Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
Issue Information
- Pages: 3665-3667
- First Published: December 2018

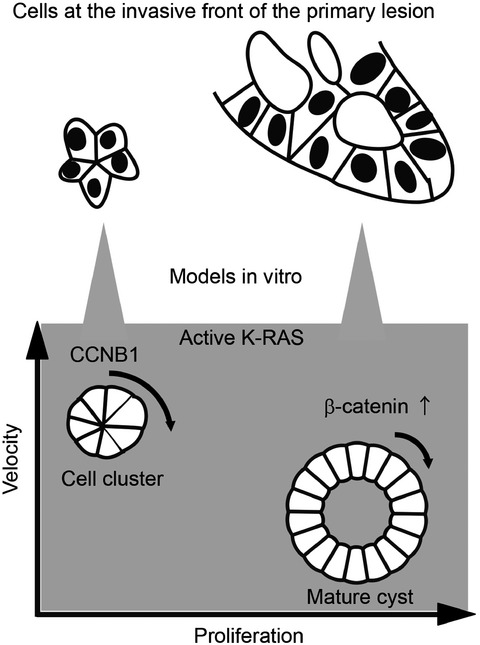
Cover of this issue. Cell clusters and cysts are rotated through distinct signaling mechanisms.see also Hirata et al. (pp. 4045–4055 of this issue).
IN THIS ISSUE
In this Issue: Volume 109, Issue 12, November 2018
- Pages: 3668-3670
- First Published: December 2018
REVIEW ARTICLES
The role of sphingosine-1-phosphate in inflammation and cancer progression
- Pages: 3671-3678
- First Published: 20 September 2018
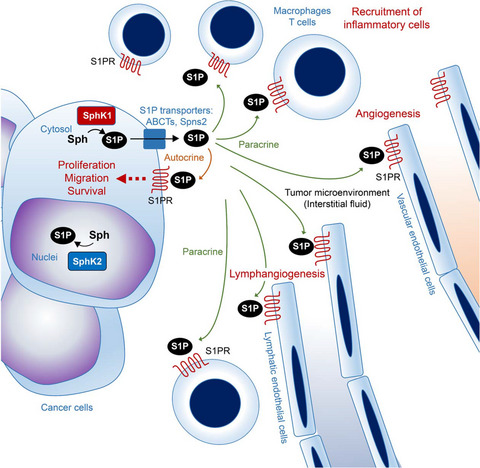
Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) is a pleiotropic lipid mediator that regulates cell survival and migration, immune cell recruitment, angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Cancer cells produce elevated levels of S1P, contributing to the tumor microenvironment and linking cancer and inflammation. Considering the critical role of S1P in linking inflammation and cancer, it is possible that the S1P signaling pathway could be a novel therapeutic target for cancers with chronic inflammation.
Acceleration of cancer science with genome editing and related technologies
- Pages: 3679-3685
- First Published: 13 October 2018
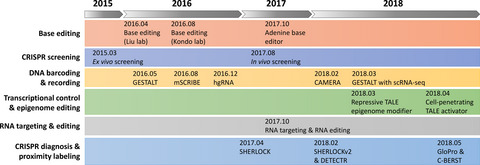
In addition to conventional genome editing strategies, tools enabling customized, site-specific recognition of particular nucleic acid sequences have been coming into wider use; for example, single base editing without DSB introduction, epigenome editing with recruitment of epigenetic modifiers, transcriptome engineering using RNA editing systems, and in vitro detection of specific DNA and RNA sequences. In this review, we provide a quick overview of the current state of genome editing and related technologies that multilaterally contribute to cancer science.
Mitochondrial network structure homeostasis and cell death
- Pages: 3686-3694
- First Published: 12 October 2018
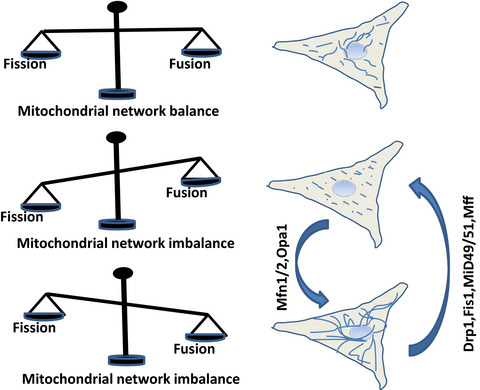
Here, we examine the relevance of the homeostasis of the mitochondrial network structure in 3 different types of cell death, including autophagy, apoptosis and necroptosis. Furthermore, a variety of cancers often exhibit a fragmented mitochondrial phenotype. Targeting the mitochondrial fission protein Drp1or other shaping proteins is becoming a topic of interest. Further studies are needed to understand the differential effects of oncogenic signaling pathways on mitochondrial dynamics and to identify additional new signaling axes that regulate mitochondrial network structure homeostasis.
