Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Front Cover, Volume 41, Issue 1
- Page: i
- First Published: 24 December 2019
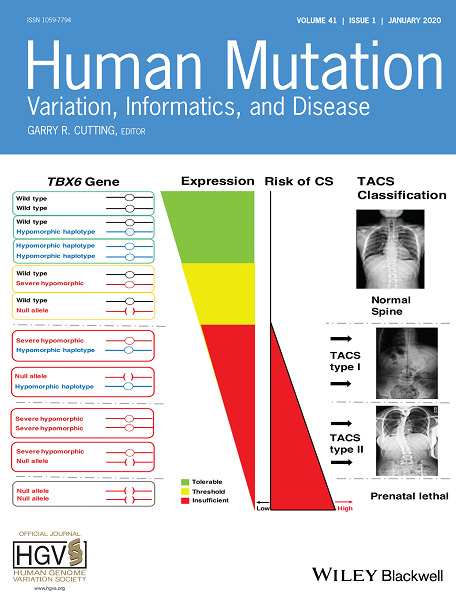
Front Cover: The cover image is based on the Research Article TBX6 missense variants expand the mutational spectrum in a non-Mendelian inheritance disease by Weisheng Chen et al., https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.23907.
Cover image © Nan Wu Images.
Inside Back Cover, Volume 41, Issue 1
- Page: ii
- First Published: 24 December 2019
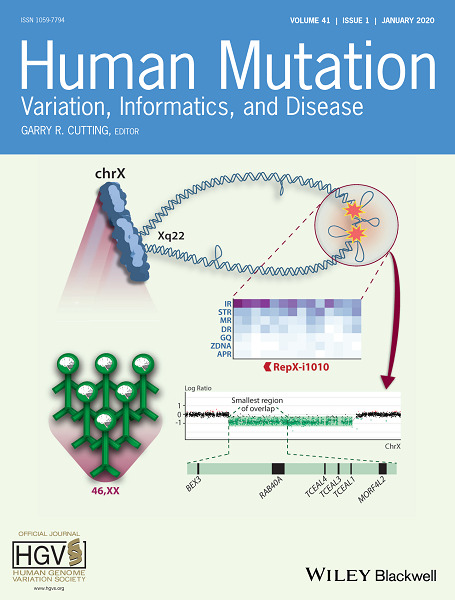
Inside Back Cover: The cover image is based on the Research Article Xq22 deletions and correlation with distinct neurological disease traits in females: Further evidence for a contiguous gene syndrome by Hadia Hijazi et al., https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.23902.
Cover image © Hadia Hijazi & Ameerah Deyab Images.
Variation in nomenclature of somatic variants for selection of oncological therapies: Can we reach a consensus soon?
- Pages: 7-16
- First Published: 25 September 2019
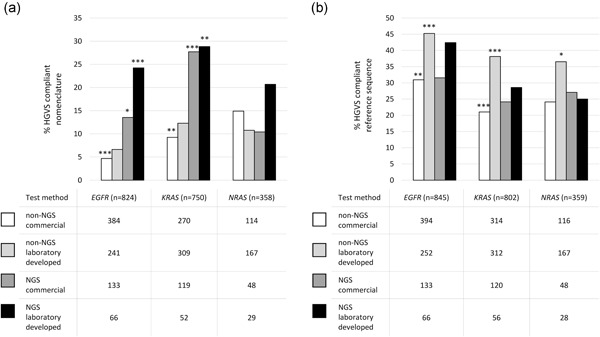
Participation to external quality assessment (EQA) improved compliance with Human Genome Variation Society (HGVS) recommendations. Compliance of variant descriptions was better for next-generation sequencing (20.9%) compared with targeted techniques (9.8%). A correct reference sequence was included for 36.0% of noncommercial versus 26.5% of commercial test methods. The residual percentage of noncompliance with HGVS suggests that laboratories, companies, and EQA providers need to collaborate for additional harmonization in clinical test reporting.
