Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Highlights
From the discovery of sodiumoxyorganoalkoxysilanes to the organosilicon dendrimers and back
- Pages: 4935-4948
- First Published: 17 June 2008
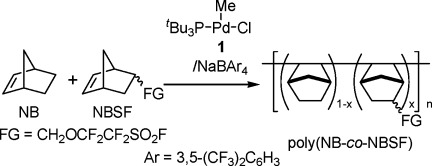
The benefit of systematic approach to dendrimers study is a wide set of objects of the same chemical nature, which are similar in all details except for some one feature. It can be either regularity, or the nature of functional groups, or number of dendrons emanating from the core. In such a case the input of that particular difference can be estimated objectively. The scheme illustrates that existence of the polyallylcarbosilane dendrimer with four dendrons automatically demonstrates availability of at least 25% of internal volume of its 3 dendron containing analog for swelling by solvent or filling by different objects. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at www.interscience.wiley.com.]
Articles
Negative-type photosensitive poly(phenylene ether) based on poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene ether), a crosslinker, and a photoacid generator
- Pages: 4949-4958
- First Published: 17 June 2008
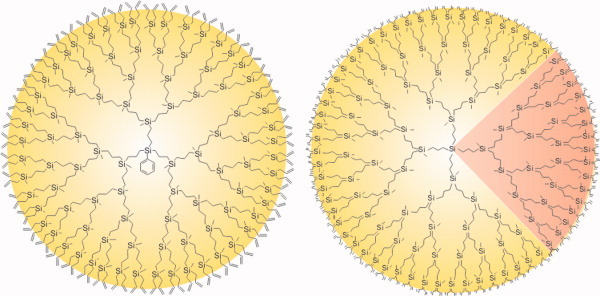
A negative-type photosensitive poly(phenylene ether) (PSPPE) based on poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene ether) (PPE), a novel crosslinker 4,4′-methylene-bis [2,6-bis (methoxymethyl)phenol] (MBMP) having good compatibility with PPE, and diphenylidonium 9,10-dimethoxy anthracene-2-sulfonate (DIAS) as a photoacid generator (PAG) has been developed.
Effect of prepolymer molecular weight on solid state polymerization of poly(bisphenol a carbonate) with nitrogen as a sweep fluid
- Pages: 4959-4969
- First Published: 17 June 2008
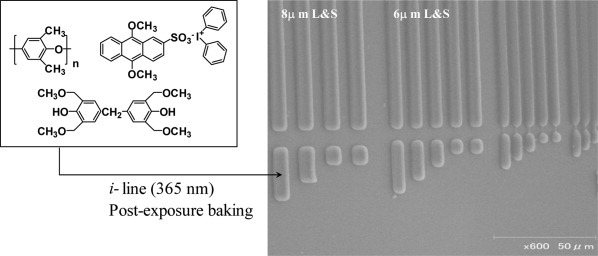
To investigate the effect of prepolymer molecular weight on the solid-state polymerization (SSP) of poly(bisphenol A carbonate) (BPA-PC), two prepolymers with different molecular weights were synthesized by melt polymerization. During SSP, the crystallinity and lamellar thickness of the polymers obtained from the higher-molecular weight prepolymer were consistently smaller than those obtained from the lower-molecular-weight prepolymer. Thus, the higher polymerization rate observed with the higher-molecular-weight prepolymer may be the result of faster end-group diffusion and chain extension. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at www.interscience.wiley.com.]
Fluorinated benzoxazines and the structure-property relationship of resulting polybenzoxazines†
- Pages: 4970-4983
- First Published: 17 June 2008
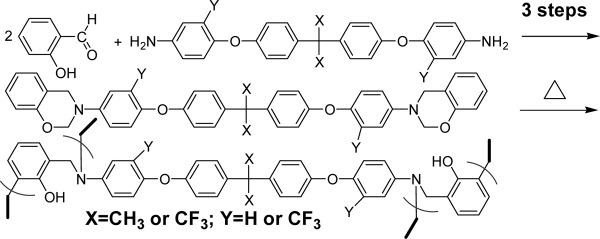
Three fluorinated benzoxazines (14–16) were synthesized by a three-step procedure using fluorinated aromatic diamines (2–4) as starting materials. The low dielectric thermosets, P(14–16), were prepared by thermal curing of (14–16). The structure-property relationship of the resulting polymer is discussed.
Facile synthesis of controlled-structure primary amine-based methacrylamide polymers via the reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer process
- Pages: 4984-4996
- First Published: 17 June 2008
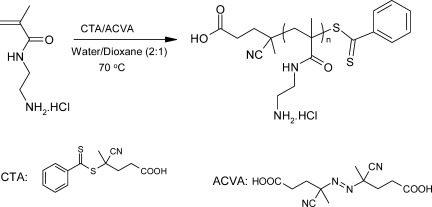
We report here a novel direct method for the syntheses of primary aminoalkyl methacrylamides that requires mild reagents and no protecting group chemistry. The reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization (RAFT) of the aminoalkyl methacrylamide revealed to be highly efficient with 4-cyanopentanoic acid dithiobenzoate (CTP) as chain transfer agent and 4,40-azobis(4-cyanovaleric acid) (ACVA) as initiator. Cationic amino-based homopolymers of reasonably narrow polydispersities (Mw/Mn < 1.30) and predetermined molecular weights were obtained without recourse to any protecting group chemistry.