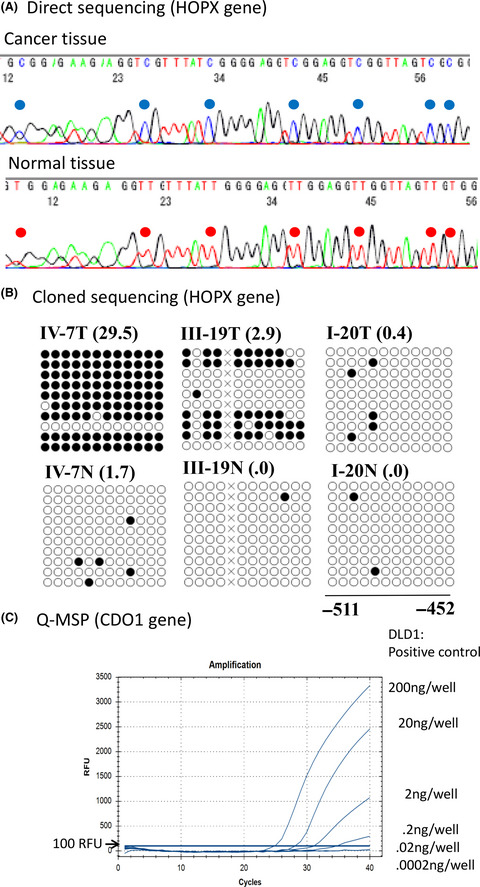
Epigenetic biomarkers of promoter DNA methylation in the new era of cancer treatment
- Pages: 3695-3706
- First Published: 27 September 2018
Langerhans cell histiocytosis in adults: Advances in pathophysiology and treatment
- Pages: 3707-3713
- First Published: 03 October 2018
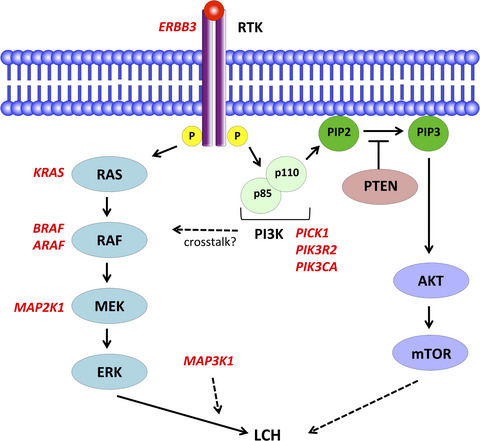
Recent studies have shown that Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) is a clonally expanding myeloid neoplasm. Although LCH is not always fatal, delayed diagnosis or treatment can result in serious impairment of organ function and decreased quality of life. This study summarizes recent advances in the pathophysiology and treatment of adult LCH, to raise awareness of this “orphan disease”.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
BASIC AND CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY
Long non-coding RNA MIF-AS1 promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation and reduces apoptosis to upregulate NDUFA4
- Pages: 3714-3725
- First Published: 20 September 2018
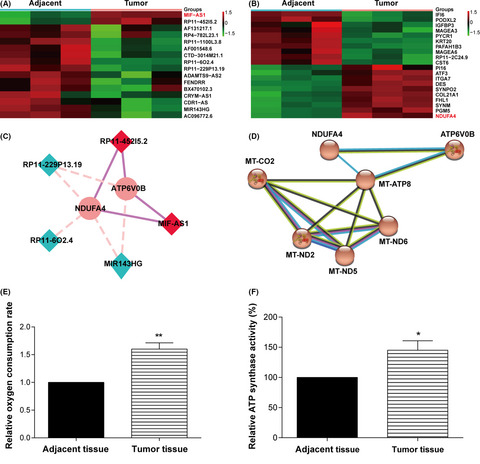
Our findings showed that lncMIF-AS1 is involved in gastric cancer tumorigenesis as a tumor activator gene. Through upregulation of NDUFA4, lncMIF-AS1 promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation and repressed apoptosis. Moreover, we showed that lncMIF-AS1 activates NDUFA4 expression by sponging to miR-212-5p in gastric cancer cells. And inhibition of lnvMIF-AS1/miR-212-5p/NDUFA4 may provide an attractive therapeutic target for the treatment of gastric cancer.
Mechanism and prognostic value of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pages: 3726-3736
- First Published: 27 September 2018
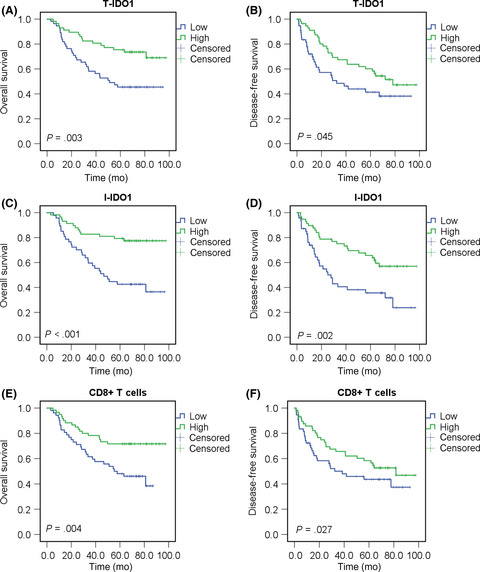
Increased indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) levels represented an adaptive immune resistance mechanism exerted by hepatocellular carcinoma cells in response to endogenous antitumor activity. Expression of IDO1 by either tumor cells or infiltrating inflammatory cells was a positive prognostic predictor in hepatocellular carcinoma.
