Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information-TOC
Table of Contents: Volume 231, Number 6
- Pages: 1183-1185
- First Published: 16 February 2016
Issue Information-Editor's Choice
Issue Information: Highlights
Highlights: Volume 231, Number 6
- Pages: 1187-1188
- First Published: 16 February 2016
From the Bench
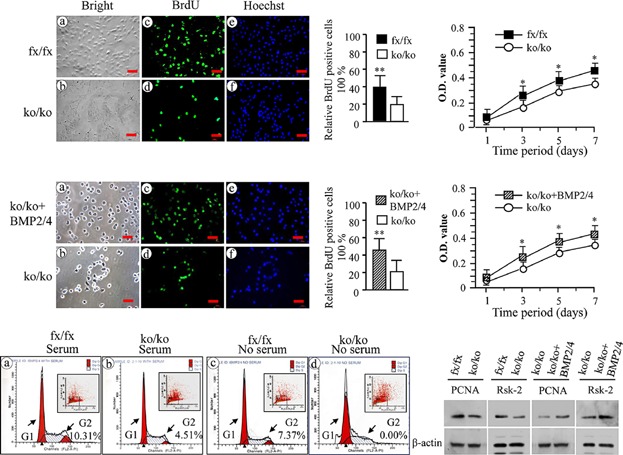
Establishment of Immortalized BMP2/4 Double Knock-Out Osteoblastic Cells Is Essential for Study of Osteoblast Growth, Differentiation, and Osteogenesis
- Pages: 1189-1198
- First Published: 23 November 2015
Review Article
Evidence-Based Theory for Integrated Genome Regulation of Ontogeny—An Unprecedented Role of Nuclear FGFR1 Signaling
- Pages: 1199-1218
- First Published: 05 January 2016
Rapid Communication
Modulation of 17β-Estradiol Signaling on Cellular Proliferation by Caveolin-2
- Pages: 1219-1225
- First Published: 19 October 2015
Original Research Articles
Effect of Docosahexaenoic Acid on Cell Cycle Pathways in Breast Cell Lines With Different Transformation Degree
- Pages: 1226-1236
- First Published: 19 October 2015
TNF-α/TNFR2 Regulatory Axis Stimulates EphB2-Mediated Neuroregeneration Via Activation of NF-κB
- Pages: 1237-1248
- First Published: 22 October 2015
Different Blood-Borne Human Osteoclast Precursors Respond in Distinct Ways to IL-17A
- Pages: 1249-1260
- First Published: 22 October 2015
Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Ca2+ Overload Contributes to Hesperidin Induced Paraptosis in Hepatoblastoma Cells, HepG2
- Pages: 1261-1268
- First Published: 22 October 2015
Coordinated Dynamics of RNA Splicing Speckles in the Nucleus
- Pages: 1269-1275
- First Published: 23 October 2015
Differential Regulation of Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase Promoter Activation and Protein Degradation by Histone Deacetylase Inhibition
- Pages: 1276-1282
- First Published: 27 October 2015
Mechanical Stimulation and IGF-1 Enhance mRNA Translation Rate in Osteoblasts Via Activation of the AKT-mTOR Pathway
- Pages: 1283-1290
- First Published: 27 October 2015
cAMP and cGMP Play an Essential Role in Galvanotaxis of Cell Fragments
- Pages: 1291-1300
- First Published: 30 October 2015
Ex Vivo Assay of Electrical Stimulation to Rat Sciatic Nerves: Cell Behaviors and Growth Factor Expression
- Pages: 1301-1312
- First Published: 30 October 2015
Effects of Sleep Deprivation on Mice Bone Marrow and Spleen B Lymphopoiesis
- Pages: 1313-1320
- First Published: 30 October 2015
The Transcription Factor EB (TFEB) Regulates Osteoblast Differentiation Through ATF4/CHOP-Dependent Pathway
