Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLE
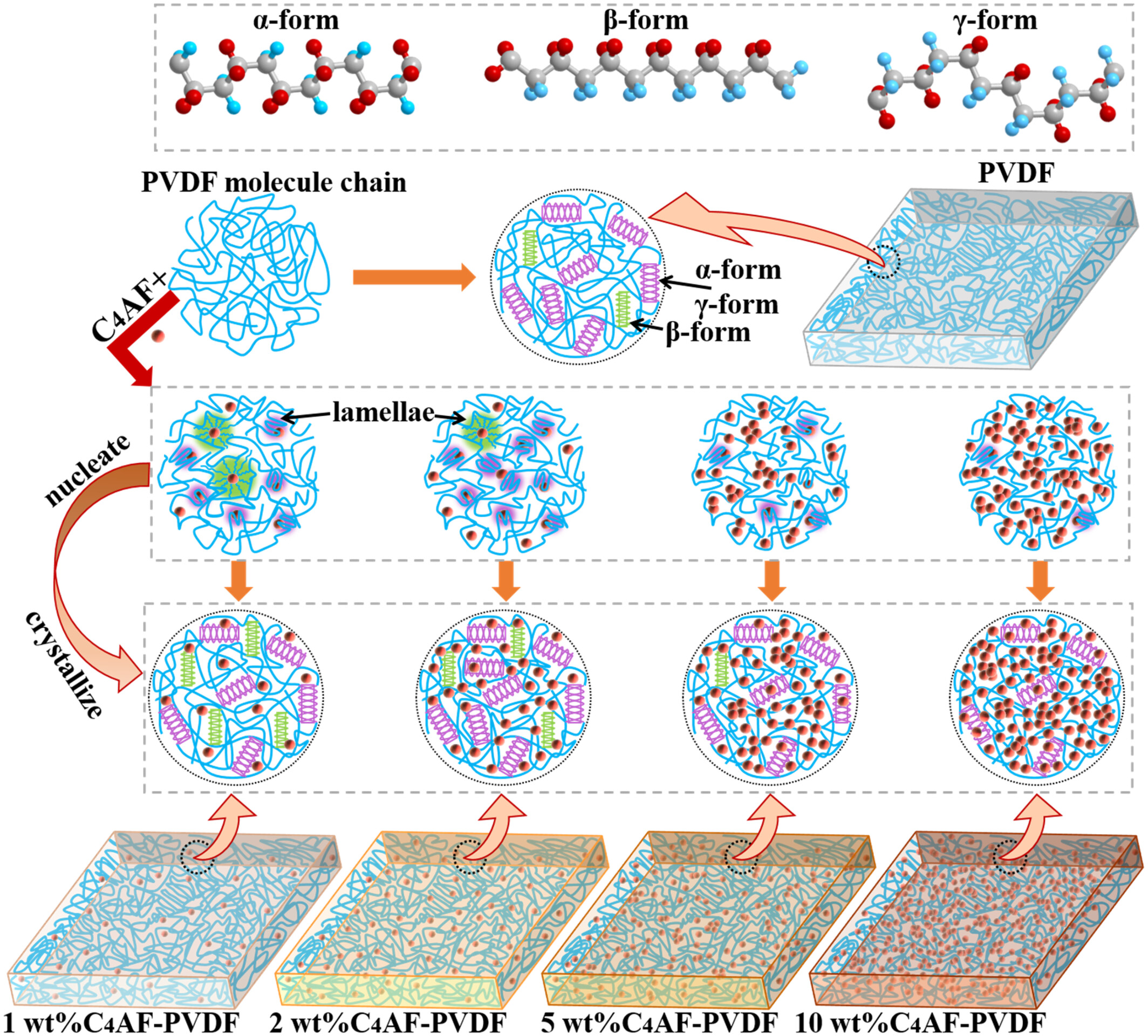
Effect of Ultrafine Cement Mineral Phase C4AF on the Properties of PVDF Composite Films
- First Published: 26 January 2025
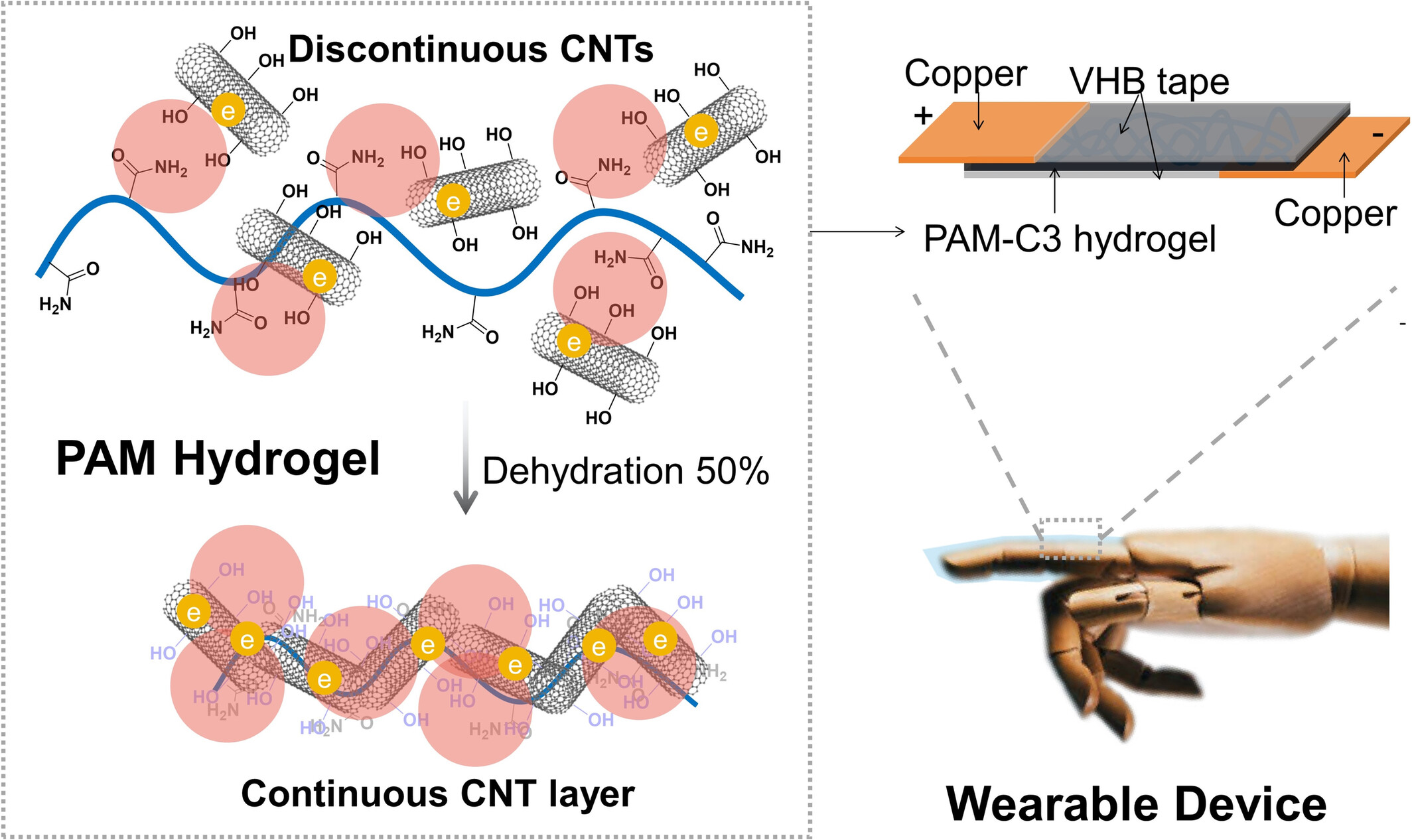
Enhancing Conductivity of Polyacrylamide Hydrogel With Surface-Coated Hydroxylated Carbon Nanotubes for Wearable Device Applications
- First Published: 26 December 2024
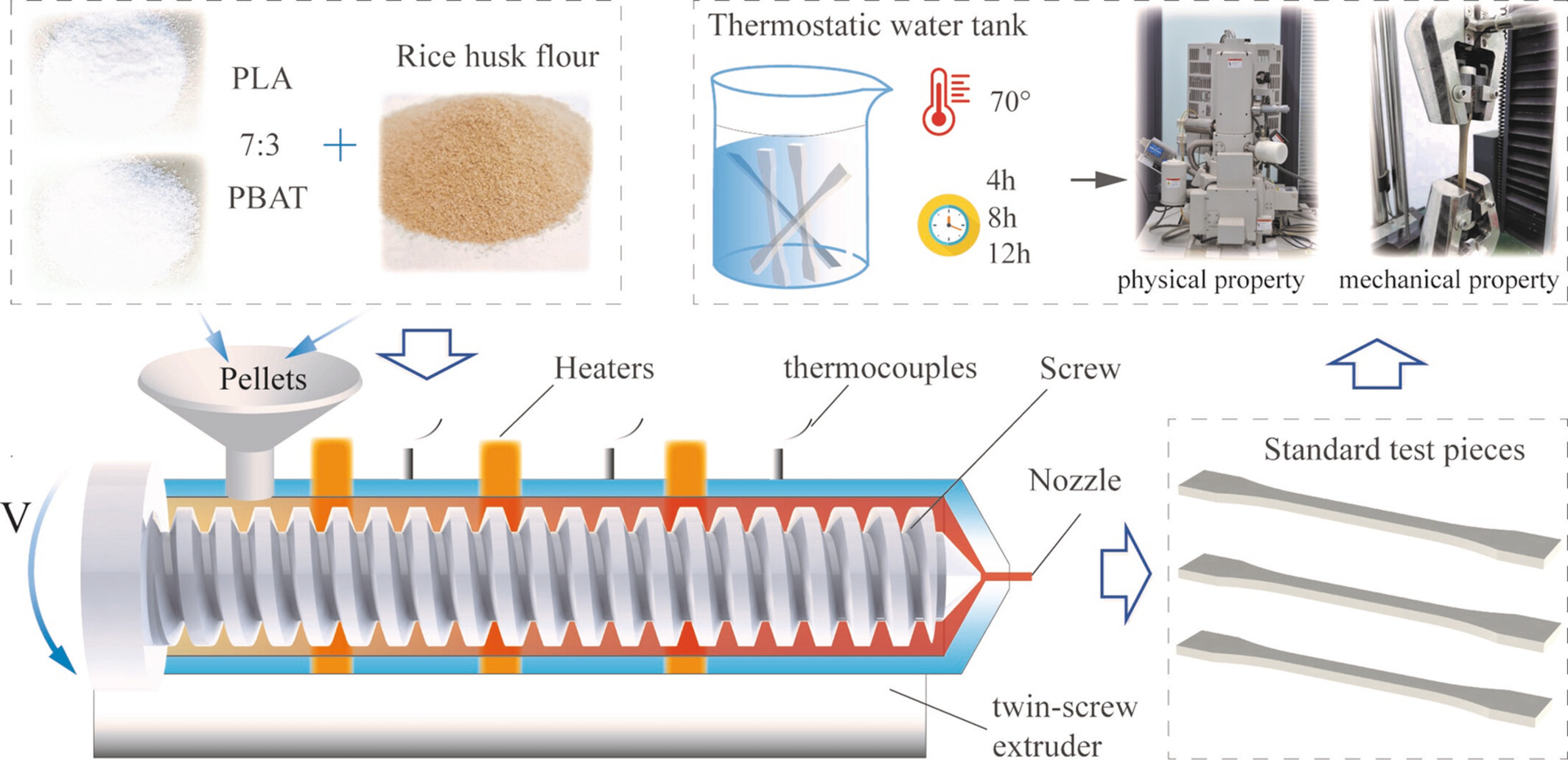
Degradation Behavior of Rice Husk Fiber-Reinforced PLA/PBAT Composites in Short-Term Hydrothermal Environment
- First Published: 02 January 2025
Assessing the Integrity of N95 Mask Elastomer Straps With Decontamination and Reuse
- First Published: 04 January 2025
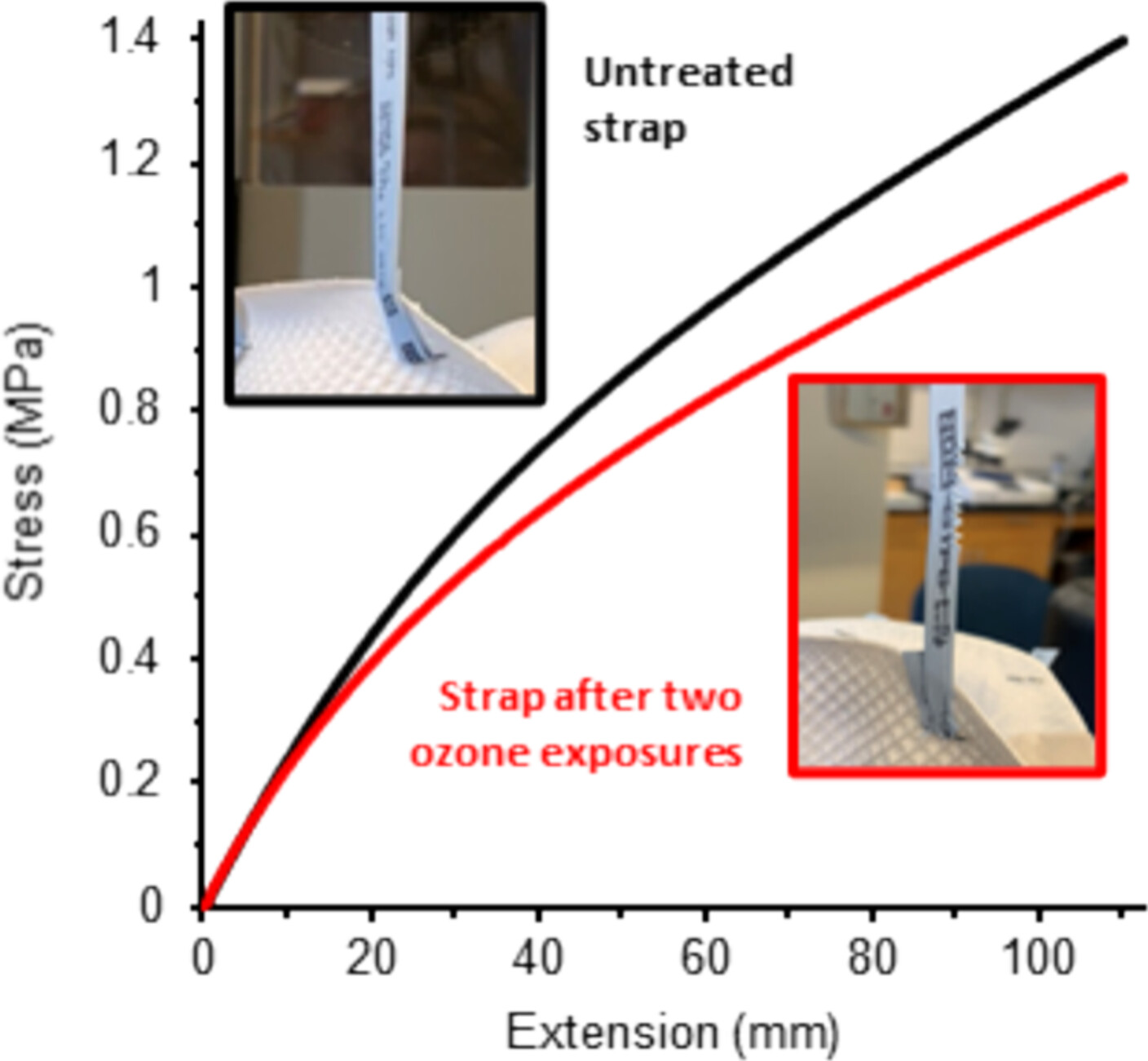
This research investigates how decontamination changes the properties of N95 mask strap assemblies and examines the ability of materials characterization techniques to detect these changes. The mechanical response of the mask strap assembly was found to be a reliable method to evaluate degradation of the mask strap material due to decontamination, both in the strap and at its attachment point.
