Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
Issue Information
- Pages: 1034-1036
- First Published: 14 April 2020

Cover of this issue. Multiplex fluorescent immunohistochemistry of esophageal cancer biopsies. CD86 (red), CD163 (green), CD206 (magenta) and DAPI (blue) are shown. See also Yamamoto et al. (pp. 1103–1112 of this issue).
IN THIS ISSUE
In this issue: Volume 111, Issue 4, April 2020
- Pages: 1037-1038
- First Published: 14 April 2020
REVIEW ARTICLES
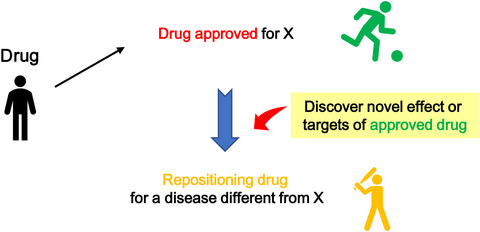
Drug repositioning in cancer: The current situation in Japan
- Pages: 1039-1046
- First Published: 19 January 2020
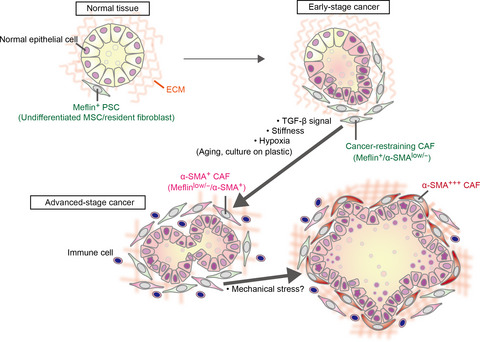
Cancer-associated fibroblasts that restrain cancer progression: Hypotheses and perspectives
- Pages: 1047-1057
- First Published: 14 February 2020
Targeting DNA binding proteins for cancer therapy
- Pages: 1058-1064
- First Published: 19 February 2020
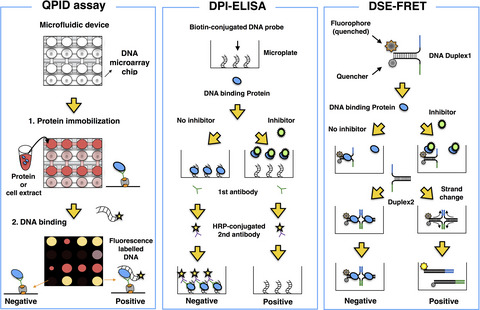
Alteration of transcription factor (TF) activity occurs in numerous cancer tissues due to gene amplification, deletion, and point mutations, and epigenetic modification. The development of drugs targeting these TFs has historically been difficult due to the lack of high-throughput screening methods. Recent advances in technology for identification and selective inhibition of DNA binding proteins enable cancer researchers to develop novel therapeutics targeting cancer-associated TFs.
Application of the microRNA-302/367 cluster in cancer therapy
- Pages: 1065-1075
- First Published: 20 January 2020
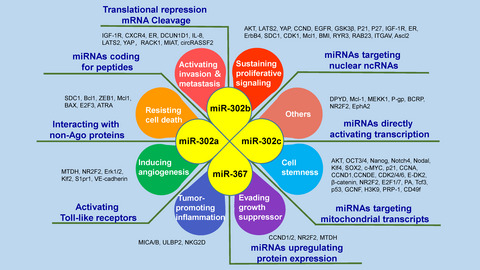
The microRNA (miR)-302/367 cluster has been implicated in several peculiarities of cancer including evading growth suppressors, sustaining proliferative signaling, and evading cell death and senescence, angiogenesis, invasion and metastasis. This review provides a critical overview of miR-302/367 cluster dysregulation and the subsequent effects in cancer and demonstrates the indispensable roles of this cluster as therapeutic targets and novel biomarkers at current state researches.
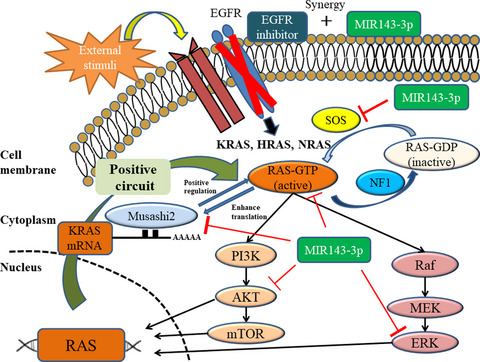
Effects of MIR143 on rat sarcoma signaling networks in solid tumors: A brief overview
- Pages: 1076-1083
- First Published: 19 February 2020
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
BASIC AND CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY
Prediction of overall survival in resectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: ISICC-applied prediction model
- Pages: 1084-1092
- First Published: 23 January 2020

Using tissue microarray, we examined the density of 16 immune biomarkers in 280 ICC patients who underwent hepatectomy, and established a novel ISICC-based prediction model (IPM) to predict patients’ overall survival with bilirubin, tumor numbers, CEA, CA19-9, γ-glutamyl transferase (GGT), HBsAg and ISICC. The new model may provide a better prediction performance for the overall survival of patients with resectable ICC in clinical practice.