- Pages: 1321-1333
- First Published: 31 October 2015
Inhibition of Polyamine Uptake Potentiates the Anti-Proliferative Effect of Polyamine Synthesis Inhibition and Preserves the Contractile Phenotype of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells
- Pages: 1334-1342
- First Published: 03 November 2015
Interaction Between Human Polyomavirus BK and Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1 alpha
- Pages: 1343-1349
- First Published: 03 November 2015
Identification of a Hematopoietic Cell Dedifferentiation-Inducing Factor
- Pages: 1350-1363
- First Published: 03 November 2015
Complex-I Alteration and Enhanced Mitochondrial Fusion Are Associated With Prostate Cancer Progression
- Pages: 1364-1374
- First Published: 04 November 2015
The Role of Kv1.2 Channel in Electrotaxis Cell Migration
- Pages: 1375-1384
- First Published: 18 November 2015
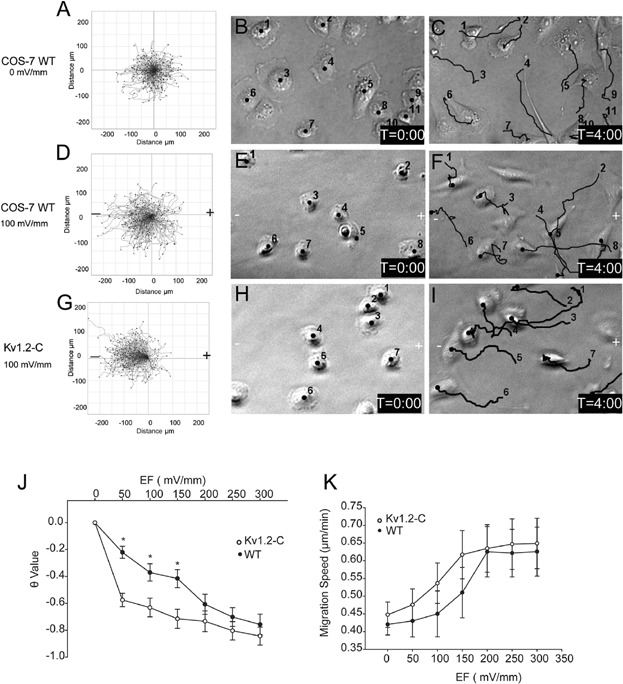
In this study we propose a model of EF-dependent re-localisation of Kv1.2 channels at the cathode-facing membrane of electrotaxing cells, where cortactin coordinates protein binding of Kv1.2 channel with actin in cytoskeleton and establishes a directional migration. Over expression of Kv1.2 channels or pharmacological inhibition respectively resulted in increased and reduced electrotactic response, respectively, indicating pivotal role of Kv1.2 channels in EF-sensing.
Effects of Nandrolone Stimulation on Testosterone Biosynthesis in Leydig Cells
- Pages: 1385-1391
- First Published: 02 December 2015
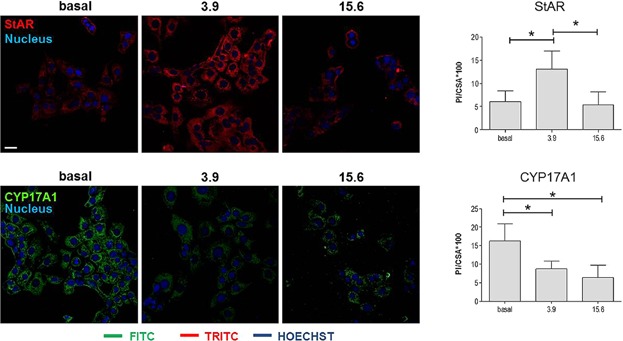
Anabolic androgenic steroids (AAS) are among the drugs most used by athletes for improving physical performance, as well as for aesthetic purposes. This study investigates the effects of nandrolone on testosterone biosynthesis in Leydig cells using various methods. The results obtained show that testosterone levels increase at a 3.9 µM concentration of nandrolone and return to the basal level a 15.6 µM dose of nandrolone. Nandrolone-induced testosterone increment was associated with upregulation of StAR and downregulation of CYP17A1.
E11/Podoplanin Protein Stabilization Through Inhibition of the Proteasome Promotes Osteocyte Differentiation in Murine in Vitro Models
- Pages: 1392-1404
- First Published: 07 December 2015
Erratum
Erratum: Bisphenol-A Induces Podocytopathy With Proteinuria in Mice by Nuria Olea-Herrero, María Isabel Arenas, Carmen Muñóz-Moreno, Rafael Moreno-Gómez-Toledano, Marta González-Santander, Ignacio Arribas and Ricardo J. Bosch
- Page: 1405
- First Published: 16 February 2016