Synthesis of adaptative and amphiphilic polymer model conetworks by versatile combination of ATRP, ROP, and “Click chemistry”
- Pages: 4997-5013
- First Published: 17 June 2008
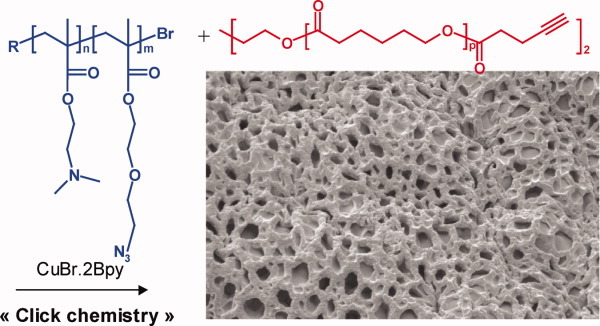
Well-defined amphiphilic polymer model conetworks have been successfully synthesized according to an original strategy combining ROP, ATRP and “click chemistry”. Final amphiphilic and adaptative properties have been demonstrated by swelling experiments in organic solvent and aqueous solutions of different pH, respectively. SEM analysis reveals the formation of polymer conetworks with homogeneous morphology and characterized by a 3D-opened structure resembling strongly to a Bruges lace. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at www.interscience.wiley.com.]
Tailor-made hybrid nanostructure of poly(ethyl acrylate)/clay by surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization
- Pages: 5014-5027
- First Published: 17 June 2008
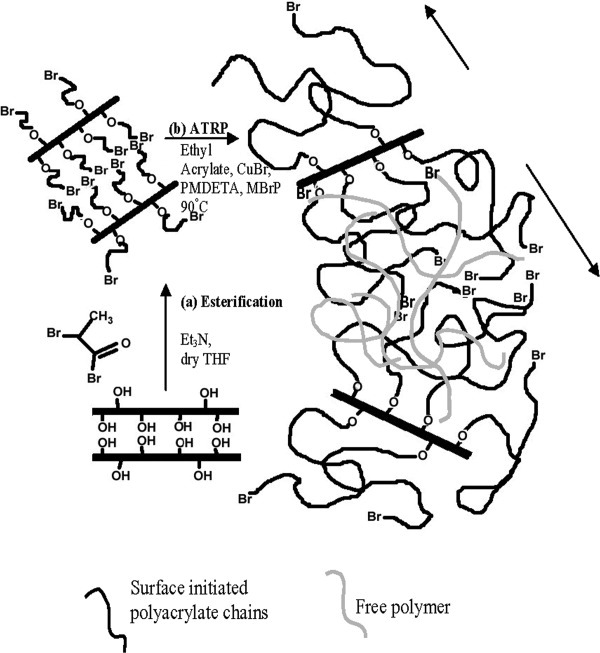
Hybrid nanoarchitecture of tailor-made Poly(ethyl acrylate)/clay was prepared by surface initiated atom transfer radical polymerization (SI-ATRP), by tethering ATRP initiator on to the surface of clay platelets as well as at the hydroxyl terminated edges of the modifier of organo clay (Cloisite 30B). Poly(ethyl acrylate) chains with controlled polymerization and narrow polydispersities were forced to be grown from the clay gallery (intergallery) as well as from the outer surface (extragallery) of the clay platelets. This facilitates in peeling out the clay tactoids, leading to extensive exfoliation.
Self-assembly of thermo- and pH-responsive poly(acrylic acid)-b-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) micelles for drug delivery
- Pages: 5028-5035
- First Published: 17 June 2008
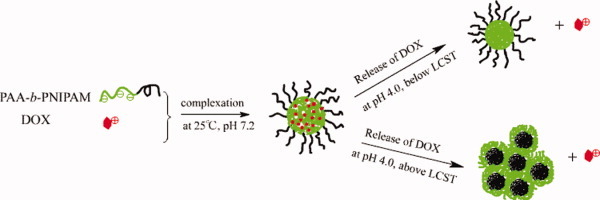
Complexation of DOX with PAA-b-PNIPAM induced by the electrostatic interaction exhibited pH-responsive and thermo-responsive drug release profile. The release of DOX from the complex micelles was suppressed at pH 7.2 and accelerated at pH 4.0 due to the protonation of carboxyl groups. The cumulative release of DOX from complex micelles is enhanced around LCST arising from the structure deformation of the micelles. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at www.interscience.wiley.com.]
