Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION - COVER AND EDITORIAL BOARD
ISSUE INFORMATION - TOC
IN THIS ISSUE
EDITORIALS
The Molecular Allergology User's Guide version 2.0 is freely available!
- Pages: 1139-1141
- First Published: 12 January 2023
Introducing peanut early in life – Ready for the general population?
- Pages: 1142-1144
- First Published: 16 February 2023
Multiple comparisons and effect size: Statistical recommendations for authors planning to submit an article to Allergy
- Pages: 1145-1147
- First Published: 08 March 2023
REVIEW ARTICLES
Protease allergens as initiators–regulators of allergic inflammation
- Pages: 1148-1168
- First Published: 16 February 2023
Rhinitis associated with asthma is distinct from rhinitis alone: The ARIA-MeDALL hypothesis
- Pages: 1169-1203
- First Published: 17 February 2023
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Basic and Translational Allergy Immunology
Identification of redundancy between human FcεRIβ and MS4A6A proteins points toward additional complex mechanisms for FcεRI trafficking and signaling
- Pages: 1204-1217
- First Published: 24 November 2022
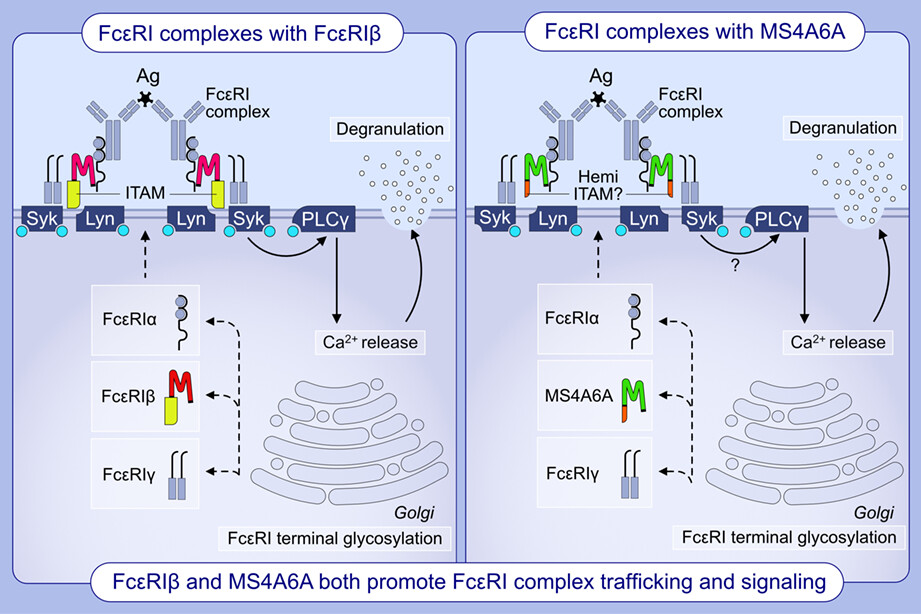
We identify that MS4A6A is expressed in human mast cells and has high sequence homology to FcεRIβ. We show that MS4A6A contains a putative hemi-ITAM that may function similarly to the FcεRIβ ITAM. We demonstrate that MS4A6A and FcεRIβ perform at least partially redundant roles in FcεRI complex trafficking and function.Abbreviations: Ag, antigen; Ca2+, calcium ion; FcεRI, high-affinity IgE receptor; ITAM, immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif; Lyn, Src family tyrosine kinase; MS4A6A, membrane-spanning 4-domains A6A; PLC, phospholipase C; Syk, spleen associated tyrosine kinase
Asthma and Lower Airway Disease
Dietary digestible carbohydrates are associated with higher prevalence of asthma in humans and with aggravated lung allergic inflammation in mice
