Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
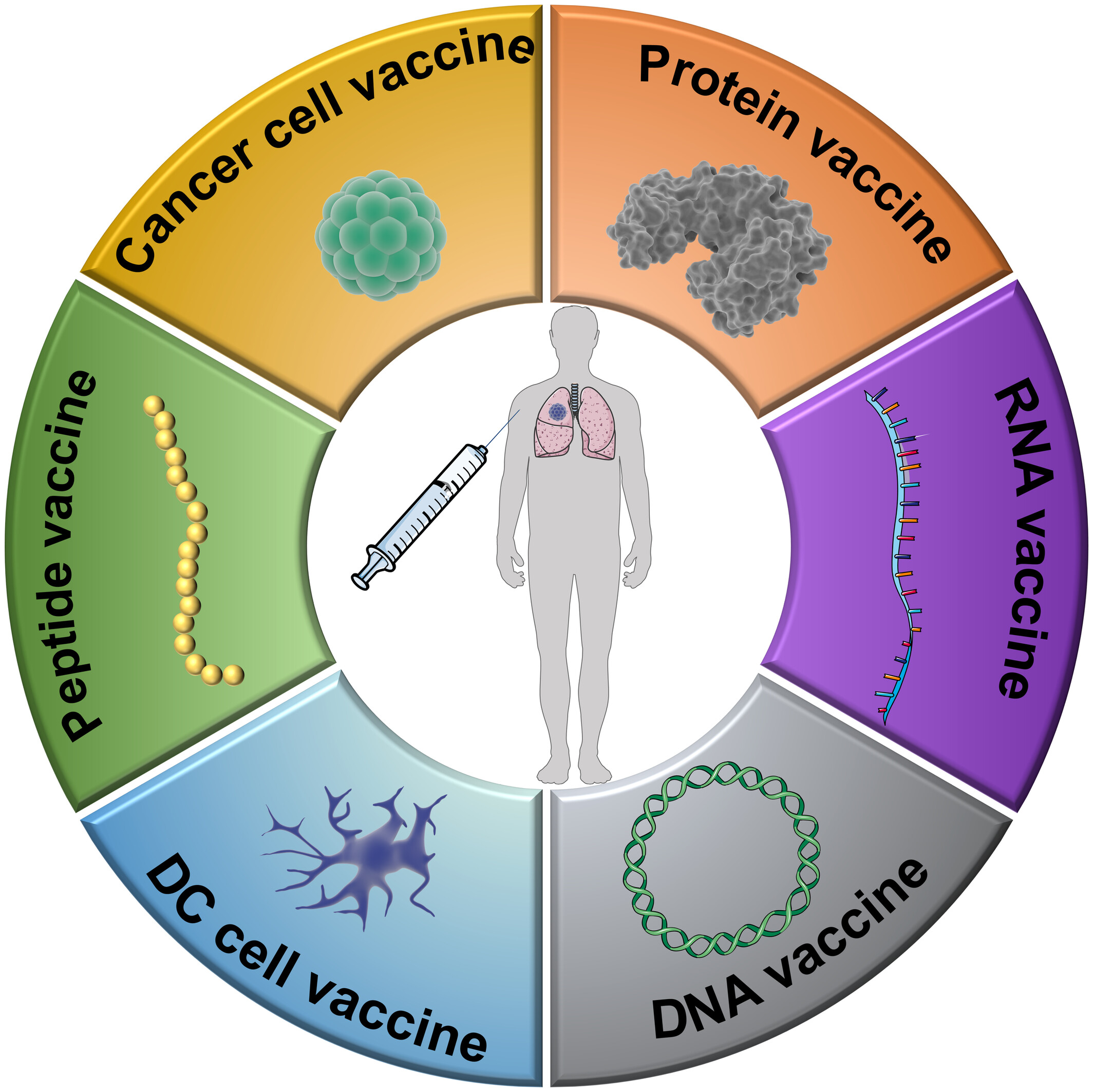
The current therapeutic cancer vaccines landscape in non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 1909-1927
- First Published: 07 August 2024
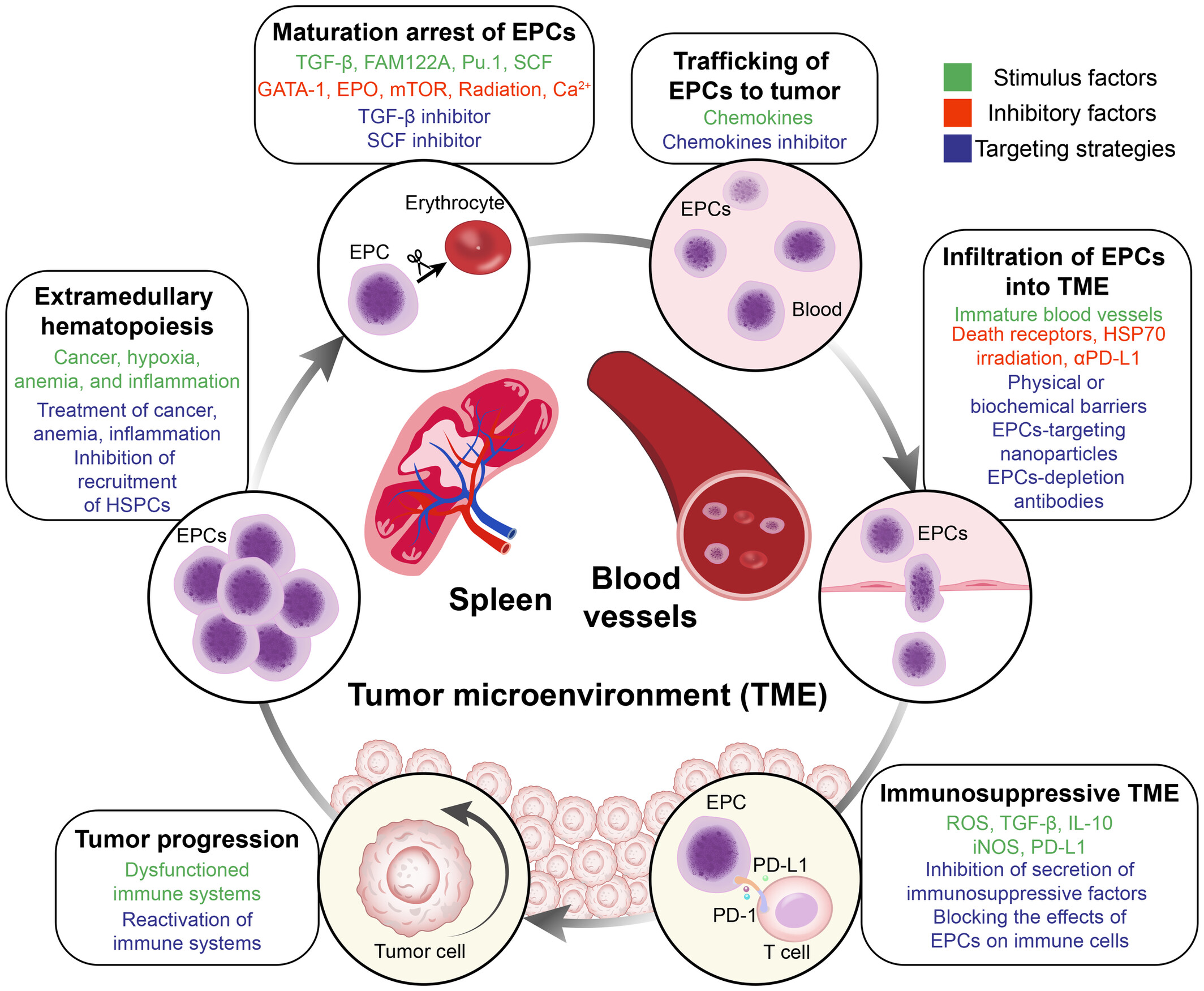
Targeting erythroid progenitor cells for cancer immunotherapy
- Pages: 1928-1938
- First Published: 22 July 2024
SHORT REPORT
Cancer Therapy and Prevention
Improving the clinical meaning of surrogate endpoints: An empirical assessment of clinical progression in phase III oncology trials
- Pages: 1939-1943
- First Published: 13 August 2024

What's new?