β-Cyclodextrin polymer brushes based on hyperbranched polycarbosilane: Synthesis and characterization
- Pages: 5036-5052
- First Published: 17 June 2008
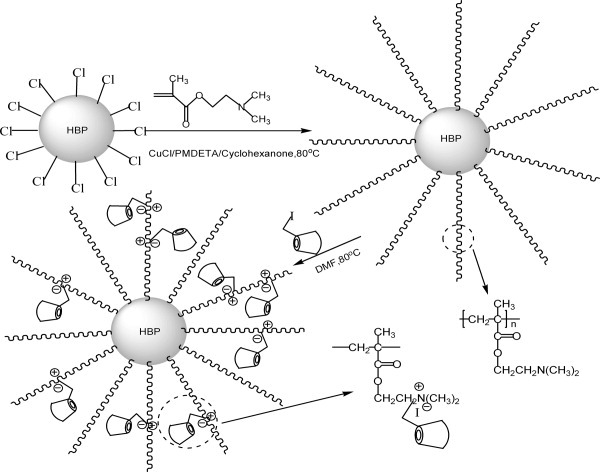
One β-cyclodextrin polymer brush with the amphiphilic core-shell structure was first prepared via atom transfer radical polymerization using N, N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate as the monomer, and then, iodide substituted β-cyclodextrin units were immobilized into the hydrophilic shell. Interestingly, β-cyclodextrin polymer brush possesses two different glass transition temperatures and molecular inclusion capability.
Ways of selective polycondensation of L-lysine towards linear α- and ε-poly-L-lysine
- Pages: 5053-5063
- First Published: 17 June 2008
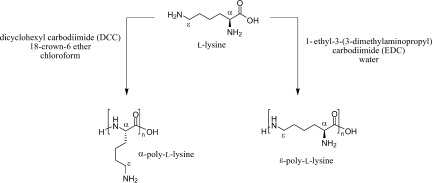
This contribution describes two ways to synthesize poly-L-lysines via polycondensation of L-lysine without the use of protecting groups. The polymerization of the monomer in water using EDC as activating agent resulted in pure epsilon-poly-L-lysine. Dissolving the monomer in chloroform in the presence of a crown ether and polymerizing it with DCC gave selectively alpha-poly-L-Lysine.
Dendronized tricyanopyrroline-based chromophores in nonlinear optical active host polymer
- Pages: 5064-5076
- First Published: 17 June 2008
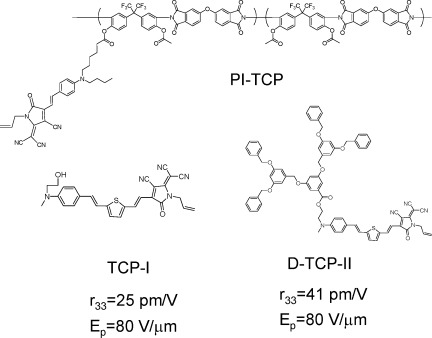
We synthesized new nonlinear optical (NLO) chromophores containing a 3,5-bis-(3,5-bis-benzyloxy-benzyloxy)-benzoate dendron. A soluble polyimide containing 6-({4-[2-(1-allyl-4-cyano-5-dicyanomethylene-2-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrol-3-yl)-vinyl]-phenyl}-butyl-amino)-hexanoyl group in the side chain was also prepared as an NLO active host polymer. When comparing the EO properties of three chromophores, we could observe that under same poling conditions (Ep = 80 V/μm), the films bearing the dendronized chromophore, D-TCP-II exhibited an r33 value of 41 pm/V that is higher than the sample containing the TCP-I chromophore, indicating a significant improvement of poling efficiency.
One-pot synthesis and characterization of hyperbranched poly(ester-amide)s from commercially available dicarboxylic acids and multihydroxyl secondary amines
- Pages: 5077-5092
- First Published: 17 June 2008
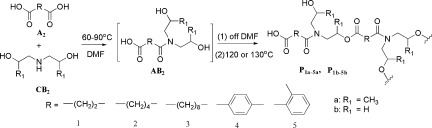
A series of novel hyperbranched poly(ester-amide)s was synthesized in one-pot via “A2+CB2” approach without any catalyst. The branched architecture and unique properties of the resulted hyperbranched polymers were thoroughly characterized. Terminals groups were modified to tune the thermal property and solubility of the hyperbranched polymers.
End group transformations of RAFT-generated polymers with bismaleimides: Functional telechelics and modular block copolymers
- Pages: 5093-5100
- First Published: 17 June 2008
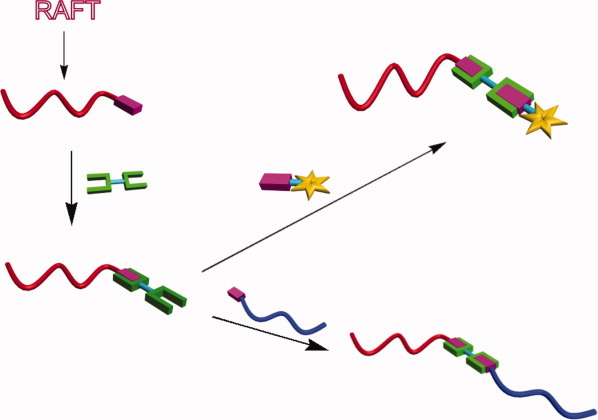
End group activation of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) prepared by RAFT polymerization was accomplished by conversion of thiocarbonylthio end groups to thiols and subsequent reaction with excess of a bismaleimide. The resulting maleimido-terminated polymers were coupled with model low molecular weight thiols or dienes by Michael or Diels-Alder reactions, respectively. Coupling of maleimide-activated PNIPAM with sulfhydryl-terminated polystyrene proved to be an efficient modular strategy to prepare block copolymers. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at www.interscience.wiley.com.]
