Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ISSUE INFORMATION - TOC
IN THIS ISSUE: GRAPHICAL ABSTRACTS
EDITORIAL
Short-chain fatty acids modulate mast cell activation
- Pages: 1848-1849
- First Published: 11 April 2020
EAACI POSITION PAPER
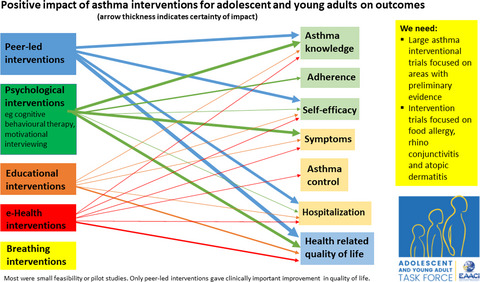
Understanding the challenges faced by adolescents and young adults with allergic conditions: A systematic review
- Pages: 1850-1880
- First Published: 06 March 2020
The effectiveness of interventions to improve self-management for adolescents and young adults with allergic conditions: A systematic review
- Pages: 1881-1898
- First Published: 11 March 2020
EAACI COMMITTEE REPORT
EAACI Research and Outreach Committee: Improving standards and facilitating global collaboration through a Research Excellence Network
- Pages: 1899-1901
- First Published: 27 April 2020
REVIEW ARTICLES
Epithelial cell dysfunction, a major driver of asthma development
- Pages: 1902-1917
- First Published: 27 May 2020
REVIEWS
Stability of regulatory T cells in T helper 2–biased allergic airway diseases
- Pages: 1918-1926
- First Published: 03 March 2020
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Atopic Dermatitis, Urticaria and Skin Disease
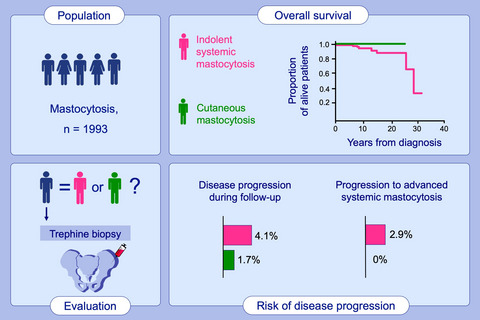
Clinical features and survival of patients with indolent systemic mastocytosis defined by the updated WHO classification
- Pages: 1927-1938
- First Published: 28 February 2020
Basic and Translational Allergy Immunology
Maternal ω3 docosapentaenoic acid inhibits infant allergic dermatitis through TRAIL-expressing plasmacytoid dendritic cells in mice
- Pages: 1939-1955
- First Published: 06 February 2020
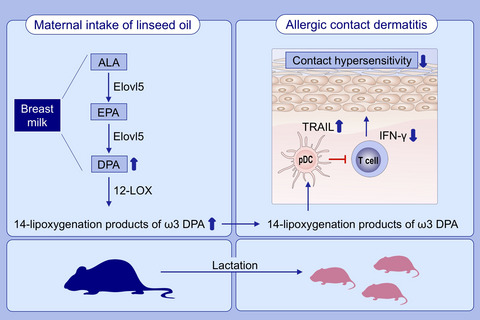
Maternal intake of α-linolenic acid increased ω3 DPA and its 14-lipoxygenation products in the breast milk of dams. 14-lipoxygenation products of ω3 DPA increased TRAIL expression on plasmacytoid dendritic cells in the pups, which suppressed the IFN-γ-producing T cells and consequently inhibited infant allergic dermatitis.
Structure of intact IgE and the mechanism of ligelizumab revealed by electron microscopy
- Pages: 1956-1965
- First Published: 09 February 2020
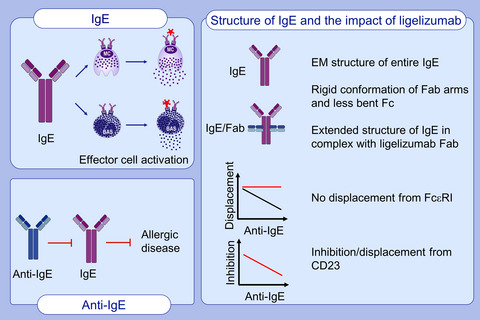
Electron microscopy and solution scattering reveal that the structure of entire IgE is highly rigid with a spatial organization differing from current models. The Fab arms are rigidly tethered to the Fc and lack flexibility. Ligelizumab traps IgE in an extended conformation retaining the Fab arm assembly. The localization of the epitope enables inhibition of binding to both IgE receptors.