For patients in oncology clinical trials, disease progression generally is assessed by radiologic criteria. However, changes in clinical status are highly relevant to patient quality of life, and often warrant a shift in the therapeutic approach. Here, the authors evaluated more than 200 phase III trials to better understand the scope of clinical progression assessment. Despite the importance of tumor-related symptoms to patients, only 13 percent of trials included clinical progression criteria. The findings indicate that clinical progression is underevaluated and understudied in phase III trials, highlighting a need for greater inclusion of patient-centric endpoints in clinical trials.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Cancer Epidemiology
One-carbon metabolism biomarkers and upper gastrointestinal cancer in the Golestan Cohort Study
- Pages: 1944-1957
- First Published: 07 August 2024
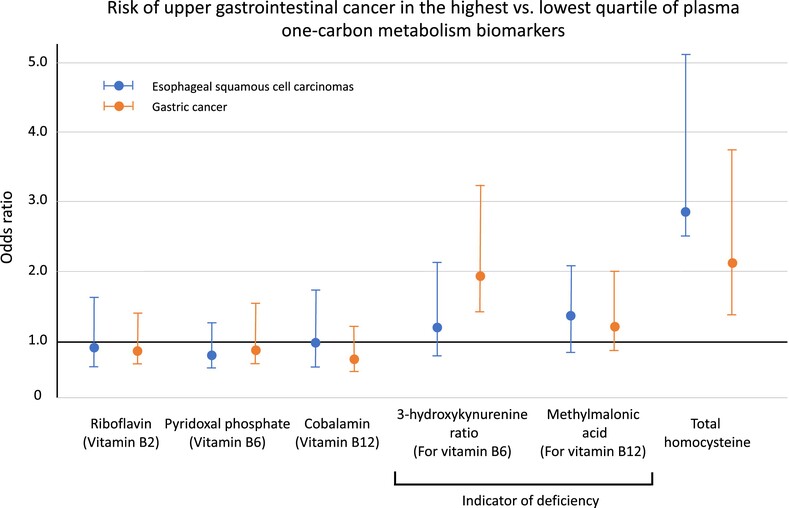
What's new?
One-carbon metabolism (OCM) refers to a series of biochemical reactions essential for DNA methylation, synthesis, and repair. These reactions are often catalyzed by enzymes and cofactors derived from B vitamins, and B vitamin deficiency has been linked to cancer. Here, the authors investigated the relationship between B vitamin deficiency and risk of esophageal and gastric cancers in Iran, where the incidence of these cancers is high. Elevated levels of plasma biomarkers that indicate vitamin B6 and B12 deficiency were associated with higher risk of esophageal and gastric cancers, they found. Improving vitamin intake could reduce the incidence of these cancers in the populations with high prevalence of vitamin B deficiency.