Side chain liquid crystal poly(fumarate)s bearing tolane-based mesogens
- Pages: 5101-5114
- First Published: 17 June 2008
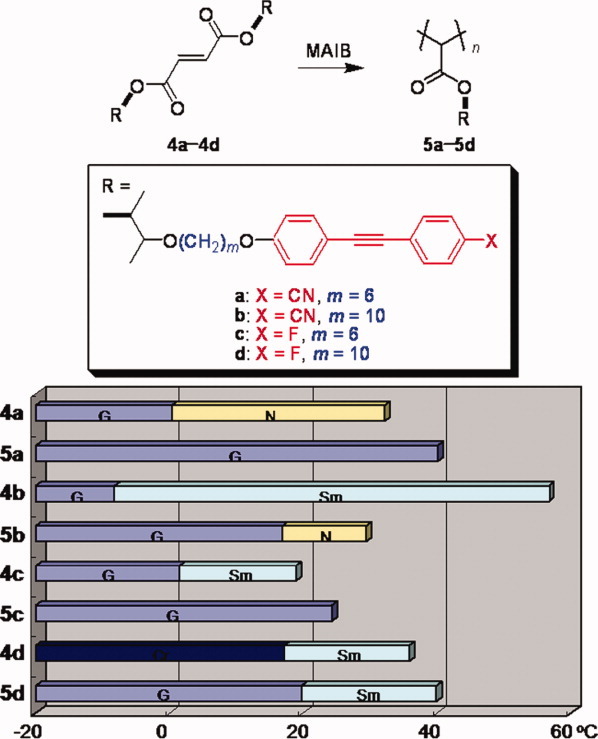
A series of liquid crystal fumarates bearing tolane-based mesogens, prepared under basic conditions, was polymerized in the presence of the azo-type radical initiator to give the poly(fumarate)s with an exceptionally narrow polydispersity. Their liquid crystallinity was comprehensively investigated by differential scanning calorimetry, polarized optical microscopy, and X-ray diffraction analysis, which revealed that polymerization reduces the liquid crystal temperature range but sometimes retains the higher-order liquid crystal phase of the smectic phase when fluorotolane mesogens are employed. As compared to vinyl polymers, poly(fumarate) was revealed to be an excellent main chain to realize higher-order mesophases of side chain liquid crystal polymers. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at www.interscience.wiley.com.]
Synthesis and characterization of a novel polymer based on anthracene moiety for organic thin film transistor
- Pages: 5115-5122
- First Published: 17 June 2008
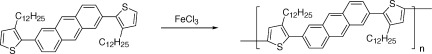
We designed poly[2,6-bis(3′-dodecylthiophene-2′-yl)anthracene](PDTAn) which is composed with anthracene moiety and dodecyl alkyl thiophene unit for solution processable OTFT. The polymer was synthesized by oxidative polymerization using iron (III) chloride. A field-effect mobility of 1.1 × 10−4 cm2 V–1 S–1, a current on/off ratio of 105 and the Vth at −15.2 V had been obtained for OTFTs using this polymer semiconductor by solution coating.
Synthesis and magnetic properties of comb-like copolymeric complexes based on thiazole ring and ionic liquid
- Pages: 5123-5132
- First Published: 18 June 2008
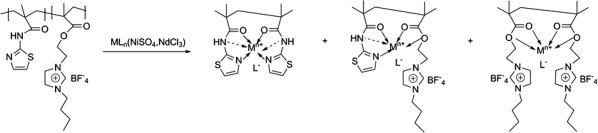
Two comb-like copolymers (BIMT and PMB) based on thiazole ring and ionic liquid were synthesized using conventional free radical polymerization and RAFT polymerization. The magnetic properties of their metal complexes were studied. The coordinated complexes display three possible chelating structures, which induced various magnetic phenomena. The incorporated ionic liquid brings better magnetic performance for the copolymeric complexes than the homopolymeric complexes. These reveal a guidance for the molecular design and exploitation of organic magnetic materials and also give us an inspire steering for the study of magnetism of the liquid state.