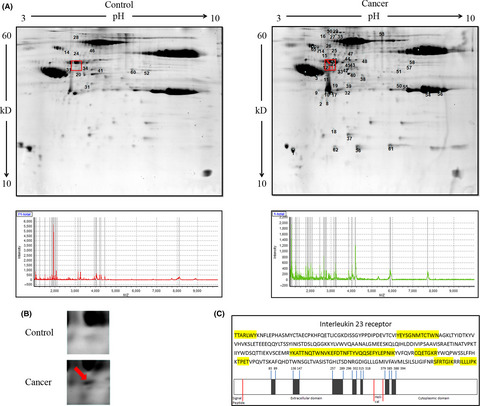
Prognostic value of serum soluble interleukin-23 receptor and related T-helper 17 cell cytokines in non-small cell lung carcinoma
- Pages: 1093-1102
- First Published: 05 February 2020
Tumor-infiltrating M2 macrophage in pretreatment biopsy sample predicts response to chemotherapy and survival in esophageal cancer
- Pages: 1103-1112
- First Published: 24 January 2020
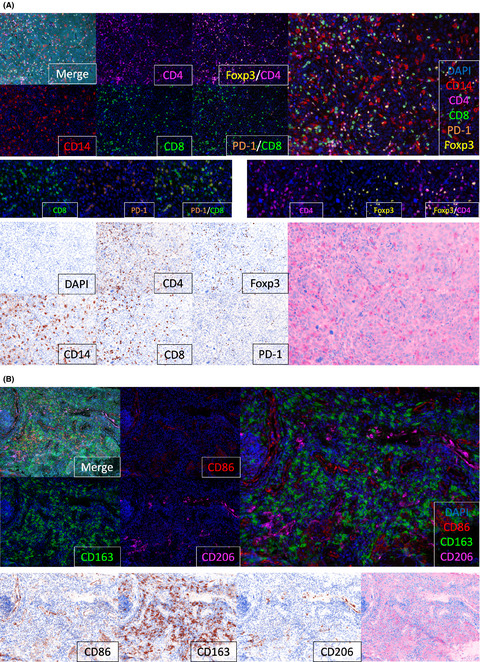
The present study confirmed that pre–therapeutic M2 macrophage infiltration would be a useful biomarker in predicting the response to NAC and unfavorable survival among a variety of immune cells in EC patients. Our results support the possibility of using immunotherapy, targeting M2 macrophages, alongside conventional neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Cisplatin-induced programmed cell death ligand-2 expression is associated with metastasis ability in oral squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 1113-1123
- First Published: 03 February 2020
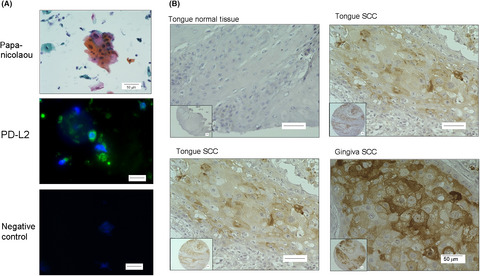
Our findings indicate that cisplatin-upregulated PD-L2 expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cells via STAT1/3 activation and the expression of PD-L2 are likely to be associated with malignancy in OSCC. The PD-L2 expression in cisplatin-resistant OSCC cells may be a critical factor in the prognosis of advanced OSCC patients.
CD4/CD8 ratio is a prognostic factor in IgG nonresponders among peptide vaccine-treated ovarian cancer patients
- Pages: 1124-1131
- First Published: 14 February 2020
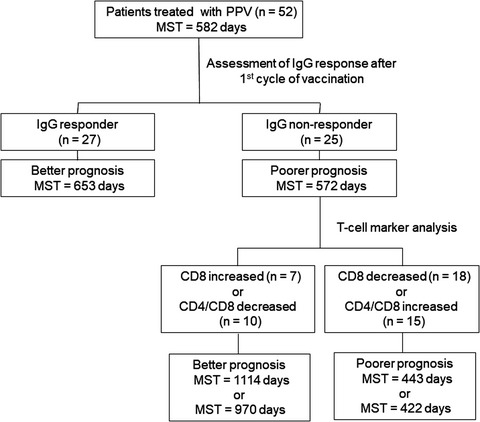
Early induction of the IgG response has been reported as a useful biomarker of favorable prognosis for cancer patients treated with a peptide vaccination, but a portion of these patients (IgG nonresponders) fail to achieve an early induction of IgG response yet experience long-term survival. Here we found the usefulness of classical T-cell markers (ie, the CD8 content and the CD4/CD8 ratio in peripheral blood) as biomarkers in IgG nonresponders among ovarian cancer patients treated with a personalized peptide vaccination.
