Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ISSUE INFORMATION - TOC
IN THIS ISSUE
EDITORIAL
Translation of experimental immunotherapy
- Pages: 12-13
- First Published: 06 August 2020
GUIDELINES
EAACI Biologicals Guidelines—Recommendations for severe asthma
- Pages: 14-44
- First Published: 02 June 2020
Efficacy and safety of dupilumab for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: A systematic review for the EAACI biologicals guidelines
- Pages: 45-58
- First Published: 21 July 2020
Efficacy and safety of treatment with omalizumab for chronic spontaneous urticaria: A systematic review for the EAACI Biologicals Guidelines
- Pages: 59-70
- First Published: 07 August 2020
EAACI POSITION PAPERS
Biologicals in atopic disease in pregnancy: An EAACI position paper
- Pages: 71-89
- First Published: 18 March 2020
Immune modulation via T regulatory cell enhancement: Disease-modifying therapies for autoimmunity and their potential for chronic allergic and inflammatory diseases—An EAACI position paper of the Task Force on Immunopharmacology (TIPCO)
- Pages: 90-113
- First Published: 27 June 2020
EAACI TASK FORCE REPORT
Current perspective on eicosanoids in asthma and allergic diseases: EAACI Task Force consensus report, part I
- Pages: 114-130
- First Published: 12 April 2020
REVIEWS
Past, present, and future of allergen immunotherapy vaccines
- Pages: 131-149
- First Published: 06 April 2020
The complexity of T cell–mediated penicillin hypersensitivity reactions
- Pages: 150-167
- First Published: 08 May 2020
ARIA digital anamorphosis: Digital transformation of health and care in airway diseases from research to practice
- Pages: 168-190
- First Published: 08 June 2020
Economic considerations on the usage of biologics in the allergy clinic
- Pages: 191-209
- First Published: 13 July 2020
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Allergen-Specific Immunotherapy and Biologics
Laser-facilitated epicutaneous immunotherapy with hypoallergenic beta-glucan neoglycoconjugates suppresses lung inflammation and avoids local side effects in a mouse model of allergic asthma
- Pages: 210-222
- First Published: 03 July 2020
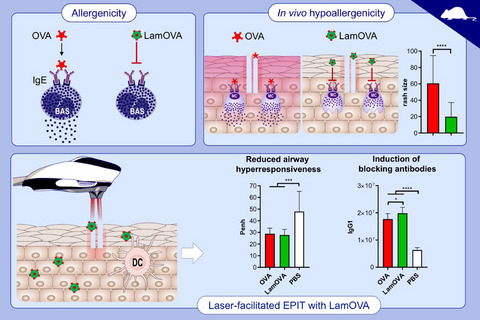
Epicutaneous immunotherapy (EPIT) targets a tissue rich in antigen-presenting cells. Laser-facilitated EPIT combines controlled and efficient barrier disruption with a laser-induced adjuvant effect. However, application of native allergens to the skin can induce unwanted side effects. Coupling the β-glucan laminarin to allergens can markedly reduce their IgE binding capacity. β-glucan neoglycoconjugates efficiently target dendritic cells via the C-type lectin receptor dectin-1, boosting their immunogenicity. In a mouse model of allergic asthma, laminarin-ovalbumin conjugates (LamOVA) diminished local side effects in vivo, while inducing higher levels of blocking IgG compared with uncoupled OVA. EPIT with LamOVA was equally efficient in improving lung functions compared to classical SCIT. Abbreviations: EPIT, epicutaneous immunotherapy; LamOVA, laminarin-ovalbumin conjugates; OVA, ovalbumin; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; Penh, resistance and compliance data are shown as area under the curve (AUC) of a methacholine challenge dose response curve; SCIT, subcutaneous immunotherapy
Asthma and Lower Airway Disease
Characteristics of Specialist-Diagnosed Asthma-COPD Overlap in Severe Asthma: Observations from the Korean Severe Asthma Registry (KoSAR)
- Pages: 223-232
- First Published: 06 July 2020
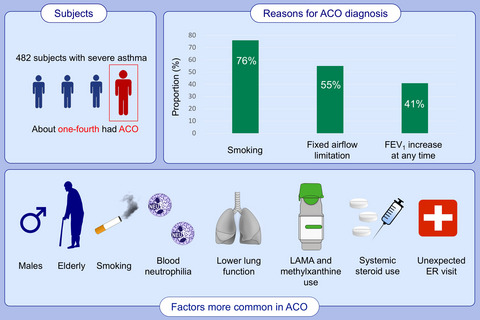
We found that about one-fourth of patients with severe asthma was diagnosed with ACO by specialists. The most common reason for ACO diagnosis was smoking history. ACO patients were predominantly male, older, and had more smoking history compared with non-ACO patients. ACO patients had higher blood neutrophil count, but lower lung function. ACO patients used more LAMA, methylxanthine, and systemic corticosteroid and had more frequent exacerbations related to ER visits compared with those with severe asthma only. Abbreviations: ACO, asthma-COPD overlap; ER, emergency room; FEV1, forced expiratory volume in one second.
