Editor-in-Chief: Joseph Krumpfer
Journal of Polymer Science, a Wiley polymers journal, publishes outstanding and in-depth research in all disciplines of polymer science.
As a well-established resource, we feature both the core sub-disciplines and research at the frontiers of the field in a unified, inclusive, and dynamic forum. Our broad scope covers all aspects of polymer science, including chemistry, physics, and engineering, as well as application-focused research on emerging polymers and polymeric materials.
Journal Metrics
- 6.3CiteScore
- 3.6Journal Impact Factor
- 32%Acceptance rate
- 10 days Submission to first decision
On the Cover
Articles
Solution‐Like Water Transport Across Molecular to Macroscopic Length Scales in Crosslinked Poly(Ethylene Glycol Diacrylate) Networks With Tailored Sidechains
- Journal of Polymer Science
- 19 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
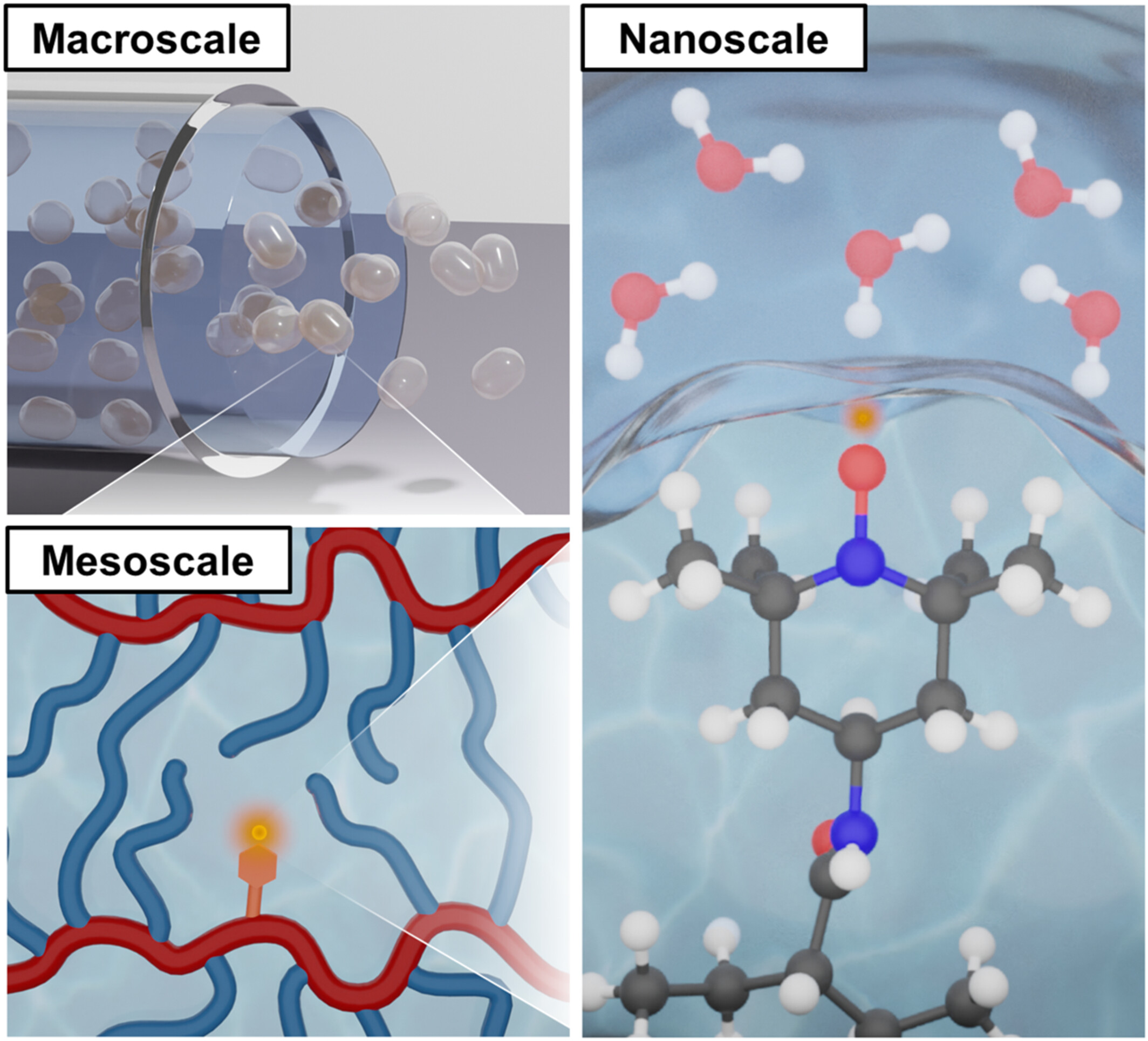
Cross-linked PEGDA network microparticles are synthesized with spin labels to sense local water motion. From the nanoscale to the macroscale, PEGDA exhibits rapid, solution-like water transport as measured by spectroscopic techniques. Addition of side chain chemistries further modulates local water diffusion. PEGDA’s ability to quickly diffuse water highlights its efficacy as a membrane material.