CARCINOGENESIS
Anthrax toxin receptor 1/tumor endothelial marker 8 promotes gastric cancer progression through activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Pages: 1132-1145
- First Published: 24 January 2020
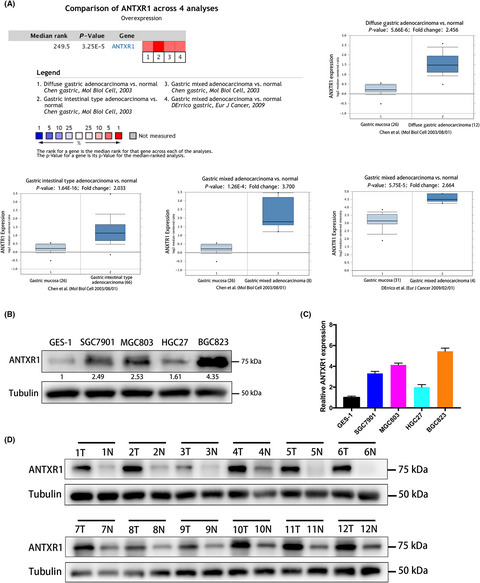
The authors observed that anthrax toxin receptor 1 (ANTXR1) expression was significantly upregulated in gastric cancer (GC) tissue and its overexpression was associated with poor prognosis of GC patients. A series of in vitro and in vivo assays were carried out through strategies of loss- or gain-of-function and rescue assays to find that ANTXR1 promotes gastric cancer progression through activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.
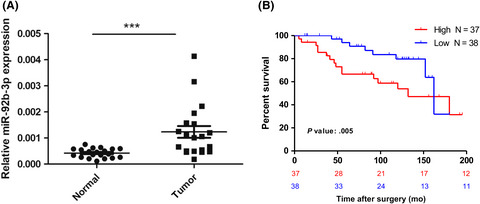
MicroRNA-92b-3p is a prognostic oncomiR that targets TSC1 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- Pages: 1146-1155
- First Published: 23 January 2020
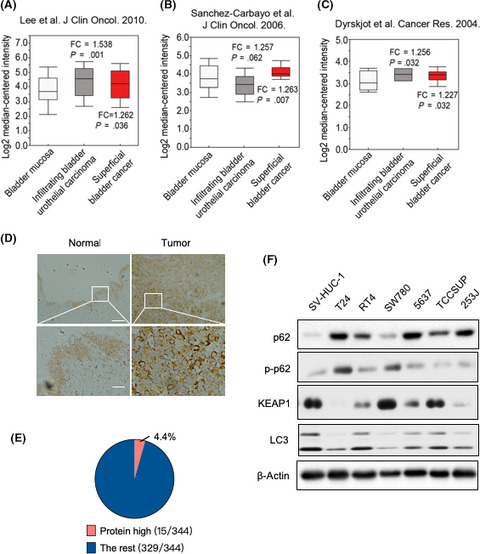
p62 promotes bladder cancer cell growth by activating KEAP1/NRF2-dependent antioxidative response
- Pages: 1156-1164
- First Published: 22 January 2020
Luteolin suppresses bladder cancer growth via regulation of mechanistic target of rapamycin pathway
- Pages: 1165-1179
- First Published: 29 January 2020
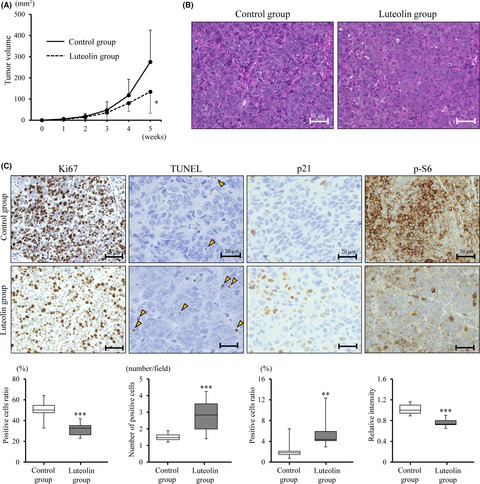
Luteolin suppresses cell proliferation through downregulation of mTOR signaling and upregulation of p21 in bladder cancers both in vitro and in vivo. mTOR activity is correlated with invasive ability in human bladder cancer cases. A metabolite of luteolin decreases cell viability and squamous differentiation in in vivo rat bladder cancer models.
Frequent homozygous deletion of Cdkn2a/2b in tremolite-induced malignant mesothelioma in rats
- Pages: 1180-1192
- First Published: 20 February 2020
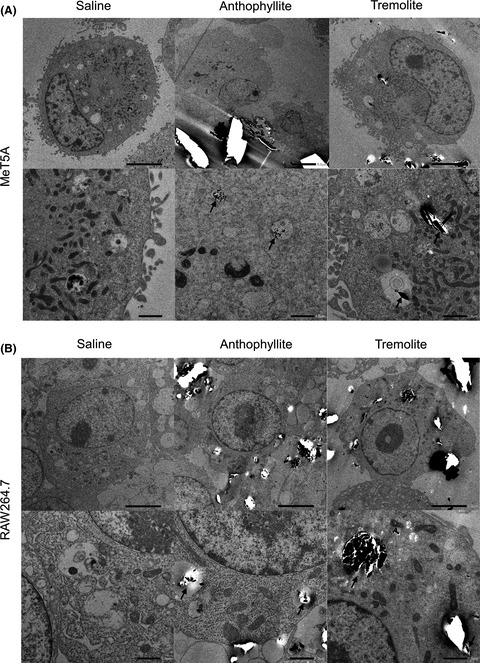
MeT5A (immortalized mesothelial cells) and RAW264.7 (macrophage lineage cells) were damaged by tremolite but not anthophyllite. Tremolite induced diffuse peritoneal thickening, whereas anthophyllite induced focal fibrosis. Furthermore, tremolite-induced malignant mesothelioma frequently lost Cdkn2a/2b.