Polymerization of norbornene with a pendent sulfonyl fluoride group catalyzed by palladium complex bearing tBu3P ligand
- Pages: 5133-5141
- First Published: 18 June 2008
On the anionic homo- and copolymerization of ethyl- and butyl-2-cyanoacrylates
- Pages: 5142-5156
- First Published: 18 June 2008
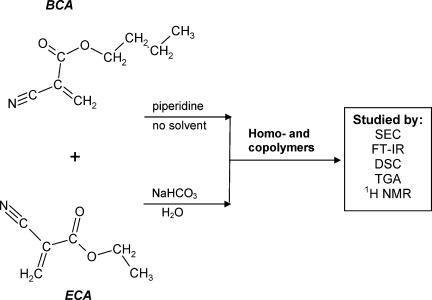
Stabilized ethyl- and butyl-2-cyanoacrylate monomers were synthesized and polymerized anionically to get the respective homopolymers and various copolymers. The polymers were characterized by spectral, chromatographic and thermal methods. It was concluded that controlling the monomer feed and the catalyst type phase-separated or homogeneous copolymers can be prepared.
Polymerization and nanocomposites properties of multifunctional methylmethacrylate POSS
- Pages: 5157-5166
- First Published: 18 June 2008
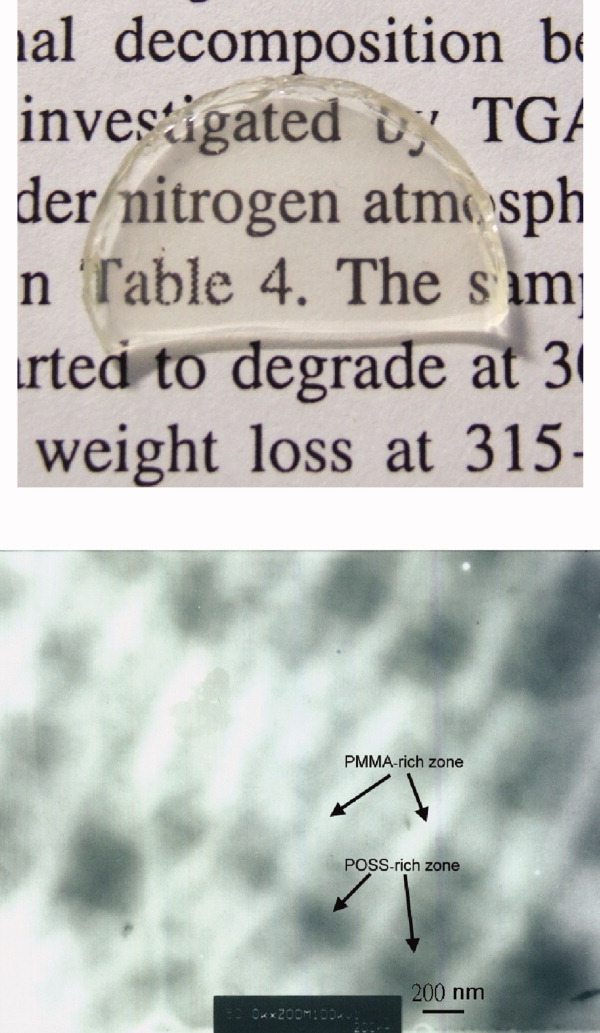
Thermally induced polymerization of multifunctional methylmethacrylate POSS (MMA-POSS) was studied in this work for preparation of polymer/POSS nanocomposites. The polymerization of MMA-POSS could be promoted with benzoyl peroxide (BPO). Self-assembly of POSS into a layer-by-layer structure in the MMA-POSS polymer (TP-MMA-POSS) is observed with a transmission electron microscopy. A ultra-low-k value of about 1.85 is measured with TP-MMA-POSS. In addition, polyimide-POSS nanocomposites are also prepared. These nanocomposites demonstrate good homogeneity and enhanced mechanical properties. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at www.interscience.wiley.com.]
Polyesters analogous to PET and PBT based on O-benzyl ethers of xylitol and L-arabinitol
- Pages: 5167-5179
- First Published: 18 June 2008
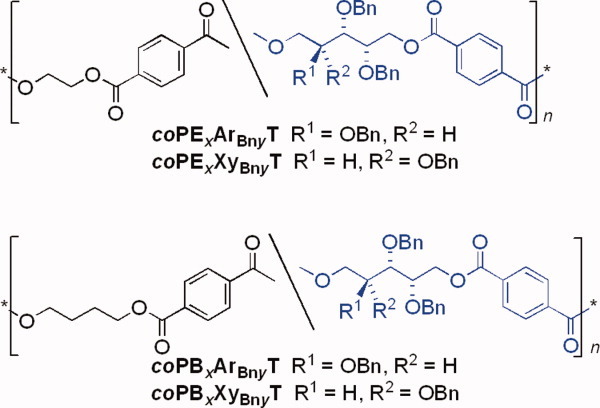
A series of aromatic homopolyesters and copolyesters analogous to PET and PBT containing sugar-derived moieties with the secondary hydroxyl groups blocked as benzyl ethers has been synthesized and characterized to study the effect of the new protecting group on the properties of the polymers. These new polyesters can also be deprotected by hydrogenolysis to give the corresponding hydroxylated polymers displaying enhanced higroscopicity. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at www.interscience.wiley.com.]