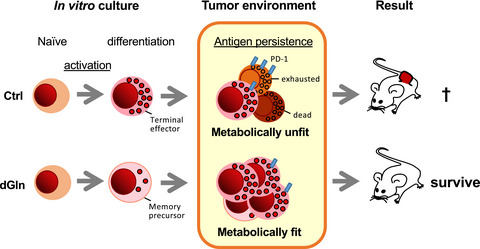
Reinforce the antitumor activity of CD8+ T cells via glutamine restriction
- Pages: 3737-3750
- First Published: 09 October 2018
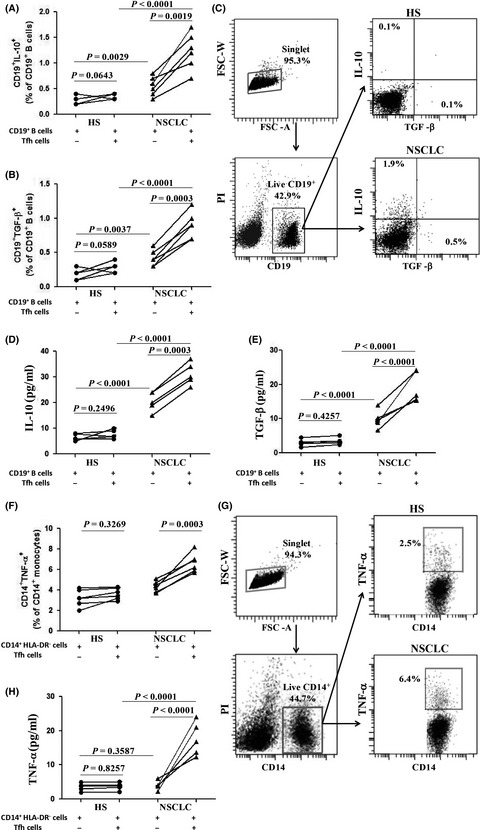
Functionally impaired follicular helper T cells induce regulatory B cells and CD14+ human leukocyte antigen-DR− cell differentiation in non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 3751-3761
- First Published: 16 October 2018
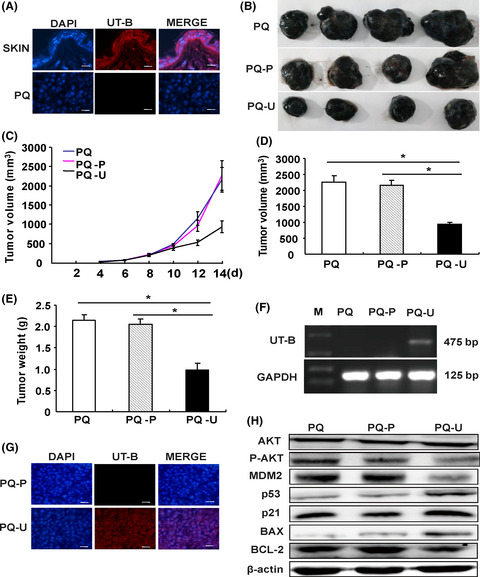
Urea transport B gene induces melanoma B16 cell death via activation of p53 and mitochondrial apoptosis
- Pages: 3762-3773
- First Published: 05 October 2018
CARCINOGENESIS
Silencing human epidermal growth factor receptor-3 radiosensitizes human luminal A breast cancer cells
- Pages: 3774-3782
- First Published: 27 September 2018
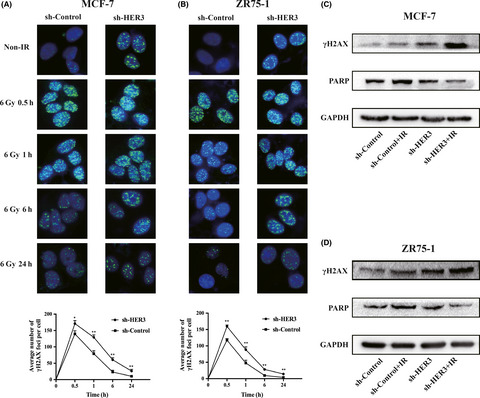
The purpose of this study is to elucidate the effect of human epidermal growth factor receptor-3 (HER3) in radiotherapy resistance and further assess whether HER3 could be a potential target for radiosensitivity. We concluded that silencing HER3 could significantly increase the radiosensitivity of luminal A breast cancer cells and HER3 could be a potential target for radiotherapy.
p53-inducible gene 3 promotes cell migration and invasion by activating the FAK/Src pathway in lung adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 3783-3793
- First Published: 03 October 2018
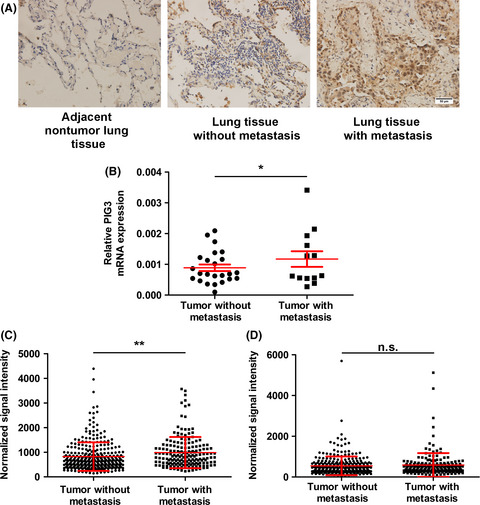
Our data demonstrated that PIG3 might function as a FAK regulator in NSCLC and could serve as a novel prognostic biomarker or therapeutic target in the treatment of NSCLC metastasis. This evidence will further help scientists to understand NSCLC progression and to develop new therapeutic strategies.
