Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Maternal SMC2 is essential for embryonic development via participating chromosome condensation in mice
- Pages: 2535-2545
- First Published: 29 August 2023
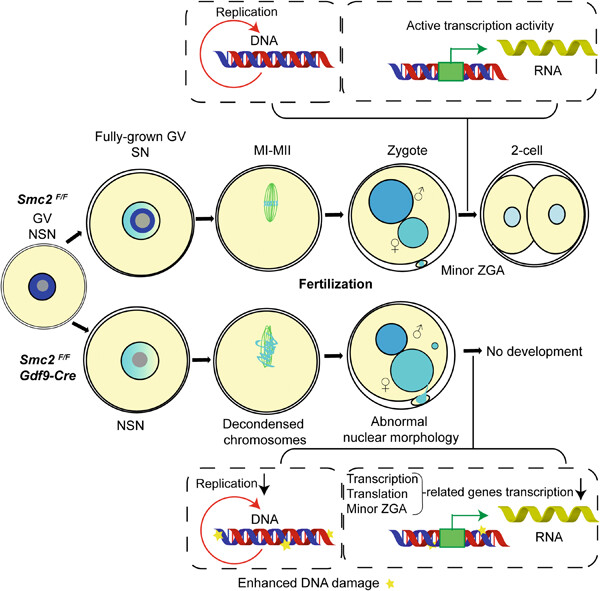
Summary of maternal SMC2 functions during oocyte growth, maturation and zygote development. In oocytes, the SMC2-deleted oocytes have defects in NSN-SN transition in GV stage, and further chromosome condensation. After fertilization, Depletion of maternal SMC2 causes abnormal nuclear morphology, impaired pronuclear function and accumulated DNA damage, which prevented the development of embryos beyond the zygote stage.
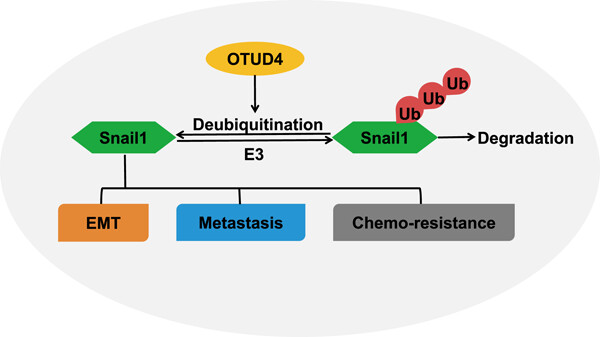
OTUD4 regulates metastasis and chemoresistance in melanoma by stabilizing Snail1
- Pages: 2546-2555
- First Published: 29 August 2023
Mutations of family with sequence similarity 20-member C gene causing lethal and nonlethal Raine syndrome causes hypophosphatemia rickets
- Pages: 2556-2569
- First Published: 12 September 2023
Diverse regulated cell death modes predict the immune microenvironment and drug sensitivity in lung adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 2570-2585
- First Published: 16 October 2023
BMP6 participates in the pathogenesis of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis by regulating osteopenia
- Pages: 2586-2599
- First Published: 05 October 2023
Primary cilium-mediated signaling cascade suppresses age-related biliary fibrosis
- Pages: 2600-2611
- First Published: 08 September 2023
circAP1M2 activates ATG9A-associated autophagy by inhibiting miR-1249-3p to promote cisplatin resistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 2612-2624
- First Published: 03 September 2023
Effect of the secretome of mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing BMP-9 on osteoblast differentiation and bone repair
- Pages: 2625-2637
- First Published: 03 September 2023
Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay suppresses injury-induced muscle regeneration via inhibiting MyoD transcriptional activity
- Pages: 2638-2650
- First Published: 08 September 2023
Targeting phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase for inhibiting maxillary bone resorption
- Pages: 2651-2667
- First Published: 10 October 2023
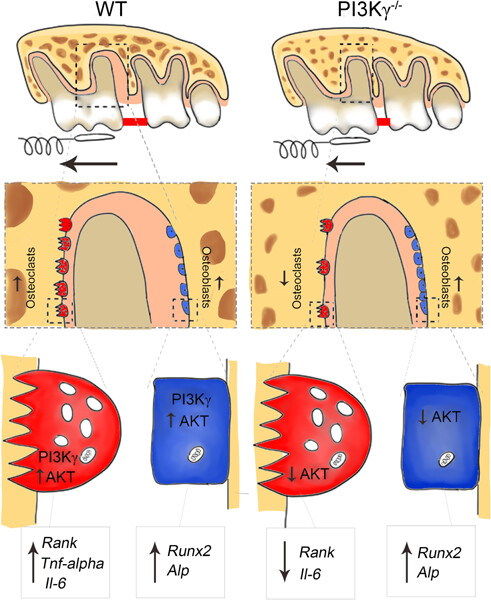