- Pages: 1218-1233
- First Published: 24 November 2022
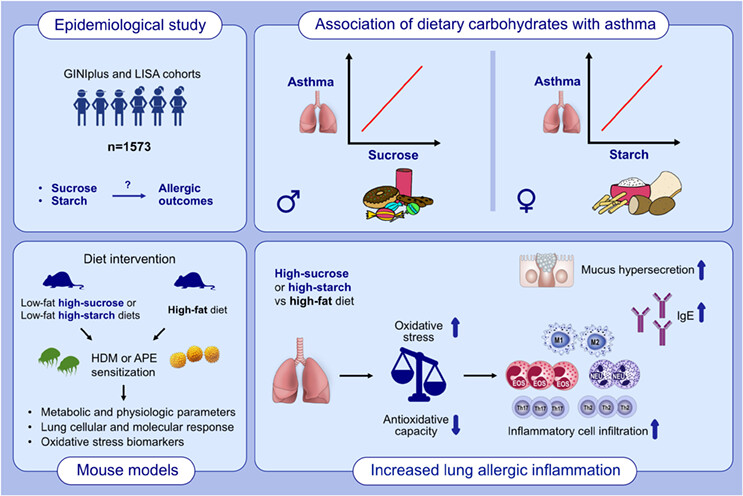
Epidemiological study discovers novel associations between high intake of dietary sucrose and starch with current asthma in males and females, respectively. High-carbohydrate feeding in mice aggravates allergic outcomes: serum IgE, lung inflammatory cell infiltration, TH2- or TH2-TH17 profiles and mucus hypersecretion. Dietary carbohydrate-driven enhanced pulmonary oxidative stress and decreased systemic anti-oxidative capacity are involved in this context.Abbreviations: APE, aqueous pollen extract; EOS, eosinophils; GINIplus, German Infant study on the Influence of Nutrition Intervention plus environmental and genetic influences on allergy development; HDM, house dust mite; IgE, immunoglobulin E; LISA, life-style related factors on the development of the Immune System and Allergies in East and West Germany; M, macrophages; NEU, neutrophils; Th, T helper
Prepregnancy body mass index and risk of childhood asthma
- Pages: 1234-1244
- First Published: 27 November 2022
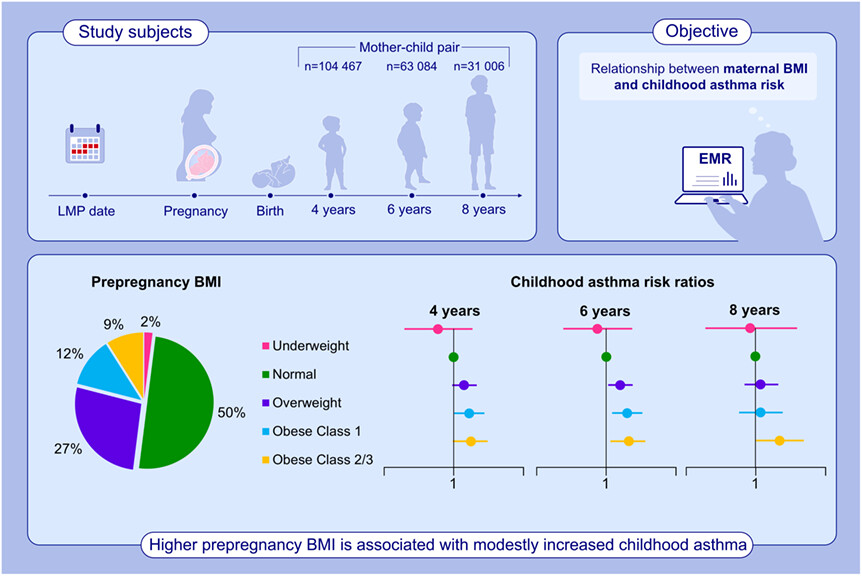
This study investigated the relationship between maternal prepregnancy BMI and childhood asthma risk. Mothers were followed throughout their pregnancy, and children were followed up to age 4, 6, or 8 years using electronic medical records. Asthma was assessed at each follow-up age. Higher prepregnancy BMI was associated with a modest increase in childhood asthma risk.Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index; EMR, electronic medical records; LMP, last menstrual period
Intranasal administration of Acinetobacter lwoffii in a murine model of asthma induces IL-6-mediated protection associated with cecal microbiota changes
- Pages: 1245-1257
- First Published: 02 December 2022
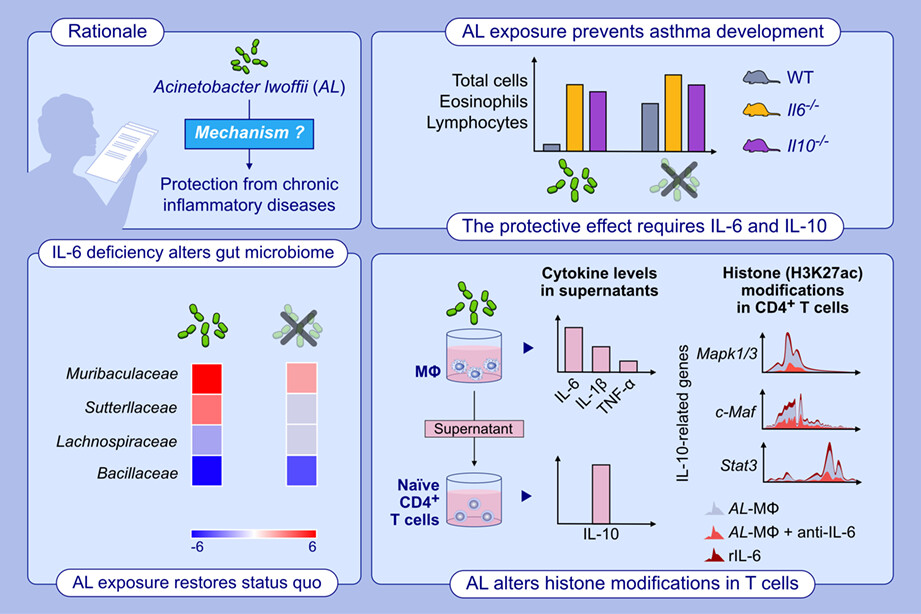
