Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Top Cited Articles 2021
Clinical characteristics and outcomes of COVID-19 in patients with type 2 diabetes in Turkey: A nationwide study (TurCoviDia)
土耳其2型糖尿病患者患有COVID-19的临床特征和结果:一项全国性研究(TurcoviDia)
- First Published: 02 March 2021
Highlights
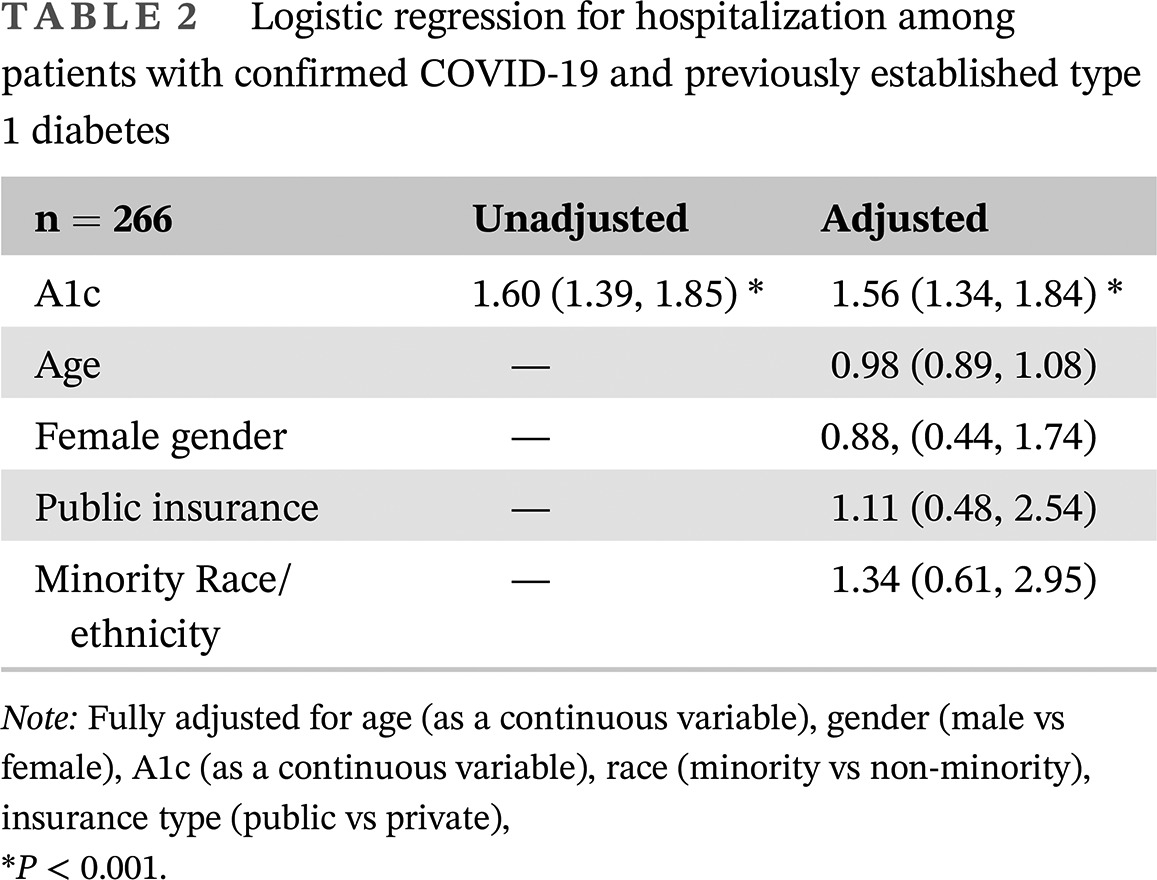
- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) takes an unfavorable course in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and the risk increases in individuals with certain conditions, some of which are not modifiable.
- This study showed significantly higher mortality due to COVID-19 in hospitalized patients with T2DM than without (13.6% vs 8.7%; hazard ratio 1.75; 95% CI, 1.58-1.93).
- Older age, male gender, obesity, preexisting insulin treatment, low lymphocyte count, and pulmonary involvement on admission were the significant associates of COVID-19 mortality.