Asthma and Lower Airway Diseases
Cross-reactive carbohydrate determinant-specific IgE obscures true atopy and exhibits ⍺-1,3-fucose epitope-specific inverse associations with asthma
- Pages: 233-246
- First Published: 22 June 2020
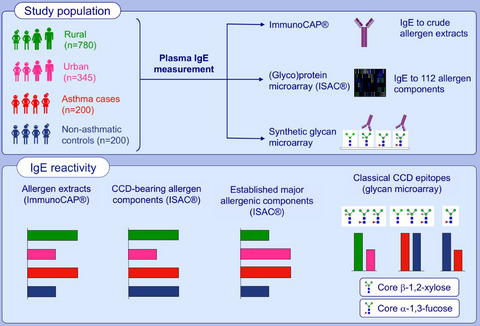
Reactivity to crude allergen extracts and classical CCD epitope (core β-1,2-xylose, α-1,3-fucose)-modified N-glycans is positively associated with the rural, Schistosoma mansoni-endemic environment. However, a higher proportion of urban, compared to rural participants, recognise recombinant established major allergenic components. There are inverse associations between reactivity to a subset of core α-1,3-fucose-substituted N-glycans and asthma, but not for CCD-specific IgE in general. Abbreviation: CCD, cross-reactive carbohydrate determinant.
Asthma and Lower Airway Disease
Clinical correlates of rhinovirus infection in preschool asthma
- Pages: 247-254
- First Published: 03 July 2020
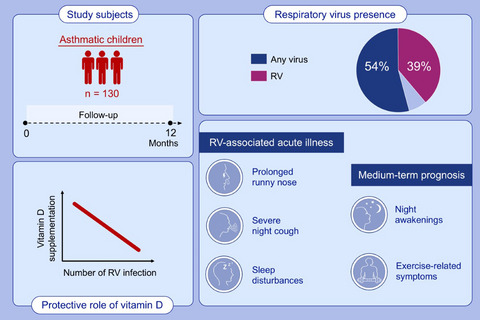
This study investigated the role of rhinovirus (RV) infections in preschool asthma in 130 asthmatic children from PreDicta cohort over 1-year follow-up. During all visits, RV was the most commonly detected virus. Vitamin D supplementation was associated with decreased number of rhinovirus infections in preschool children with asthma. Detection of RV was associated with more severe course of acute illness (more severe nighttime coughing, more sleep disturbances, and more days with runny nose) and more compromised medium-term prognosis (more nights with awakenings and more days of exercise-related symptoms).