This study confirms that IL-6-deficient mice are resistant to asthma-protective effect driven by Acinetobacter lwoffii (AL). Downstream of IL-6, the asthma-blocking properties is mediated by IL-10, but not IL-17. In IL-6-deficient mice, exposure to AL increases Muribaculaceae and Sutterellaceae, and decreases Lachnospiraceae and Bacillaceae, compared to the unexposed mice, restoring the status quo observed in the wild-type littermates mice. In vitro experiments demonstrate modulations in the epigenetic landscape of histone mark H3K27ac at the promoter regions of the Il10 pathway-related genes (Mapk1/3, Stat3, and c-MAF) in the CD4+ T-cells cultured with AL-conditioned macrophage supernatant (AL-Mφ). These changes were reversed by anti-IL-6 treatment (AL-Mφ + anti-IL-6) and phenocopy by adding rIL-6 alone.Abbreviations: AL, Acinetobacter lwoffii; AL-Mφ, AL-conditioned macrophage; c-Maf, c-musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma transcription factor; IL, interleukin; Il6−/−, Il6 knockout; Il10−/−, Il10 knockout; Mφ, macrophages; Mapk1/3, mitogen-activated protein kinase 1/3; rIL-6, recombinant IL-6; Stat3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; WT, wild-type
Rhinitis, Sinusitis and Upper Airway Disease
Respiratory virome profiles reflect antiviral immune responses
- Pages: 1258-1268
- First Published: 03 January 2023
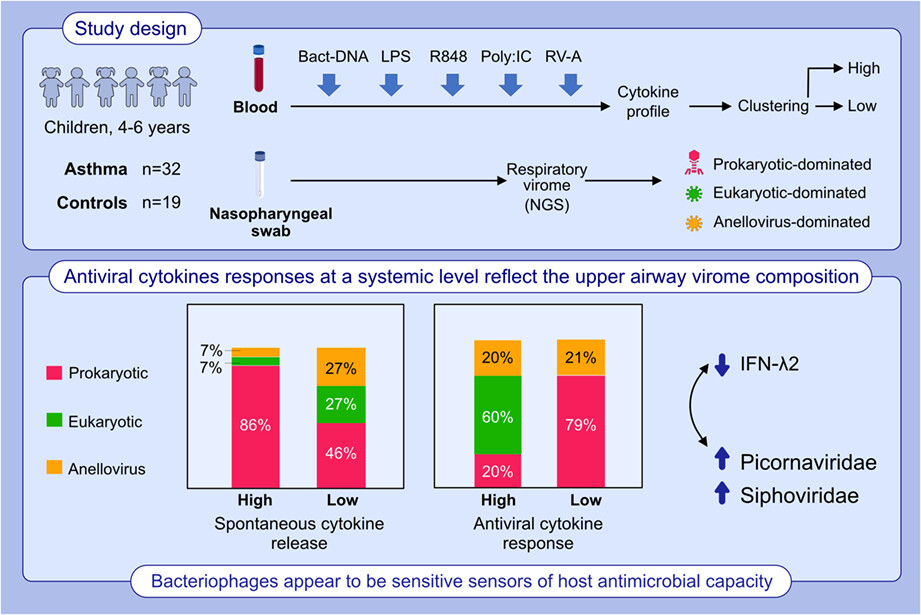
Respiratory virome profiles of preschool children were associated with spontaneous cytokine release and stimulated antiviral responses from PBMCs, independent of asthma/allergy status. Prokaryotic (bacteriophage)-type viromes dominated the high spontaneous cytokine release responder cluster. High antiviral responders included more eukaryotic-dominated profiles, while low interferon lambda release correlated with increased presence of Picornaviridae and Siphoviridae.Abbreviations: Bact-DNA, endotoxin-free bacterial DNA; LPS, lipopolysaccharides from E. coli 0111:B4; NGS, next generation sequencing; PBMCs, peripheral blood mononuclear cells; Poly I:C, polyinosinic–polycytidylic acid potassium salt; R848, resiquimod; RV-A, rhinovirus A