PI3Kγ/Akt plays an important role in the physiological and mechanically induced maxillary. The absence of the PI3Kγ enzyme and the loss of its kinase activity increased maxillary bone mass and root volume. Accordingly, PI3Kγ−/− mice exhibited a reduction in bone remodeling induced by mechanical loading with less OTM and opening of the maxillary suture. The mechanisms involve greater reduction of p-Akt protein, differentiation of osteoblasts, as demonstrated by cell counts and increased expression of Runx2 and Alp under steady-state conditions. Moreover, under mechanical stimulation, PI3Kγ−/− mice showed lack of osteoclast responsiveness, which was possibly linked to a reduced expression of Rank and Il-6.
Loss of miR-204 and miR-211 shifts osteochondral balance and causes temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis
- Pages: 2668-2678
- First Published: 12 September 2023
Porphyromonas gingivalis outer membrane vesicles shape trophoblast cell metabolism impairing functions associated to adverse pregnancy outcome
- Pages: 2679-2691
- First Published: 16 October 2023
Simulated microgravity-induced oxidative stress and loss of osteogenic potential of osteoblasts can be prevented by protection of primary cilia
- Pages: 2692-2709
- First Published: 05 October 2023
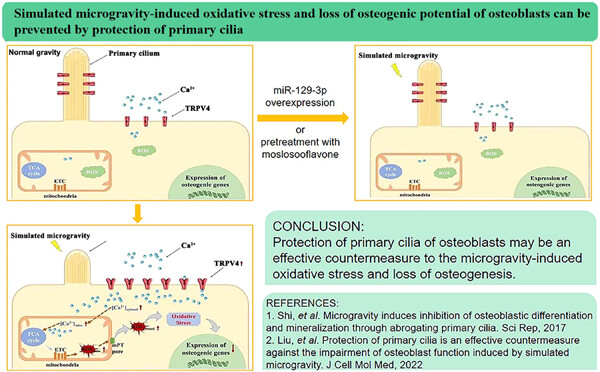
Primary cilium on most mammalian cells is a microtubule structure protruding from cell surface where many receptors and ion channels such as TRPV4 are localized. In this study, primary cilia of rat calvarial osteoblasts were found to become shorter and even disappeared when the cells were exposed to a random positioning machine-simulated microgravity, accompanied by increased expression and overactive Ca2+ channel of TRPV4, which induced overload Ca2+ influx, mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and loss of osteogenesis. Protection of primary cilia by overexpression of miR-129-3p or moslosooflavone prevented the TRPV4-mediated overload Ca2+ influx and all above-mentioned changes, indicating that protection of primary cilia should be an effective countermeasure to the simulated microgravity-induced oxidative stress and loss of osteogenic potential of osteoblasts.
CBX8 promotes lung adenocarcinoma growth and metastasis through transcriptional repression of CDKN2C and SCEL
- Pages: 2710-2723
- First Published: 21 September 2023
Integrated transcriptomics and metabolomics reveal protective effects on heart of hibernating Daurian ground squirrels
- Pages: 2724-2748
- First Published: 21 September 2023