Forkhead box C1 boosts triple-negative breast cancer metastasis through activating the transcription of chemokine receptor-4
- Pages: 3794-3804
- First Published: 05 October 2018
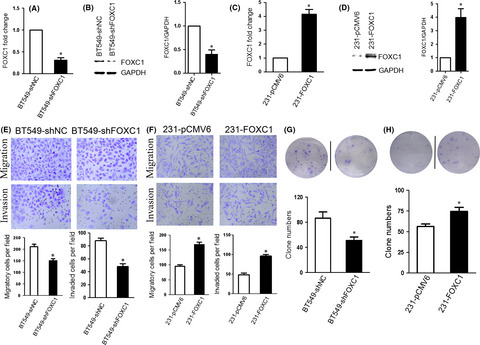
Forkhead box C1 (FOXC1) shows tumor-promoting activity that increases the growth, invasion, and metastasis of basal-like breast cancer (BLBC) cells in vitro. Downregulation of CXC chemokine receptor-4 expression inhibits FOXC1-induced migration and invasion. FOXC1 could be of value as a potential therapeutic target for BLBC.
Phosphorylation of serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 1 at tyrosine 19 promotes cell proliferation in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Pages: 3805-3815
- First Published: 15 October 2018
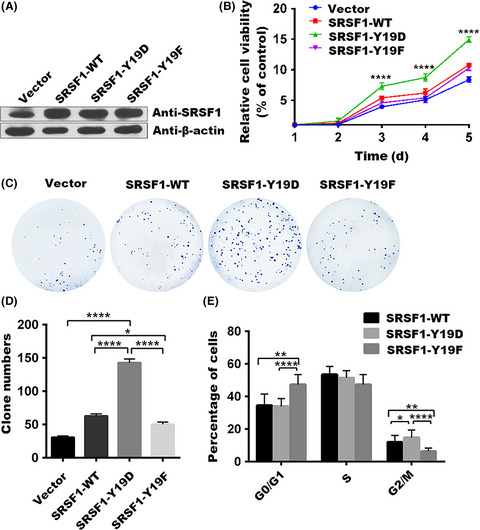
Our results underscore the phosphorylation of serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 1 (SRSF1) at the tyrosine 19 (Tyr-19) residue disrupts subcellular localization of SRSF1 and promotes cell proliferation in leukemic cells by accelerating cell-cycle progression. This study undoubtedly adds a new layer in understanding of how the posttranslational mechanism supports leukemia progression. Inhibitors targeting Tie2 kinase that could catalyze Tyr-19 phosphorylation of SRSF1 offer a promising therapeutic target for the treatment of pediatric ALL.
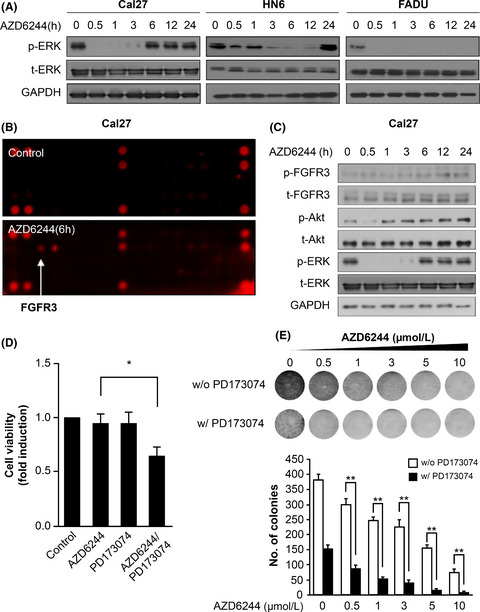
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3-mediated reactivation of ERK signaling promotes head and neck squamous cancer cell insensitivity to MEK inhibition
- Pages: 3816-3825
- First Published: 21 October 2018
CELL, MOLECULAR, AND STEM CELL BIOLOGY
Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 and CXCL2 produced by tumor promote the generation of monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells
- Pages: 3826-3839
- First Published: 27 September 2018
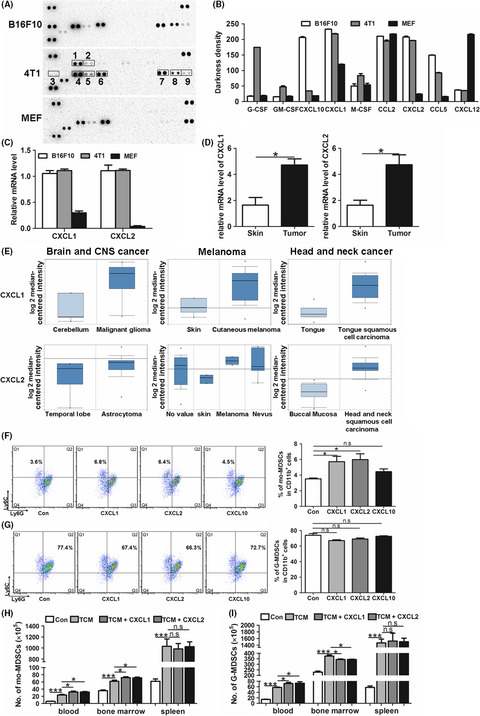
Our results elucidated that CXCL1 and CXCL2, which were originally characterized as chemokines of neutrophils, specifically promoted the expansion of mo-MDSC, a subtype of MDSC, in the presence of GM-CSF. Moreover, we found that, in addition to the tumor cells, tumor-infiltrated CD11b+ myeloid cells also expressed CXCL1 and CXCL2. Therefore, inhibition of CXCL1 and CXCL2 could decrease mo-MDSC generation and improve host immunosurveillance.