Atopic Dermatitis, Urticaria and Skin Disease
Anti-KIT antibody, barzolvolimab, reduces skin mast cells and disease activity in chronic inducible urticaria
- Pages: 1269-1279
- First Published: 16 November 2022
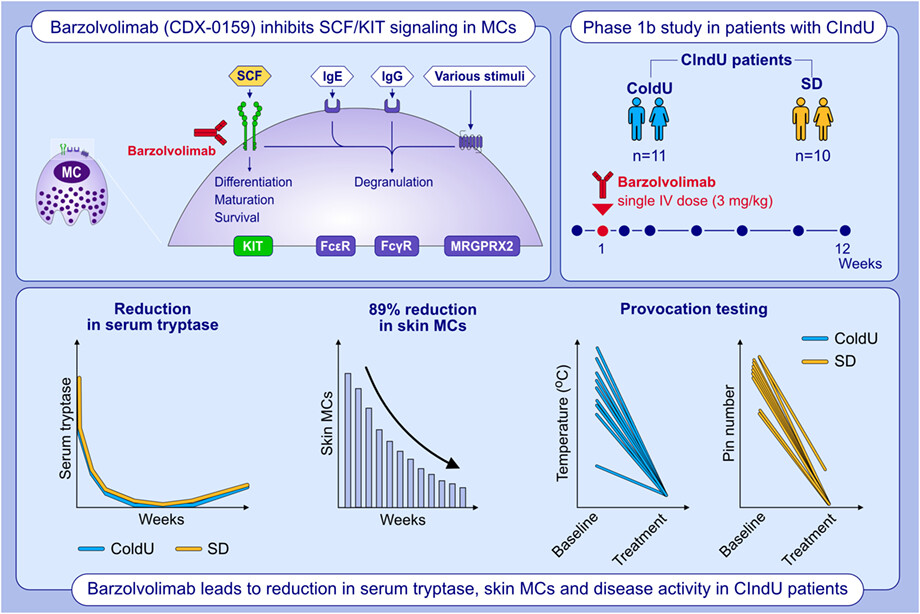
In this Phase 1b study of CIndU (ColdU and SD) patients, barzolvolimab, a humanized antibody that inhibits KIT activation by SCF, was well tolerated. Barzolvolimab demonstrated marked, rapid, durable depletion of skin MCs, circulating tryptase, reductions in clinical activity, and significant improvements in disease control and QoL. Barzolvolimab has potential as a therapy for MC-mediated diseases.Abbreviations: CIndU, chronic inducible urticaria; ColdU, cold urticaria; FcR, Fc receptor; Ig, immunoglobulin; KIT, KIT proto-oncogene, receptor tyrosine kinase; MC, mast cell; MRGPRX2, mas-related G protein-coupled receptor-X2; QoL, quality of life; SCF, stem cell factor; SD, symptomatic dermographism
Intravenous immunoglobulins, cyclosporine, and best supportive care in epidermal necrolysis: Diverse effects on systemic inflammation
- Pages: 1280-1291
- First Published: 04 December 2022
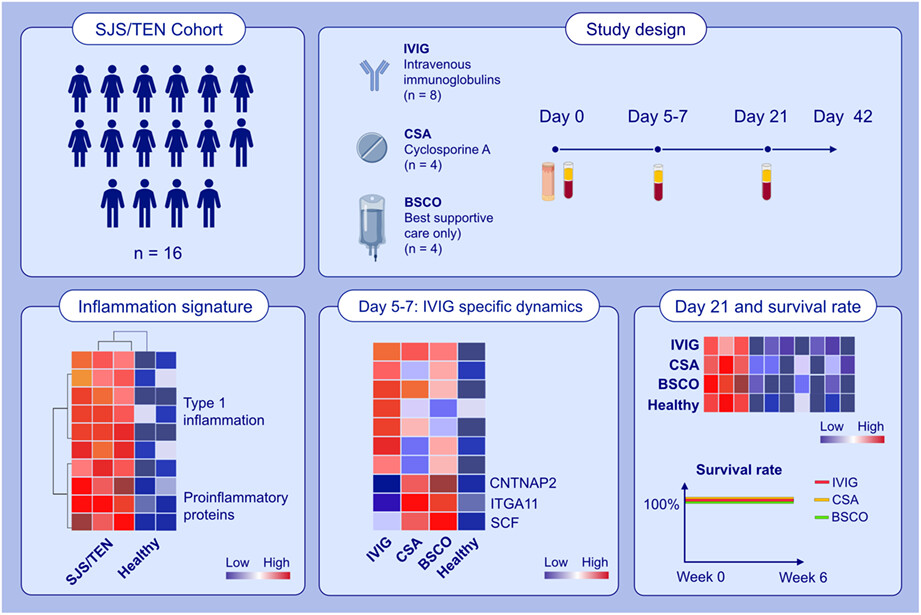
This study characterizes molecular effects of best supportive care only (BSCO) or in combination with intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIG) or cyclosporine A (CSA) in the acute phase of Stevens–Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN). Serum inflammatory profiles show massive upregulation of type 1 immune response and proinflammatory markers. IVIG-treated patients present different dynamics and most significant proteomic changes in an early phase (Day 5–7). In all treatment groups, type 