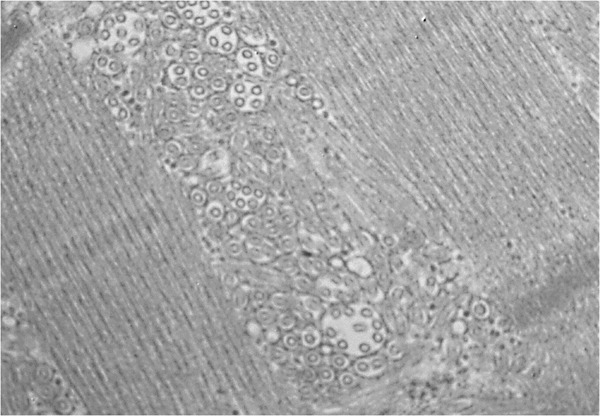
Tubular aggregate myopathy and Stormorken syndrome: Mutation spectrum and genotype/phenotype correlation
- Pages: 17-37
- First Published: 26 August 2019
SERPING1 mutation update: Mutation spectrum and C1 Inhibitor phenotypes
- Pages: 38-57
- First Published: 13 September 2019
Mutation update for the NR5A1 gene involved in DSD and infertility
- Pages: 58-68
- First Published: 12 September 2019
Expanding the genetic and phenotypic relevance of KCNB1 variants in developmental and epileptic encephalopathies: 27 new patients and overview of the literature
- Pages: 69-80
- First Published: 12 September 2019
Curating the gnomAD database: Report of novel variants in the globin-coding genes and bioinformatics analysis
- Pages: 81-102
- First Published: 25 September 2019
Fumarate hydratase FH c.1431_1433dupAAA (p.Lys477dup) variant is not associated with cancer including renal cell carcinoma
- Pages: 103-109
- First Published: 24 August 2019
CRAT missense variants cause abnormal carnitine acetyltransferase function in an early-onset case of Leigh syndrome
- Pages: 110-114
- First Published: 26 August 2019
Primary ciliary dyskinesia gene contribution in Tunisia: Identification of a major Mediterranean allele
- Pages: 115-121
- First Published: 30 August 2019
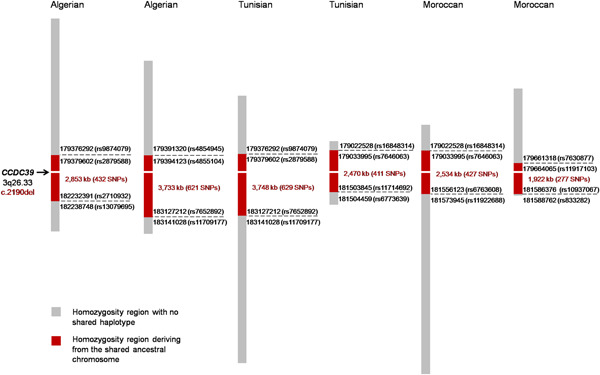
CCDC39 mutations are a major cause for primary ciliary dyskinesia in Tunisia (44% of independent cases). One CCDC39 founder mutation, c.2190del, is found in 24% of patients. This ancestral allele is identified in other Mediterranean patients and it is estimated to have arisen at least 1,400 years ago.
A founder variant in the South Asian population leads to a high prevalence of FANCL Fanconi anemia cases in India
- Pages: 122-128
- First Published: 12 September 2019
Minigene splicing assessment of 20 novel synonymous and intronic glucokinase gene variants identified in patients with maturity-onset diabetes of the young
- Pages: 129-132
- First Published: 17 September 2019
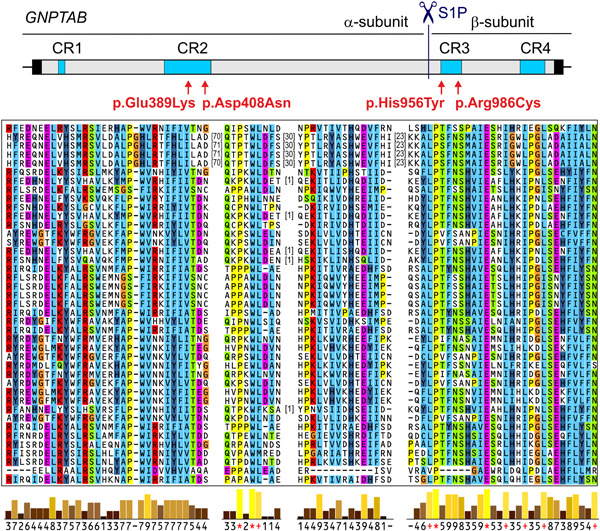
Combined in vitro and in silico analyses of missense mutations in GNPTAB provide new insights into the molecular bases of mucolipidosis II and III alpha/beta
- Pages: 133-139
- First Published: 03 October 2019
Graphical abstract
Mucolipidosis (ML) II and III alpha/beta are inherited lysosomal storage disorders caused by mutations in GNPTAB encoding the α/β-precursor of GlcNAc-1-phosphotransferase. In this study, we report on four disease-associated, highly conserved amino acid residues in the so-called stealth domains of the GlcNAc-1-phosphotransferase, which are strictly required for enzymatic activity and thus may be directly involved in the enzymatic catalysis.