Estrogen receptor-α signaling increases allergen-induced IL-33 release and airway inflammation
- Pages: 255-268
- First Published: 10 July 2020
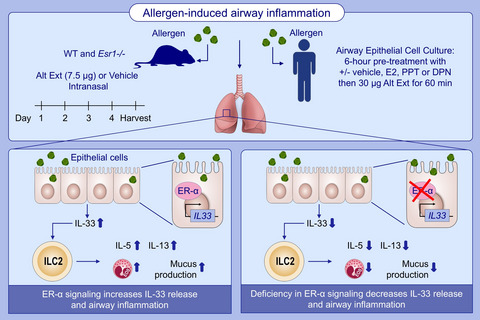
Allergen-induced airway inflammation is increased by estrogen signaling. Compared to WT mice, Alt Ext challenged Esr1 −/− mice have decreased IL-5 and IL-13 production, eosinophils number, and IL-33 release. Estrogen receptor-α signaling has no direct effect on ILC2 proliferation or cytokine expression. Abbreviations: Alt Ext, Alternaria extract; DPN, diarylpropionitrile; E2, 17β-estradiol; Eos, eosinophils; Esr1 −/−, estrogen receptor alpha deficient mice; ER-α, estrogen receptor α; ILC2, group 2 innate lymphoid cells; PPT, propyl-pyrazole-triol; WT, wild-type
Dupilumab is effective in type 2-high asthma patients receiving high-dose inhaled corticosteroids at baseline
- Pages: 269-280
- First Published: 03 October 2020
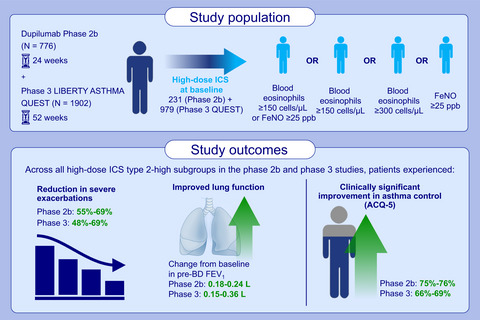
This study examines dupilumab efficacy in type 2-high asthma patients receiving high-dose ICS at baseline. Dupilumab reduces severe exacerbations, improves lung function and asthma control in patients on high-dose ICS with elevated baseline blood eosinophils or FeNO. Dupilumab efficacy is rapid and sustained throughout treatment and comparable across type 2-high asthma patients receiving high-dose ICS at baseline. Abbreviations: ACQ-5, 5-item Asthma Control Questionnaire; FeNO, fractional exhaled nitric oxide; FEV1, forced expiratory volume in 1 second; ICS, inhaled corticosteroids; ppb, parts per billion; pre-BD, prebronchodilator.
Th2 cell markers in peripheral blood increase during an acute asthma exacerbation
- Pages: 281-290
- First Published: 04 August 2020
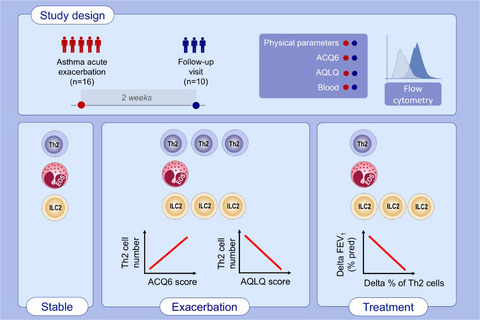
Th2 cell number in peripheral blood correlates with asthma control and quality of life during asthma exacerbations. Patients with asthma exacerbations have a higher % of Th2 cells (CD4+ T cells expressing CRTh2) in peripheral blood compared to patients with stable asthma, and this parameter decreases after treatment. Eosinophils and ILC2 cells in peripheral blood do not change during asthma exacerbations. The decrease in the % of Th2 cells seen during the follow-up visit correlates with the improvement in lung function. Abbreviations: ACQ, asthma control questionnaire; AQLQ, asthma quality of life questionnaire; FEV1, forced expiratory volume in 1 sec; ILC2: group 2 innate lymphoid cell; pred, predicted.
Atopic Dermatitis, Urticaria and Skin Disease
Inhibition of mite-induced dermatitis, pruritus, and nerve sprouting in mice by the endothelin receptor antagonist bosentan
- Pages: 291-301
- First Published: 14 June 2020
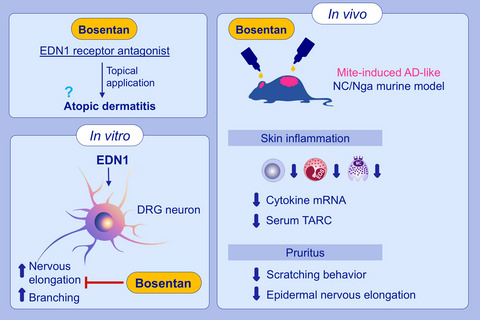
Topical application of EDN1 receptor antagonist, bosentan, significantly attenuated the development of mite induced AD-like skin inflammation, scratching bouts and epidermal nervous elongation in NC/Nga mice. While EDN1 significantly elongated the nerves of dorsal root ganglion cells, bosentan treatment attenuated this. Topical bosentan is a potential protective candidate for AD. Abbreviations: AD, atopic dermatitis; DRG, dorsal root ganglion; EDN1, endothelin 1; TARC, thymus and activation-regulated chemokine.