Representation of women in clinical trials supporting FDA-approval of contemporary cancer therapies
- Pages: 1958-1968
- First Published: 19 August 2024
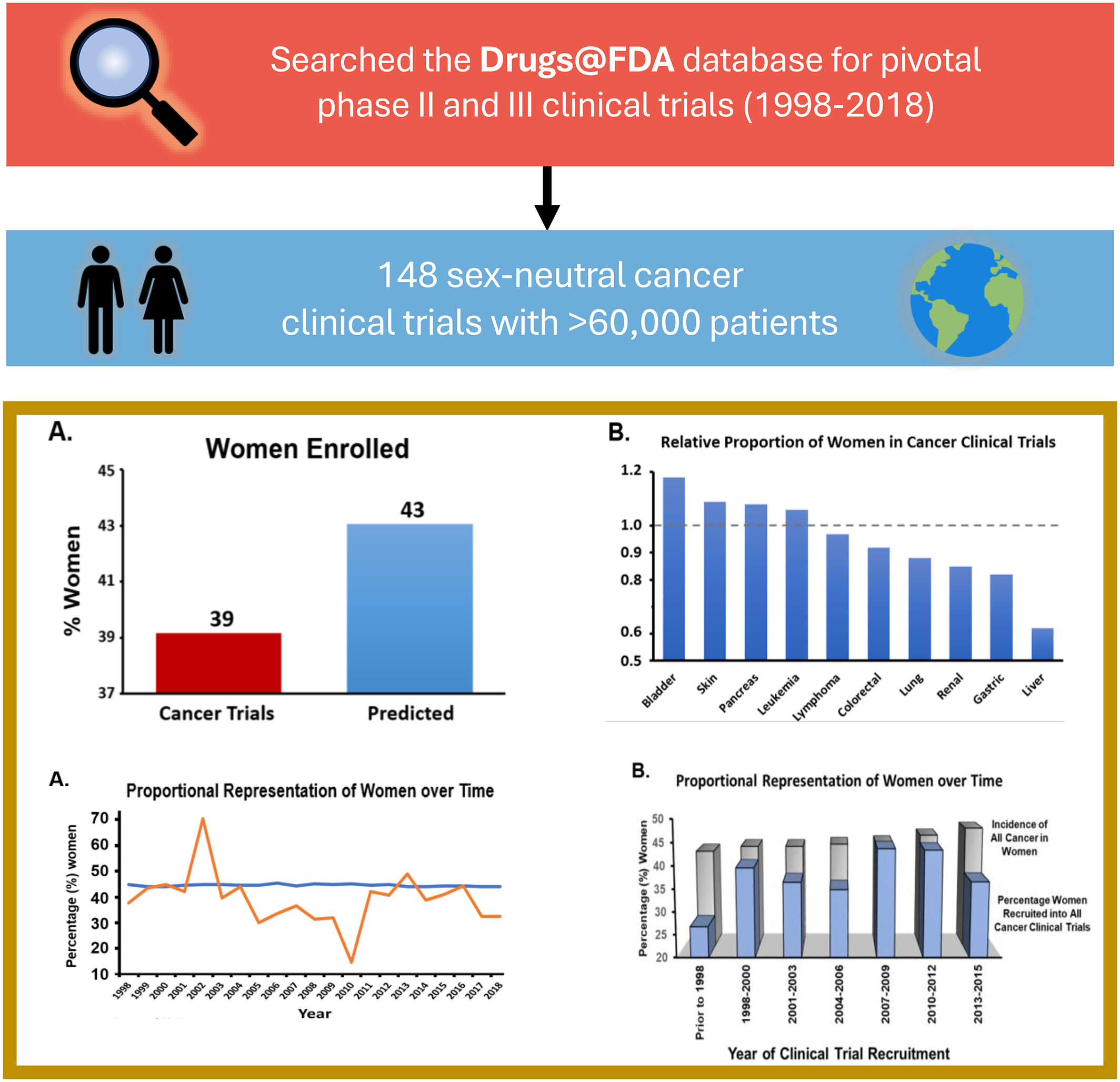
What's new?
Contemporary anticancer therapies frequently have different efficacy and side effects in men and women. Yet, whether women are well represented in pivotal trials is unknown. Here, the authors offer a comprehensive assessment of the representation of women and the reporting of sex-based analyses among pivotal clinical trials supporting FDA-approved anticancer therapies. The results show that among the more than 60,000 phase II and III clinical trial participants for the testing of nearly 100 anticancer therapies approved between 1998 and 2018, women were frequently under-represented, with sex-specific efficacy and safety outcomes commonly unreported.
Clinical and molecular features of early onset pancreatic adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 1969-1981
- First Published: 15 August 2024
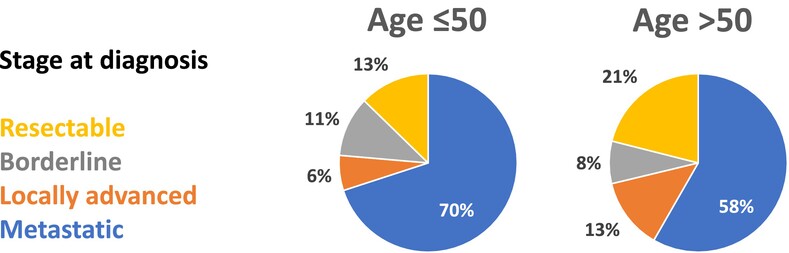
What's new?
Early-onset pancreatic cancer has a rising incidence, but its clinical and molecular features remain poorly understood. In this retrospective study, early-onset pancreatic cancer was diagnosed at a more advanced stage and liver metastases were more prevalent at diagnosis. Early-onset patients did not have a longer overall survival than their older counterparts, contrary to previous reports. Early-onset pancreatic cancer displayed specific molecular features, including a lower mutational burden, fewer mutations in CDKN2A/B, and a lower prevalence of the basal-like subtype.
Pre-diagnostic plasma advanced glycation end-products and soluble receptor for advanced glycation end-products and mortality in colorectal cancer patients
- Pages: 1982-1995
- First Published: 26 July 2024
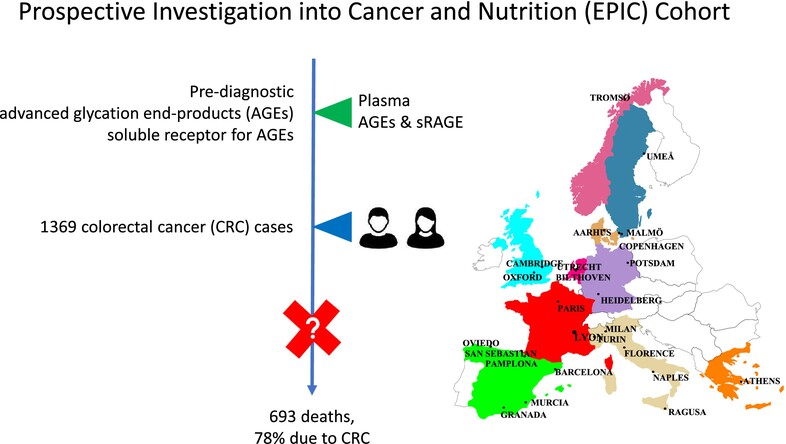
What's new?
Advanced glycation end-products (AGEs), sometimes called glycotoxins, can trigger inflammation and may play a role in colorectal cancer (CRC) progression. Here, the authors investigated the association between pre-diagnostic circulating AGEs and colorectal cancer outcomes. Over a period of 96 months, they did not find an association between AGEs and either CRC-specific mortality or overall mortality. However, patients with higher levels of soluble receptor for AGEs (sRAGE) had higher CRC-specific and overall mortality rates. As the first prospective study to examine the association between AGEs and CRC survival, this work provides a foundation for additional research on this potential link.
Human papillomavirus prevalence, genotype distribution, and prognostic factors of vaginal cancer
- Pages: 1996-2008
- First Published: 24 July 2024

What's new?
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is a leading risk factor for squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) vaginal cancer (VC). Associations between HPV and prognosis of the SCC subtype of VC, however, remain unclear. In this study, HPV prevalence and genotype distribution were investigated in the context of VC prognosis. HPV DNA sequences were detected in 98.6% of SCC and 83.3% of non-SCC cases. HPV types 16, 52, and 58 were the most commonly detected sequences. Advanced stage disease and lymph node metastasis were associated with poor prognosis, while prognosis was better among those with p16- or HPV-positivity.