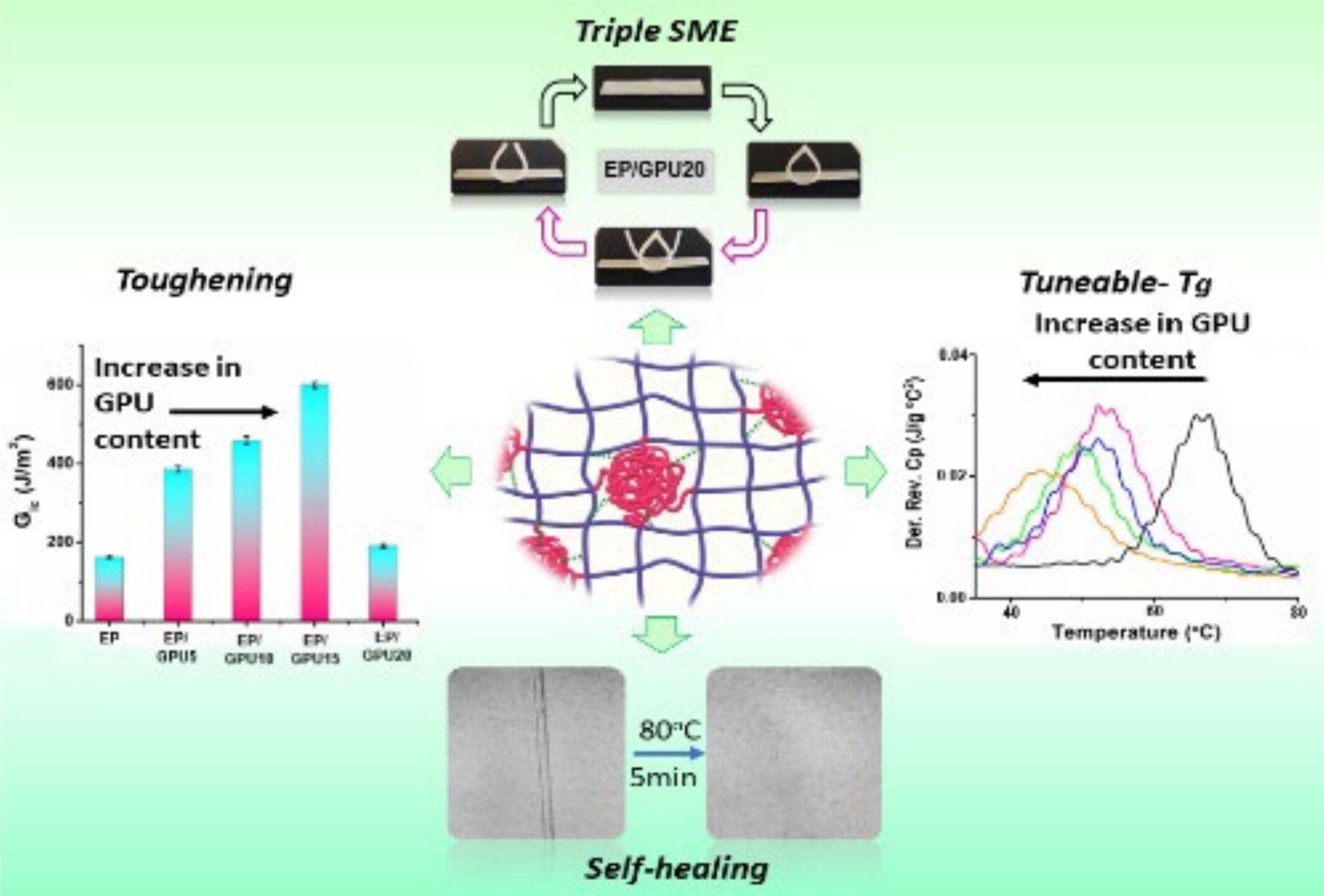
Toughened Thermoset Blend of Epoxy With Glycidyl Terminated Polyurethane Exhibits Simultaneous Self‐Healing and Shape Memory Properties
- Journal of Polymer Science
- 19 July 2025
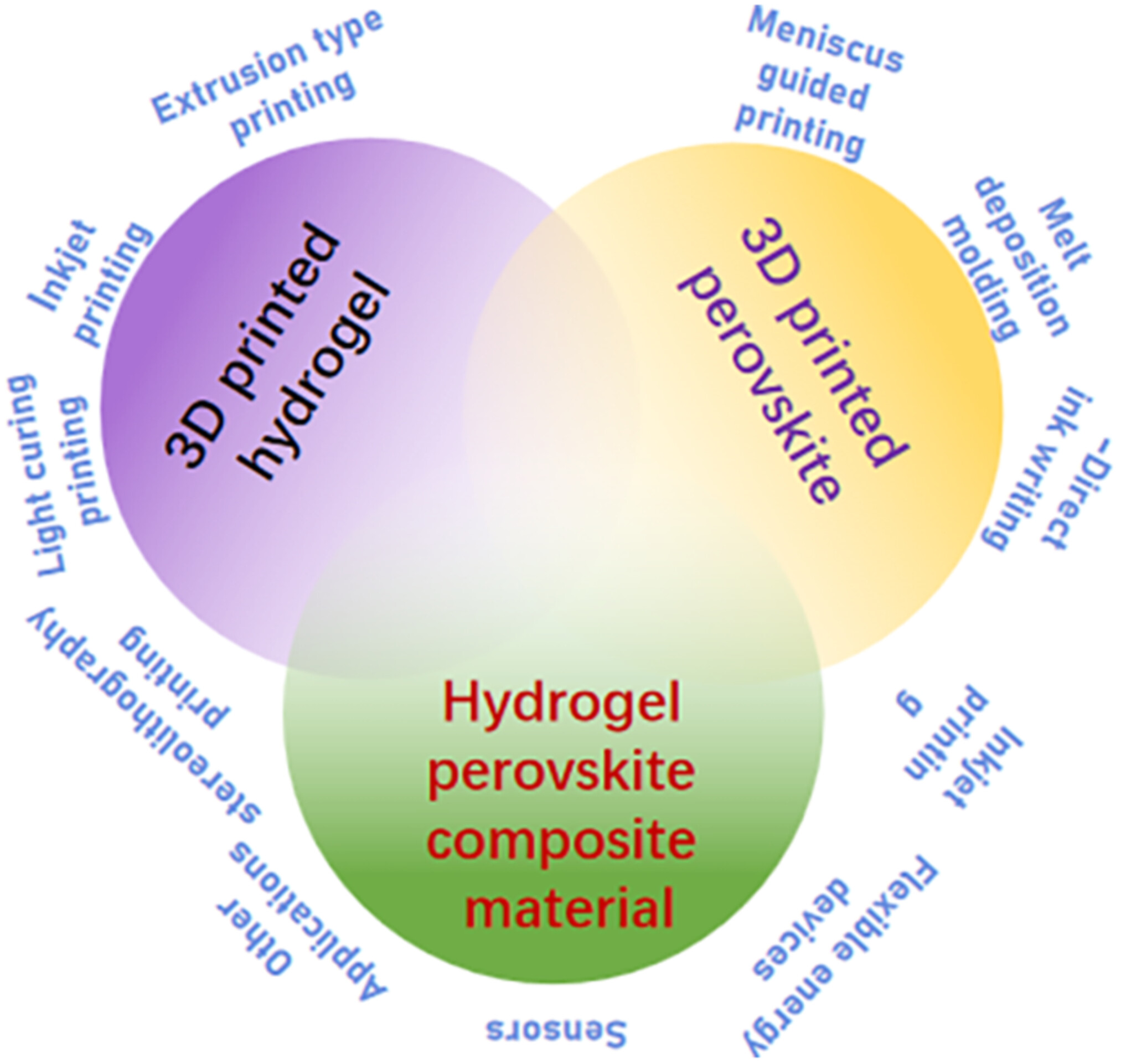
3D Printing Hydrogel, Perovskite Technology, and Preparation and Application of Hydrogel Perovskite Composite Materials