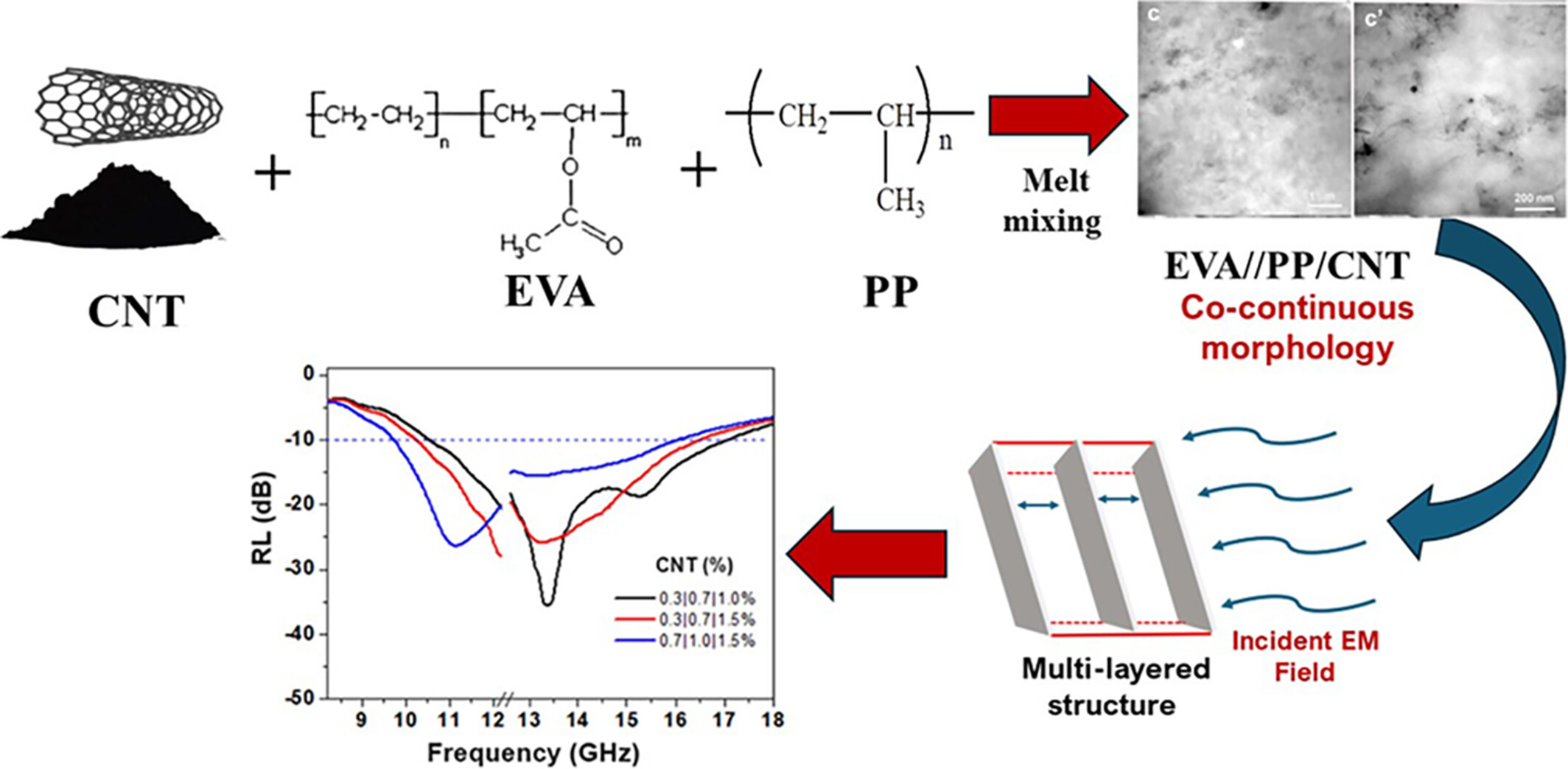
Multi-Layered Structure as an Efficient Design for Improving Electromagnetic Wave Absorbing Properties of Polypropylene/EVA/Carbon Nanotube Composites
- First Published: 21 January 2025
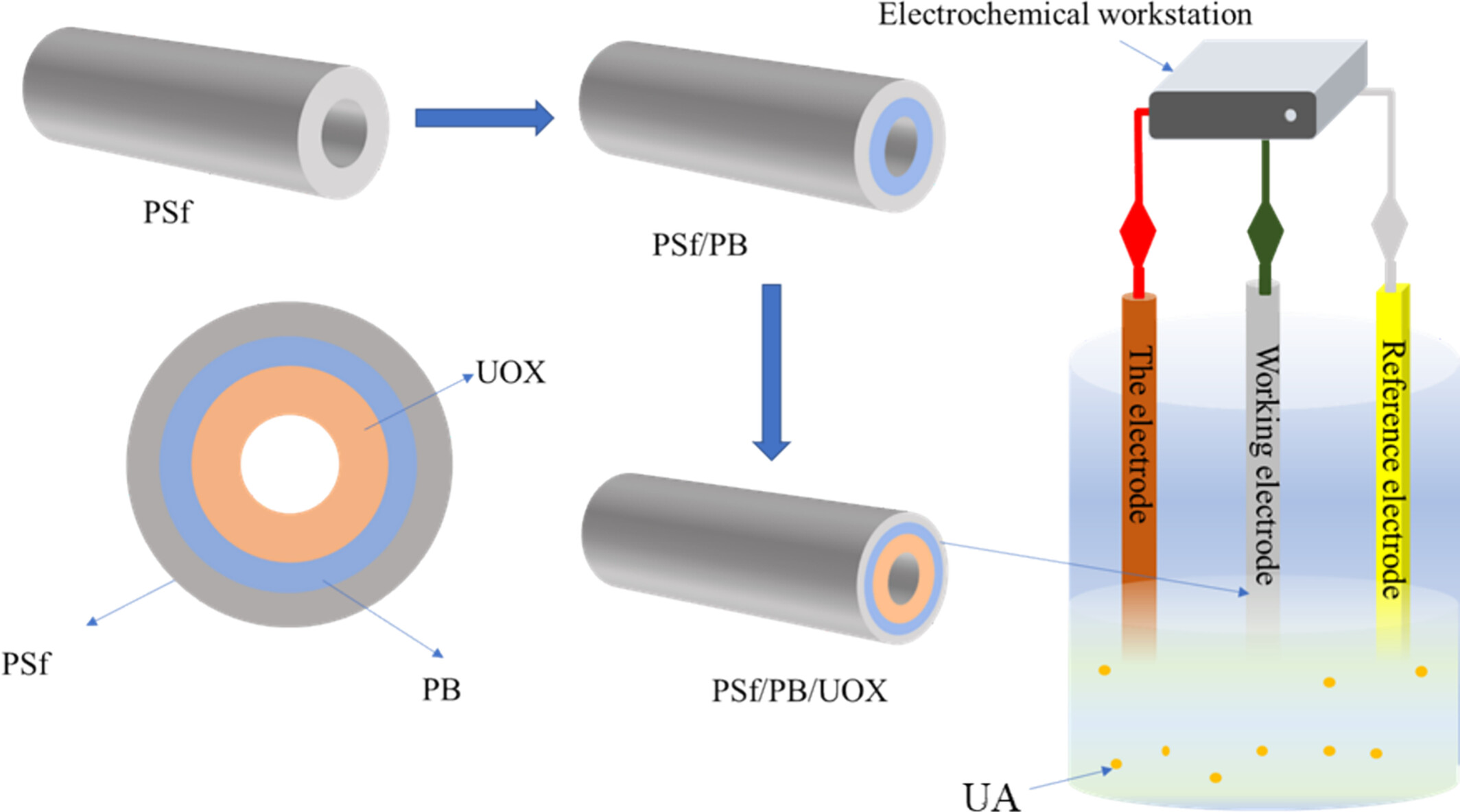
Prussian Blue and Polyvinylpyrrolidone-Embedded Hollow Fiber Gradient Polysulfone Membrane for Uric Acid Biosensor Application
- First Published: 30 December 2024
Enhanced Conductivity of Chitosan Composite Membranes With Fractionated Kraft and Organosolv Lignin
- First Published: 27 December 2024
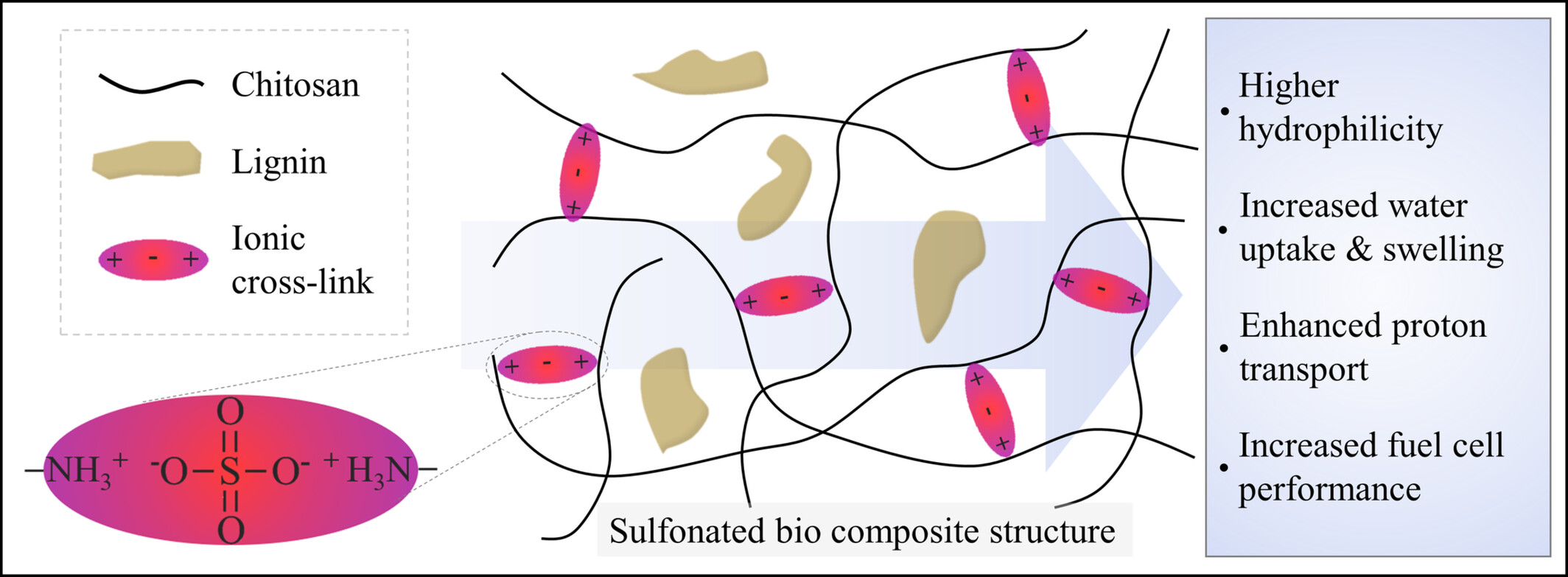
Bio-based chitosan composite membranes containing kraft or organosolv lignin submitted to successive extraction steps (ethyl acetate and ethanol) are immersed in a sulfuric acid solution. This process incorporates sulfate groups and disrupts crystallinity, which improves oxidative stability, increases water uptake, and enhances the biocomposite's proton conductivity and H2/O2 fuel cell performance, while maintaining low bulk electron conductivity.