Butyrate inhibits human mast cell activation via epigenetic regulation of FcεRI-mediated signaling
- Pages: 1966-1978
- First Published: 28 February 2020
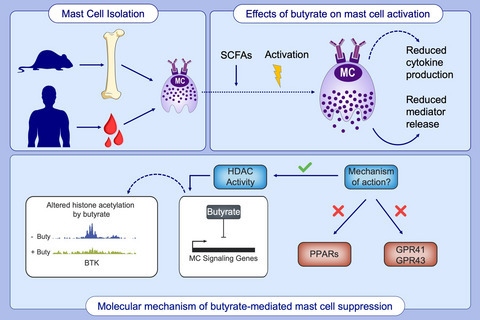
Short-chain fatty acids suppress primary human mast cell activation via HDAC inhibition and not via PPAR or GPR signaling. Butyrate induces transcriptional changes of genes important for signaling and activation of human mast cells. Butyrate triggers a redistribution of global H3K27 acetylation levels, leading to decreased acetylation at the transcription start site of genes encoding key FcεRI-mediated signaling molecules.
Asthma and Lower Airway Disease
Antibiotic use during pregnancy increases offspring asthma severity in a dose-dependent manner
- Pages: 1979-1990
- First Published: 16 February 2020
Ceramide/sphingosine-1-phosphate imbalance is associated with distinct inflammatory phenotypes of uncontrolled asthma
- Pages: 1991-2004
- First Published: 18 February 2020
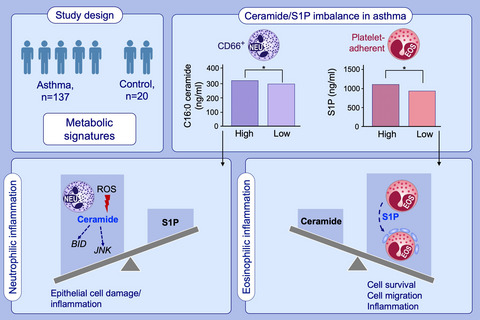
Asthmatics patients with high level of CD66+ neutrophils have high C16:0 ceramide levels and enhanced ceramide-mediated pro-apoptotic signals (BID and JNK). Asthmatics patients with high level of platelet-adherent eosinophils (CD61+ platelets/Siglec8+ eosinophils) have high S1P levels. The level of CD66+ neutrophils correlates with ROS production from neutrophils. The level of platelet-adherent eosinophils is associated with asthma control symptom scores.
IL-1β prevents ILC2 expansion, type 2 cytokine secretion, and mucus metaplasia in response to early-life rhinovirus infection in mice
- Pages: 2005-2019
- First Published: 22 February 2020
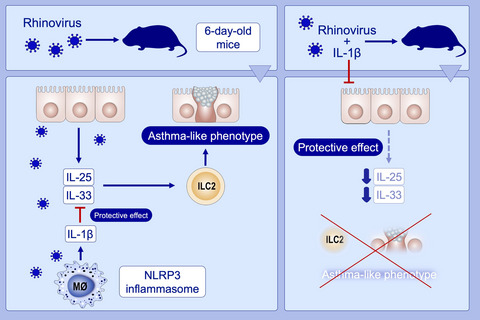
Early-life rhinovirus infection increases epithelial expression of the innate cytokines IL-25 and IL-33, expands (type 2 innate lymphoid cells) ILC2s, and enhances development of an asthma-like phenotype. Rhinovirus causes macrophage (NLR family, pyrin domain containing 3) NLRP3 inflammasome activation and bioactive IL-1β production. IL-1β production, which is deficient in immature mice, attenuates production of IL-25 and IL-33, thereby protecting against rhinovirus-induced asthma development.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
ASTHMA AND LOWER AIRWAY DISEASE
Orally applied bacterial lysate in infants at risk for atopy does not prevent atopic dermatitis, allergic rhinitis, asthma or allergic sensitization at school age: Follow-up of a randomized trial
- Pages: 2020-2025
- First Published: 22 February 2020
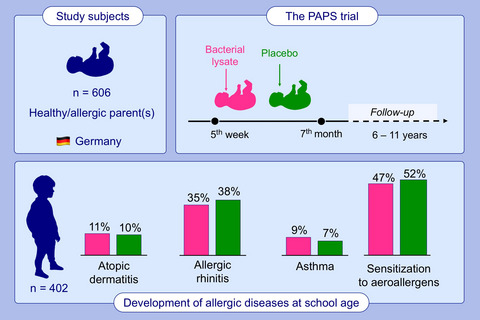
