants in C1R and C1S, characterized by early-onset severe periodontitis with premature tooth loss, easy bruising, pretibial hyperpigmentation and skin fragility. We report 13 novel pEDS patients carrying heterozygous pathogenic variants in C1R and C1S. In addition to the main pEDS clinical signs, including complete tooth loss before the age of 30 years in three patients, three patients and one relative displayed widespread venous insufficiency leading to persistent leg ulcers. One patient suffered an intracranial aneurysm with familial vascular complications including aortic dissection and intracranial aneurysm rupture in several relatives. Brain MRI showed in two patients periventricular white matter hyperintensities. Rare vascular complications exist including venous insufficiency and arterial dissection that can be fatal. More cases with enhanced vascular characterization are required in order to determine if a systematic vascular monitoring, including both arterial and venous assessment, would be recommended.
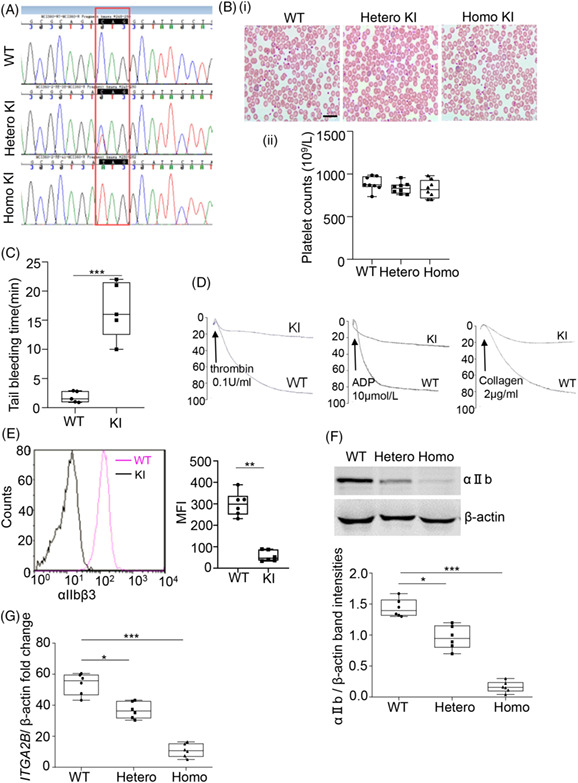
Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay efficiency influences bleeding severity in ITGA2B c.2659C > T (p.Q887X) knock-in mice
- Pages: 213-218
- First Published: 29 April 2021
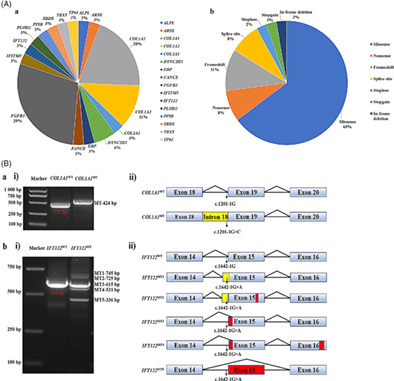
Molecular diagnosis for 55 fetuses with skeletal dysplasias by whole-exome sequencing: A retrospective cohort study
- Pages: 219-226
- First Published: 03 May 2021
PPP3CA truncating variants clustered in the regulatory domain cause early-onset refractory epilepsy
- Pages: 227-233
- First Published: 08 May 2021
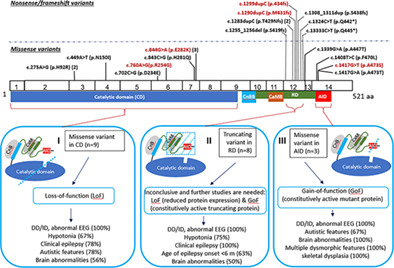
We provided molecular and clinical findings of five new patients with de novo PPP3CA variants. Interestingly, the two frameshift variants in this study and the six truncating variants previously reported are all clustered within a small 26-amino acid region in the regulatory domain (RD). Genotype-phenotype correlation of the 21 patients with PPP3CA mutations and expression studies on truncating mutations in this study and previous studies suggested that the truncating variants in the RD cause more severe early-onset refractory epilepsy, representing a type of variants distinct from loss-of-function missense variants in the catalytic domain or gain-of-function missense variants in the auto-inhibitory domain.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
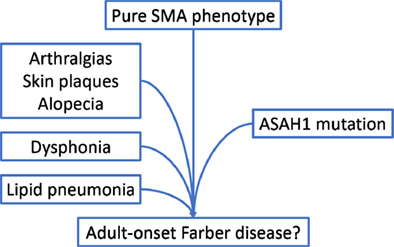
A case of ASAH1-related pure SMA evolving into adult-onset Farber disease
- Pages: 234-235
- First Published: 08 July 2021