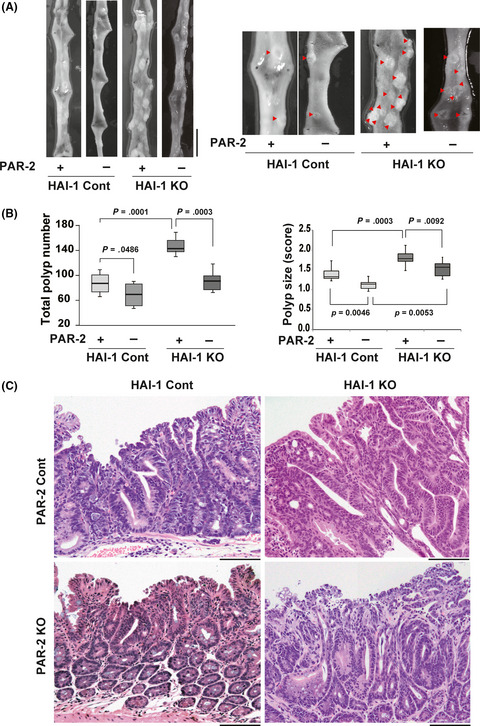
Protease-activated receptor-2 accelerates intestinal tumor formation through activation of nuclear factor-κB signaling and tumor angiogenesis in ApcMin/+ mice
- Pages: 1193-1202
- First Published: 30 January 2020
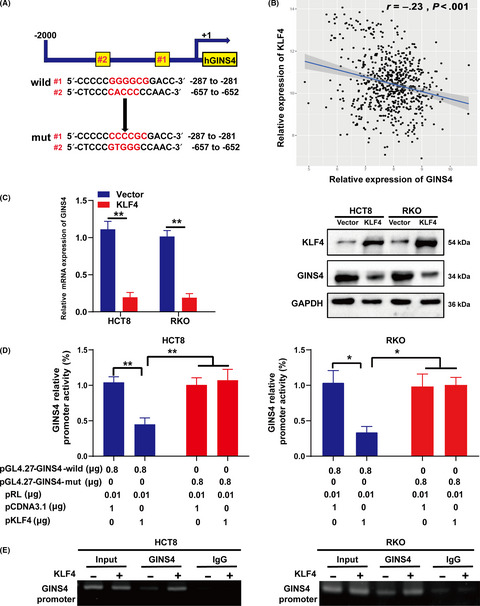
GINS complex subunit 4, a prognostic biomarker and reversely mediated by Krüppel-like factor 4, promotes the growth of colorectal cancer
- Pages: 1203-1217
- First Published: 03 February 2020
CELL, MOLECULAR, AND STEM CELL BIOLOGY
Induction of tryptophan hydroxylase in the liver of s.c. tumor model of prostate cancer
- Pages: 1218-1227
- First Published: 30 January 2020
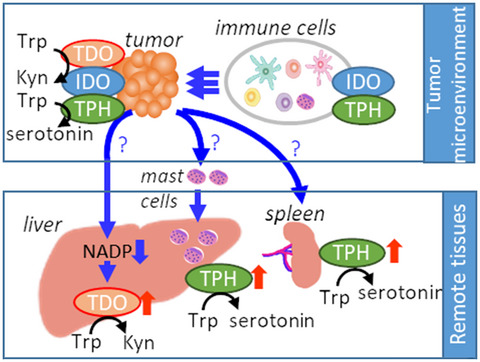
Our study reported for the first time that L-tryptophan catabolic enzymes, tryptophan-2, 3-dioxygenase (TDO) and/or tryptophan hydroxylase-1 (TPH1), are induced in remote tissues, liver and spleen, of tumor burden model. Similar TPH1 induction in remote liver tissues was observed with nonneoplastic liver samples from some of the colorectal cancer patients. Our findings suggest that Trp catabolism can be induced not only in tumor microenvironment but also in peripheral remote tisssues in cancer.
Modulation of Nqo1 activity intercepts anoikis resistance and reduces metastatic potential of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pages: 1228-1240
- First Published: 22 January 2020
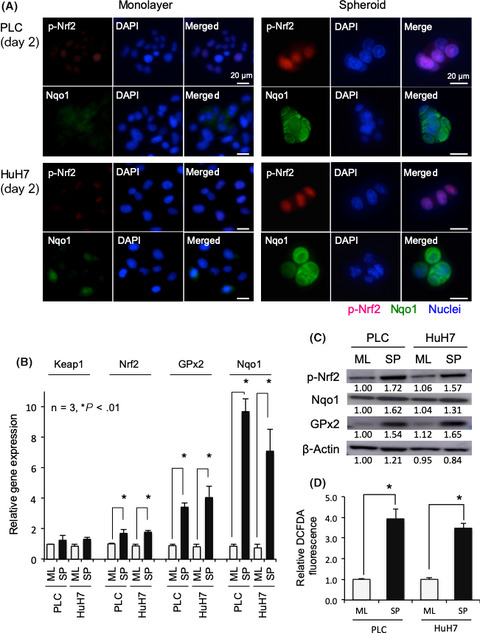
Downregulation of NADPH quinone oxidoreductase 1 (Nqo1) in suspended culture promoted intracellular reactive oxygen species production and induced anoikis, resulting in attenuated spheroid formation. Activation of Nqo1 by β-lapachone showed a similar effect on anoikis sensitivity and diminished spheroid formation. Overexpression of Nrf2/Nqo1 was associated with intrahepatic recurrence and was an independent risk factor for poor prognosis.