This study presents data from a large cohort of infants at risk for atopy. Effect of orally applied bacterial lysates during infancy on later allergic manifestations was studied in a long prospective follow-up. The early intervention with a bacterial lysate had no effect on the development of atopic dermatitis, allergic rhinitis, asthma and specific sensitization to aeroallergens at school age.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Rhinitis, Sinusitis, and Upper Airway Disease
Artemisia annua-sublingual immunotherapy for seasonal allergic rhinitis: A randomized controlled trial
- Pages: 2026-2036
- First Published: 07 February 2020
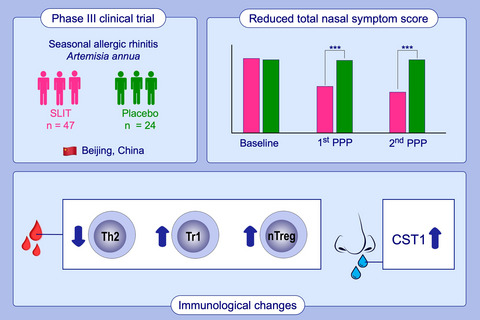
This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III clinical trial demonstrates the efficacy and favourable safety profile of the 32-week SLIT with Artemisia annua in patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis. Artemisia annua-SLIT significantly reduces total nasal symptom score at the 1st and 2nd PPP compared with placebo. Preseasonal Artemisia annua-SLIT significantly decreases Th2 cells, increases nTreg and Tr1 cells in blood and increases CST1 in nasal secretion.
The international sinonasal microbiome study: A multicentre, multinational characterization of sinonasal bacterial ecology
- Pages: 2037-2049
- First Published: 13 March 2020
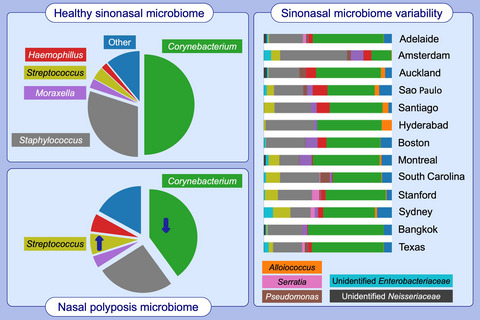
Although the sinus microbiome is highly variable between individuals, we identify a core microbiome comprised of Corynebacterium, Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Haemophilus and Moraxella species in both healthy and chronic rhinosinusitis cohorts. Amongst patients suffering from chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps, a statistically significant reduction in relative abundance of Corynebacterium was identified. Despite some measured differences in microbiome composition between participating centres in our cohort, these differences would not alter the general pattern of core organisms described above.
Allergen-Specific Immunotherapy and Biologics
Real-world evidence of subcutaneous allergoid immunotherapy in house dust mite-induced allergic rhinitis and asthma
- Pages: 2050-2058
- First Published: 20 February 2020
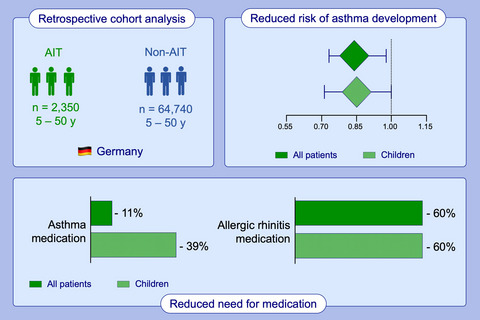
In this retrospective, real-world study in Germany, effectiveness of (allergen immunotherapy) AIT with a subcutaneous (house dust mite) HDM allergoid was analyzed in comparison with a non-AIT control group. After up to 6 years of follow-up, the probability of asthma development in patients treated with HDM allergoid was significantly lower compared to the control group. Patients treated with HDM allergoid required significantly fewer medications for allergic rhinitis and asthma, thus indicating the preventive effect of HDM allergoid AIT on asthma occurrence and progression.
