Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
COMMENTARY
In Focus: Disease promoters during epileptogenesis
- Pages: 1333-1334
- First Published: 21 August 2019
REVIEWS
Converging early responses to brain injury pave the road to epileptogenesis
- Pages: 1335-1344
- First Published: 29 November 2017
Astrocytes and Glutamine Synthetase in Epileptogenesis
- Pages: 1345-1362
- First Published: 18 July 2018
Glial source of nitric oxide in epileptogenesis: A target for disease modification in epilepsy
- Pages: 1363-1377
- First Published: 12 December 2017
RESEARCH ARTICLES
The impact of postsynaptic density 95 blocking peptide (Tat-NR2B9c) and an iNOS inhibitor (1400W) on proteomic profile of the hippocampus in C57BL/6J mouse model of kainate-induced epileptogenesis
- Pages: 1378-1392
- First Published: 15 May 2019
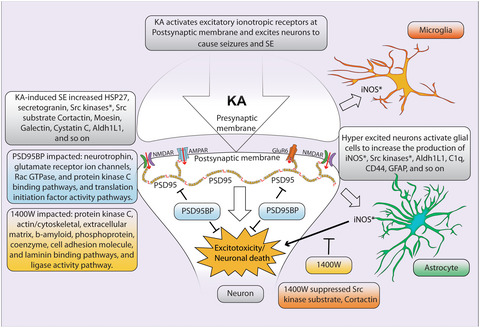
Kainate (KA)-induced status epilepticus hyperexcites neurons and activates ionotropic glutamate receptors, including NMDAR, AMPAR, and GluR6. These receptors physically interact with postsynaptic density protein 95 (PSD95) which acts as a scaffolding protein at the postsynaptic membrane. PSD95 activation and its interaction with NMDARs are mediated by Src kinases* which drive hyperexcitability and neurodegeneration. Hyperexcited neurons activate both microglia and astrocytes to induce the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS)* and Src kinase*. The products of these enzymes, and many other proteins, exacerbate hyperexcitability, and activate neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration pathways. Thus, the hypothesis is that PSD95 blocking peptide (PSD95BP; Tat-NR2B9c) and the iNOS inhibitor 1400W will impact KA-induced changes. *Note: The starred proteins were not detected in the present study.
Loss of tau and Fyn reduces compensatory effects of MAP2 for tau and reveals a Fyn-independent effect of tau on calcium
- Pages: 1393-1413
- First Published: 26 August 2019
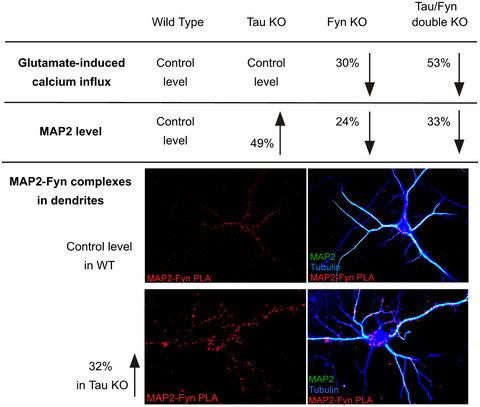
The downstream effect of the interaction between microtubule-associated protein tau and Src family non-receptor tyrosine kinase Fyn was investigated with a tau/Fyn double KO mouse. We demonstrate that tau has a Fyn-independent role in glutamate-induced calcium response and that MAP2 can compensate for tau in interacting with Fyn in dendrites.
BDNF-overexpressing human mesenchymal stem cells mediate increased neuronal protection in vitro
- Pages: 1414-1429
- First Published: 30 June 2019
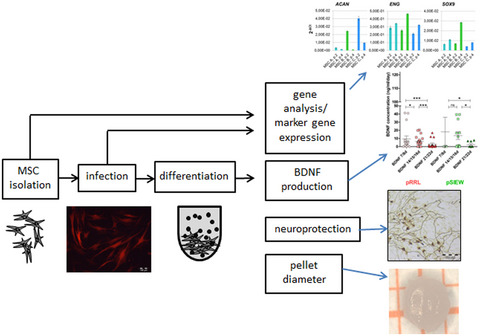
Cell-based drug delivery is a promising approach for future neuroprotective therapies. We infected human mesenchymal stem cells to overexpress BDNF and differentiated them to chondrocytes to hypothetically improve their vitality and survival in a delivery matrix. The BDNF-overexpressing hMSCs protect neurons significantly better from degeneration than native MSCs. This finding has a high potential for future clinical application of hMSCs in human neuronal disorders therapy.
Task load modulates tDCS effects on language performance
- Pages: 1430-1454
- First Published: 28 June 2019
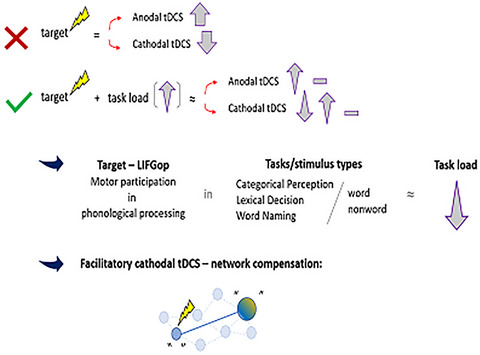
The motor role in phonological processing is weighted by the nature of the language tasks, and the consequent task load relative to the target (LIFGop) modulates tDCS effects. Improved performance following cathodal tDCS, for example, in categorical perception, suggests that compensatory mechanisms occur when tasks involve complex neuronal networks.
REVIEW
Towards a comprehensive understanding of the contributions of mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in the pathogenesis and pathophysiology of Huntington's disease
- Pages: 1455-1468
- First Published: 15 July 2019
RESEARCH ARTICLE
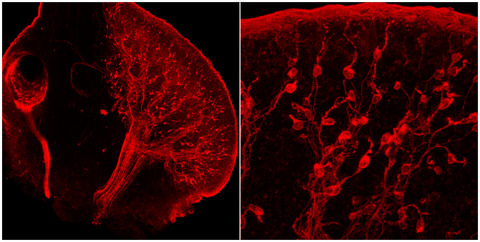
Localization of keyhole limpet hemocyanin-like immunoreactivity in the nervous system of Biomphalaria alexandrina
- Pages: 1469-1482
- First Published: 04 August 2019