- Journal of Polymer Science
- 19 July 2025
Two‐Photon Polymerizable Nanocomposites Incorporating Brazilian Red Propolis for Tailored Wound Healing Applications
- Journal of Polymer Science
- 17 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
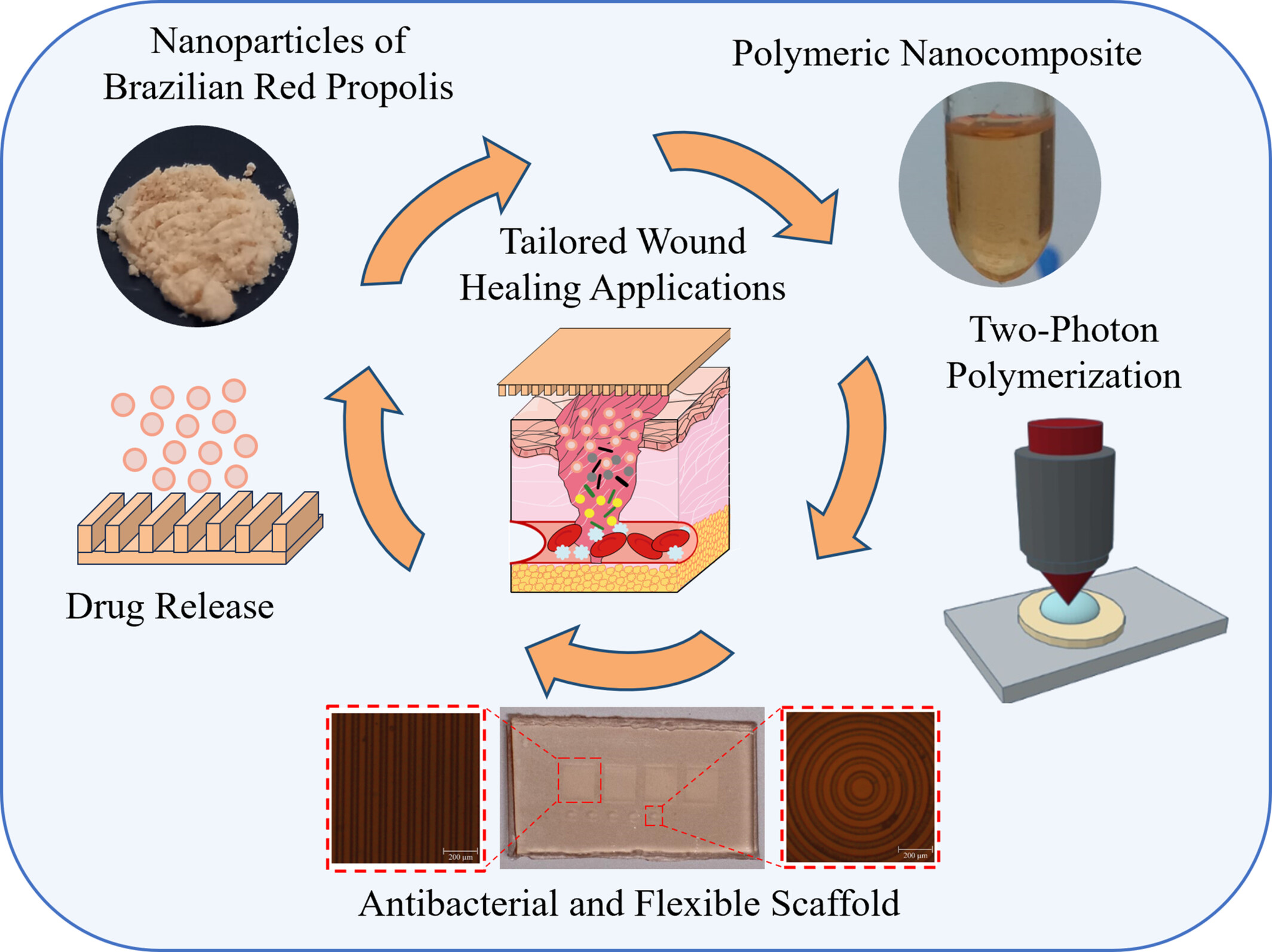
Nanocomposites combining Brazilian red propolis nanoparticles with acrylic resins exhibit controlled nanoparticle release, good flexibility, and antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus. Moreover, these materials are highly suitable for the fabrication of cellular scaffolds via two-photon polymerization, making them strong candidates for advanced wound dressing applications.