Tumor cell-derived angiopoietin-like protein 2 establishes a preference for glycolytic metabolism in lung cancer cells
- Pages: 1241-1253
- First Published: 03 February 2020
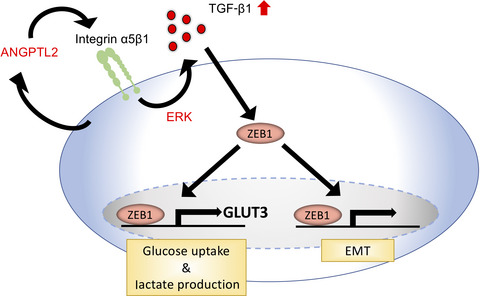
Tumor cell-derived angiopoietin-like protein 2 (ANGPTL2) accelerates metastatic capacity of tumors in an autocrine/paracrine manner by activating tumor cell motility and invasiveness and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Here we report evidence supporting a role for tumor cell-derived ANGPTL2 in establishing a preference for glycolytic metabolism. Overall, this work suggests that tumor cell-derived ANGPTL2 accelerates activities associated with glycolytic metabolism in lung cancer cells by activating TGF-β-ZEB1-GLUT3 signaling.
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived CXCL16 promotes progression of gastric cancer cells by STAT3-mediated expression of Ror1
- Pages: 1254-1265
- First Published: 03 February 2020
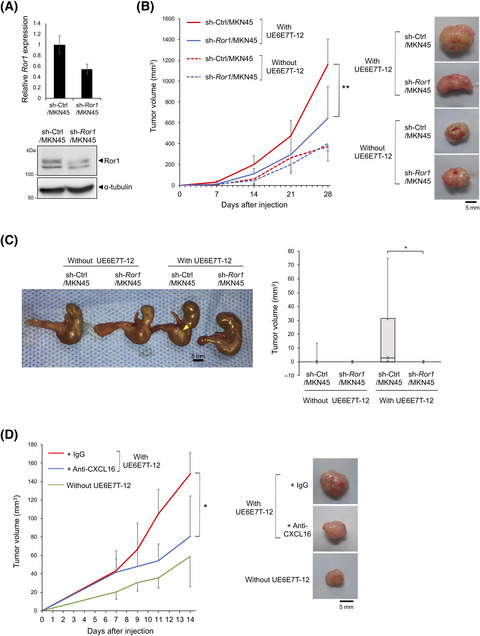
We show that CXCL16 derived from human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) induces expression of Ror1 through activation of STAT3 in MKN45 gastric cancer cells, resulting in promotion of proliferation and migration of MKN45 cells in vitro. Furthermore, tumor formation of MKN45 cells in nude mice can be accelerated by co–injection of MSC, in a manner that is inhibited by anti–CXCL16 neutralizing antibody and is dependent on Ror1 expression in MKN45 cells. These findings indicate that CXCL16 derived from MSC induces expression of Ror1 through activation of the STAT3 pathway in MKN45 cells, leading to the promotion of tumor formation.
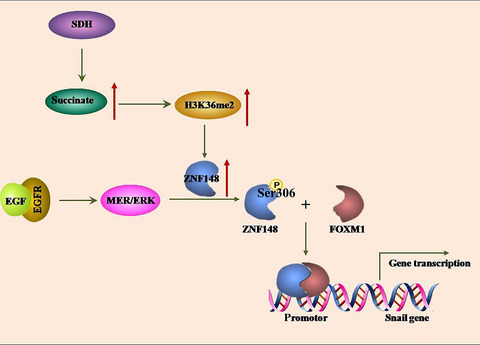
Upregulation of ZNF148 in SDHB-deficient gastrointestinal stromal tumor potentiates Forkhead box M1-mediated transcription and promotes tumor cell invasion
- Pages: 1266-1278
- First Published: 14 February 2020
Exosomes mediate intercellular transfer of non–autonomous tolerance to proteasome inhibitors in mixed-lineage leukemia
- Pages: 1279-1290
- First Published: 14 February 2020
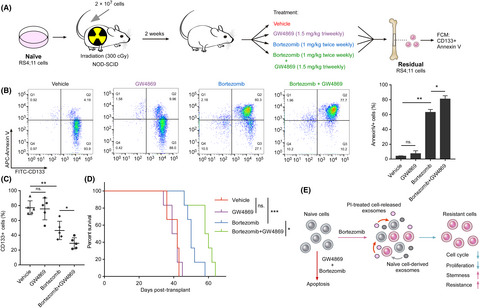
Using the integrated multi-omics analysis, our study demonstrates that exosomes derived from MLL cells under therapy stress transmit proteasome inhibitor (PI) tolerance to recipient cells through cell cycle arrest and enhanced stemness. Exosomes can act not only as a mediator of development of PI tolerance but also as a therapeutic target to overcome PI resistance, thereby enhancing clinical benefits of PI therapy in MLL.