Biofilm propensity of Staphylococcus aureus skin isolates is associated with increased atopic dermatitis severity and barrier dysfunction in the MPAACH pediatric cohort
- Pages: 302-313
- First Published: 08 July 2020
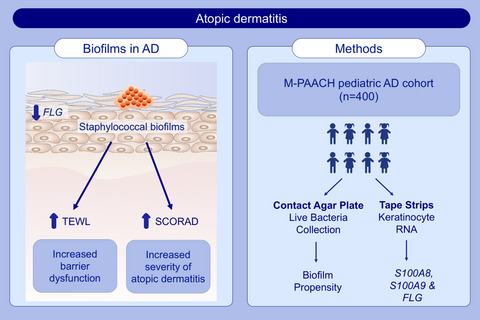
Staphylococcal biofilms are observed on the skin of children with AD in the MPAACH cohort. Staphylococcus aureus strains showing higher relative biofilm propensity (compared with S epidermidis from the same subject) are associated with increased AD severity. Staphylococcus aureus strains showing higher relative biofilm propensity are associated with increased lesional and nonlesional transepidermal water loss. Abbreviations: AD, atopic dermatitis; FLG, filaggrin; MPAACH, Mechanisms of Progression of Atopic Dermatitis to Asthma in Children; SCORAD, scoring atopic dermatitis index; S100A8, S100 Calcium-Binding Protein A8; S100A9, Calcium-Binding Protein A9; TEWL, transepidermal water loss.
Tape strips from early-onset pediatric atopic dermatitis highlight disease abnormalities in nonlesional skin
- Pages: 314-325
- First Published: 08 July 2020
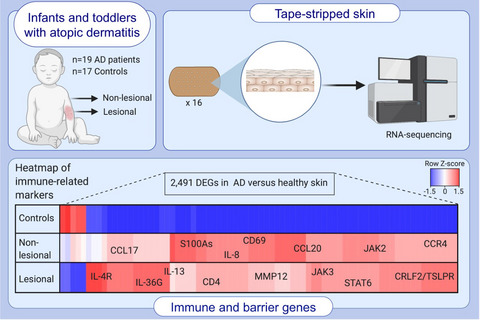
Tape strips are collected for RNA-seq profiling from 19 infants/toddlers (ages 0-5 years; lesional and nonlesional) with early-onset (≤6 months), moderate-to-severe AD and 17 healthy controls. We identify 2491 differentially expressed genes in AD vs healthy skin. We observe significant dysregulation of Th2 and Th22/Th17-related markers, largely lacking Th1 skewing. Significant decreases in barrier-related genes are seen primarily in lesional skin. Abbreviations: AD, atopic dermatitis; DEGs, differentially expressed genes.
Food Allergy and Gastrointestinal Disease
SF-6Dv2 preference value set for health utility in food allergy
- Pages: 326-338
- First Published: 13 June 2020
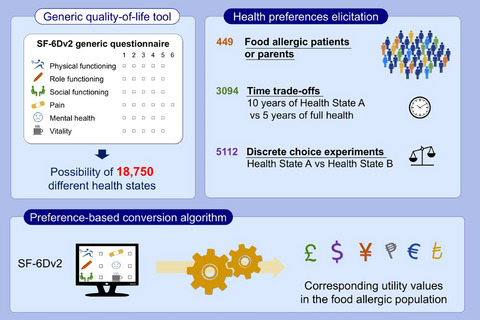
There is currently no validated instrument to calculate health utility in food allergy, which is a barrier to the conduct of cost-effectiveness analyses. Using time trade-off and discrete choice experiment approaches, options of the SF-6Dv2 generic health-related quality of life questionnaire were directly valued in the Canadian food allergic population. The resulting algorithm based on the health preferences of food allergic patients and parents can now be used to convert SF-6Dv2 answers to health utility values in this population. Abbreviation: SF-6Dv2, Short form-six dimensions version 2.