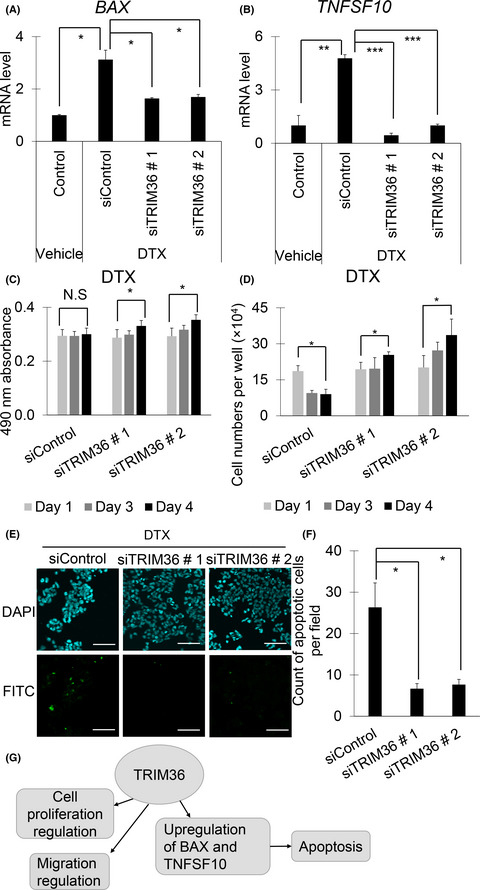
Androgen-responsive tripartite motif 36 enhances tumor-suppressive effect by regulating apoptosis-related pathway in prostate cancer
- Pages: 3840-3852
- First Published: 20 September 2018
Transduced caudal-type homeobox (CDX) 2/CDX1 can induce growth inhibition on CDX-deficient gastric cancer by rapid intestinal differentiation
- Pages: 3853-3864
- First Published: 05 October 2018
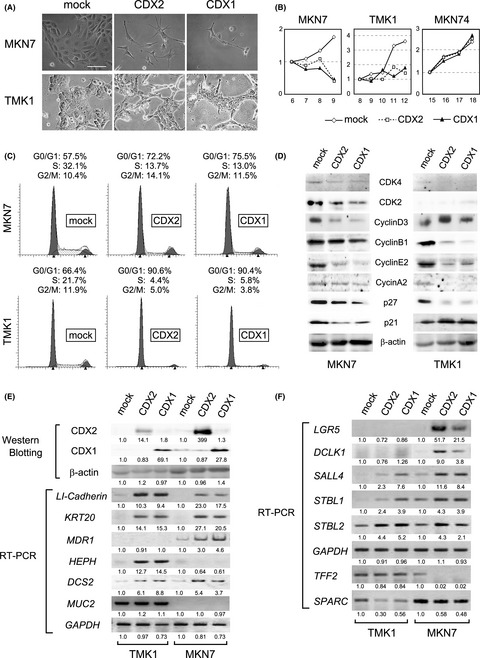
Exogenous expression of CDX2/CDX1 can lead to G0-G1 growth arrest in CDX-deficient gastric cancer cells, accompanied by induction of intestinal genes and decreased expression of gastric genes. Publicly available databases and hierarchical clustering of gastric tissue showed that gastric cancer with CDX expression has significantly better clinical outcomes. A novel therapy against gastric cancer based on induced intestinal differentiation may be possible in the future.
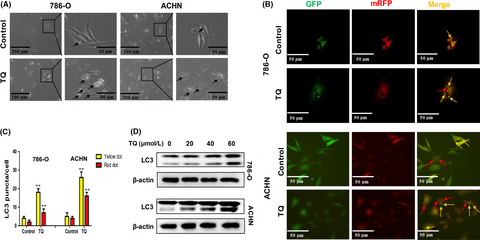
Thymoquinone inhibits the metastasis of renal cell cancer cells by inducing autophagy via AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway
- Pages: 3865-3873
- First Published: 27 September 2018
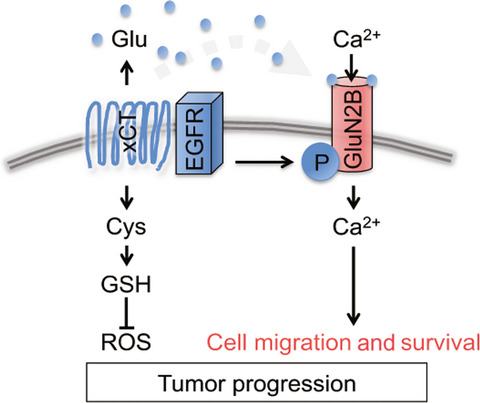
Epidermal growth factor receptor promotes glioma progression by regulating xCT and GluN2B-containing N-methyl-d-aspartate–sensitive glutamate receptor signaling
- Pages: 3874-3882
- First Published: 09 October 2018
FBXW7 modulates malignant potential and cisplatin-induced apoptosis in cholangiocarcinoma through NOTCH1 and MCL1
- Pages: 3883-3895
- First Published: 09 October 2018
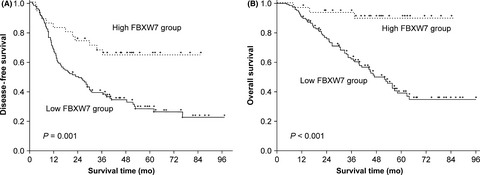
The ubiquitin ligase FBXW7 is associated with prognostic outcome in cholangiocarcinoma patients. FBXW7 was found to regulate the migration and self-renewal of cholangiocarcinoma cells through modulation of NOTCH1 as well as CDDP-induced apoptosis through MCL1 accumulation for the first time in cholangiocarcinoma cells. These findings suggest that FBXW7 modulates the malignant potential of cholangiocarcinoma through two signals, NOTCH1 and MCL1.