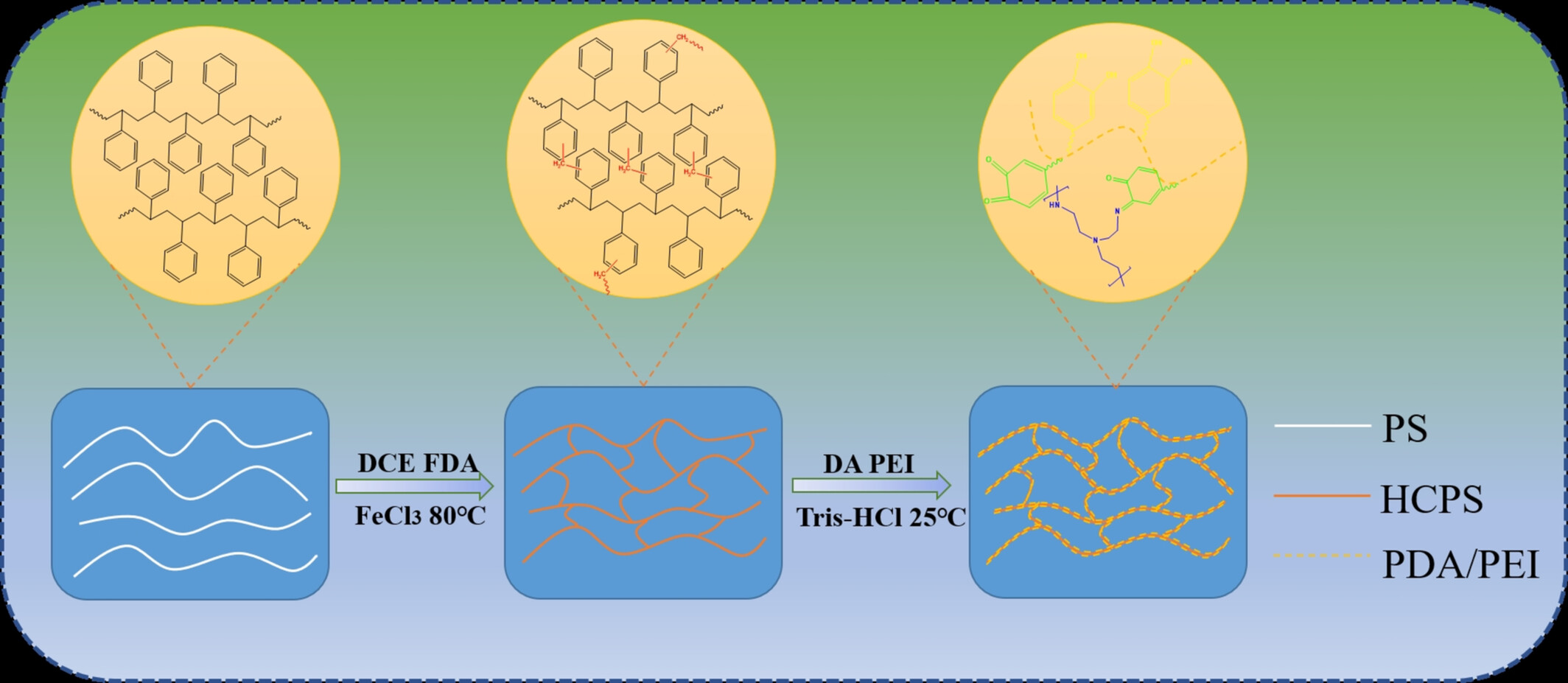
Dopamine-Assisted Polyethyleneimine Deposition Modification of Hypercrosslinked Polystyrene for Enhanced Adsorption of the Dye Congo Red
- First Published: 28 December 2024
Sunlight Self-Heating Oil-Water Separation Material and Device for Recovering High-Viscosity Oil
- First Published: 30 December 2024
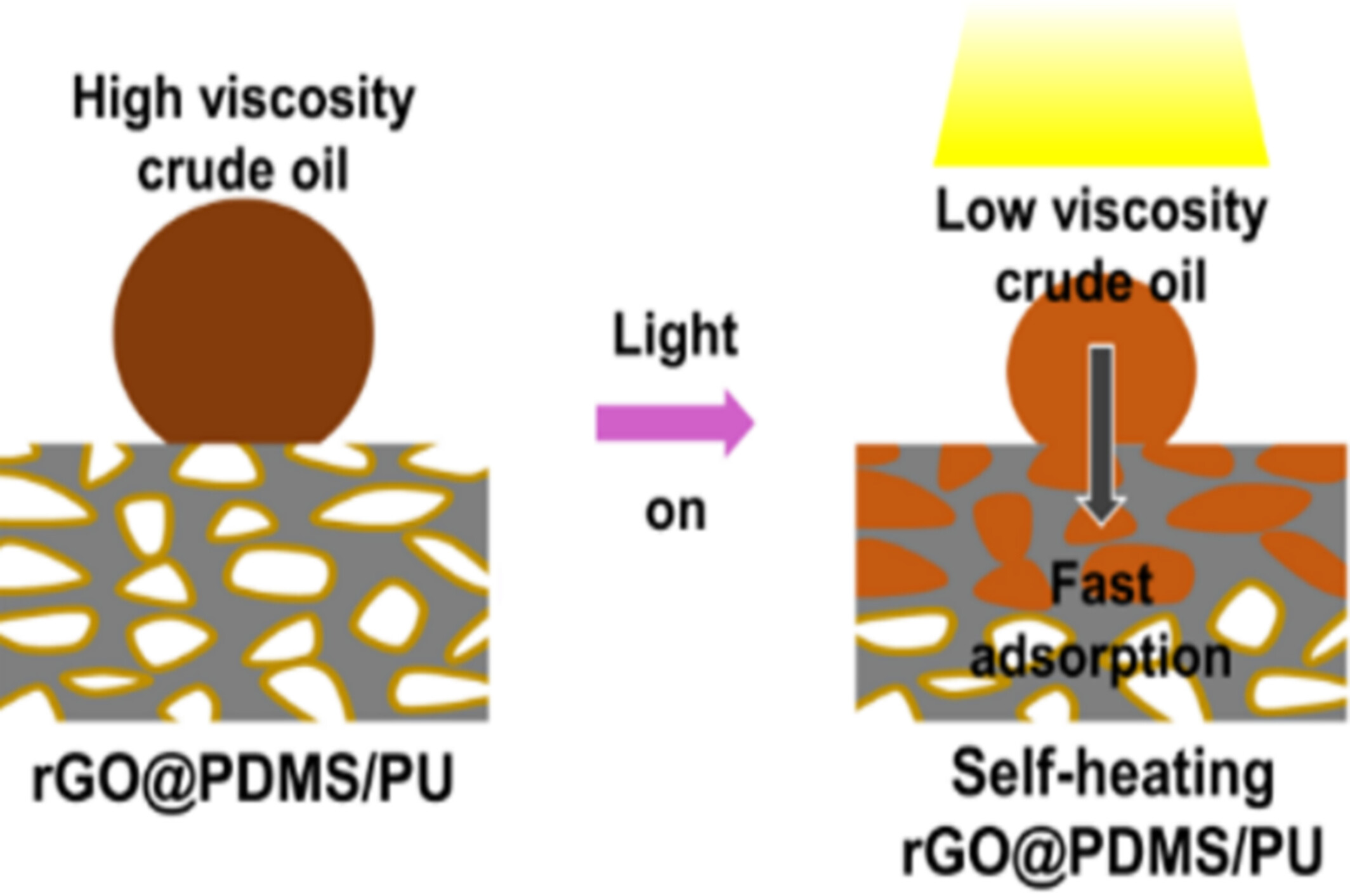
A novel superhydrophobic/superoleophilic sponge material (rGO@PDMS/PU) with excellent photothermal conversion ability was prepared and used for in situ recovery of high-viscosity oil and organic solvents. Under the irradiation of 1 sunlight intensity, the rGO@PDMS/PU's surface temperature rises to 95.4°C within 10 s. The new oil-gathering device increases the crude oil recovery rate by nearly four times.
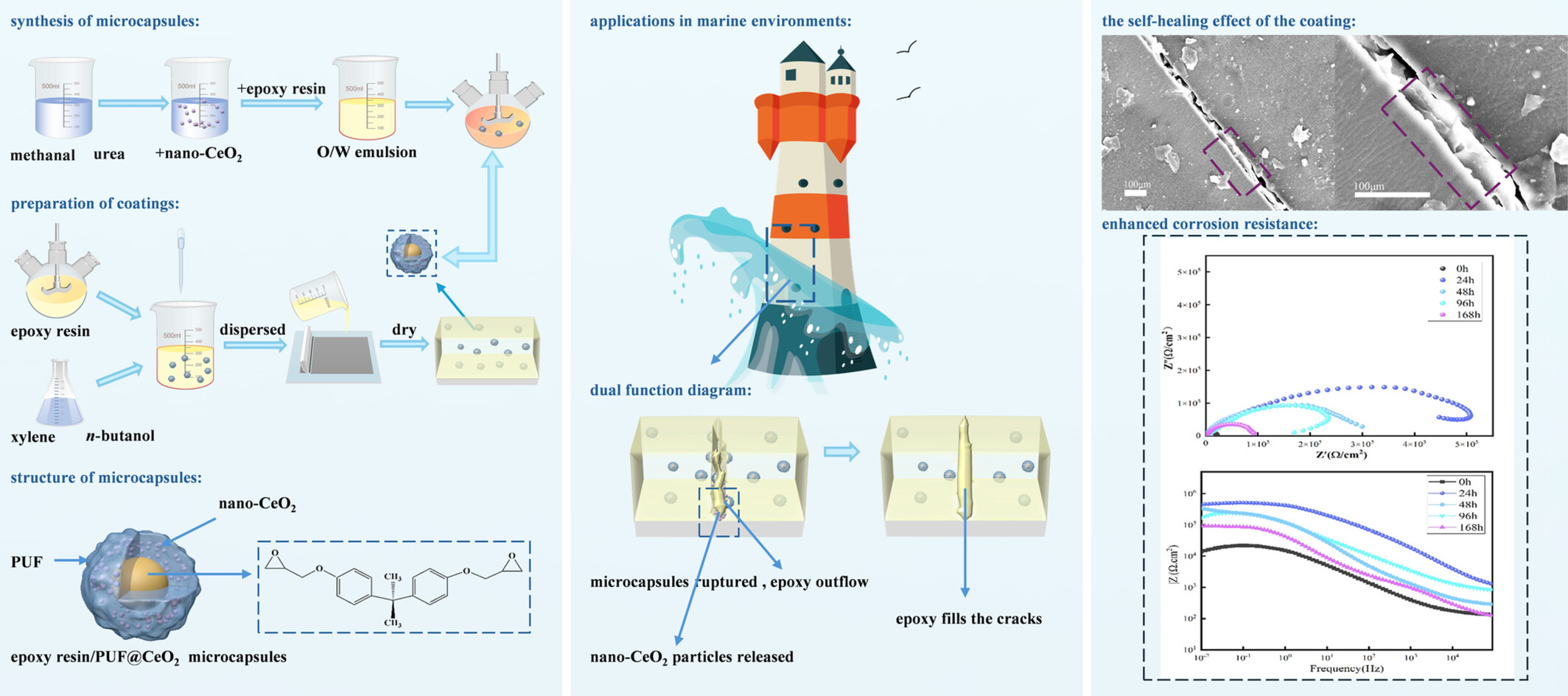
Design and Development of Dual-Function Nano-CeO2 -Integrated PUF/Epoxy Microcapsule Systems for Self-Healing and Corrosion-Resistant Epoxy Coatings
- First Published: 28 December 2024
Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles-Filled and Polyvinyl Alcohol-Grafted Copolymer Composites for Column Adsorption and Photochemical Degradation of p-Nitrophenol
- First Published: 08 January 2025
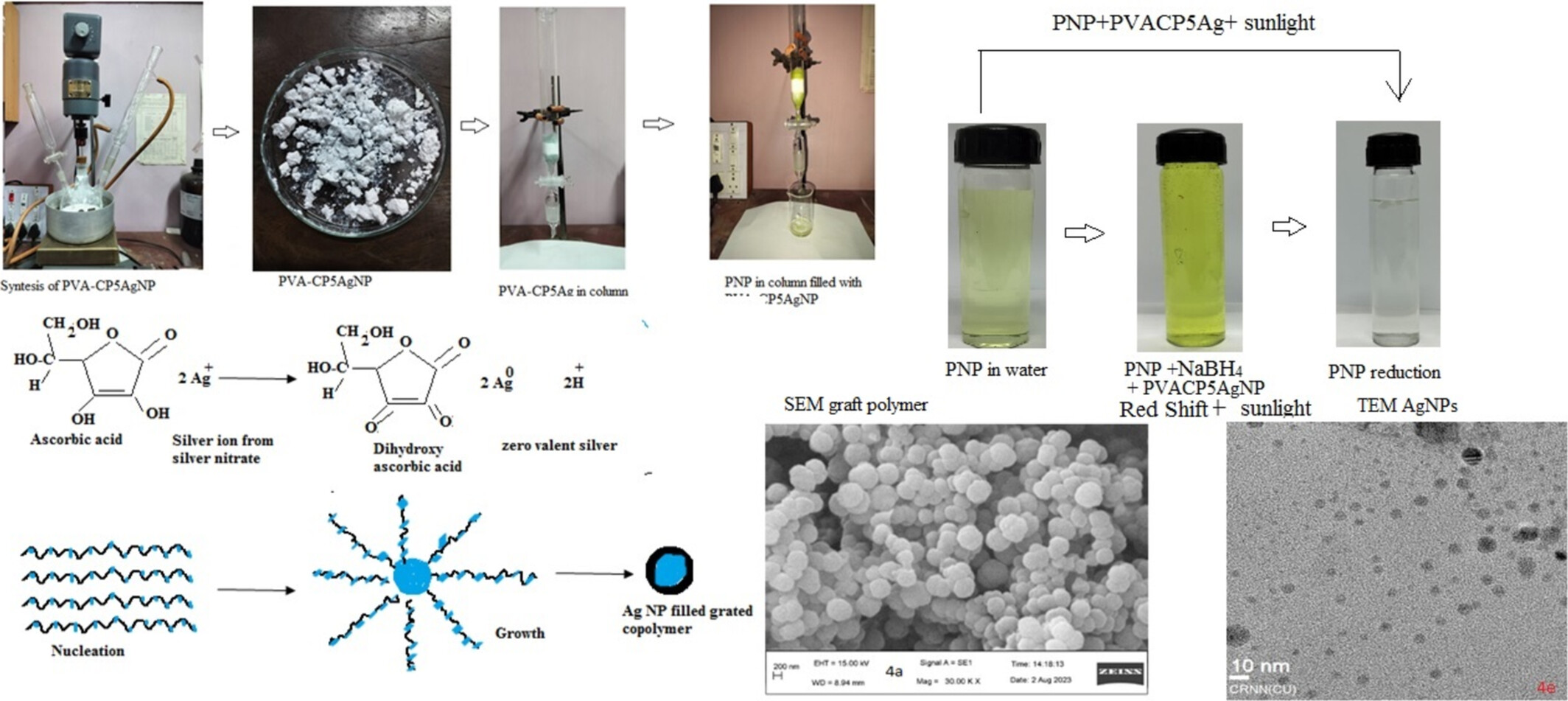
PVA was grafted to the copolymer of acrylonitrile (AN) and acrylic acid/sodium acrylate using N,N′-methylenebisacrylamide comonomer–crosslinker. Silver nanoparticles were synthesized in situ in the polymerization mixtures by reduction of AgNO3 with ascorbic acid. These nanocomposites were characterized and used for the removal and photocatalytic degradation of p-nitrophenol (PNP) from water. The nanocomposite showed high adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of PNP from water.