1−/inflammatory response markers are dampened at Day 21.Abbreviations: BSCO, best supportive care only; CNTNAP2, contactin associated protein 2; CSA, cyclosporine A; IVIG, intravenous immunoglobulins; ITGA11, integrin subunit alpha 11; SCF, stem cell factor; SJS, Stevens-Johnson-Syndrome; TEN, toxic epidermal necrolysis
Staphylococcus aureus causes aberrant epidermal lipid composition and skin barrier dysfunction
- Pages: 1292-1306
- First Published: 07 January 2023
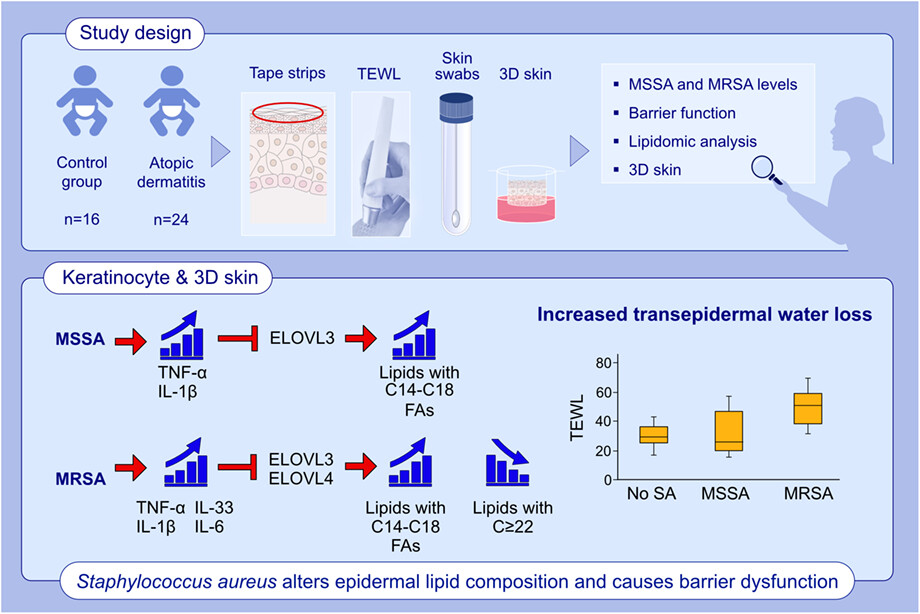
MRSA induces a broad range of cytokines, while MSSA induces IL-1β and TNF-α. Staphylococcus aureus-induced IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6 inhibit ELOVL3, resulting in accumulation of lipids with C14-C18 FAs, while MRSA-induced IL-33 inhibits both ELOVL3 and ELOVL4, concomitantly increasing lipids with C14-C18 FAs and decreasing lipids with FAs ≥ 22. S. aureus-mediated aberrant lipid profiles cause increased TEWL and skin barrier dysfunction.Abbreviations: 3D skin, organotypic skin; ELOVL, fatty acid elongase; FA, fatty acid; IL, interleukin; MRSA, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; MSSA, methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus; SA, Staphylococcus aureus; TEWL, transepidermal water loss; TNF, tissue necrosis factor
Food Allergy and Gastrointestinal Disease
Early introduction of peanut reduces peanut allergy across risk groups in pooled and causal inference analyses
- Pages: 1307-1318
- First Published: 27 November 2022
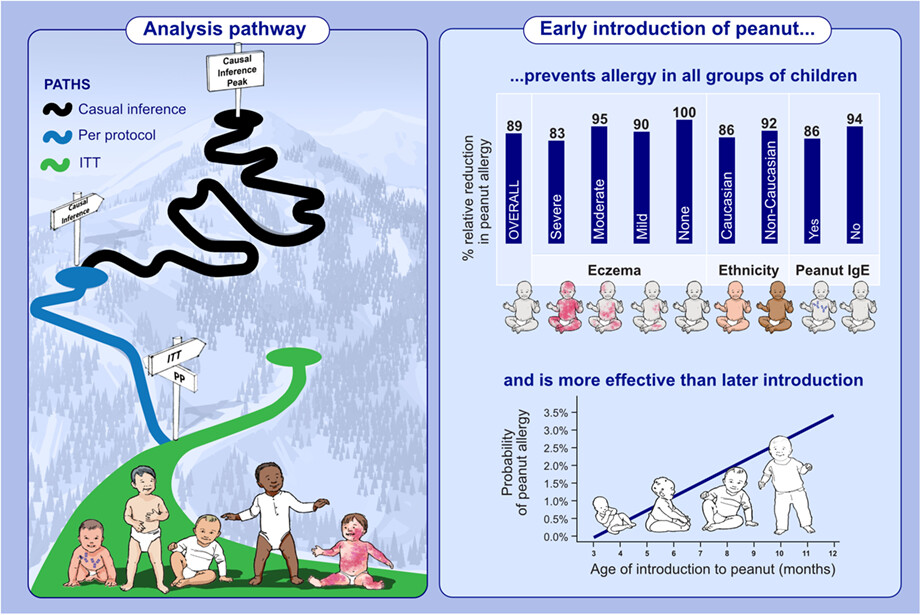
An integrated meta-analysis employing both LEAP (high risk) and EAT (normal risk) individual patient data shows that early introduction of peanut in infancy prevents the development of peanut allergy regardless of presence or severity of eczema, ethnicity and sensitization to peanut. Earlier introduction of peanut before 6 months of age is more effective than later introduction