CLINICAL RESEARCH
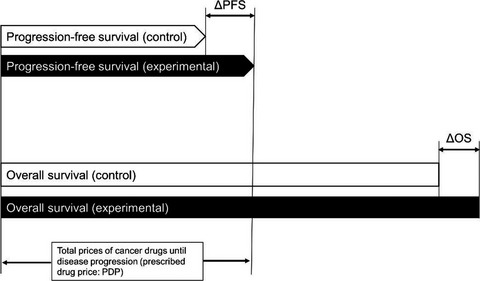
Lack of correlation between the costs of anticancer drugs and clinical benefits in Japan
- Pages: 3896-3901
- First Published: 13 October 2018
Functional intronic variant of SLC5A10 affects DRG2 expression and survival outcomes of early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer
- Pages: 3902-3909
- First Published: 03 October 2018
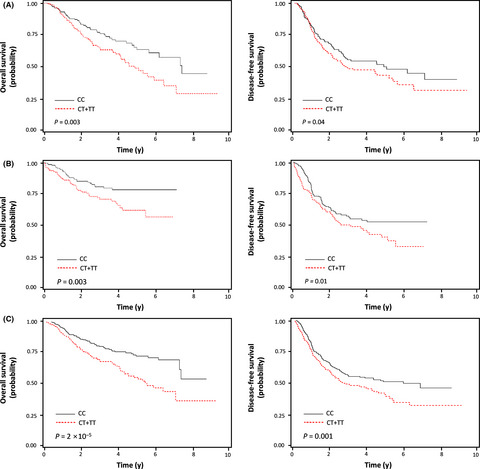
Variants in non-coding DNA may affect gene expression and, thereby, the prognosis of lung cancer patients. RegulomeDB can be used to select more putative functional variants in genetic association studies. rs2257609 C>T, which exists in the intron of SLC5A10, affected DRG2 expression and the survival outcome of lung cancer.
Possible role of p53/Mieap-regulated mitochondrial quality control as a tumor suppressor in human breast cancer
- Pages: 3910-3920
- First Published: 05 October 2018
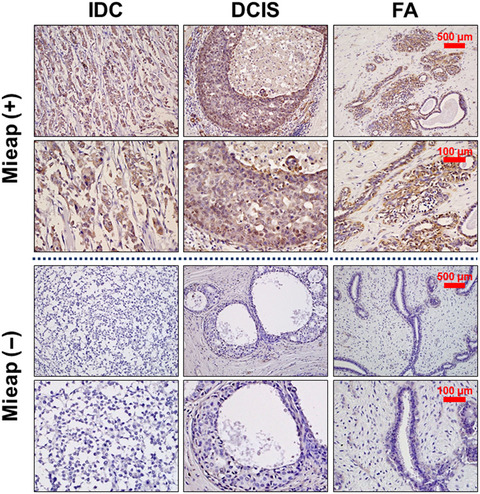
We demonstrated that enforced Mieap overexpression induced caspase-dependent apoptosis in breast cancer cells. The expression level of Mieap in invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) was significantly lower than that in ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and benign tumours in vivo. The p53/Mieap/NIX/BNIP3-regulated MQC pathway was inactivated in IDC, which resulted in significantly shortened disease-free survival.