CLINICAL RESEARCH
Metastatic role of mammalian target of rapamycin signaling activation by chemoradiotherapy in advanced rectal cancer
- Pages: 1291-1302
- First Published: 29 January 2020
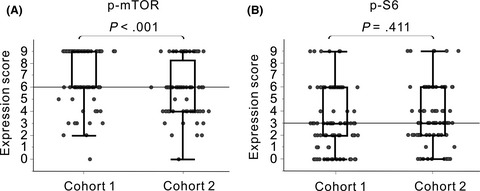
The postoperative distant recurrence is critical in rectal cancer patients who have received neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (NACRT). We investigated NACRT-mediated mTOR activation and metastatic potential of rectal cancer, identifying p-S6 expression as a NACRT predictor of postoperative distant metastasis in rectal cancer patients, suggesting that chemoradiotherapy may modulate the mTOR signaling pathway to promote metastasis.
Stathmin guides personalized therapy in oral squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 1303-1313
- First Published: 28 January 2020
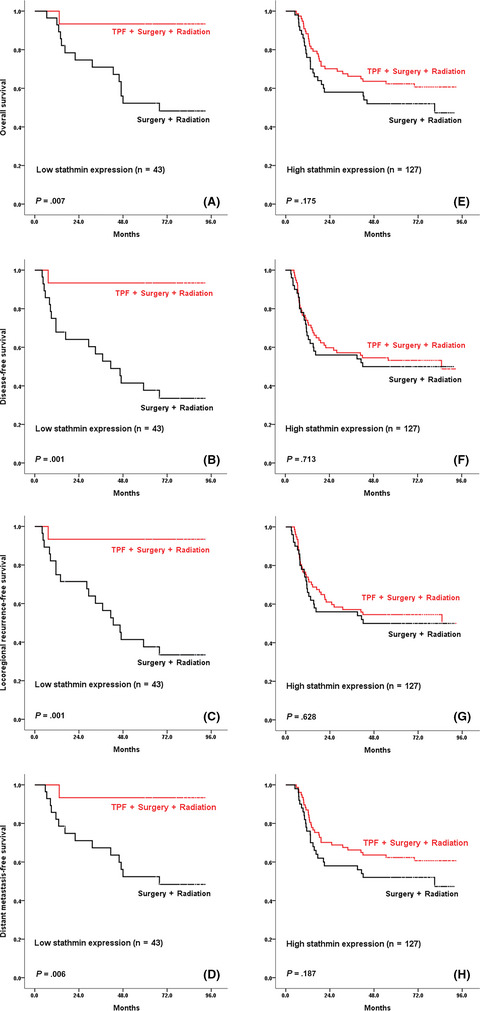
The evaluation of stathmin in biopsy tissues has potential as a clinical tool for predicting the outcomes of oral cancer patients undergoing docetaxel, cisplatin, and 5-fluorouracil (TPF) induction chemotherapy. Combination of TPF chemotherapy and PI3K signaling pathway inhibitors showed potent inhibition of oral cancer cells and xenografts, in which stathmin is highly expressed. Therefore, we are exploring personalized strategies of stathmin expression-based induction chemotherapy in oral cancer.
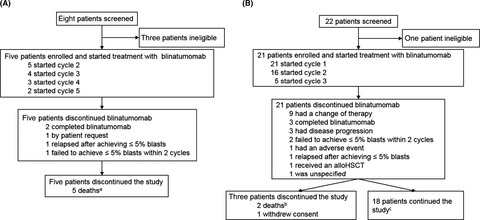
Phase 1b/2 study of blinatumomab in Japanese adults with relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Pages: 1314-1323
- First Published: 23 January 2020
Pembrolizumab monotherapy in Japanese patients with advanced ovarian cancer: Subgroup analysis from the KEYNOTE-100
- Pages: 1324-1332
- First Published: 03 February 2020
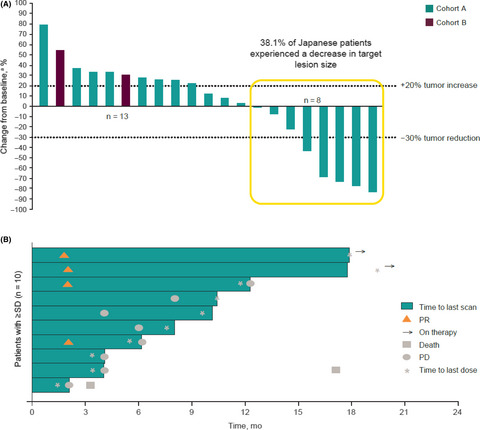
This manuscript is a subgroup analysis of Japanese patients with advanced recurrent ovarian cancer (ROC) who were treated with pembrolizumab monotherapy from the KEYNOTE-100 study. Pembrolizumab monotherapy was associated with antitumor activity in some Japanese patients with ROC, with no new safety signals identified in this subpopulation.