in the prevention of peanut allergy. Causal inference methods accurately estimated the efficacy of this strategy while addressing the problems of poor adherence in the intention-to-treat analyses and biases in the per-protocol analyses.Abbreviations: EAT, enquiring about tolerance; ITT, intention to treat; LEAP, learning early about allergy; PP, per protocol
Autoimmunity and Clinical Immunology
Deciphering the role of platelets in severe allergy by an integrative omics approach
- Pages: 1319-1332
- First Published: 17 December 2022
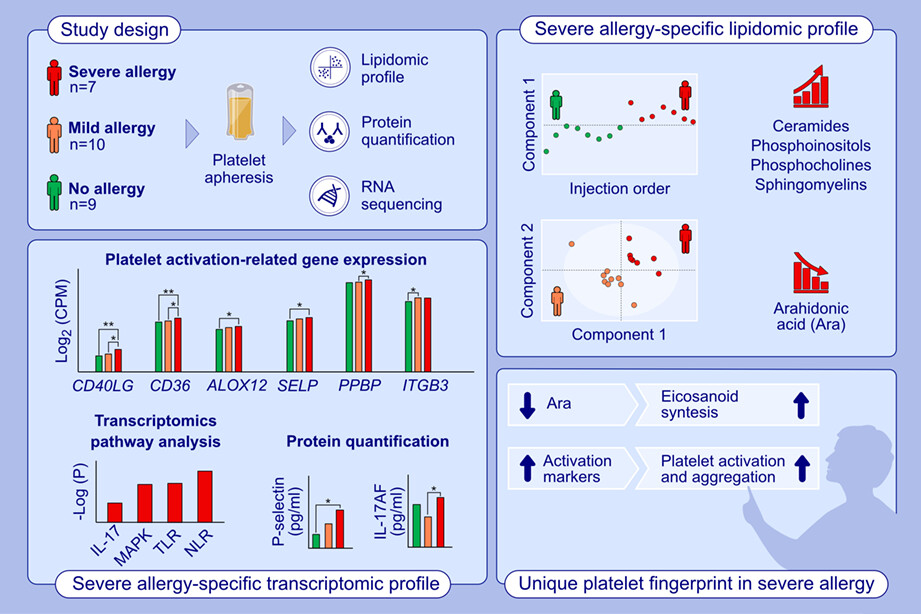
This study analyzes the lipidomic and transcriptomic profile of platelets in patients with mild and severe allergy. The lipidomic profile of platelets form severe allergic patients shows high levels of ceramides, phosphoinositols, phosphocholines, and sphingomyelins and low levels of arachidonic acid. Transcriptomics reveals a higher expression of platelet activation genes and the alteration of IL-17, MAPK, TLR, and NLR pathways in the severe phenotype, which was validated by P-Selectin and IL-17 AF protein quantification.Abbreviations: ALOX12, arachidonate 12-lipoxygenase; CD40L, CD40 ligand; CPM, counts per millon; IL, interleukin; ITGB3, integrin subunit beta 3; −Log(P), −Logarithm in base 10 of P value; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; NLR, NOD-like receptor; PPBP, pro-platelet basic protein; SELP, selectin P; TLR, Toll-like receptor
CU06-1004 alleviates vascular hyperpermeability in a murine model of hereditary angioedema by protecting the endothelium
- Pages: 1333-1346
- First Published: 14 February 2023
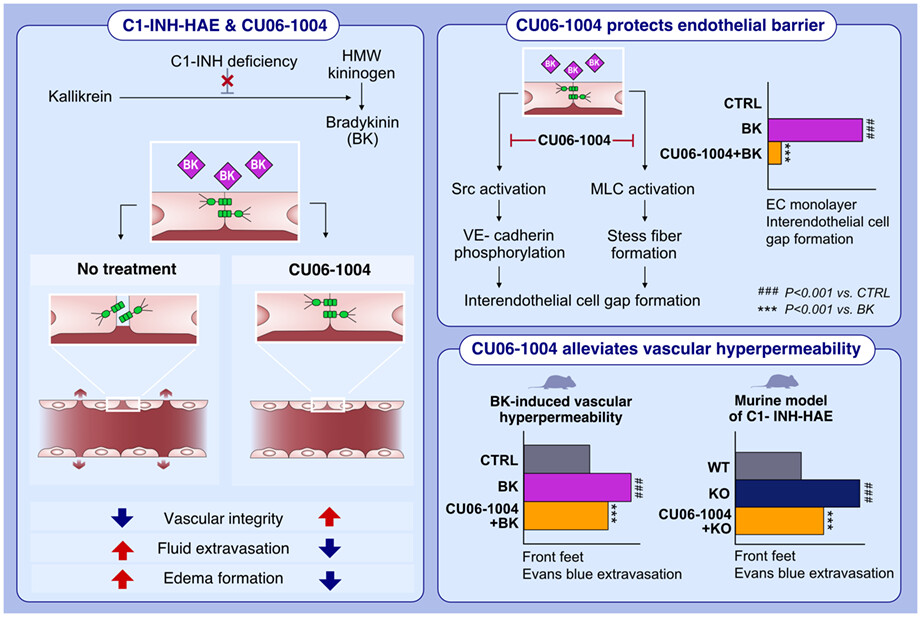