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
Potential treatment effect of the SQ tree SLIT-tablet on pollen food syndrome caused by apple
- Pages: 2059-2061
- First Published: 21 February 2020
ORMDL3 but not neighboring 17q21 gene LRRC3C is expressed in human lungs and lung cells of asthmatics
- Pages: 2061-2065
- First Published: 22 February 2020
Mining the infant gut microbiota for therapeutic targets against atopic disease
- Pages: 2065-2068
- First Published: 22 February 2020
Basophil activation test in cancer patient blood evaluating potential hypersensitivity to an anti-tumor IgE therapeutic candidate
- Pages: 2069-2073
- First Published: 22 February 2020
Retinoic acid-loading of the major birch pollen allergen Bet v 1 may improve specific allergen immunotherapy: In silico, in vitro and in vivo data in BALB/c mice
- Pages: 2073-2077
- First Published: 05 March 2020
Interleukin-36 (IL-36) system in the 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene (DNFB) mouse model of allergic contact dermatitis
- Pages: 2078-2081
- First Published: 07 March 2020
NSG mice humanized with allergen-specific T-cell lines as in vivo model of respiratory allergy
- Pages: 2081-2084
- First Published: 07 March 2020
Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin and clinical outcomes with mepolizumab in severe eosinophilic asthma
- Pages: 2085-2088
- First Published: 09 March 2020
Demonstration of distinct pathways of mast cell-dependent inhibition of Treg generation using murine bone marrow-derived mast cells
- Pages: 2088-2091
- First Published: 09 March 2020
IgE multiplex testing in house dust mite allergy is utile, and sensitivity is comparable to extract-based singleplex testing
- Pages: 2091-2094
- First Published: 12 March 2020
Desloratadine and loratadine use associated with improved melanoma survival
- Pages: 2096-2099
- First Published: 14 March 2020
Plasminogen glycoforms alteration and activation susceptibility associated with the missense variant p.Lys330Glu in HAE-PLG patients
- Pages: 2099-2102
- First Published: 17 March 2020
IL-1β and IL-17A are involved in IVIG resistance through activation of C/EBPβ and δ in a coronary artery model of Kawasaki disease
- Pages: 2102-2105
- First Published: 18 March 2020
Sputum and serum immunoglobulins in adult asthmatics with recurrent respiratory tract infections
- Pages: 2105-2108
- First Published: 18 March 2020
CCL2 mitigates cyclic AMP-suppressed Th2 immune response in human dendritic cells
- Pages: 2108-2111
- First Published: 19 March 2020
Prevalence of self-reported and confirmed penicillin allergy in a Belgian outpatient population
- Pages: 2111-2115
- First Published: 03 April 2020
Definition, aims, and implementation of GA2LEN/HAEi Angioedema Centers of Reference and Excellence
- Pages: 2115-2123
- First Published: 05 April 2020
The validity of the Canadian clinical scores for occupational asthma in European populations
- Pages: 2124-2126
- First Published: 03 April 2020
Human airway epithelial cells express a functional IL-5 receptor
- Pages: 2127-2130
- First Published: 04 April 2020
Exercise-induced bronchoconstriction: A survey of diagnostic practice in secondary care across the United Kingdom
- Pages: 2130-2132
- First Published: 06 April 2020
Tonsillar microbial diversity, abundance, and interrelations in atopic and non-atopic individuals
- Pages: 2133-2135
- First Published: 06 April 2020
NEWS AND VIEWS
Legends of Allergy and Immunology
Algorithms in Allergy and Clinical Immunology
Medical algorithms: Diagnosis and investigation of perioperative immediate hypersensitivity reactions
- Pages: 2139-2142
- First Published: 13 February 2020
Groundbreaking Discoveries in Immunology
Vitamin D supplementation in pregnancy does not prevent school-age asthma
- Pages: 2143-2144
- First Published: 26 April 2020