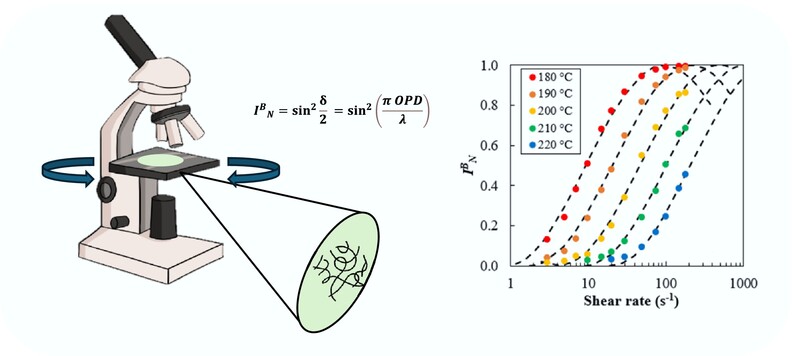
Assessment of the Relaxation Time Under Controlled Shear Flow by Rheo-Optical Characterization
- First Published: 03 January 2025
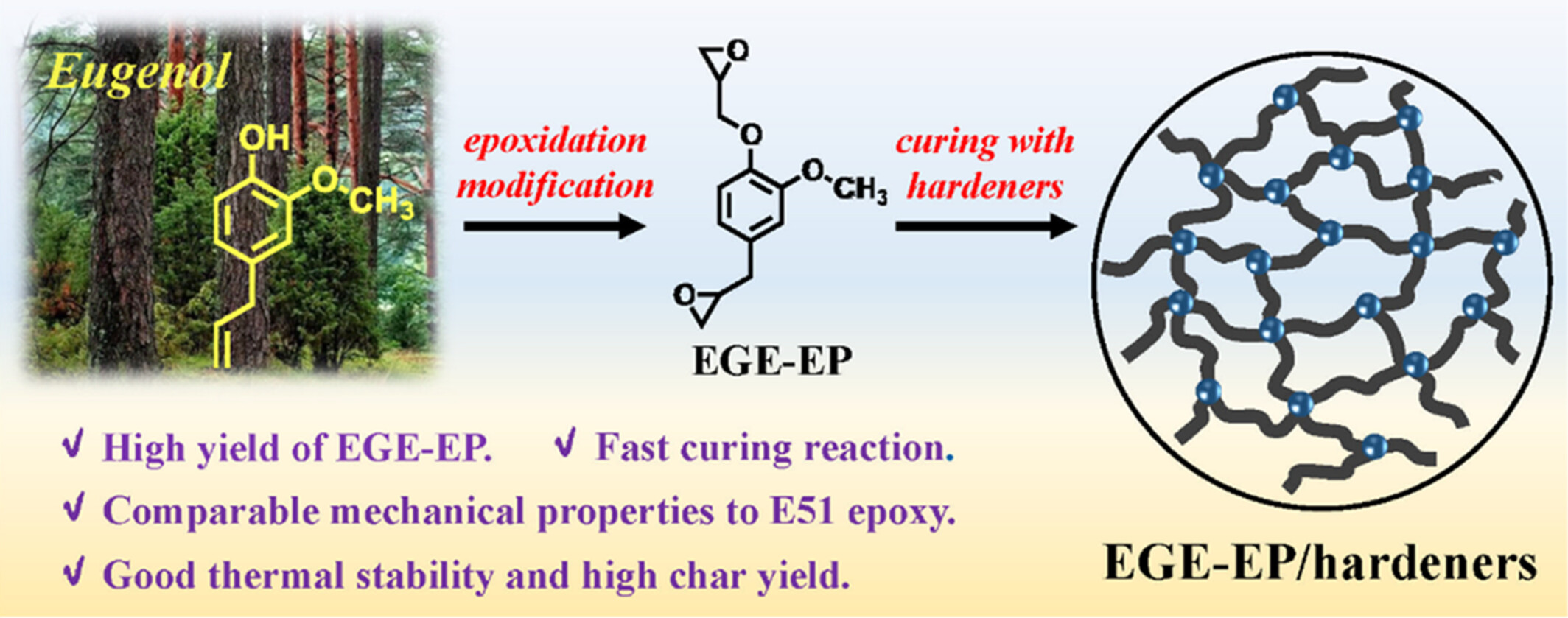
Facile Strategy to Construct Eugenol-Derived Bifunctionality Epoxy Monomer for Preparation of Thermosetting Resin System With Desired Performances
- First Published: 06 January 2025
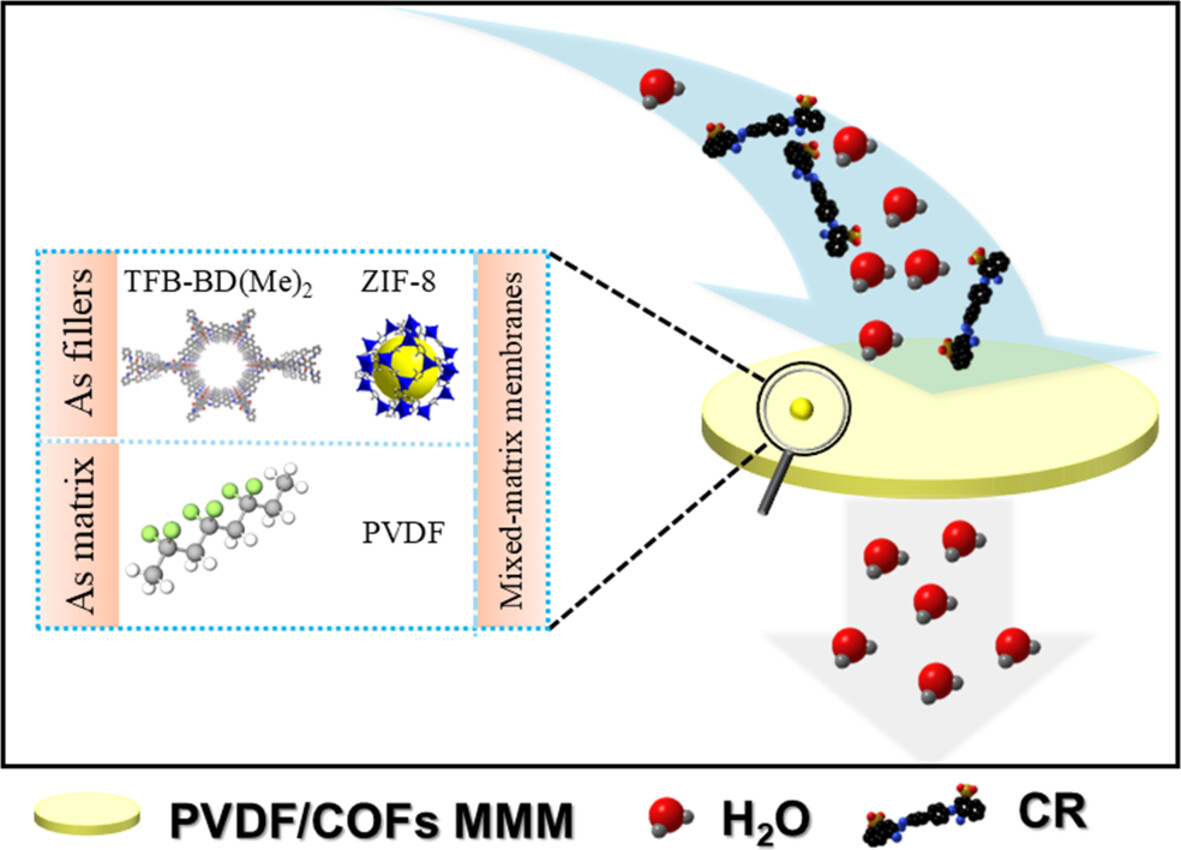
Enhanced Dye Separation With Mixed Matrix Membranes Incorporating ZIF-8@COF Binary Nanofillers
- First Published: 26 December 2024
Sequential Reactive Processing for the Synthesis of Branched Polypropylene and Propylene–Ethylene Copolymer
- First Published: 30 December 2024
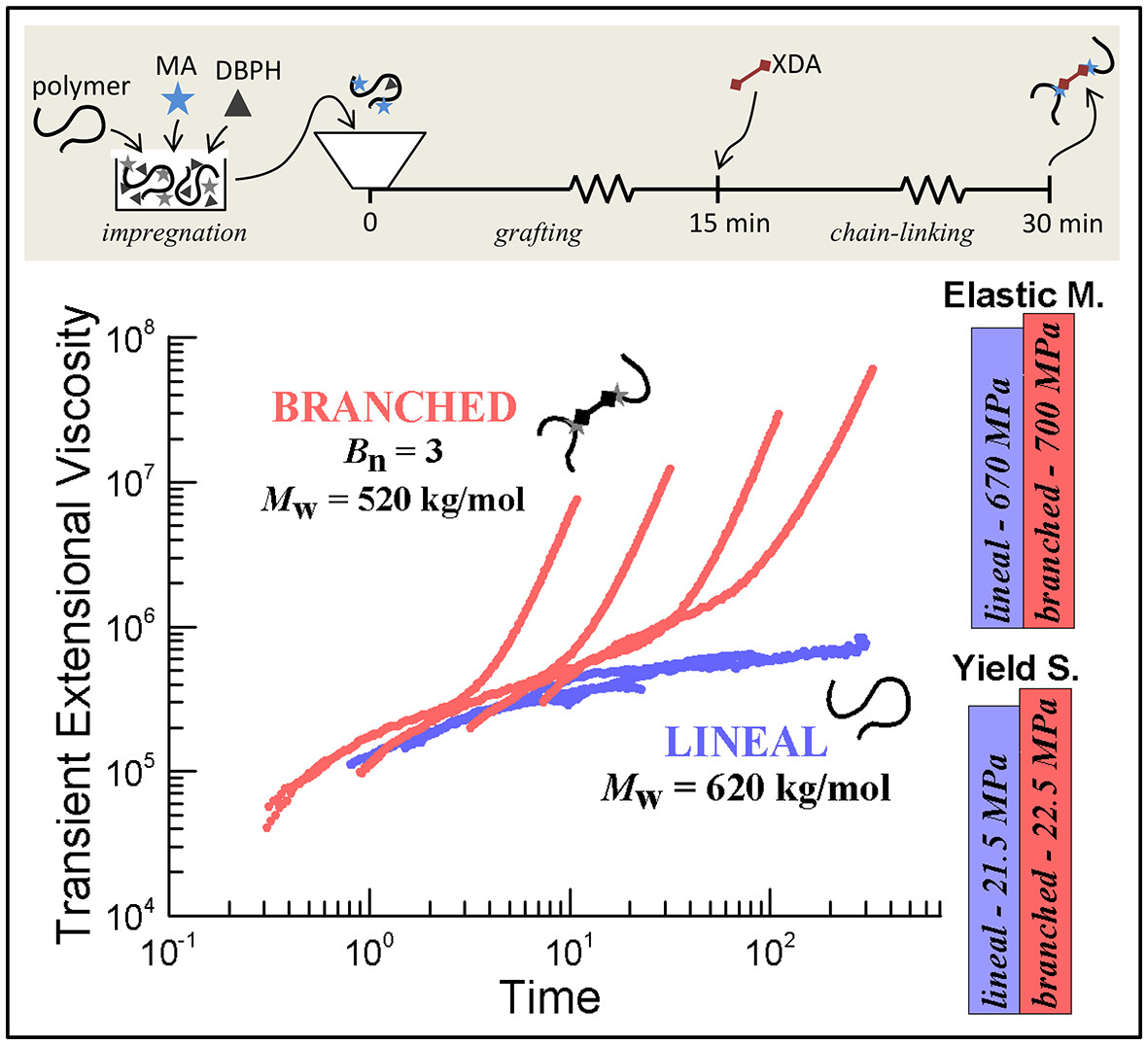
This paper presents a way to prepare long-chain branched polypropylene and propylene–ethylene copolymer by one-step reactive processing involving the sequential incorporation of maleic anhydride and m-xylylenediamine into the reactive medium. The improvement of the melt strength of the polymers is accomplished without substantially altering their average molecular weights, tensile mechanical properties, and crystallinity.
Optimizing Melamine Sponges Modified With Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles for Environmental and Industrial Applications
- First Published: 27 December 2024
Preparation and Alkali Resistance Research of Cyclotriphosphazene Based Hexa-Imidazole Compound Functionalized Addition-Type Polynorbornene Anion Exchange Membranes
- First Published: 30 December 2024
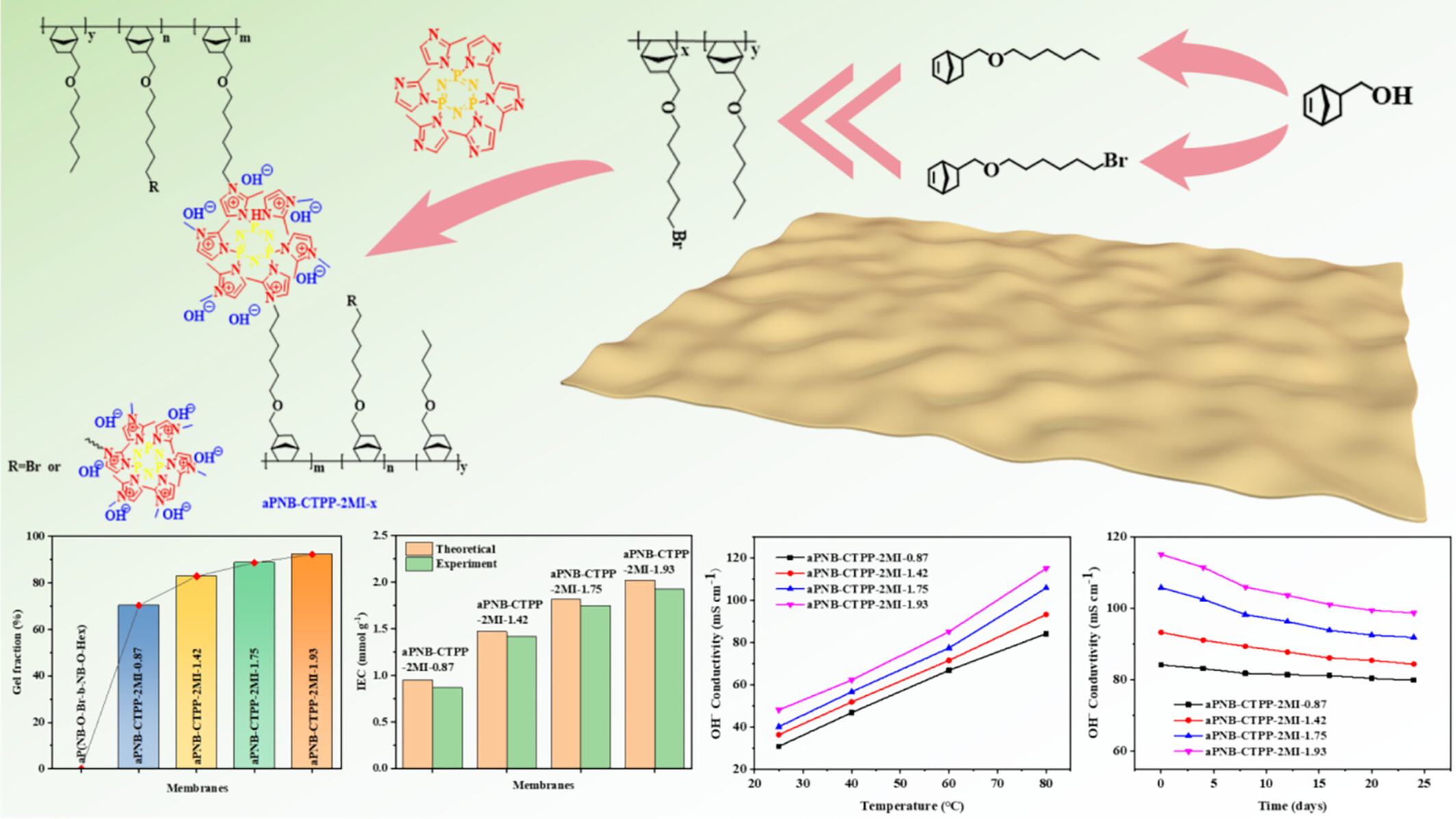
A series of hexa-imidazole ion cluster norbornene anion exchange membranes (aPNB-CTPP-2MI-x) with different ion contents were prepared by using cyclotriphosphazene based hexa-imidazole compounds as a crosslinking agent. The unique structure of aPNB-CTPP-2MI-x membrane makes it have excellent ionic conductivity and alkali resistance stability.