Food-induced immediate response of the esophagus—A newly identified syndrome in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis
- Pages: 339-347
- First Published: 14 July 2020
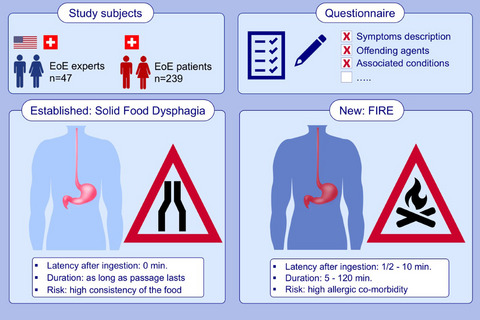
This study describes food-induced immediate response of the esophagus (FIRE), a novel syndrome frequently reported in eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) patients. Eosinophilic esophagitis expert physicians' and patients' surveys were performed to characterize FIRE. A burning and choking unpleasant or painful sensation with rapid occurrence upon ingestion of trigger food is typical of FIRE, occurring in a considerable fraction of EoE patients unrelated from classical solid food dysphagia. Abbreviations: EoE, eosinophilic esophagitis; FIRE, food-induced immediate response of the esophagus.
Epidemiology and Genetics
The neighbourhood natural environment is associated with asthma in children: A birth cohort study
- Pages: 348-358
- First Published: 12 July 2020
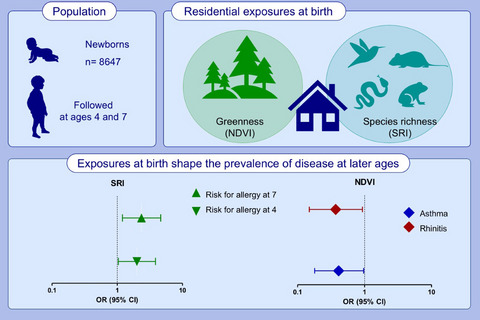
Living in a greener neighbourhood at birth is associated with a lower prevalence of asthma and rhinitis at the age of seven. Living in a neighbourhood with high numbers of fauna species is associated with an increased risk for allergic diseases and asthma in children. The associations between the contact with nature and the development of asthma are stronger among children with a later onset of disease. Abbreviations: CI, confidence intervals; OR, odds ratio; NDVI, normalized difference vegetation index; SRI, species richness index.
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
Transcriptome analysis reveals two distinct endotypes and putative immune pathways in tonsils from children with periodic fever, aphthous stomatitis, pharyngitis, and cervical adenitis syndrome
- Pages: 359-363
- First Published: 27 June 2020
High fractional exhaled nitric oxide levels may predict short-term worsening of respiratory oscillometry in asthma
- Pages: 363-366
- First Published: 04 July 2020
RNA-seq–based profiling of extracellular vesicles in plasma reveals a potential role of miR-122-5p in asthma
- Pages: 366-371
- First Published: 05 July 2020
Comparison of diagnostic accuracy of acoustic rhinometry and symptoms score for nasal allergen challenge monitoring
- Pages: 371-375
- First Published: 20 July 2020
Asthma exacerbations on benralizumab are largely non-eosinophilic
- Pages: 375-379
- First Published: 23 July 2020
Type 2-low asthma phenotypes by integration of sputum transcriptomics and serum proteomics
- Pages: 380-383
- First Published: 31 August 2020
2S albumins and 11S globulins, two storage proteins involved in pumpkin seeds allergy
- Pages: 383-386
- First Published: 24 July 2020
Health-related quality of life in patients who had partaken in milk oral immunotherapy and comparison to the general population
- Pages: 387-390
- First Published: 01 August 2020
A mouse model of asthma-chronic obstructive pulmonary disease overlap induced by intratracheal papain
- Pages: 390-394
- First Published: 02 August 2020
IgG removal significantly enhances detection of microarray allergen-specific IgE reactivity in patients' serum
- Pages: 395-398
- First Published: 01 August 2020
NEWS & VIEWS
Legends of Allergy and Immunology
Legends of allergy and immunology: Jean Julien Raoul Bousquet; a Chemist, a Pharmacist, a Biologist, a Physician and—above all—an innovative scientist
- Pages: 399-402
- First Published: 15 April 2020
Algorithms in Allergy and Clinical Immunology
Medical algorithm: Diagnosis of atopic dermatitis in early childhood (part I)
- Pages: 403-406
- First Published: 22 October 2020
Medical algorithm: Treatment of atopic dermatitis in early childhood (part II)
- Pages: 407-410
- First Published: 09 August 2020
Groundbreaking Discoveries in Immunology
Thinking small: Zinc sensing by the gut epithelium
- Pages: 411-413
- First Published: 01 August 2020






