Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Image
GABAergic innervation of the ciliary ganglion in macaque monkeys – A light and electron microscopic study
- Page: spc1
- First Published: 23 March 2017
Issue Information - TOC
The Journal of Comparative Neurology, Table of Content, Vol. 525, No. 7, May 1, 2017
- Pages: 1515-1516
- First Published: 23 March 2017
Research Articles
GABAergic innervation of the ciliary ganglion in macaque monkeys – A light and electron microscopic study
- Pages: 1517-1531
- First Published: 16 November 2016
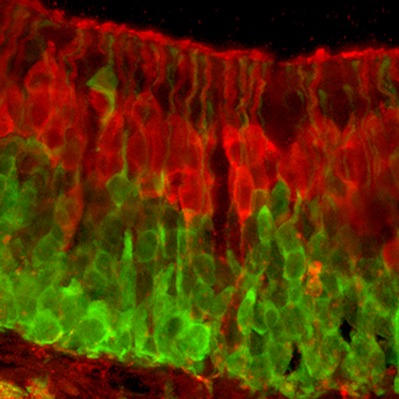
Using immunohistochemical and electron microscopic techniques, we show that in monkey a subpopulation of 17.5% of cholinergic parasympathetic postganglionic CG neurons was contacted by GABAergic terminals. These GABAergic terminals display intermediate features of classically excitatory and inhibitory synaptic contacts.
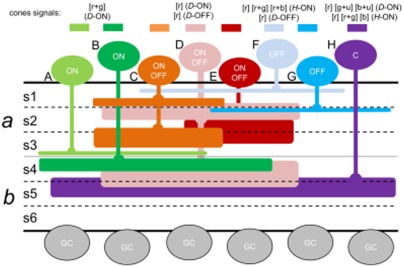
Cone signals in monostratified and bistratified amacrine cells of adult zebrafish retina
- Pages: 1532-1557
- First Published: 29 August 2016
Gene expression profiling of granule cells and Purkinje cells in the zebrafish cerebellum
- Pages: 1558-1585
- First Published: 12 September 2016
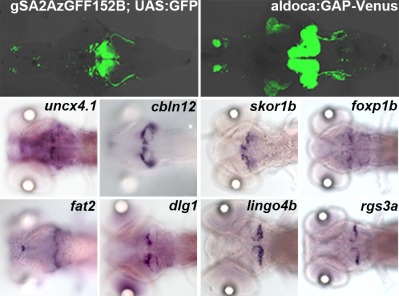
Using zebrafish transgenic larvae expressing fluorescent proteins in cerebellar circuits, the authors isolated each type of cerebellar cells by FACS and profiled their expression by RNA sequencing and ISH. A comparison of the transcriptomes identified genes that are upregulated in granule cells and Purkinje cells.
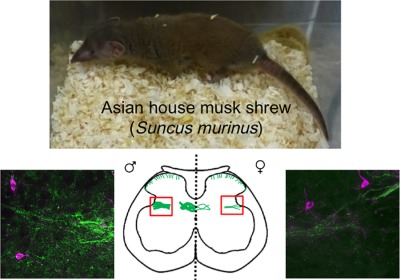
Identification of the sexually dimorphic gastrin-releasing peptide system in the lumbosacral spinal cord that controls male reproductive function in the mouse and Asian house musk shrew (Suncus murinus)
- Pages: 1586-1598
- First Published: 02 November 2016
Cellular localization of relaxin-like gonad-stimulating peptide expression in Asterias rubens: New insights into neurohormonal control of spawning in starfish
- Pages: 1599-1617
- First Published: 02 November 2016

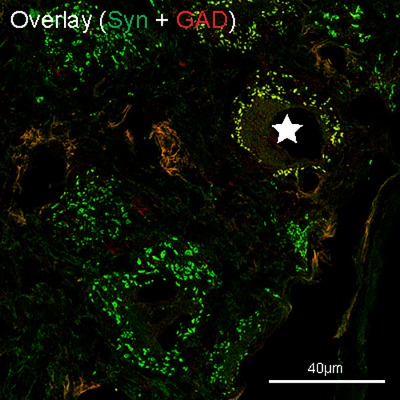
Spawning in starfish is triggered by a relaxin-like gonad-stimulating peptide (RGP). We have discovered that RGP is expressed by cells at the tips of the arms near to the terminal tentacle and optic cushion. These cells may mediate neurohormonal control of spawning in response to environmental cues.