A historical cohort study with 27,754 individuals on the association between meat consumption and gastrointestinal tract and colorectal cancer incidence
- Pages: 2009-2020
- First Published: 19 July 2024
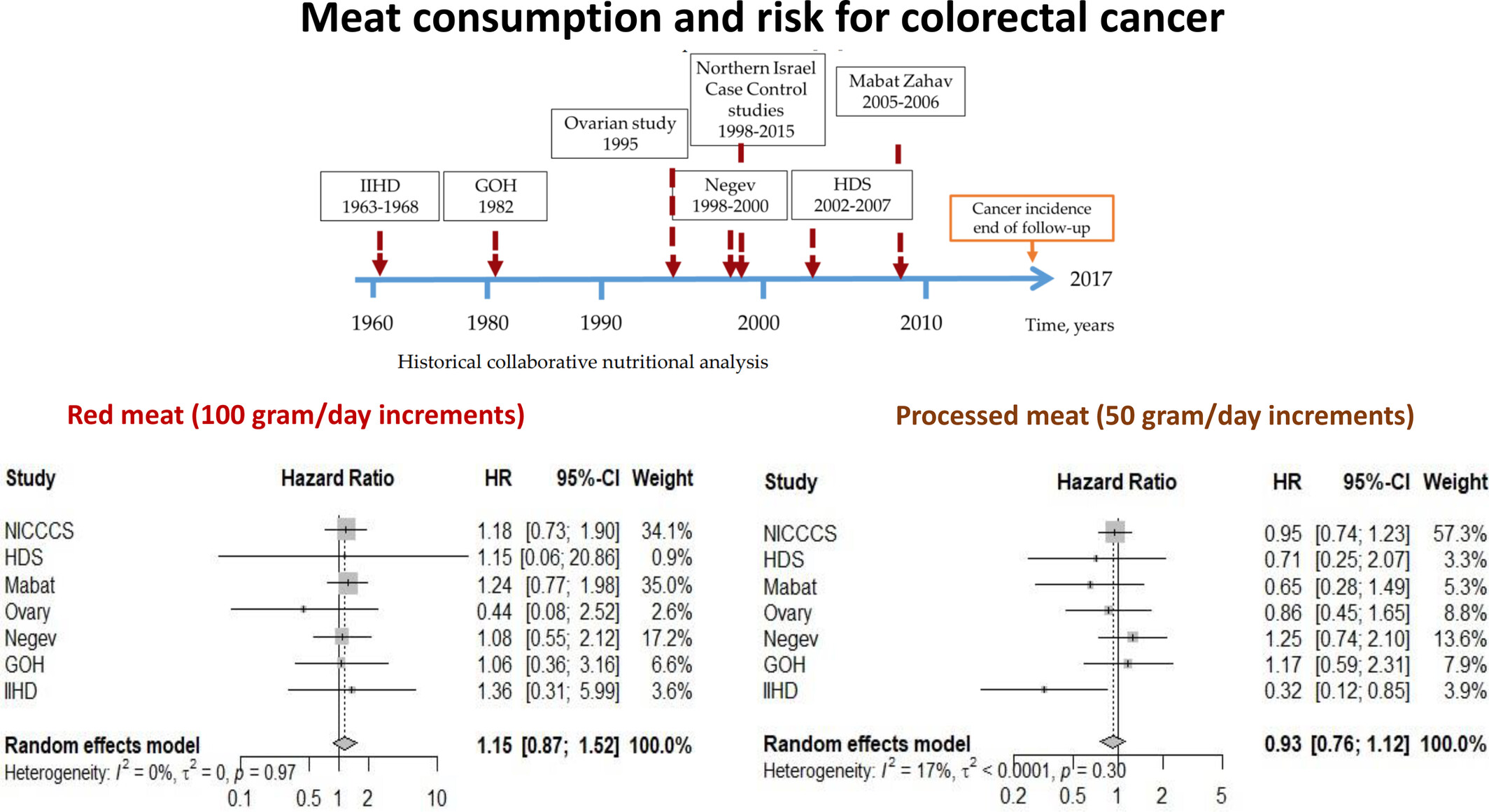
What's new?
Red and processed meat consumption in Israel has more than doubled since 1990. Adaptation to religious diet laws and factors such as high poultry consumption in Israel potentially influence relationships between diet and cancer. Here, the influence of meat consumption on gastrointestinal cancer and colorectal cancer (CRC) risk was investigated using data from historical nutritional studies conducted in Israel. Analyses found that red meat intake is associated with increased gastrointestinal cancer but not CRC risk. Risk of both cancers is specifically associated with beef consumption. Gastrointestinal cancer incidence in Israel's population can be decreased via reductions in red meat intake.