A nationwide genetic analysis of inherited retinal diseases in Israel as assessed by the Israeli inherited retinal disease consortium (IIRDC)
- Pages: 140-149
- First Published: 27 August 2019
Xq22 deletions and correlation with distinct neurological disease traits in females: Further evidence for a contiguous gene syndrome
- Pages: 150-168
- First Published: 26 August 2019
A rare heterozygous TREM2 coding variant identified in familial clustering of dementia affects an intrinsically disordered protein region and function of TREM2
- Pages: 169-181
- First Published: 29 August 2019
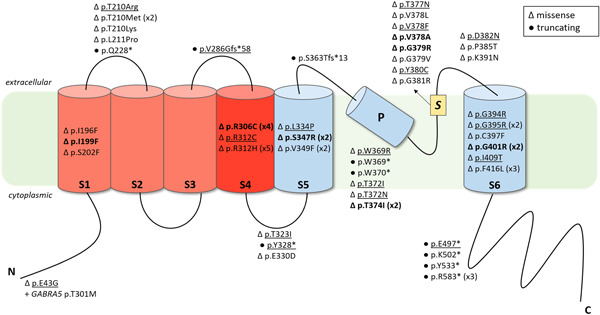
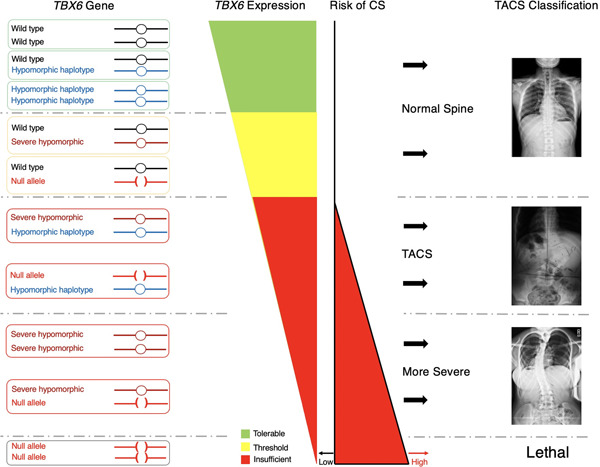
TBX6 missense variants expand the mutational spectrum in a non-Mendelian inheritance disease
- Pages: 182-195
- First Published: 31 August 2019
Mutations in RPSA and NKX2-3 link development of the spleen and intestinal vasculature
- Pages: 196-202
- First Published: 09 September 2019
A substantial proportion of apparently heterozygous TP53 pathogenic variants detected with a next-generation sequencing hereditary pan-cancer panel are acquired somatically
- Pages: 203-211
- First Published: 06 September 2019
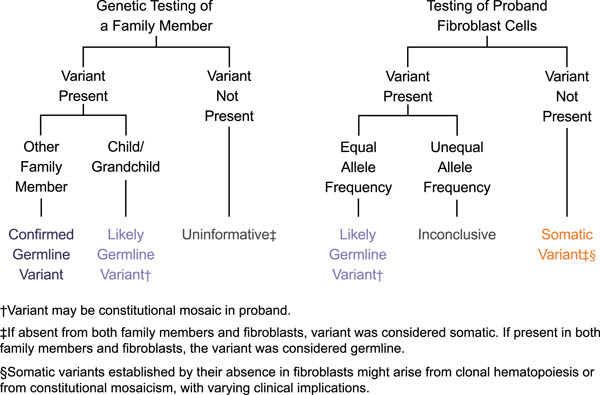
In next-generation sequencing (NGS) hereditary cancer panel testing, TP53 pathogenic variants whose NGS allele frequencies might appear consistent with those expected for germline variants, but the variant might be acquired somatically. Confirming TP53 variant origin can markedly impact medical management for tested individuals and their family members. The report highlights the need for a conservative approach to initial reporting of TP53-positive findings, along with investment in follow-up testing to deliver clinically accurate results.