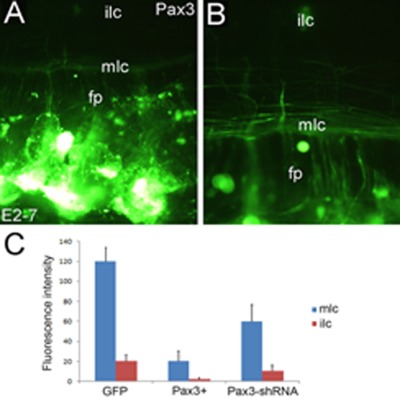
Pax3 overexpression induces cell aggregation and perturbs commissural axon projection during embryonic spinal cord development
- Pages: 1618-1632
- First Published: 16 November 2016
Synaptic distribution of individually labeled mitral cells in the external plexiform layer of the mouse olfactory bulb
- Pages: 1633-1648
- First Published: 16 November 2016
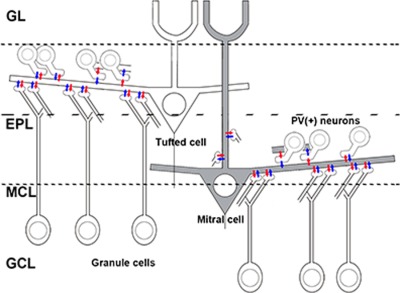
Serial viral vector and serial electron microscopic analyses reveal that synapses on mitral cells are distributed mainly within the inner half of the external plexiform layer (EPL) and that local synaptic circuits of mitral and tufted cells are distributed separately within the inner and outer halves of the EPL, respectively. EPL, external plexiform layer; GCL, granule cell layer; GL, glomerular layer; MCL, mitral cell layer.
Spatial patterning of excitatory and inhibitory neuropil territories during spinal circuit development
- Pages: 1649-1667
- First Published: 20 December 2016
Descending projections from the basal forebrain to the orexin neurons in mice
- Pages: 1668-1684
- First Published: 20 December 2016
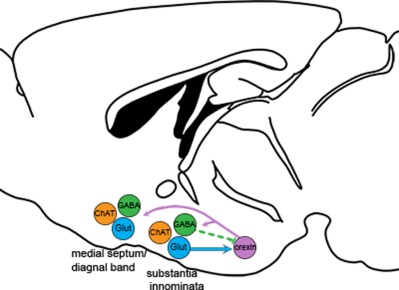
The basal forebrain and orexin neurons are both implicated in arousal and wakefulness. Glutamatergic projections from the substantia innominata (SI) excite the orexin neurons, but GABA projections from the SI appear to be silent. The medial septum (MS) and horizontal nucleus of the diagonal band (HDB) sparsely innervate the orexin neurons.
Organization of the antennal lobes in the praying mantis (Tenodera aridifolia)
- Pages: 1685-1706
- First Published: 21 December 2016
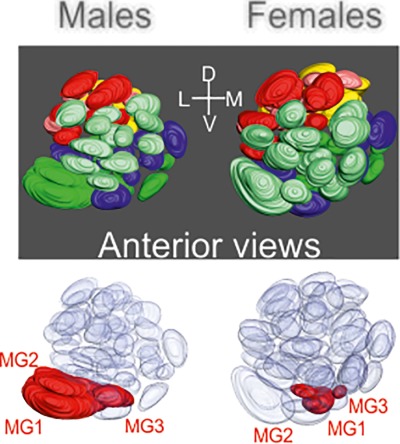
In contrast to dragonflies, which possess only two glomeruli in their antennal lobes, the praying mantis (Tenodera aridifolia) is another visually guided hunter provided with 54 glomeruli. Furthermore, we identified threemacroglomeruli in males that seem to be related to grooved peg sensilla located on the surface of antennae.
Somatic and neuritic spines on tyrosine hydroxylase–immunopositive cells of rat retina
- Pages: 1707-1730
- First Published: 30 December 2016
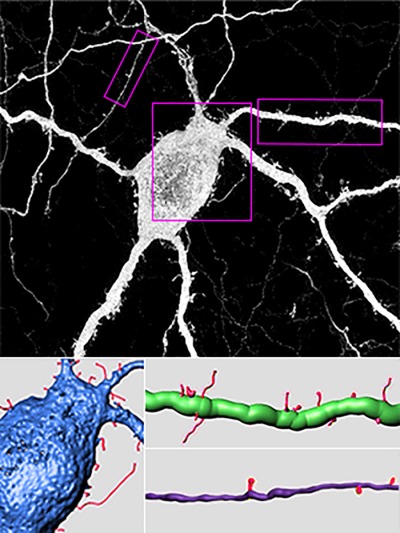
Using a modified aldehyde fixative, the authors find spines on somata and neurites of tyrosine hydroxylase-immunopositive interneurons in adult rat retina; colocalizations of glutamate receptor isoform and postsynaptic density proteins at some of these spines, neurites, and somata; and a synaptic ribbon-specific protein adjacent to some of these colocalizations.
Dorsal pallidal neurons directly link the nidopallium and midbrain in the zebra finch (Taeniopygia guttata)
- Pages: 1731-1742
- First Published: 12 January 2017
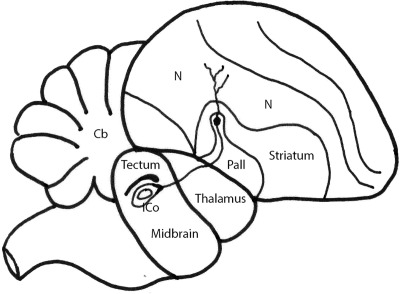
Sagittal schematic of zebra finch brain. Large dorsal pallidal (Pall) neurons were found to project on the intercollicular nucleus of the midbrain, to be calretinin positive, and to have extensive dendrites radiating into the overlying auditory and somatosensory nidopallium (N). The projection is proposed to be involved in sensory rather than motor control.
5HTR3A-driven GFP labels immature olfactory sensory neurons
- Pages: 1743-1755
- First Published: 02 February 2017