Cancer Genetics and Epigenetics
Evolution of genome and immunogenome in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas driven by neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy
- Pages: 2021-2035
- First Published: 31 July 2024
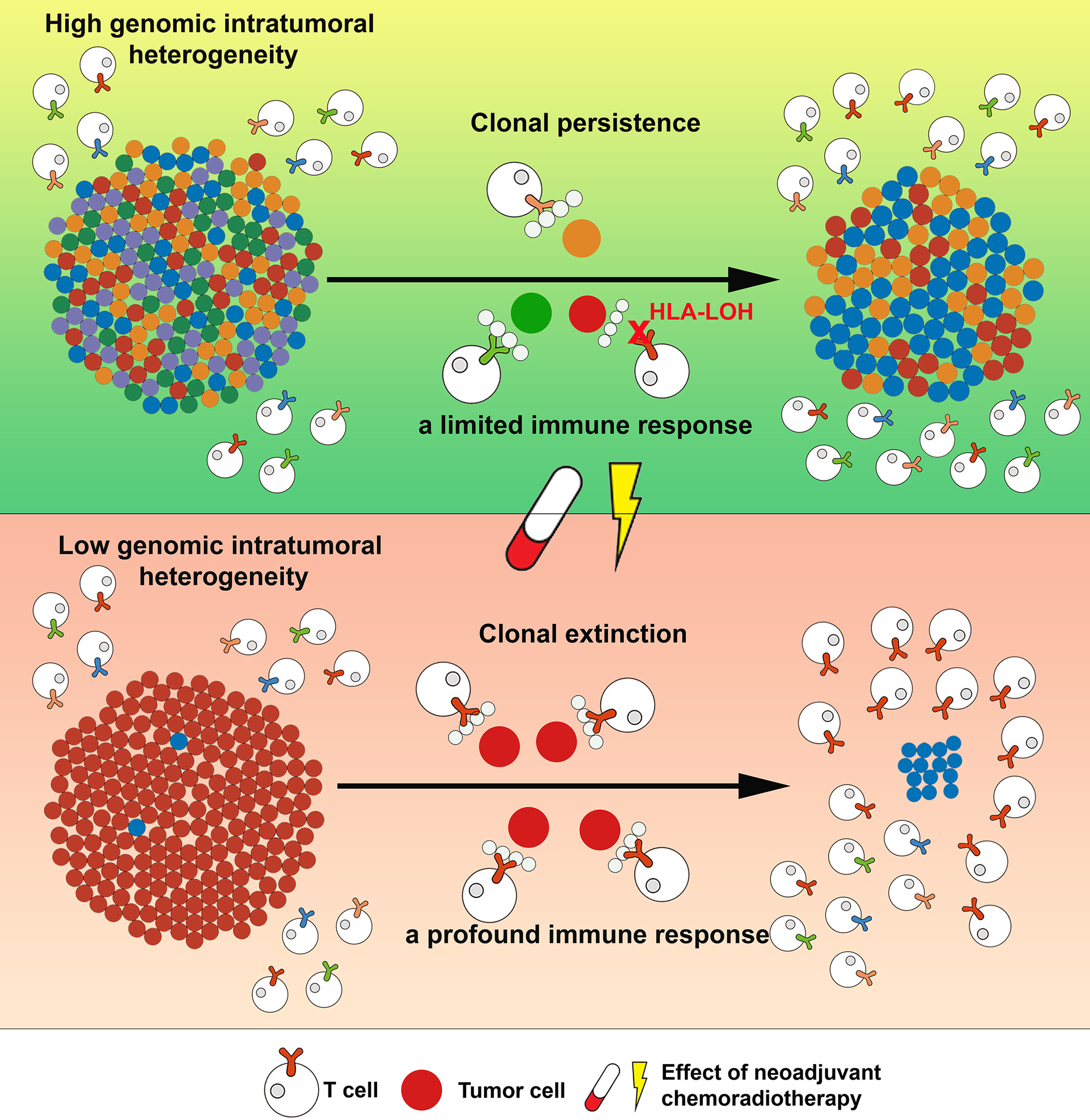
What's new?
Genetic changes and clonal evolution can influence the likelihood of cancer returning after treatment, and neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (NCRT) may impact those genetic changes. Here, the authors investigated how tumor heterogeneity affected treatment responses in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). They performed whole-exome and transcriptome sequencing on the tumor and the immune microenvironment before and after NCRT, and clonal analysis to see whether clones persisted after treatment. They identified two clonal dynamics that affected prognosis after NCRT. This study is the first to systematically describe clonal dynamics during NCRT in this way, and these findings could help identify determinants of treatment responses.
Cancer Therapy and Prevention
Clinical features and response to immune combinations in patients with renal cell carcinoma and sarcomatoid de-differentiation (ARON-1 study)
- Pages: 2036-2046
- First Published: 07 September 2024
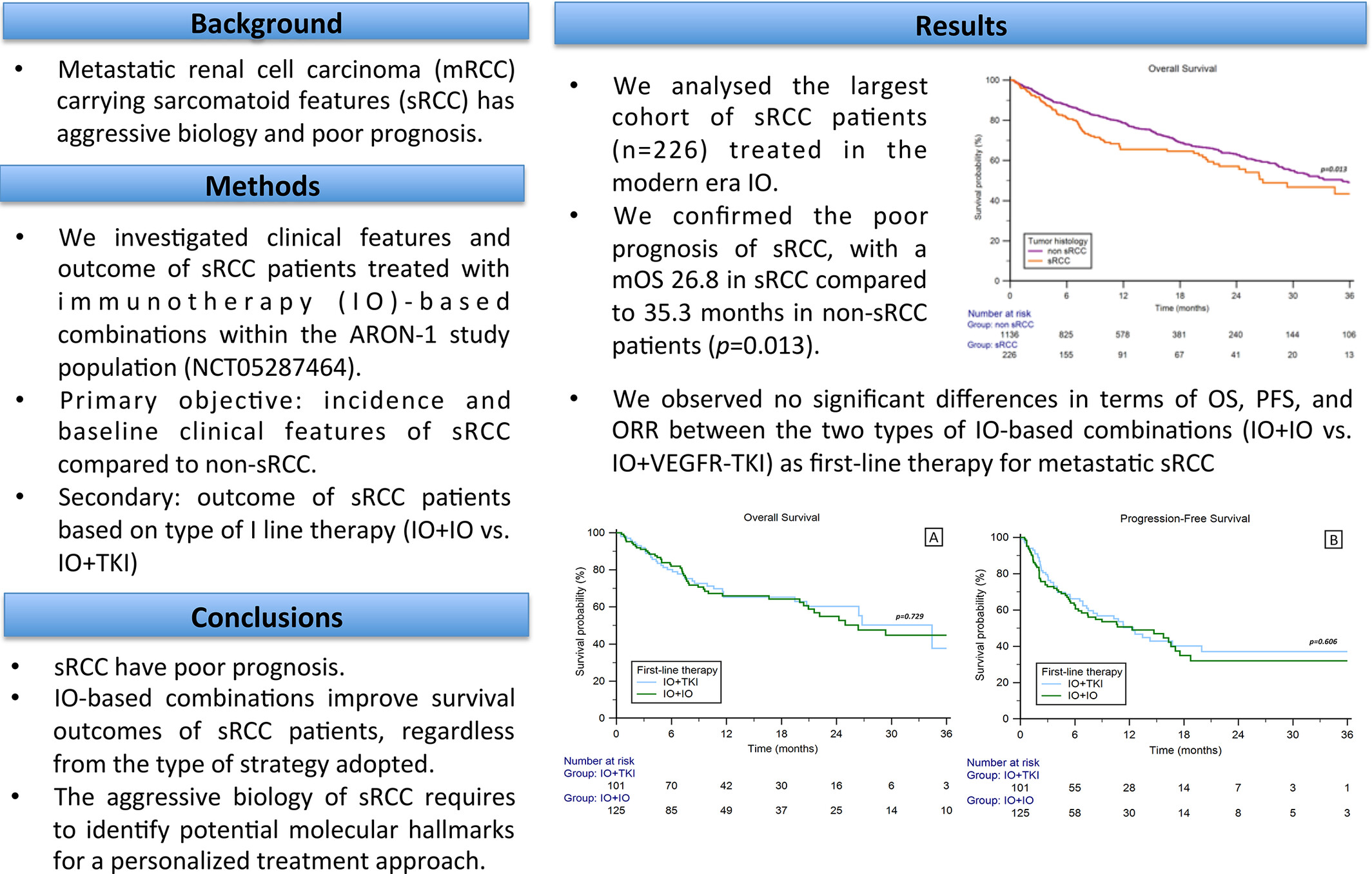
What's new?