Increased vascular permeability due to BK is the leading cause of the C1-INH-HAE. CU06-1004 oral administration significantly alleviated vascular hyperpermeability in C1-INH-HAE murine in vivo model by protecting vascular integrity. CU06-1004 protected the endothelial barrier from BK-induced interendothelial cell gap formation by inhibiting VE-cadherin phosphorylation and stress fiber formation.Abbreviations: BK, bradykinin; C1-INH, C1 esterase inhibitor; C1-INH-HAE, hereditary angioedema caused by C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency; CTRL, control; CU06-1004, endothelial dysfunction blocker; EC, endothelial cell; F-actin, filamentous actin; HMW kininogen, high-molecular-weight kininogen; KO, knock-out; MLC, myosin light chain; Src, non-receptor tyrosine kinase; VE-cadherin, vascular endothelial cadherin; WT, wild type
KITD816V mutation in blood for the diagnostic screening of systemic mastocytosis and mast cell activation syndromes
- Pages: 1347-1359
- First Published: 16 November 2022
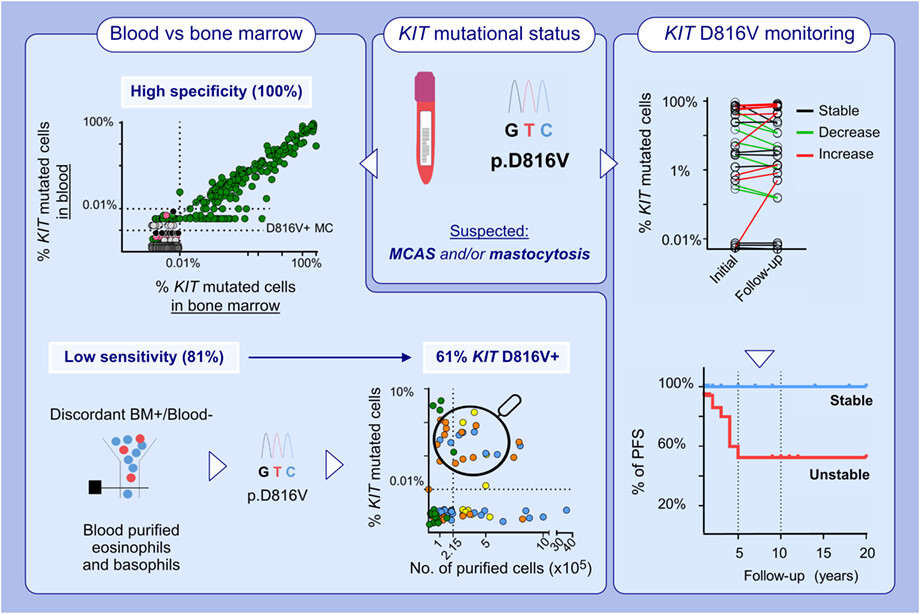
This study evaluates the utility of KITD816V mutational status in blood (vs. bone marrow) for the diagnostic screening of SM and MCAS patients, having a high specificity but a limited sensitivity in patients presenting with clonal MCAS without skin lesions. Assessment of KITD816V in blood-purified myeloid cell populations increases the diagnostic sensitivity of this mutation in 61% of patients. Further, an unstable (decrease or increase) KIT mutation cell burden during follow-up is a strong predictor of shortened progression-free survival in SM.Abbreviations: BM, bone marrow; KITD816V, somatic mutation in codon 816 of the stem cell growth factor receptor gene; MC, mast cell; MCAS, mast cell activation syndromes; No., number; PFS, progression-free survival; SM, systemic mastocytosis
LETTERS
Pest sensitization to cockroach, mouse, and rat: An Italian multicenter study
- Pages: 1360-1363
- First Published: 18 November 2022
Depletion of Mcpt8-expressing cells reduces lung mast cells in mice with experimental asthma
- Pages: 1363-1366
- First Published: 27 November 2022