Expression, mutation, and methylation of cereblon-pathway genes at pre- and post-lenalidomide treatment in multiple myeloma
- Pages: 1333-1343
- First Published: 15 February 2020
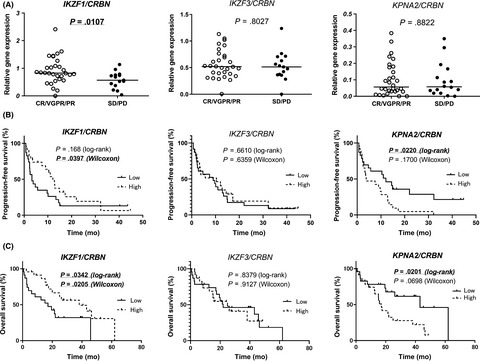
This study investigated the prognostic value of the expression of cereblon (CRBN)-pathway genes on the clinical relevance of lenalidomide treatment and evaluated the levels of CRBN-binding proteins, mutations in these genes, and the methylation status of the CRBN promoter sequence. In conclusion, a decreased expression of IKZF1 and increased expression of KPNA2 compared to that of CRBN mRNA predicts poor outcomes of lenalidomide and dexamethasone therapy.
DRUG DISCOVERY AND DELIVERY
Liposomal simvastatin sensitizes C26 murine colon carcinoma to the antitumor effects of liposomal 5-fluorouracil in vivo
- Pages: 1344-1356
- First Published: 20 January 2020
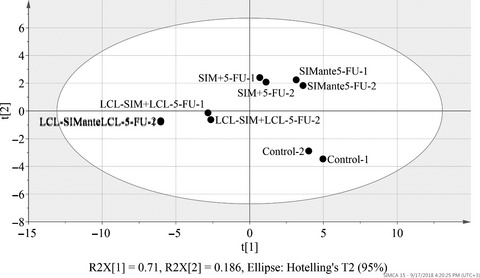
Liposomal simvastatin sensitizes C26 cells to liposomal 5-fluorouracil treatment. The combination therapy based on the administration of liposomal simvastatin and 5-fluorouracil has the potential to become a successful cancer-targeted therapy, mainly due to the inhibitory effects on the intratumor angiogenesis.
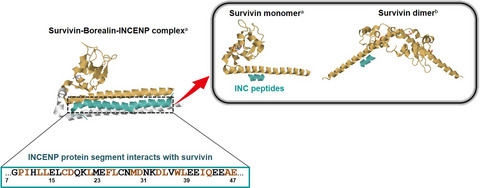
Discovery of inner centromere protein-derived small peptides for cancer imaging and treatment targeting survivin
- Pages: 1357-1366
- First Published: 28 January 2020
EPIDEMIOLOGY AND PREVENTION
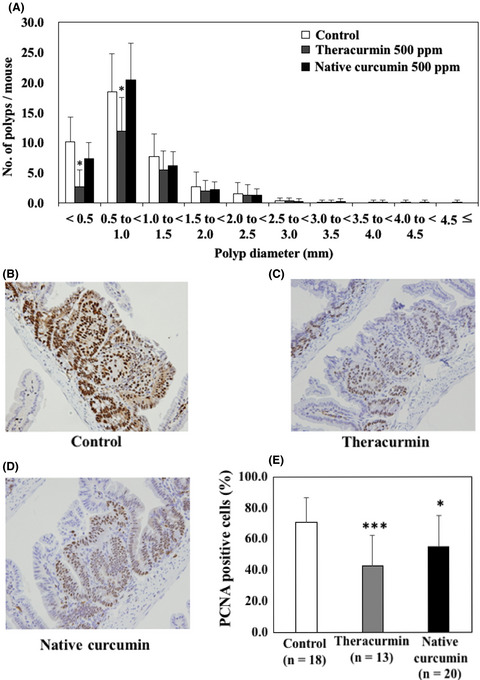
Theracurmin inhibits intestinal polyp development in Apc-mutant mice by inhibiting inflammation-related factors
- Pages: 1367-1374
- First Published: 28 January 2020
GENETICS, GENOMICS, AND PROTEOMICS
Using next-generation sequencing to redefine BRCAness in triple-negative breast cancer
- Pages: 1375-1384
- First Published: 20 January 2020
Genome organization in proximity to the BAP1 locus appears to play a pivotal role in a variety of cancers
- Pages: 1385-1391
- First Published: 19 January 2020
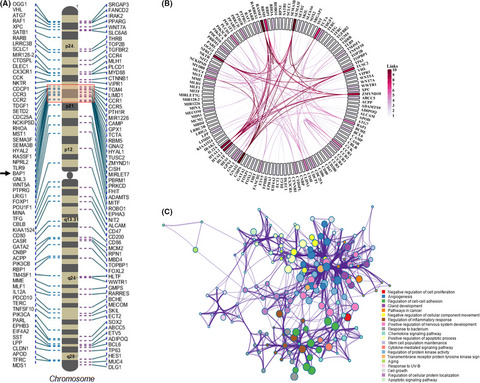
Cancer-associated genes on chromosome 3 are enriched with repetitive elements and show strong intrachromosomal chromatin interactions. The genomic hotspot in the vicinity of the BAP1 locus appears to be involved in multiple cancers. Cross-species comparison revealed a shared synteny of these genes and inversions near the hotspot region in closer primates.