Patients who have metastatic renal cell carcinoma with sarcomatoid features (sRCC) have a very poor prognosis. Here, the authors describe the clinical characteristics and analyze outcomes of sRCC in patients in the ARON-1 study, the largest cohort of sRCC patients treated with first-line immunotherapy. Patients received immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in combination with either anti-CTLA antibodies or VEGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor. They found no significant difference in progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), and objective response rate (ORR) between patients treated with the different immunotherapy combinations.
Prospective evaluation of quantitative response parameter in patients with Gastrointestinal Stroma Tumor undergoing tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy—Impact on clinical outcome
- Pages: 2047-2057
- First Published: 18 July 2024
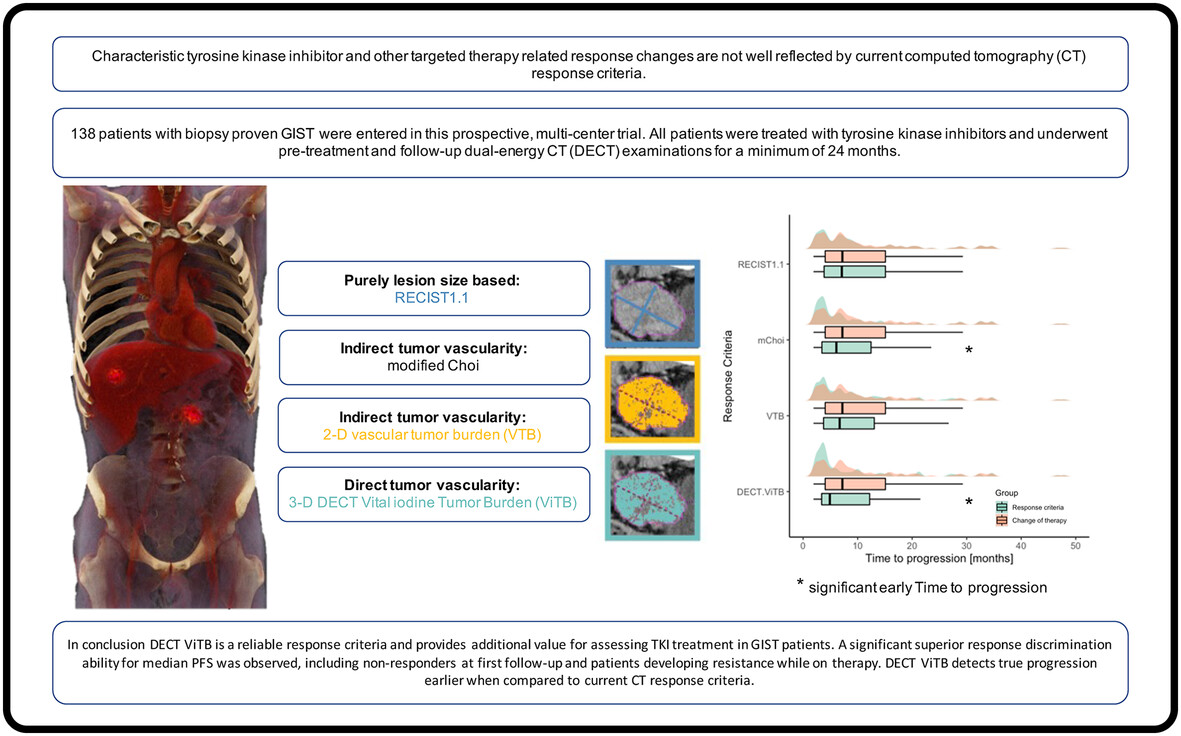
What's new?
Although the use of spectral computed tomography-based tumor markers has been advocated for tumor vascularity and response assessment, prospective evaluation is necessary. In this prospective observational study in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors undergoing tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy, spectral computed tomography-based response criteria demonstrate a superior response discrimination ability for progression-free survival in both responders and non-responders. The criteria can detect true progression earlier when compared to current computed tomography response criteria. Spectral computed tomography-based response criteria could potentially improve response assessment in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors and others undergoing tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment.
Innovative Tools and Methods
Adherence to melanoma screening and surveillance skin check schedules tailored to personal risk
- Pages: 2058-2067
- First Published: 23 August 2024
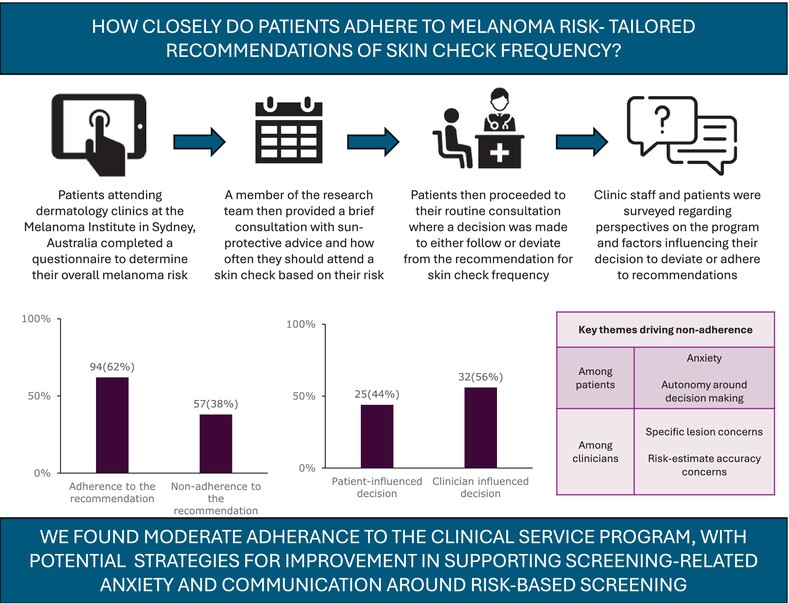
What's new?