Host copolymers containing pendant carbazole and oxadiazole groups: Synthesis, characterization and optoelectronic applications for efficient green phosphorescent OLEDs
- Pages: 5180-5193
- First Published: 18 June 2008
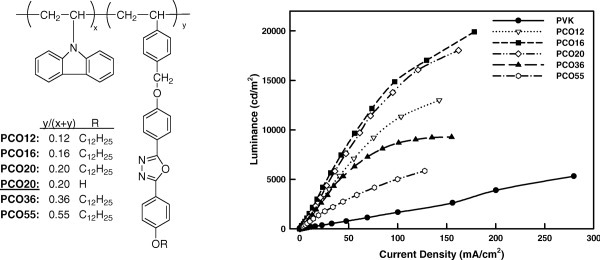
Vinyl copolymers (PCOn) were prepared and used as host materials for green phosphor Ir(ppy)3. Phosphorescent EL devices (ITO/PEDOT:PSS/host copolymers:Ir(ppy)3/BCP/Ca/Al) exhibited efficient green emission, The maximal luminance efficiency (17.9 cd/A) and the maximal luminance (19,903 cd/m 2) were obtained when employing PCO16 as the host and 4 wt % Ir(ppy)3 as the guest. The PCO20 device exhibited much better performance than PCO20, which have been attributed to good compatibility of PCO20 with Ir(ppy)3.
Cationic photopolymerization of liquid fullerene derivative under visible light
- Pages: 5194-5201
- First Published: 18 June 2008
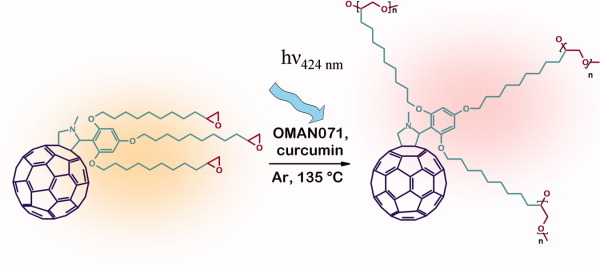
We describe the synthesis and cationic photopolymerization of a C60 derivative bearing alkylic chains capped with epoxy groups. By reducing monomer viscosity with alkylic side chains and applying a visible light harvesting initiator system, it is possible to photopolymerize thin layers of fullerene derivative without additional solvents, making the method useful for practical applications. The viscosity of the monomer sets the minimum temperature for photoinitiation to above 130 °C. Using a photoinitiator system of curcumin, absorbing at 424 nm, and p-(octyloxyphenyl) phenyliodonium hexafluoroantimonate, it is possible to use visible light for photopolymerization as fullerene strongly absorbs in the UV region. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at www.interscience.wiley.com.]
“Push-pull” supramolecular chromophores supported on cyclopolymers
- Pages: 5202-5213
- First Published: 18 June 2008
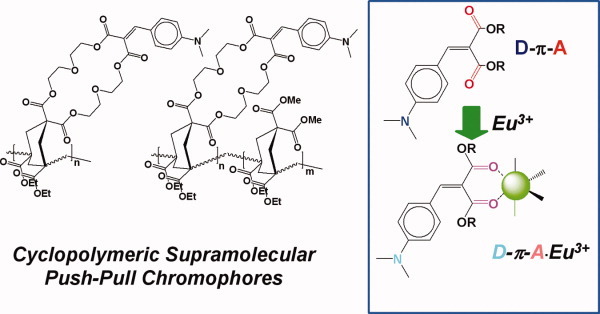
We report on the evaluation of a series of cyclopolymers and cyclocopolymers of novel design and conception, in which “push-pull”, supramolecularly polarizable chromophores are incorporated at various loadings. The macromolecules have been obtained through free-radical cyclopolymerization and cyclocopolymerization of difunctional and acrylic-like monomers, one of them containing the “push-pull” chromophore which is able to form 1:1 complexes with Eu3+ ions in solution. Using Eu(OTf)3 as the supramolecular probe, UV/Vis titrations revealed how adjacent chromophores within the multivalent scaffold, virtually independent from each other, possess a binding ability towards the probe which is still clearly detectable. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at www.interscience.wiley.com.]