Highly Selective, Catalyst-Free, and Low Temperature Depolymerizable Styrene Copolymer With Incorporated α-Methylstyrene Structural Units
- First Published: 27 December 2024
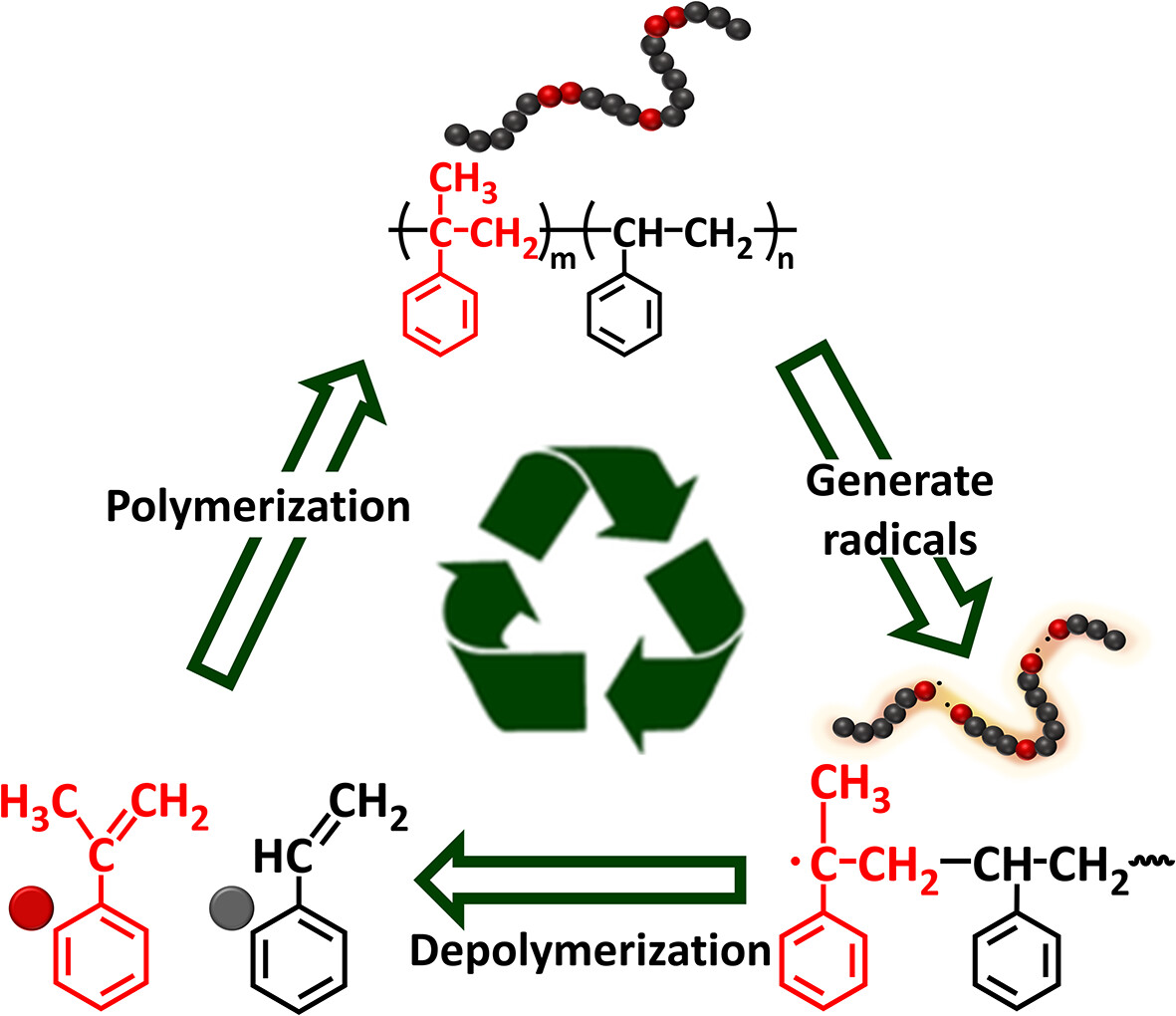
Intrinsic and easy upcycling capability is introduced into polystyrene by incorporating α-methylstyrene structural units into the copolymer. Then, these copolymers can undergo depolymerization into styrene and α-methylstyrene without catalyst. In addition, the properties of the new copolymers prepared with the reclaimed monomers are comparable with those of the virgin copolymers.
Flammability Performance of Ceramifiable Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) Composites With Needle-Like Wollastonite
- First Published: 02 January 2025
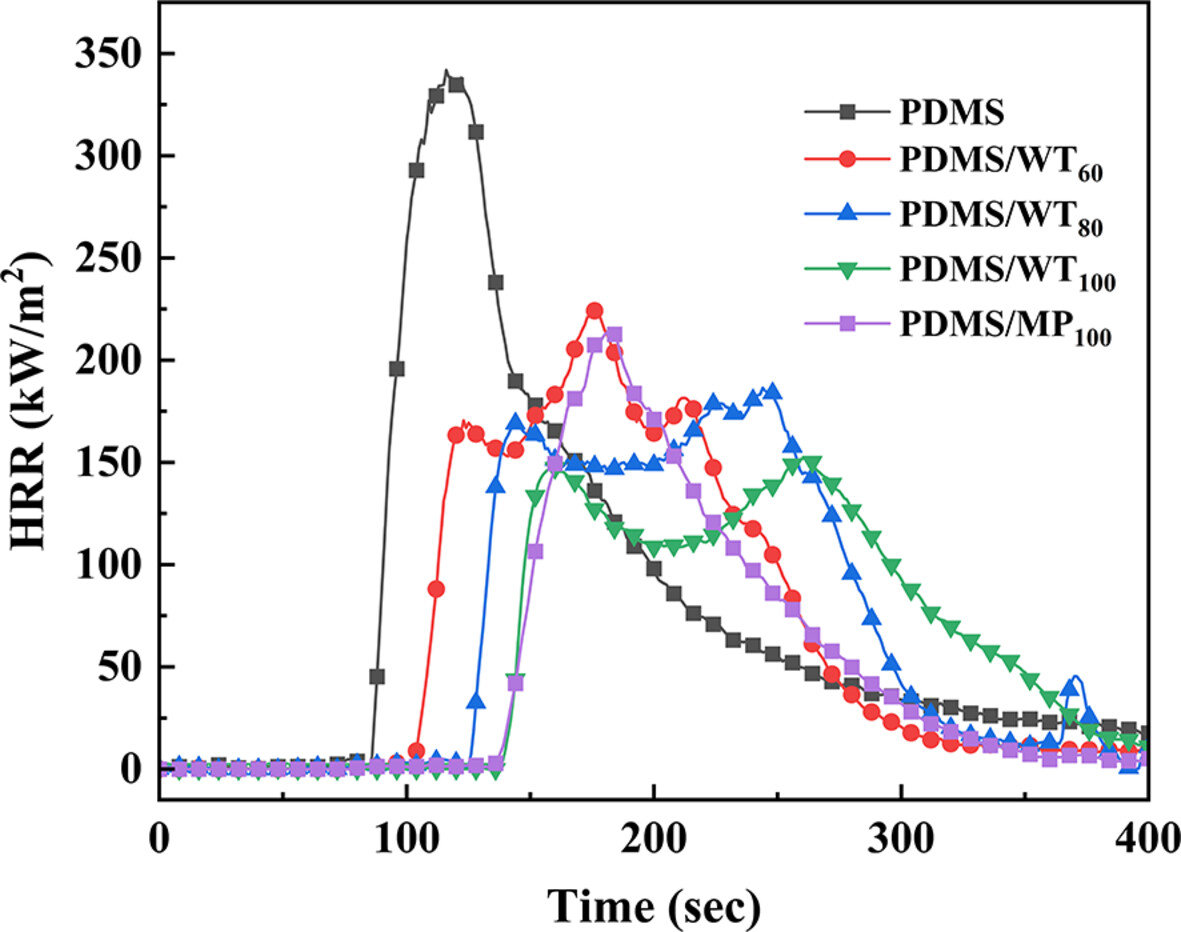
The wollastonite (WT) shows a good mechanical reinforcement effect on PDMS.
The optimized PDMS/WT/ZB/ATH/GP system passes the UL-94 V-0 rating and exhibits an increased limiting oxygen index.
WT is effective in reducing the peak heat release rate and delaying ignition.
The flame retardant mechanism attributed to WT accelerates the eutectic reaction and facilitates the formation of a ceramic barrier at low temperatures.
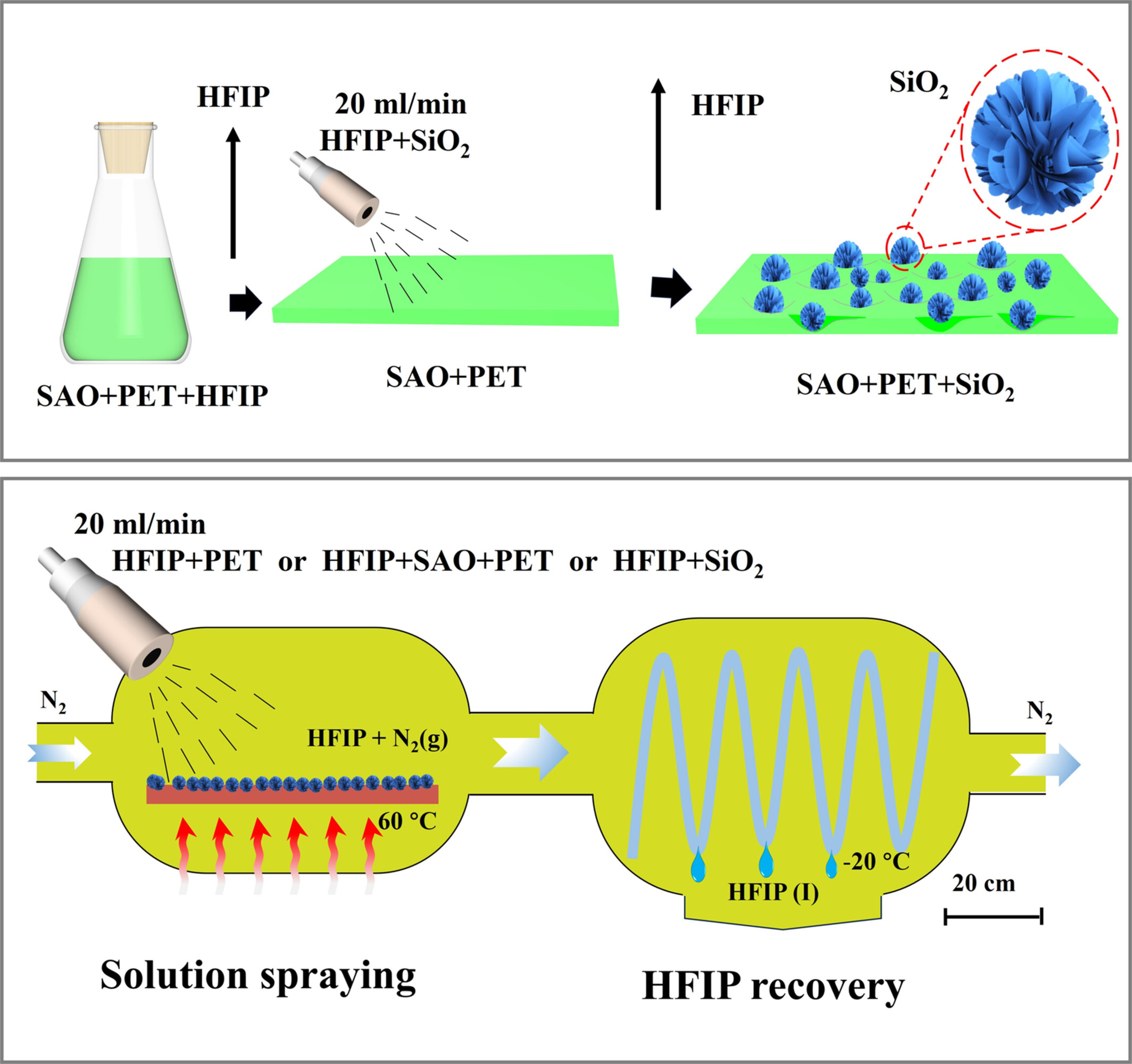
Self-Cleaning of Fluorescent Polyester: Construction of Superhydrophobic Coatings by Surface Microsolubility Particle Semi Embedding Technology