In most countries including Australia, skin checks for early melanoma detection occur as opportunistic and patient-driven screening. Here, the authors present an innovative clinical model for personal risk-tailored melanoma screening and surveillance based on validated risk prediction tools and evaluate adherence to the risk-tailored recommendations. The observed moderate adherence was influenced by both patient and clinician factors, with a key barrier being anxiety of developing melanoma among low-risk groups. The study further supports the feasibility of implementing melanoma risk tools in practice and their potential use to tailor skin check schedules for melanoma screening and surveillance.
Molecular Cancer Biology
Identification of epigenetic modifiers essential for growth and survival of AML1/ETO-positive leukemia
- Pages: 2068-2079
- First Published: 15 August 2024
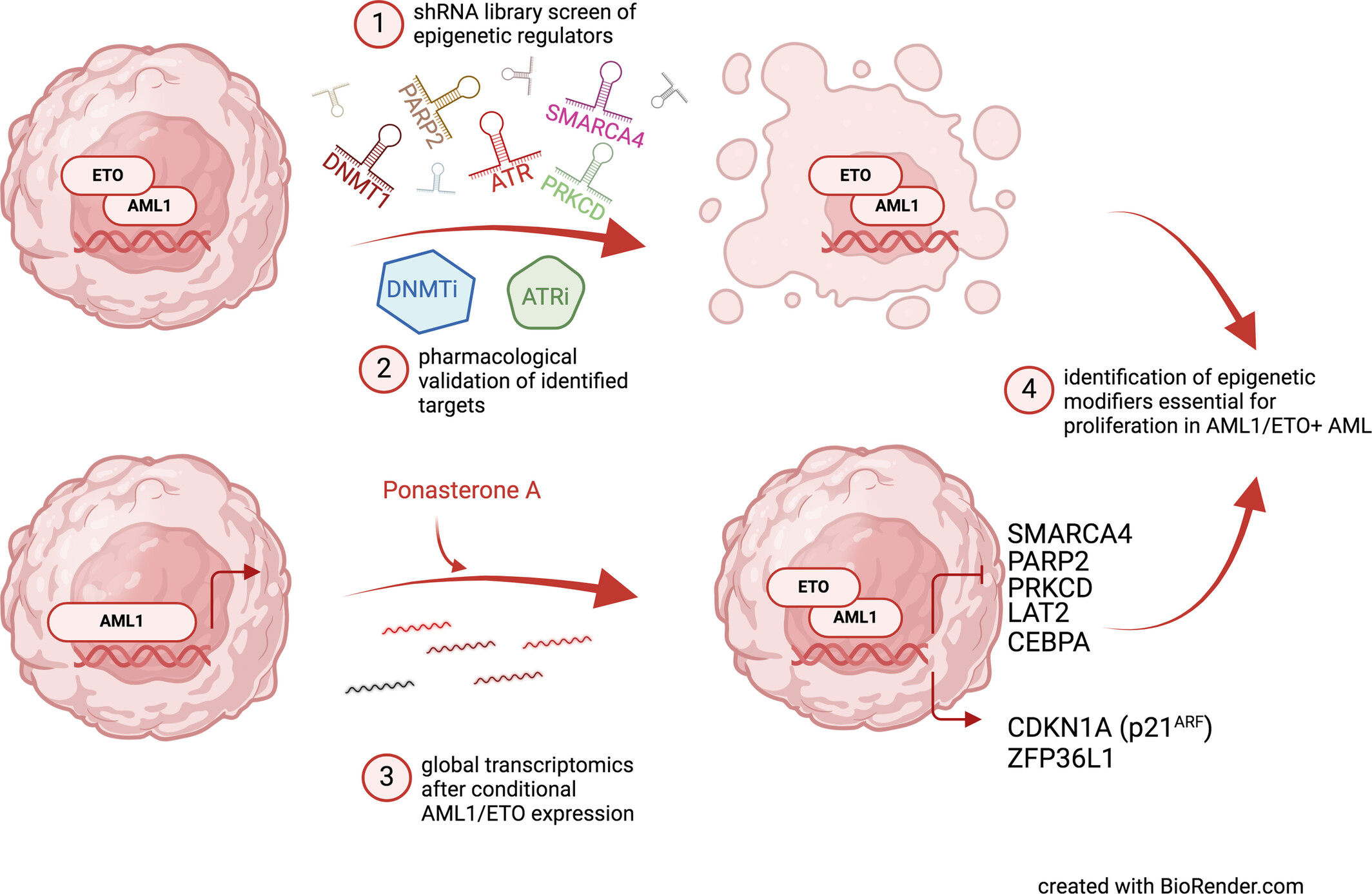
What's new?
Aberrant gene expression patterns observed in acute myeloid leukemia with balanced chromosomal translocations have been linked to effects by the leukemia-specific fusion proteins on the epigenome of malignant cells. Here, the authors explored critical and potentially druggable epigenetic modifiers in AML1/ETO-positive AML cells using shRNA library screens and global transcriptomics approaches. DNMT1 and ATR were identified and validated genetically and pharmacologically, showing promising preclinical and clinical efficacy in two AML1/ETO-positive cell lines. Several differentially expressed genes were also identified, including PARP2, PRKCD, and SMARCA4 that were both downregulated after AML1/ETO induction and identified in shRNA screens.