Ring-opening polymerization of 1,4-dioxan-2-one initiated by lanthanum isopropoxide in bulk
- Pages: 5214-5222
- First Published: 18 June 2008
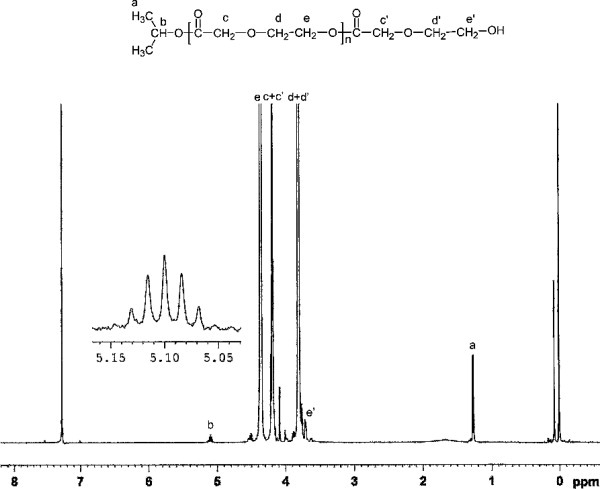
Lanthanum isopropoxide (La(OiPr)3) has been synthesized and employed for ring-opening polymerization of 1,4-dioxan-2-one in bulk as a single-component initiator. The influences of reaction conditions such as initiator concentration, reaction time and reaction temperature on the polymerization were investigated. The kinetics indicated that the polymerization is first-order with respect to the monomer concentration. The Mechanistic investigations according to 1H NMR spectrum analysis demonstrated that the polymerization of PDO proceeded through a coordination-insertion mechanism with a rupture of the acyl-oxygen bond of the monomer rather than the alkyl-oxygen bond cleavage.
Synthesis of soluble poly(para-phenylene) with a long polymer chain: Characteristics of regioregular poly(1,4-phenylene)
- Pages: 5223-5231
- First Published: 18 June 2008
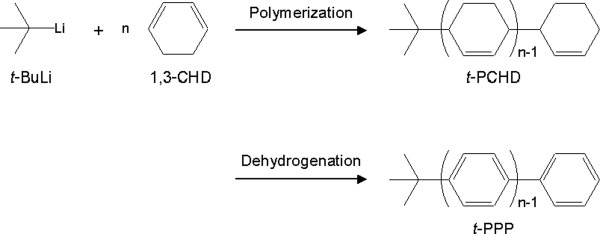
Poly(para-phenylene) was synthesized with a tert-butyl end-group (t-PPP) and was found to have improved solubility and excellent optical properties. Poly(1,3-cyclohexadiene) (PCHD) consisting of only 1,4-cyclohexadiene (1,4-CHD) units was synthesized with a tert-butyl end-group (t-PCHD), and completely dehydrogenated to obtain t-PPP. This end-group effectively prevented the crystallization of t-PPP, and polymers containing up to sixteen repeat units were soluble in tetrahydrofuran. Optical analyses of t-PPP provided strong evidence for a linear polymer chain structure. A block copolymer of t-PPP and a soluble polyphenylene (PPH) was then synthesized, and the excellent optical properties were retained by this block copolymer along with its solubility.
Facile electrosyntheses of high tensile strength alkyl-bridged dicarbazole polymer films and its fluorescence spectra
- Pages: 5232-5241
- First Published: 18 June 2008
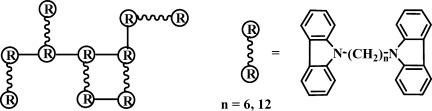
Homogeneous and high-quality free-standing poly(1,6-bis (carbazolyl)hexane) (P2Cz-H) and poly(1,12-bis(carbazolyl)dodecane) (P2Cz-D) films were electrochemically synthesized in CH2Cl2 + 0.1 M tetrabutylammonium tetrafluoroborate solution. These internal cross-linking structures, constituted by stiff bicarbazyl chromophores linked by flexible long carbon segments, led to the electrodeposition of free-standing polycarbazole films with high tensile strength as 165 kg kg cm−2.
A solution-processible poly(p-phenylene vinylene) without alkyl substitution: Introducing the cis-vinylene segments in polymer chain for improved solubility, blue emission, and high efficiency
- Pages: 5242-5250
- First Published: 18 June 2008
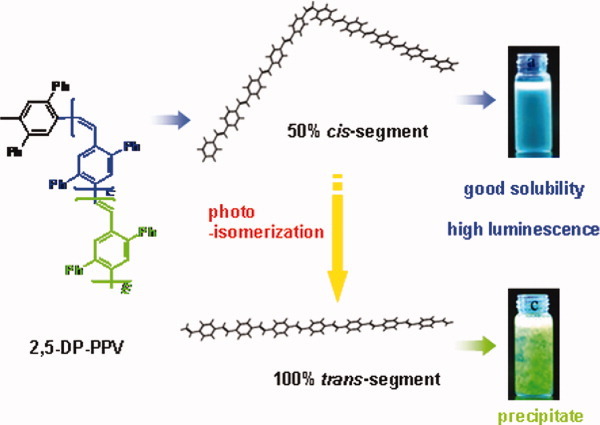
A soluble all-aromatic poly (1,4-phenylenevinylene) (PPV) with the cis-vinylene unit contents up to 50% in backbone is synthesized. The twisted cis-segments in polymer backbone reduce the interchain interactions and enhance solubility of the polymer in common organic solvents. The polymer film exhibits a blue light emission (λmax = 485 nm) and a very high photoluminescence efficiency of 78%. The cis–-trans transition of this polymer in solution and film and their impact on the optical properties were also investigated. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at www.interscience.wiley.com.]