- First Published: 21 January 2025
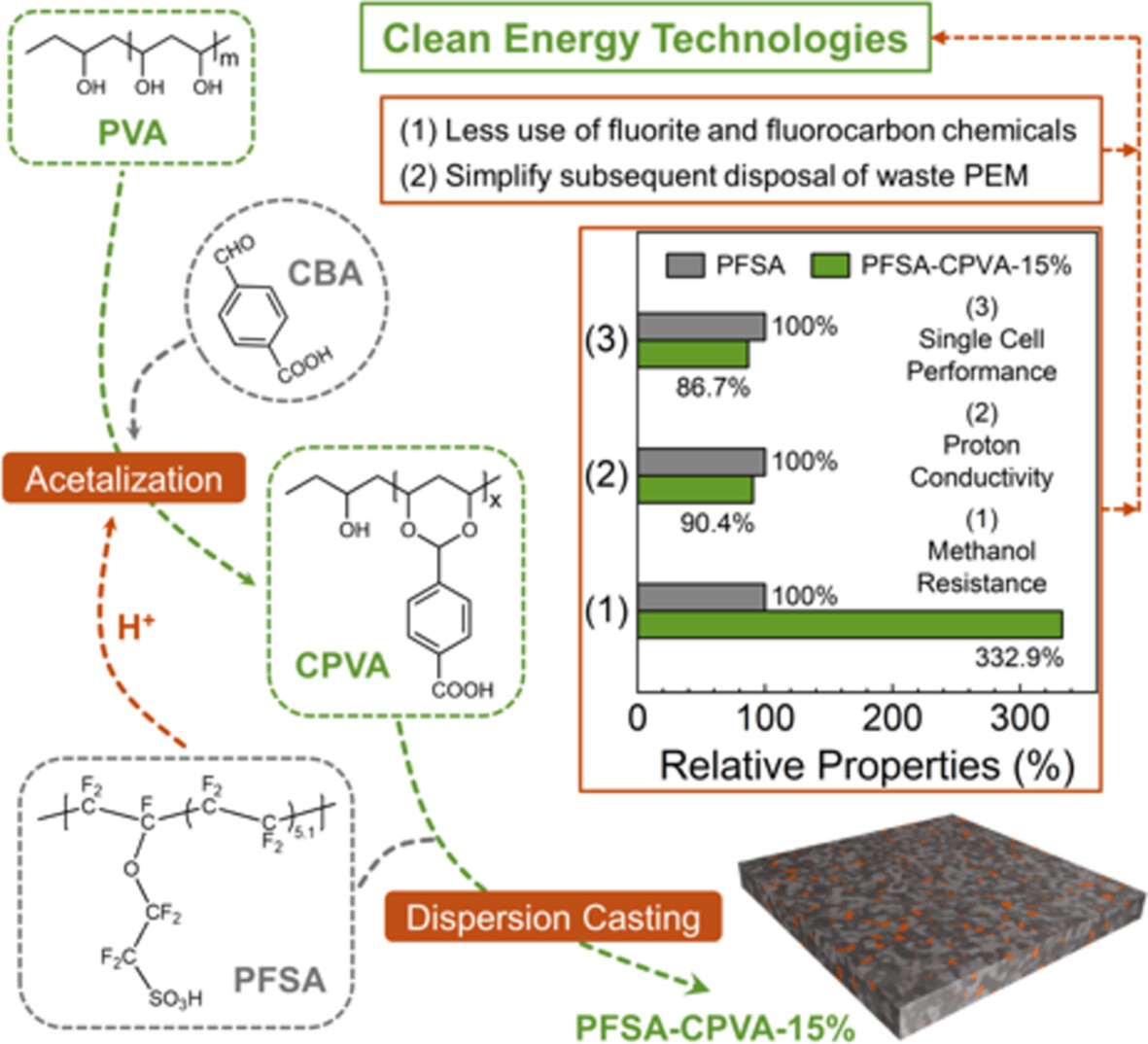
Nanophase Structure and Performances of Proton-Exchange Membranes Based on Perfluorinated Sulfonic Acid Ionomer and Carboxylated Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)
- First Published: 30 December 2024
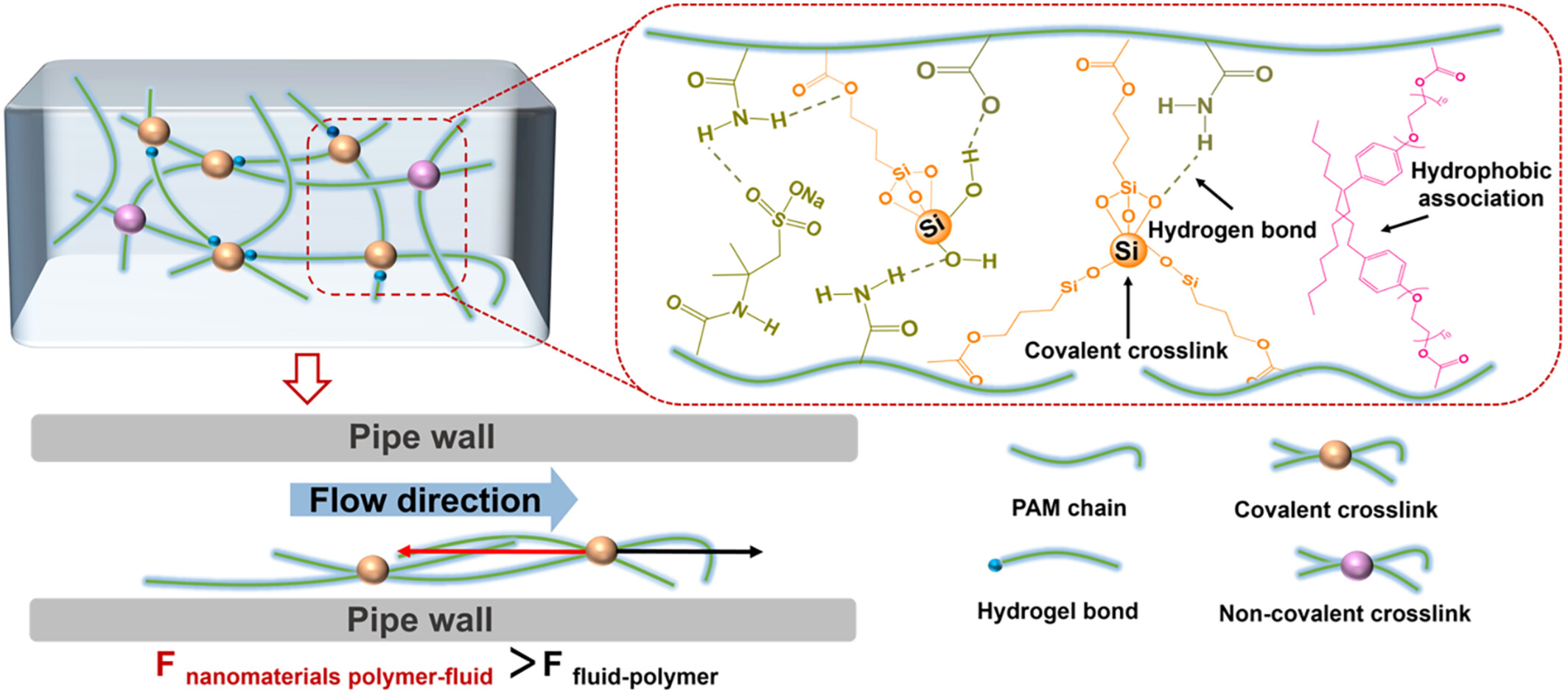
Preparation and Performance of Shear-Resistant and Fast-Dissolving Drag Reduction With Multiple Cross-Linking Effects
- First Published: 02 January 2025
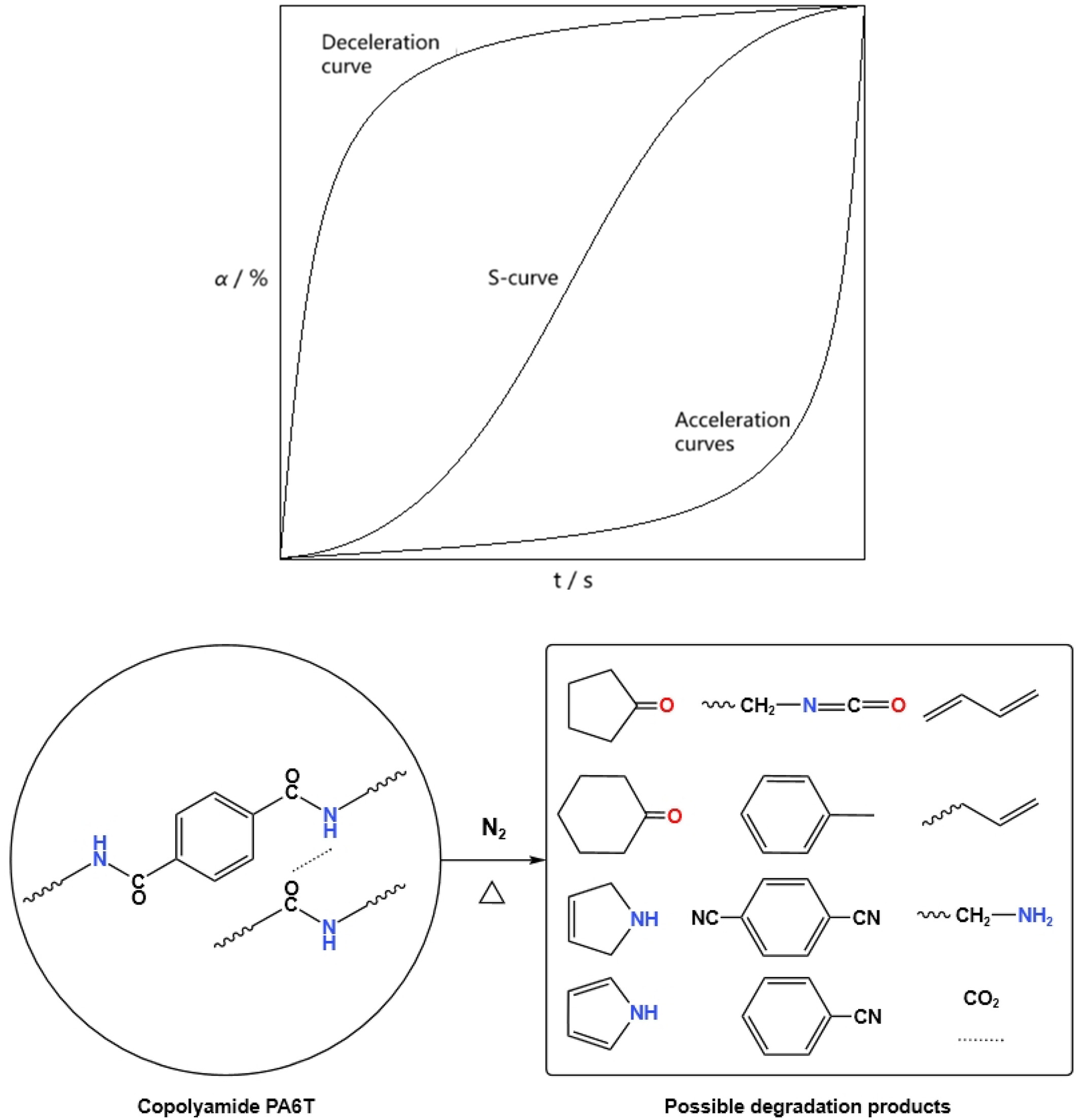
Synthesis and Thermal Degradation Kinetics of PA6T/66 and PA6T/610 Copolyamides
- First Published: 02 January 2025
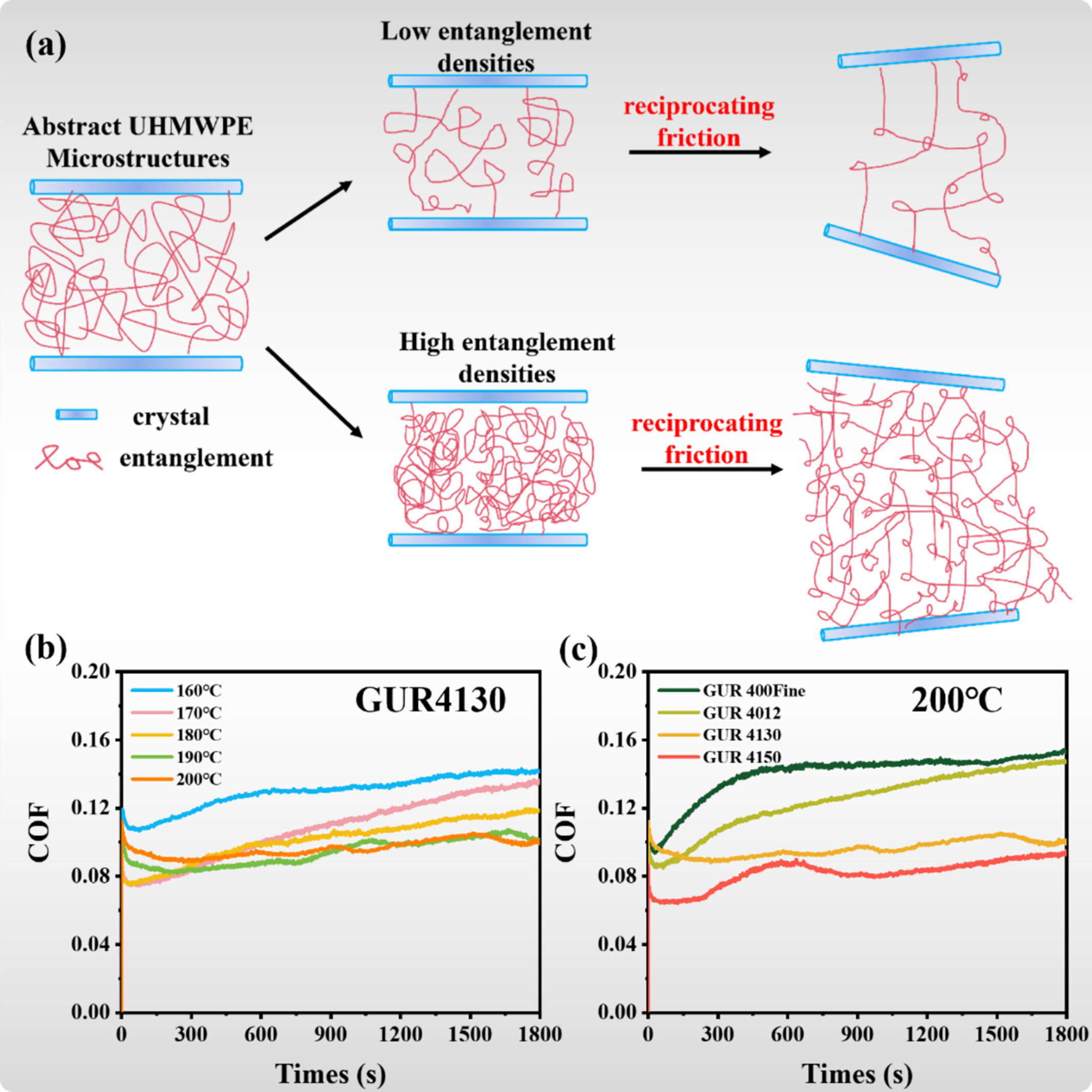
Revealing the Relationship Between the Entanglement Densities and Tribological Performance of UHMWPE
- First Published: 27 December 2024
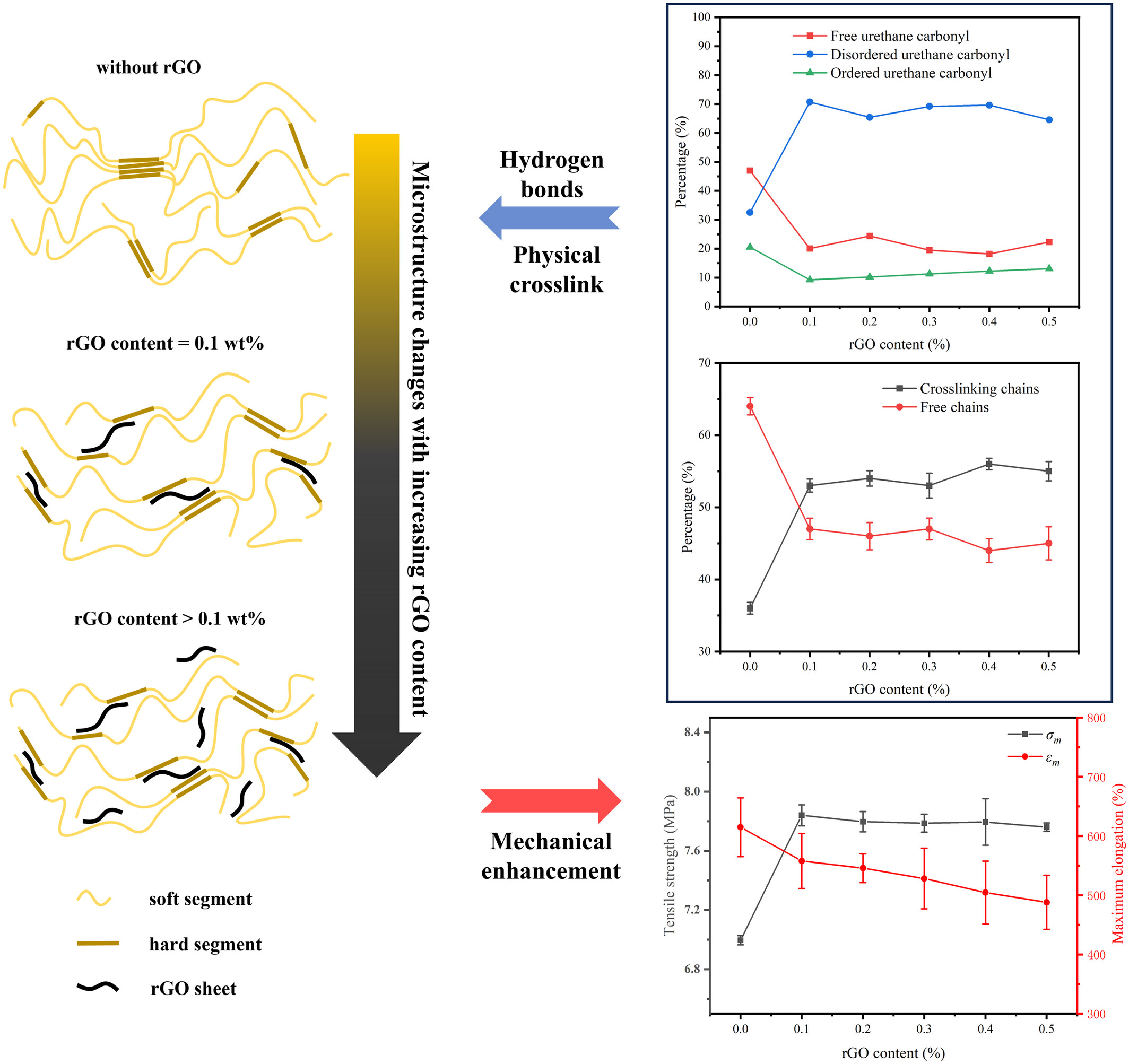
Effect of Graphene on the Mechanical Properties of Glycidyl Azide Polymer-Based Energetic Thermoplastic Elastomer
- First Published: 21 January 2025
Water-Soluble Supramolecular Polymer With Silver Ion Responsiveness
- First Published: 27 December 2024
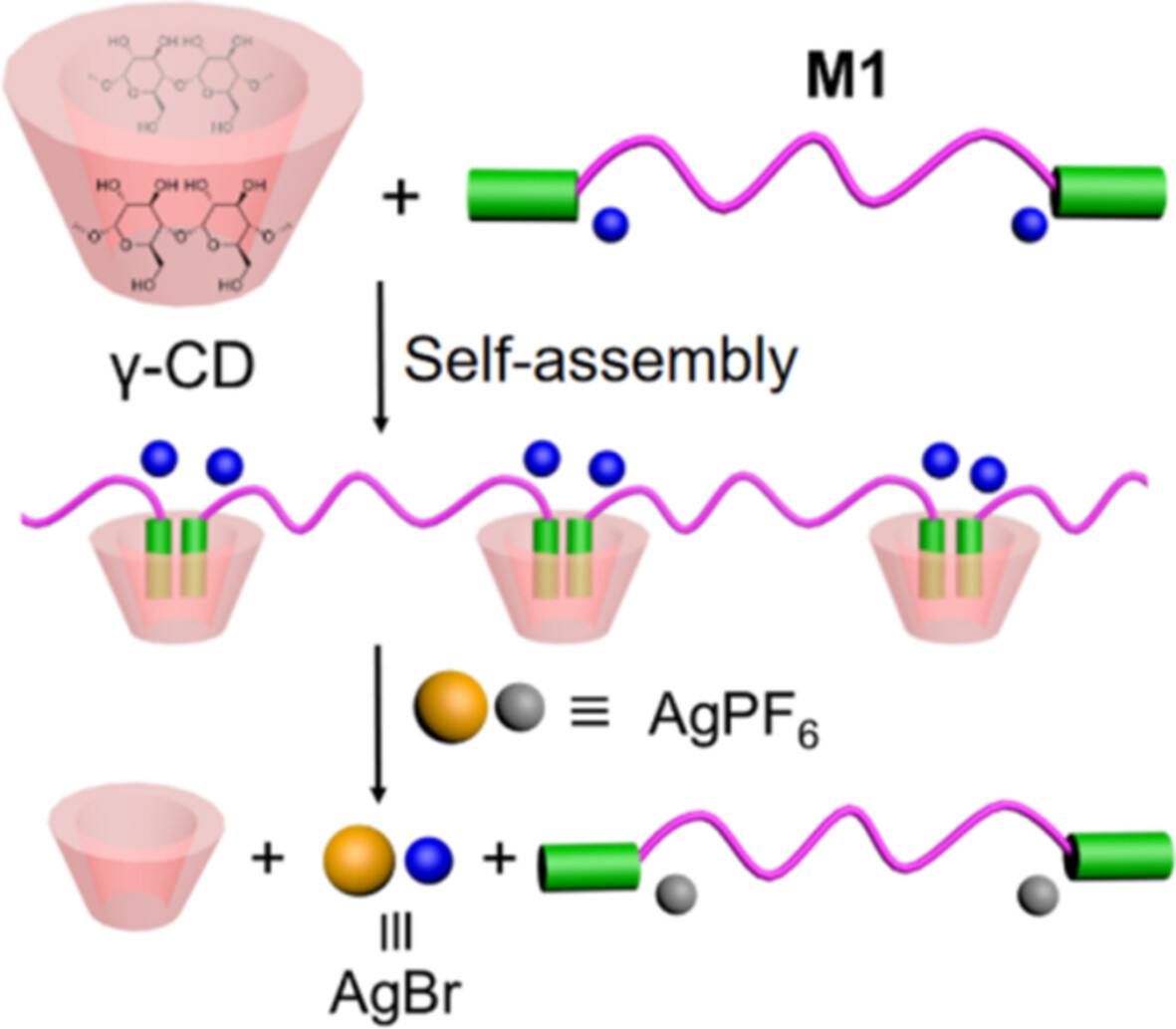