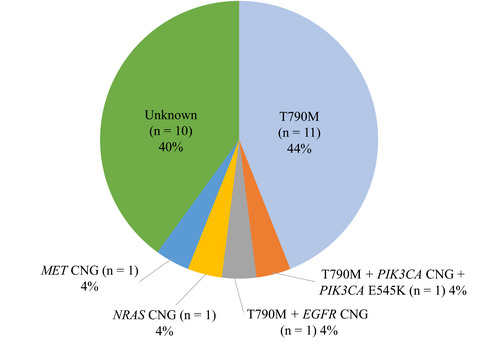
Exploration of resistance mechanisms for epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors based on plasma analysis by digital polymerase chain reaction and next-generation sequencing
- Pages: 3921-3933
- First Published: 05 October 2018
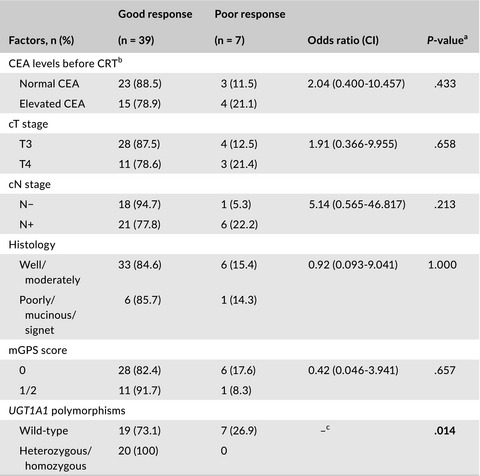
UGT1A1 polymorphisms in rectal cancer associated with the efficacy and toxicity of preoperative chemoradiotherapy using irinotecan
- Pages: 3934-3942
- First Published: 23 September 2018
Primary breast diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the rituximab era: Therapeutic strategies and patterns of failure
- Pages: 3943-3952
- First Published: 09 October 2018
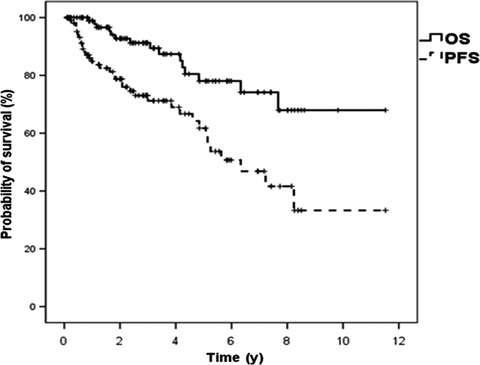
Primary breast diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (PB-DLBCL) has a continuous pattern of relapse, especially with frequent late relapses in the central nervous system (CNS) and contralateral breast. Rituximab and radiotherapy confer complementary benefit in the reduction of relapse. However, neither the addition of rituximab nor prophylactic intrathecal chemotherapy could effectively prevent CNS relapse for PB-DLBCL patients.
Preliminary report of a single-channel applicator in high dose rate afterloading brachytherapy for cervical cancer
- Pages: 3953-3961
- First Published: 23 October 2018
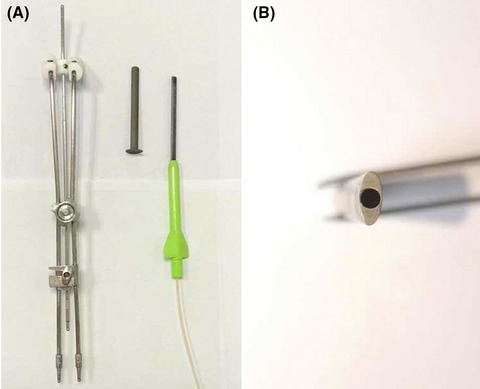
Preliminary results show that a patented single-channel intracavitary applicator might be able to provide protection for the rectum and bladder and seems to have the same clinical efficacy as the standard Fletcher-type 3-channel applicator in high dose rate brachytherapy for carcinoma of the cervix.
Phase 1 study of olaratumab plus doxorubicin in Japanese patients with advanced soft-tissue sarcoma
- Pages: 3962-3970
- First Published: 24 October 2018
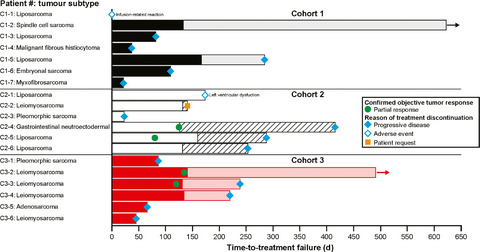
This phase 1 study investigated the safety, pharmacokinetics and antitumor activity of olaratumab (olara), a human IgG1 monoclonal antibody targeting platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha, plus doxorubicin (DOX) in Japanese patients with soft-tissue sarcoma (STS). Olara plus DOX had an acceptable safety profile in patients with STS. A loading dose of olara 20 mg/kg was effective for achieving minimum serum concentrations above the target trough level in Cycle 1.
Vitamin D deficiency is associated with inferior survival of patients with extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma
- Pages: 3971-3980
- First Published: 21 October 2018
Pattern and prognostic value of FLT3-ITD mutations in Chinese de novo adult acute myeloid leukemia
- Pages: 3981-3992
- First Published: 15 October 2018
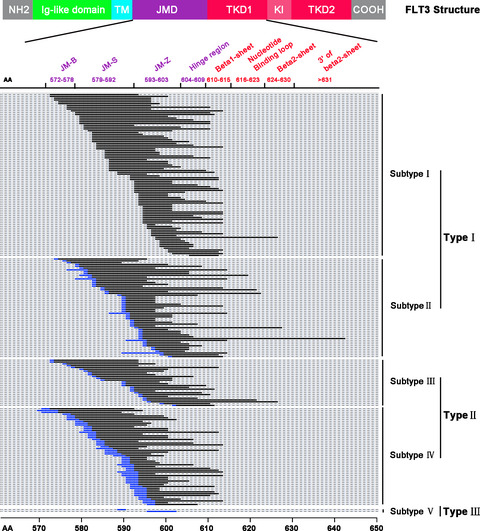
A total of 227 FLT3-ITD sequences were analyzed from 227 Chinese adult de novo acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients. ITD could be classified into 3 types based on molecular profiles. ITD integration sites in the hinge region or beta1-sheet region are an unfavorable prognostic factor in adult AML patients with FLT3-ITD mutations.