Chinese newborn screening for the incidence of G6PD deficiency and variant of G6PD gene from 2013 to 2017
- Pages: 212-221
- First Published: 06 September 2019
Multiplex targeted high-throughput sequencing in a series of 352 patients with congenital limb malformations
- Pages: 222-239
- First Published: 10 September 2019
Novel IQCE variations confirm its role in postaxial polydactyly and cause ciliary defect phenotype in zebrafish
- Pages: 240-254
- First Published: 24 September 2019
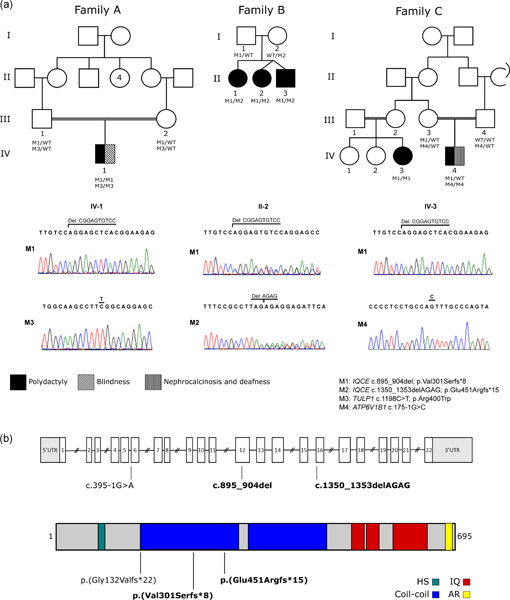
In this study, we report the confirmation of IQCE as a gene whose defects cause isolated postaxial polydactyly. Whole-exome sequencing has been applied to three families and revealed biallelic pathogenic variations in IQCE. Further functional analysis using the patient's cells (skin fibroblast) revealed no effect on the formation of the cilia but a mislocalization of the EVC2 and a defective hedgehog signaling. Zebrafish experiments demonstrated a full spectrum of phenotypes associated with defective cilia: Body curvature, kidney cysts, left–right asymmetry, misdirected cilia in the pronephric duct, and retinal defects.
Deep-intronic variants in CNGB3 cause achromatopsia by pseudoexon activation
- Pages: 255-264
- First Published: 23 September 2019
Heterozygous pathogenic variants in GLI1 are a common finding in isolated postaxial polydactyly A/B
- Pages: 265-276
- First Published: 24 September 2019
Next-generation sequencing for the diagnosis of MYH9-RD: Predicting pathogenic variants
- Pages: 277-290
- First Published: 28 September 2019
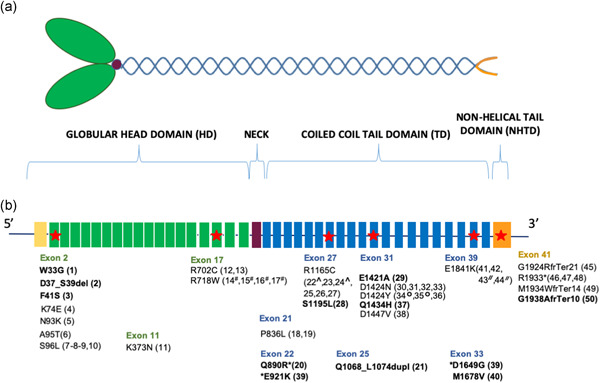
MYH9-related disorder diagnosis is still challenging in clinical practice. We analyzed the genetic variants in more than 3,000 patients with a bleeding or platelet disorder and identified 50 patients with a rare variant in MYH9. In the presence of an unclassified platelet disorder with macrothrombocytes, MYH9-RD should always be considered.
Disease-associated polymorphisms within the conserved ECR1 enhancer differentially regulate the tissue-specific activity of the cannabinoid-1 receptor gene promoter; implications for cannabinoid pharmacogenetics
- Pages: 291-298
- First Published: 14 October 2019
Clinical spectrum of individuals with pathogenic NF1 missense variants affecting p.Met1149, p.Arg1276, and p.Lys1423: genotype–phenotype study in neurofibromatosis type 1
- Pages: 299-315
- First Published: 08 October 2019
Systematic quantification of the anion transport function of pendrin (SLC26A4) and its disease-associated variants
- Pages: 316-331
- First Published: 09 October 2019
Sequencing-based microsatellite instability testing using as few as six markers for high-throughput clinical diagnostics
- Pages: 332-341
- First Published: 31 August 2019