A Ag+-responsive, water-soluble supramolecular polymers was prepared through host–guest interaction between γ-CD and the bis(phenyl ethenyl)pyridine guest monomer M1. When AgPF6 was added into the solution of the supramolecular polymer, AgBr and bis(phenyl ethenyl)pyridine monomer-PF6 precipitated out of the solution, leaving only the host molecule γ-CD in the solution, resulting in the depolymerization of the polymer.
A Comparison Study of the Synergistic Influence of Discrepancy in Exothermic Behavior of Polyacrylonitrile-Based Precursor Fibers and the Continuous Gradient Pre-Oxidation Condition on Stabilization Structure
- First Published: 22 January 2025
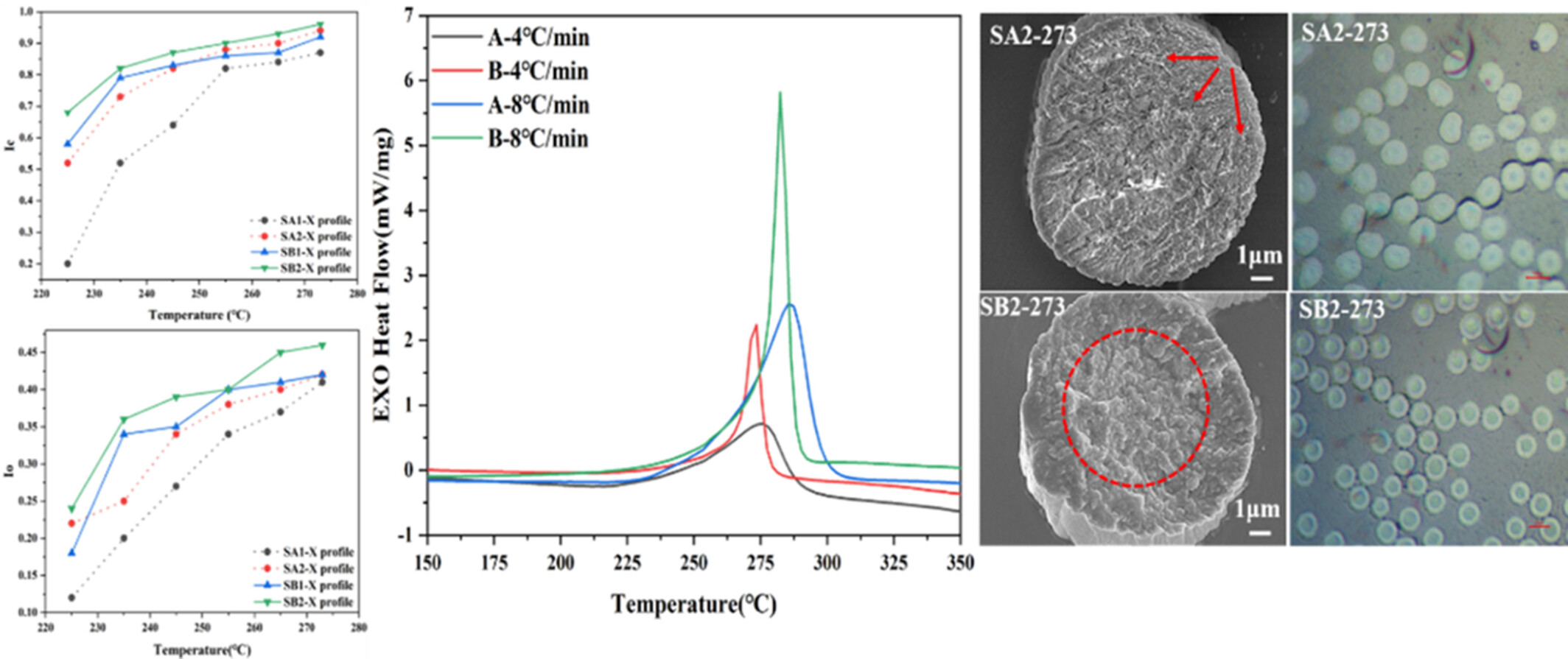
The effects of exothermic characteristics of polyacrylonitrile-based precursor fibers and pre-oxidation conditions on thermal stabilization were studied. Significant differences in stabilization behavior show that the cyclization index (Ic), oxidation index (Io), dehydrogenation index (Id), and aromatization index (AI) of precursor fiber B are far greater than A. Different radial heterogeneous structure was observed, which mainly contributed to the stabilization degree and reaction rates. To promote oxygen diffusion, the Ic, Io, and AI values at the initial stage should be controlled below 0.8%, 0.36%, and 32%, respectively. Combined with actual industrialization, in order to avoid skin-core structure and violent reaction, selecting appropriate temperature procedure is necessary according to exothermic characteristics and stabilization behavior of specific fibers.