DRUG DISCOVERY AND DELIVERY
Immunomodulatory activity of lenvatinib contributes to antitumor activity in the Hepa1-6 hepatocellular carcinoma model
- Pages: 3993-4002
- First Published: 16 November 2018
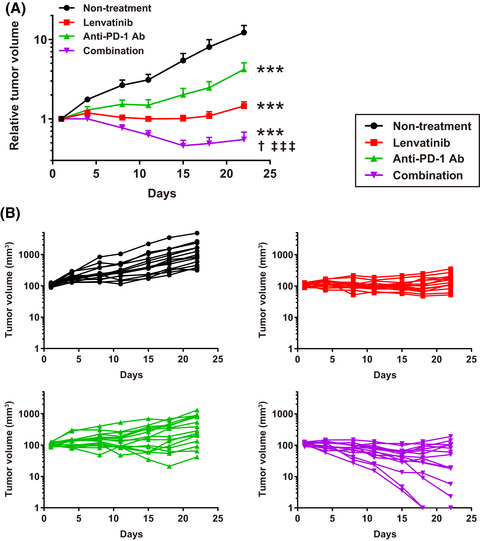
Lenvatinib is a multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor that selectively inhibits VEGFR1-3, FGFR1-4, PDGFRα, RET and KIT. Here, we show that lenvatinib has immunomodulatory activity, which plays a role in the antitumor activity of single lenvatinib treatment, and enhances the antitumor activity of anti-PD-1 antibody in the combination treatment in the Hepa1-6 mouse HCC syngeneic tumor model.
RK-287107, a potent and specific tankyrase inhibitor, blocks colorectal cancer cell growth in a preclinical model
- Pages: 4003-4014
- First Published: 20 September 2018
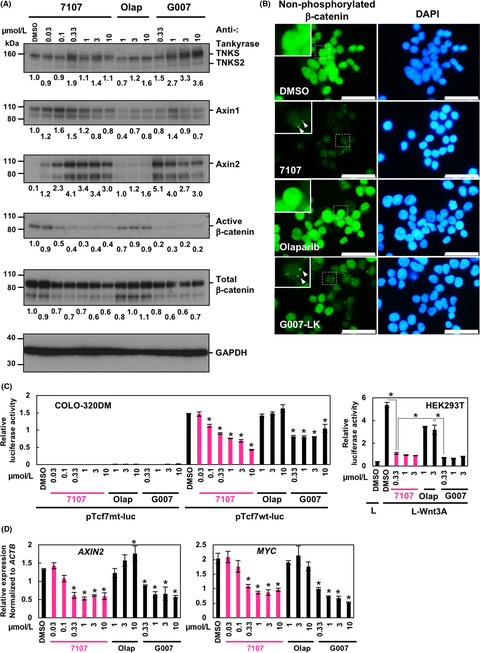
Aberrant activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling causes tumorigenesis and promotes the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells. We report a novel tankyrase-specific PARP inhibitor RK-287107, which inhibits tankyrase-mediated PARylation of Axin and downregulates β-catenin signaling in APC-mutated colorectal cancer cells. RK-287107 exerts a proof-of-concept antitumor effect in vivo, and thus may have potential for cancer therapy.
GENETICS, GENOMICS, AND PROTEOMICS
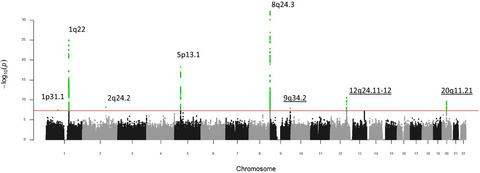
Genome-wide association study identifies gastric cancer susceptibility loci at 12q24.11-12 and 20q11.21
- Pages: 4015-4024
- First Published: 03 October 2018
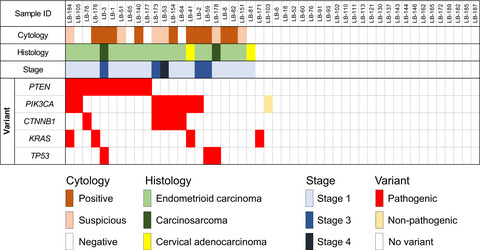
Efficacy of liquid-based genetic diagnosis of endometrial cancer
- Pages: 4025-4032
- First Published: 05 October 2018
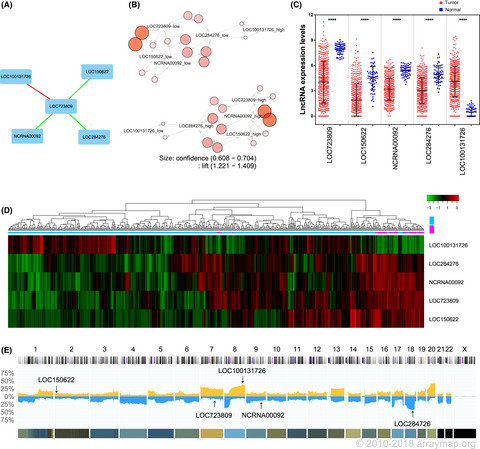
A group of long noncoding RNAs identified by data mining can predict the prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 4033-4044
- First Published: 05 October 2018
PATHOLOGY
Active K-RAS induces the coherent rotation of epithelial cells: A model for collective cell invasion in vitro
- Pages: 4045-4055
- First Published: 03 October 2018