Reduced intra-subject variability of an automated skin prick test device compared to a manual test
- Pages: 1366-1368
- First Published: 10 December 2022
Lanadelumab for the prevention of hereditary angioedema attacks: A real-world UK audit
- Pages: 1369-1371
- First Published: 12 December 2022
A gene variant of AKR1C3 contributes to interindividual susceptibilities to atopic dermatitis triggered by particulate air pollution
- Pages: 1372-1375
- First Published: 16 December 2022
Real-world evidence on the risk of cancer with anti-IL-5 and anti-IL-4Ra biologicals
- Pages: 1375-1377
- First Published: 26 December 2022
An artificial intelligence algorithm-based smartphone application for daily cough monitoring
- Pages: 1378-1380
- First Published: 01 January 2023
Berotralstat for the prophylaxis of hereditary angioedema—Real-world evidence data from the United Kingdom
- Pages: 1380-1383
- First Published: 07 January 2023
Severe cutaneous adverse reactions after COVID-19 vaccination: A systematic review
- Pages: 1383-1386
- First Published: 10 January 2023
Protease allergen-induced HMGB1 contributes to NLRC4 inflammasome-mediated inflammation in experimental asthma
- Pages: 1387-1392
- First Published: 07 February 2023
NEWS & VIEWS
Legends of Allergy and Immunology
Legends of allergy and immunology: Kurt Blaser and major contributions to deciphering the role of T cells in allergic disease
- Pages: 1393-1394
- First Published: 31 January 2023
Legends of Allergy and Immunology—Dean D. Metcalfe
- Pages: 1395-1396
- First Published: 26 January 2023
Algorithms in Allergy and Clinical Immunology
Medical algorithm: Diagnosis and treatment of house dust mite-driven allergic asthma
- Pages: 1397-1399
- First Published: 23 January 2023
Groundbreaking Discoveries in Clinical and Basic Science
Some OPA once told me “LKB1 is going to rule me”: The OPA1-LKB1 axis in immune response
- Pages: 1400-1402
- First Published: 13 February 2023