Tumor Immunology and Microenvironment
S100a8/a9 regulated by LPS/TLR4 axis plays an important role in Salmonella-based tumor therapy and host defense
- Pages: 2080-2093
- First Published: 11 August 2024
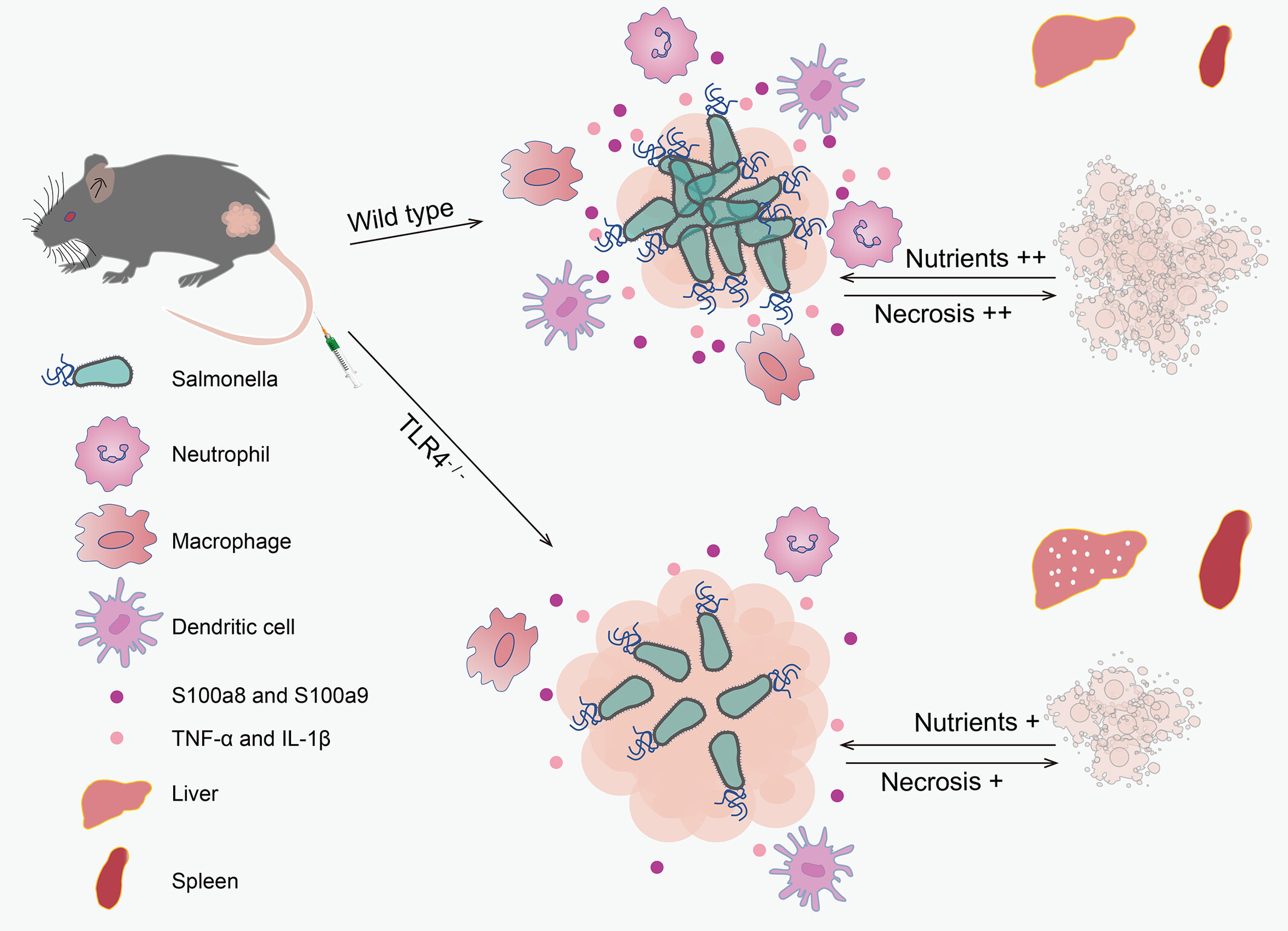
What's new?
Colonizing bacteria in tumor tissues can kill tumor cells directly or facilitate the infiltration and activation of innate immune cells and initiate antitumor responses. Here, the authors show that the TLR4 signaling pathway is critical for Salmonella-mediated tumor targeting and tumor suppression as well as for liver and spleen protection. Moreover, S100a8/a9 upregulated by the lipopolysaccharide/TLR4 pathway promotes the production of TNF-α and IL-1β, playing a pivotal role in tumor suppression and host antibacterial defense. The findings shed light on Salmonella-mediated anticancer mechanisms and identify potential therapeutic targets for clinical translation of oncolytic bacteria.
Tumor Markers and Signatures
A targeting nanoplatform for chemo-photothermal synergistic therapy of small-cell lung cancer
- Pages: 2094-2106
- First Published: 10 July 2024
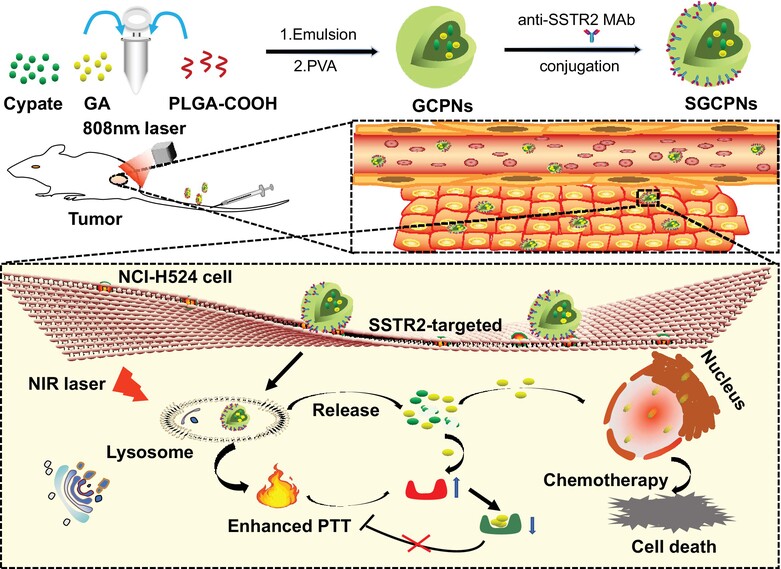
What's new?
Multifunctional nanosystems that combine drug and photothermal therapy (PTT) are promising anticancer treatment strategies. Here, the authors investigated the therapeutic potential of SGCPN, a novel nanoparticle drug-delivery system that combines the PTT dye cypate and the antitumor drug gambogic acid (GA), with somatostatin receptor 2 (SSTR2)-specific targeting capability imparted by antibodies on the nanoparticle surface. SGCPNs were readily internalized by SSTR2-positive small cell lung cancer (SCLC) cells and effectively targeted SSTR2-positive xenograft tumors. In vivo, SGCPNs were precisely delivered to deep-seated SCLC tumor sites and overcame depth-attenuation of light, with near-infrared laser irradiation triggering GA release and tumor cell death.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Comments on “Psychosocial factors, health behaviours and risk of cancer incidence: Testing interaction and effect modification in an individual participant data meta-analysis”
- Pages: 2107-2108
- First Published: 14 August 2024
RETRACTION
RETRACTION: High-density lipoprotein of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus elevates the capability of promoting migration and invasion of breast cancer cells
- Page: E15
- First Published: 28 August 2024