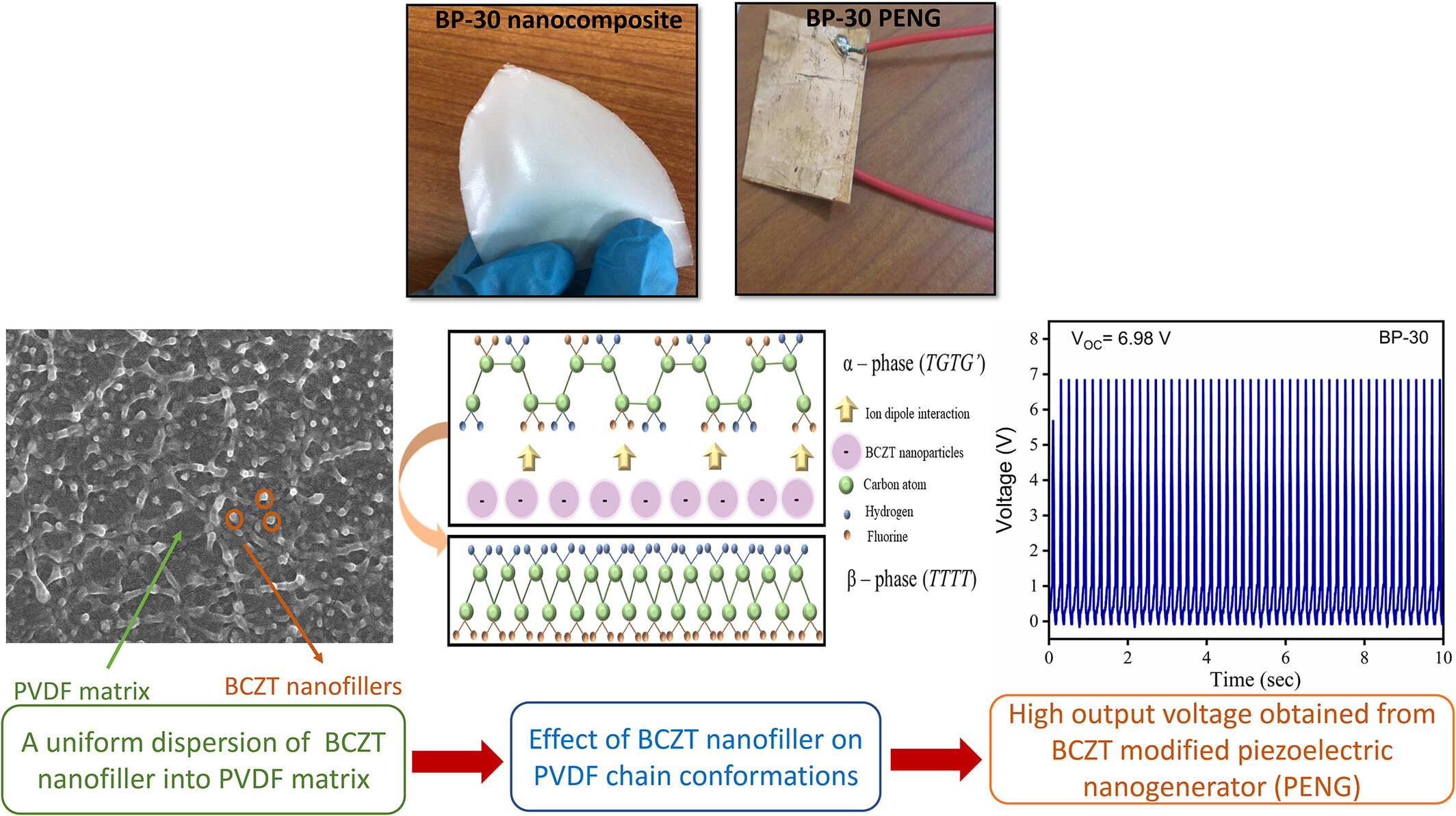
Flexible PVDF Piezoelectric Nanogenerator Embedded With B0.85Ca0.15Zr0.1Ti0.9O3 for Wearable Electronics
- First Published: 28 December 2024
Synthesis and Conformational Relationship of New Fluorinated Acrylate Polymer-Based Internal Mold Release Agents
- First Published: 12 January 2025
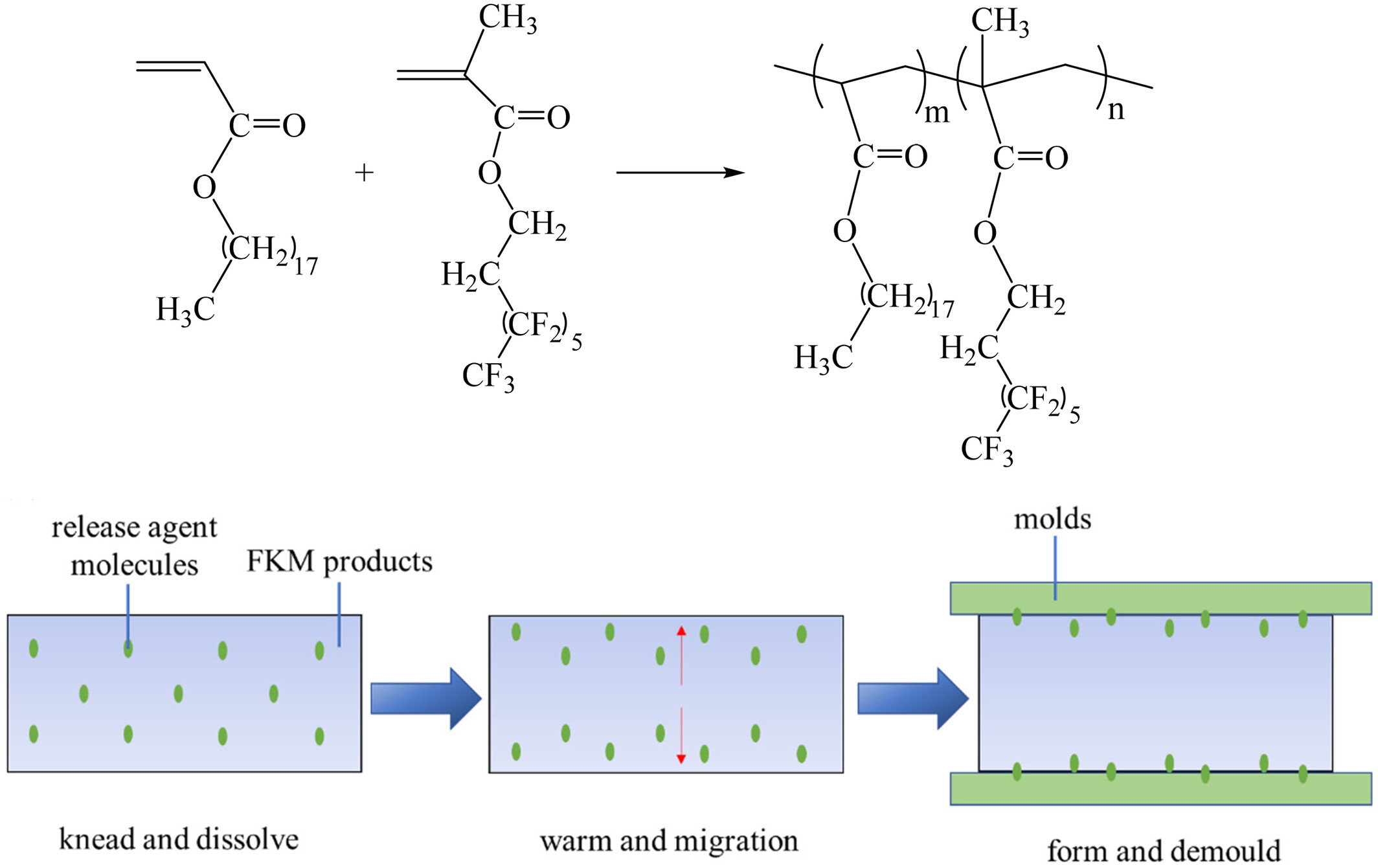
In this study, a series of fluorinated acrylate polymers (FAP) were synthesized by solution polymerization using perfluorohexylethyl methacrylate with a short fluorocarbon chain (PFOL, R f = 6) and octadecyl acrylate with a long hydrocarbon chain (SA, R = 18). The synthesized FAP not only have excellent properties, but also avoid bioaggregation toxicity, making them ideal mold release materials. We present the synthetic reaction mechanism of the process and provide insights into the evolution of mold release agents for use in fluoroelastomers.
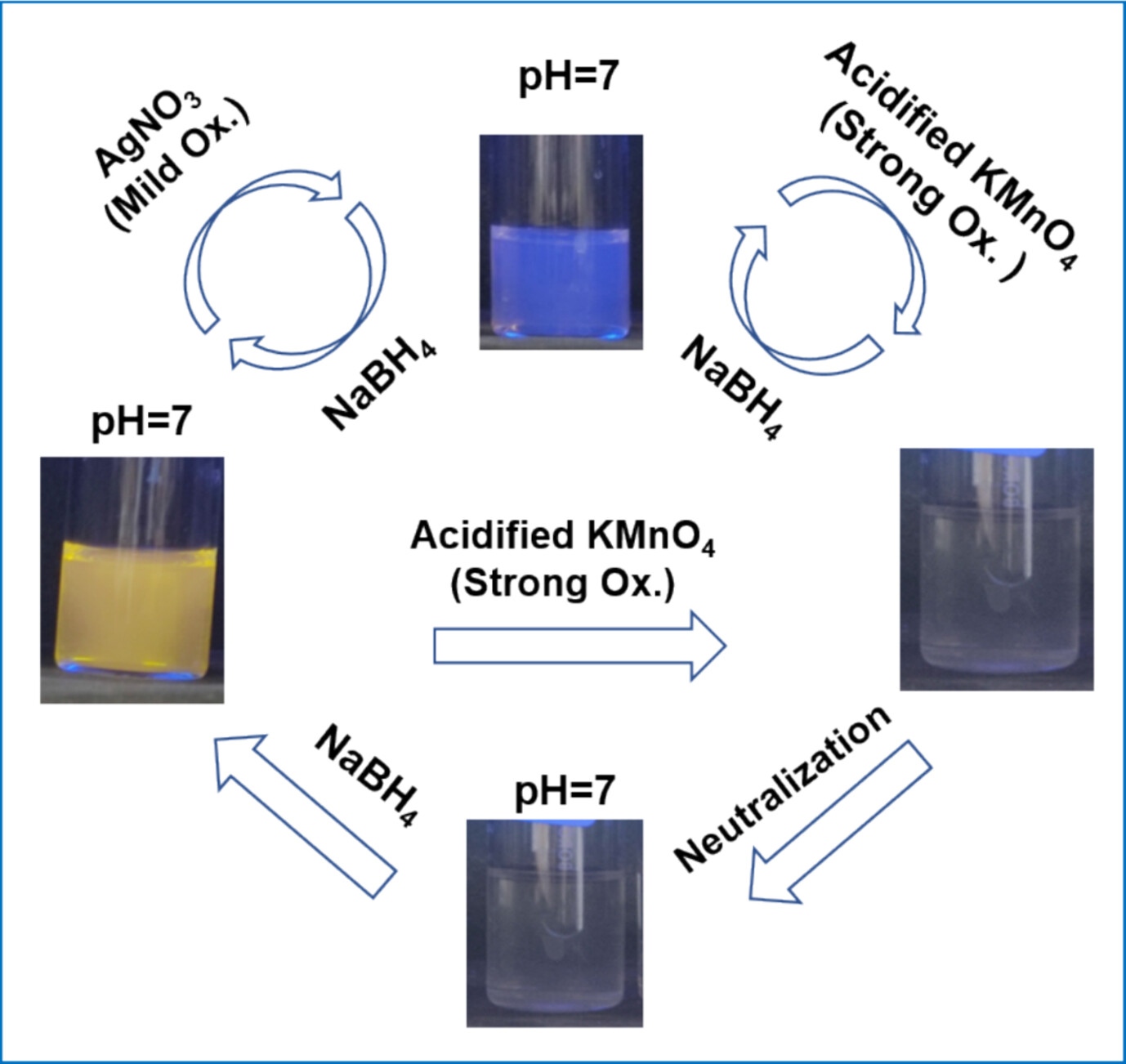
Dual-Mode Fluorescence Sensing of Multiple Oxidizing Analytes by Selective Oxidation of Poly(N-Phenyl Anthranilic Acid-Co-o-Phenylenediamine) Random Copolymers
- First Published: 06 January 2025
Chitosan/Graphene Oxide/Ag Nanocomposites Loaded in Polyvinyl Alcohol Films as Biodegradable, UV-Blocking, and Antibacterial Film for Fruit Packaging
- First Published: 06 January 2025
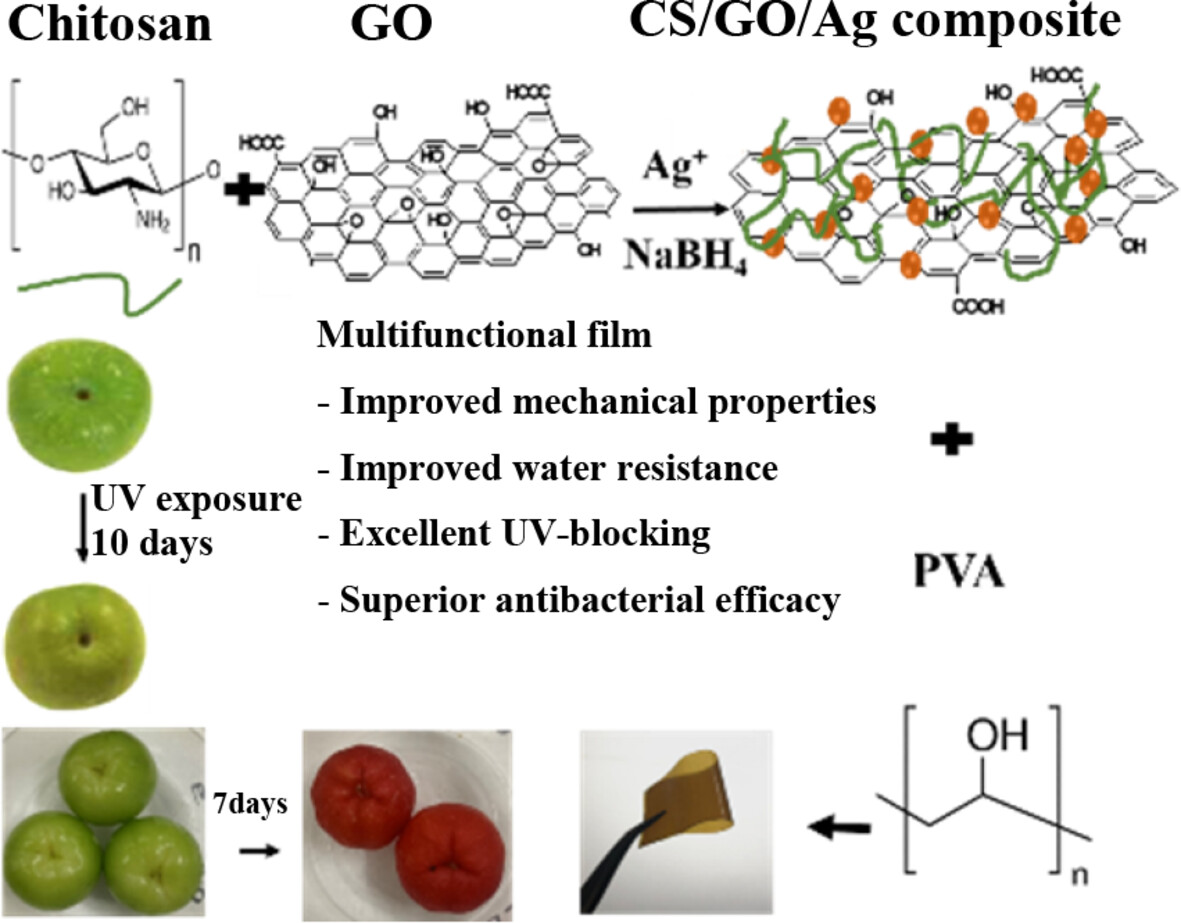
The work describes a facile method to fabricate multifunctional active food packaging films by incorporating chitosan/graphene oxide/Ag composites into polyvinyl alcohol membranes for preserving green plums and acerola fruits. The PVA/CS/GO/Ag film demonstrates significantly improved mechanical properties, water resistance, UV-blocking effect, and antibacterial efficiency compared to the pristine PVA film. The presented film also effectively prolongs the freshness and shelf life of packed fruits.