Advances and approaches for chemical recycling of plastic waste
- Journal of Polymer Science
- 1347-1364
- 15 May 2020
Graphical Abstract
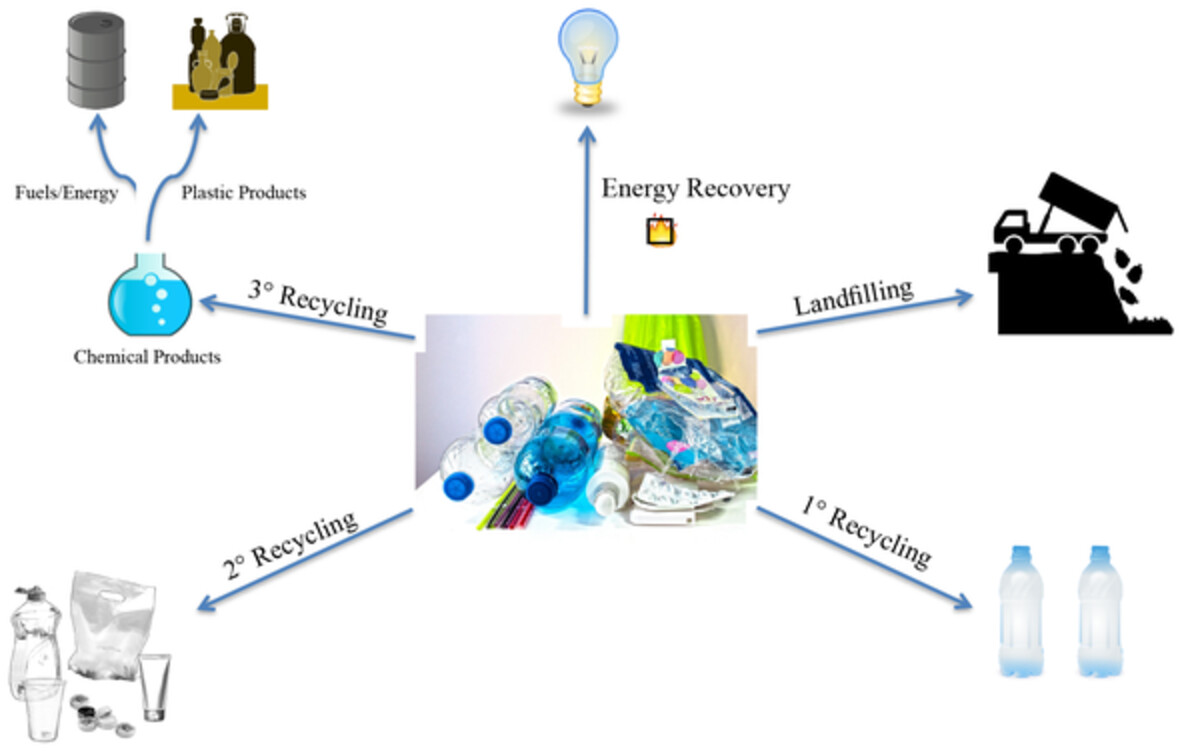
The global production and consumption of plastics have increased significantly over the years. The major current recycling processes are limited by the sorting and pretreatment of plastic waster and degradation. This review covers the most recent academic and industrial efforts to recycle conventional plastics and mixed waste.
Biomedical applications of biodegradable polymers
- Journal of Polymer Science Part B: Polymer Physics
- 832-864
- 15 Jun 2011
Graphical Abstract
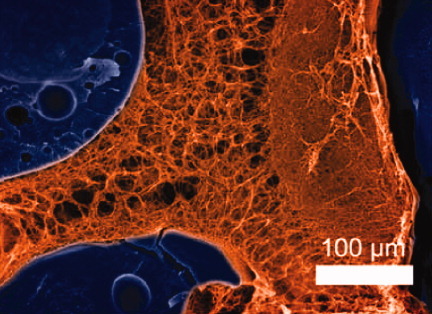
Polymers have shown tremendous capacity as biomaterials with degradable polymers holding particular promise. Control over their microstructure and nanostructure as indicated by the blue and orange regions, respectively, allow for the design of complex materials that have desired interactions with host cells and tissues. This review overviews the wide range of degradable polymers that are available to biomedical researchers paying specific attention to new advances that have been made in the past 4 years.
Rupture of rubber. I. Characteristic energy for tearing
- Journal of Polymer Science
- 291-318
- 1 Mar 1953
Cellulose nanocrystals and related nanocomposites: Review of some properties and challenges
- Journal of Polymer Science Part B: Polymer Physics
- 791-806
- 15 Jun 2014
Graphical Abstract
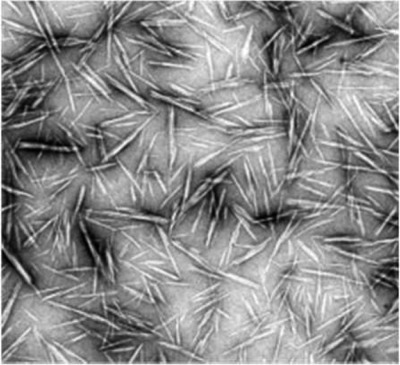
Impressive mechanical properties and reinforcing capability, abundance, low weight, renewability, and biodegradability make cellulose nanocrystals ideal candidates for use in polymer nanocomposites. This Review also looks at the broad range of potential applications of these nanoparticles, as well as the remaining questions in the field.