Isoprene polymerization with indolide-imine supported rare-earth metal alkyl and amidinate complexes†
- Pages: 5251-5262
- First Published: 18 June 2008
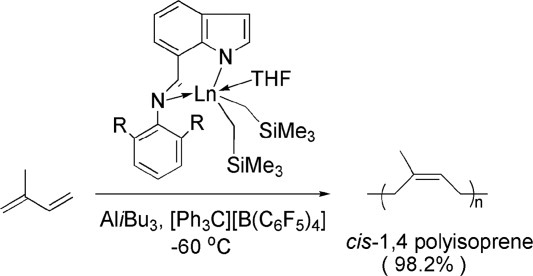
Rare-earth metal alkyl complexes and the corresponding amidinate derivatives bearing indolide-imine ligands have been prepared and well characterized. These complexes with the activation of AlR3 and borate formed homogeneous single-site catalysts for the polymerization of isoprene with high activities and cis-1,4 selectivities under the concert effects of the electronics and spacial sterics of the employed complexes and the polymerization conditions.
“Click” chemistry for in situ formation of thermoresponsive P(NIPAAm-co-HEMA)-based hydrogels
- Pages: 5263-5277
- First Published: 18 June 2008
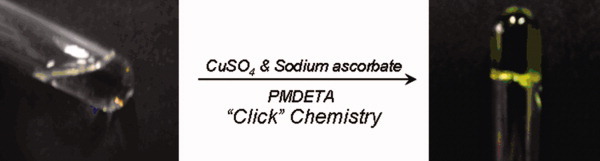
A series of novel in situ formed thermoresponsive P(NIPAAm-co-HEMA)-based hydrogels were designed and prepared via “click” chemistry. The strategy demonstrated here presents a potential alternative to the traditional synthesis techniques for the in situ formation of thermoresponsive hydrogels. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at www.interscience.wiley.com.]
Rapid Communications
Efficient oxidative coupling polymerization for synthesis of thermosetting poly(phenylene ether) copolymer with a low dielectric loss
- Pages: 5278-5282
- First Published: 18 June 2008
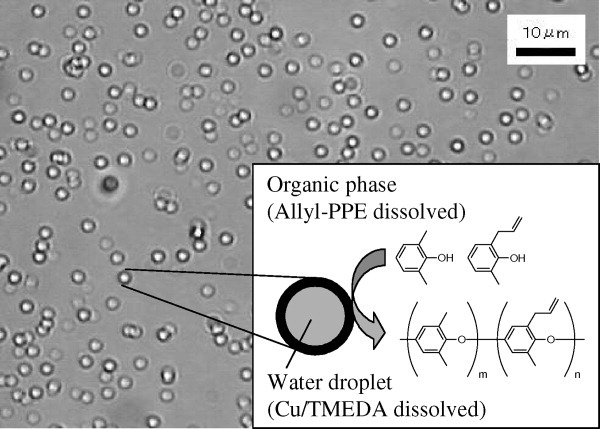
A novel oxidative coupling polymerization using a water/toluene heterogeneous system for the synthesis of thermosetting Poly(phenylene ether) copolymer (Allyl-PPE) was developed. Allyl-PPE with a narrow molecular weight distribution and a low copper content was obtained in the presence of a Cu/TMEDA catalyst dissolved in water droplets. This method solved the problems during the synthesis of the Allyl-PPE with conventional Cu/pyridine catalysts. The resulting Allyl-PPE exhibited excellent dielectric properties (ε′ = 2.4, tan δ = 0.002 at 10 GHz), and it will be useful for applications to high-speed and high-frequency printed circuit boards.
Novel main-chain polyrotaxanes synthesized via ATRP of HPMA in aqueous media
- Pages: 5283-5293
- First Published: 18 June 2008
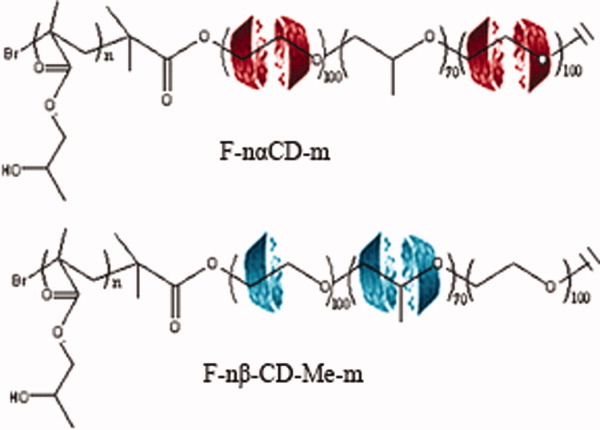
A kind of novel main-chain polyrotaxanes was synthesized in situ via the ATRP of HPMA initiated with polypseudorotaxanes self-assembled from a distal 2-bromoisobutyryl end-capped Pluronic F127 with α- or β-CDs in the presence of Cu(I)Br/PMDETA at 25 °C in aqueous media. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at www.interscience.wiley.com.]