Replisome genes regulation by antitumor miR-101-5p in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- Pages: 1392-1406
- First Published: 23 January 2020
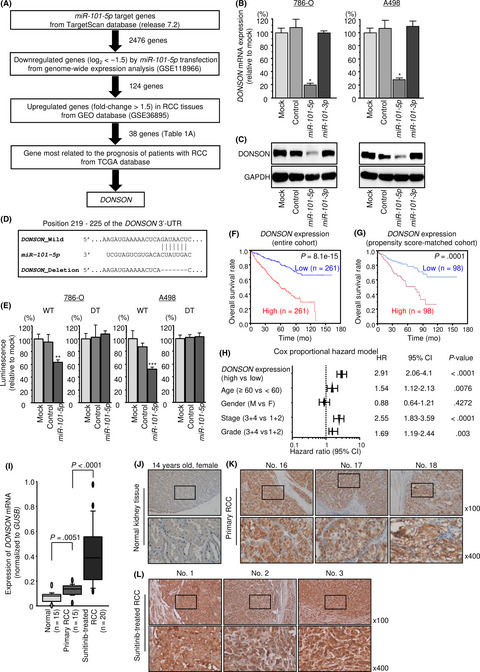
MicroRNA-101-5p expression was downregulated in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) tissues and functioned as tumor-suppressive microRNA. MicroRNA-101-5p directly regulated DONSON, which was highly expressed in ccRCC and sunitinib-resistant RCC tissues. DONSON and other replisome-related genes have a potential to be diagnostic and therapeutic targets in ccRCC.
Establishment of epigenetic markers to predict irradiation efficacy against oropharyngeal cancer
- Pages: 1407-1416
- First Published: 03 February 2020
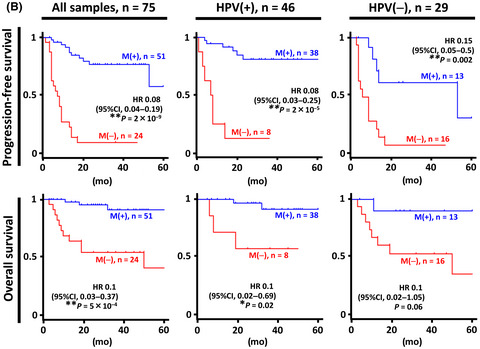
We investigated the association between promoter DNA methylation and irradiation efficacy against oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OPSCC), so that an appropriate stratification by establishing molecular classifier markers could help therapeutic optimization and de–escalation of OPSCC treatment. A methylation marker panel was developed to act as an efficacy predictor with high sensitivity, specificity and accuracy in the training samples. It is noteworthy that the utility of the established prediction marker panel was consistent regardless of human papillomavirus status, and that multivariate analysis verified the methylation status of the marker panel as the only independent prognostic factor.
Gene expression profiling of primary vitreoretinal lymphoma
- Pages: 1417-1421
- First Published: 14 February 2020
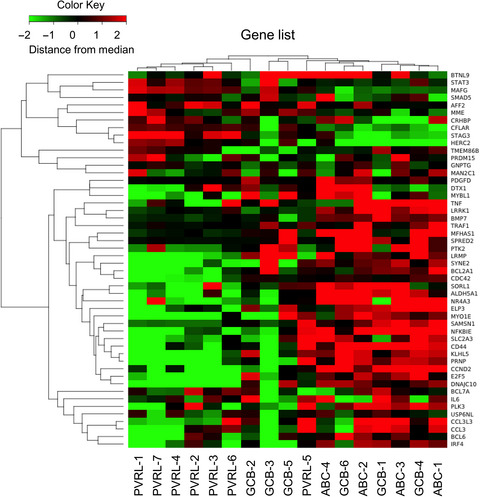
To determine the subtype and biological characteristics of tumor cells of primary vitreoretinal lymphoma (PVRL), we performed gene expression profiling analysis using RNA extracted from vitreous samples upon diagnosis. PVRL had unique genetic features: an expression pattern different from ABC-type and relatively close to GCB-type DLBCL. CD79B mutations showed potential to serve as prognostic markers for CNS progression.
PATHOLOGY
Suppression of KIF3A inhibits triple negative breast cancer growth and metastasis by repressing Rb-E2F signaling and epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- Pages: 1422-1434
- First Published: 03 February 2020

KIF3A,a member of kinesin super family, was over-expressed in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) tissues and such high KIF3A expression was associated with tumor recurrence and lymph node. Silencing of KIF3A suppressed TNBC cells proliferation, migration and invasion by repressing the Rb-E2F signaling and EMT. And the tumor size and lung metastatic nodules were less in KIF3A depletion xenograft mice.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Is the catch-up program of HPV vaccination for Japanese adult women effective or not?
- Pages: 1435-1436
- First Published: 26 February 2020