Measuring the global, regional, and national burden of type 2 diabetes and the attributable risk factors in all 194 countries
衡量全球194个国家2型糖尿病及其危险因素的疾病负担研究
- First Published: 24 January 2021
Highlights
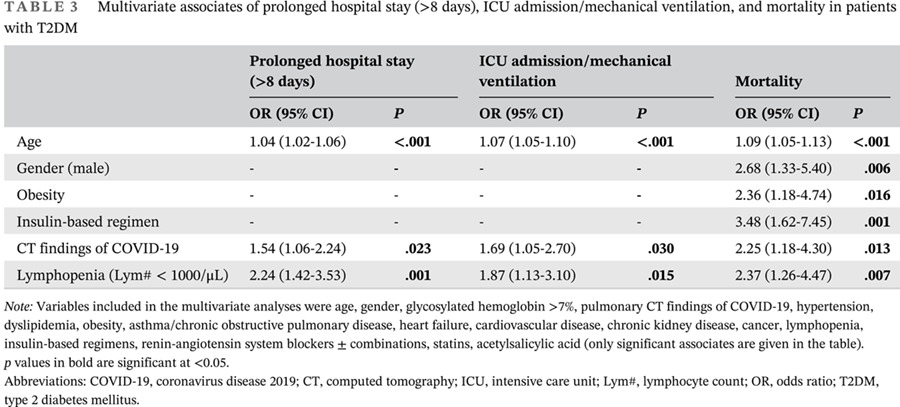
- We revealed a high disease burden in the low-middle sociodemographic index (SDI) quintile, Southeast Asia, and Iran, the United Kingdom, Indonesia, Georgia, and the Czech Republic, and determined that the increased burden of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) is mainly attributable to lifestyle factors (eg, high body mass index, low physical activity, high fasting plasma glucose, and high sugar-sweetened beverage and red meat intakes).
- Our study adds important information about the spatial distribution of T2DM burden and the contributions of risk factors to T2DM DALYs globally.
Metabolic syndrome and clinical outcomes in patients infected with COVID-19: Does age, sex, and race of the patient with metabolic syndrome matter?
COVID-19患者的代谢综合征和临床结局:代谢综合征患者的年龄、性别和种族重要吗?
- First Published: 16 January 2021
Highlights
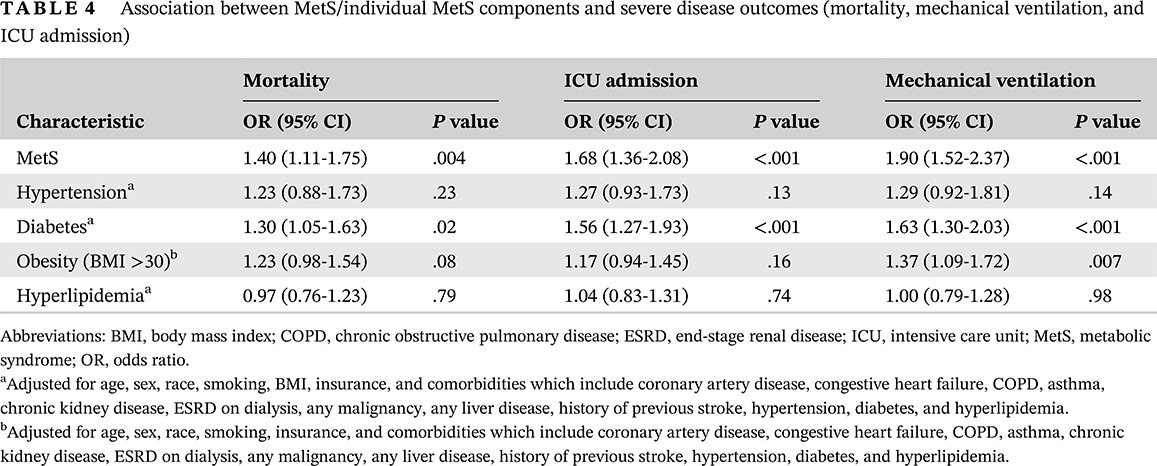
- Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is a vital prognostic indicator of outcomes in coronavirus disease 2019.
- Patients with MetS had worse clinical outcomes compared with the ones without MetS.
- Patients with MetS had a higher need for intensive care unit irrespective of their age, sex, or race.
- Need for mechanical ventilation was higher for all patients with MetS except Caucasians.
- Females, younger patients (<65), and African Americans with MetS had higher mortality.
Determinants of mental health outcomes among people with and without diabetes during the COVID-19 outbreak in the Arab Gulf Region
新型冠状病毒肺炎暴发期间阿拉伯海湾地区糖尿病患者和非糖尿病患者心理健康结果的决定因素
- First Published: 22 December 2020
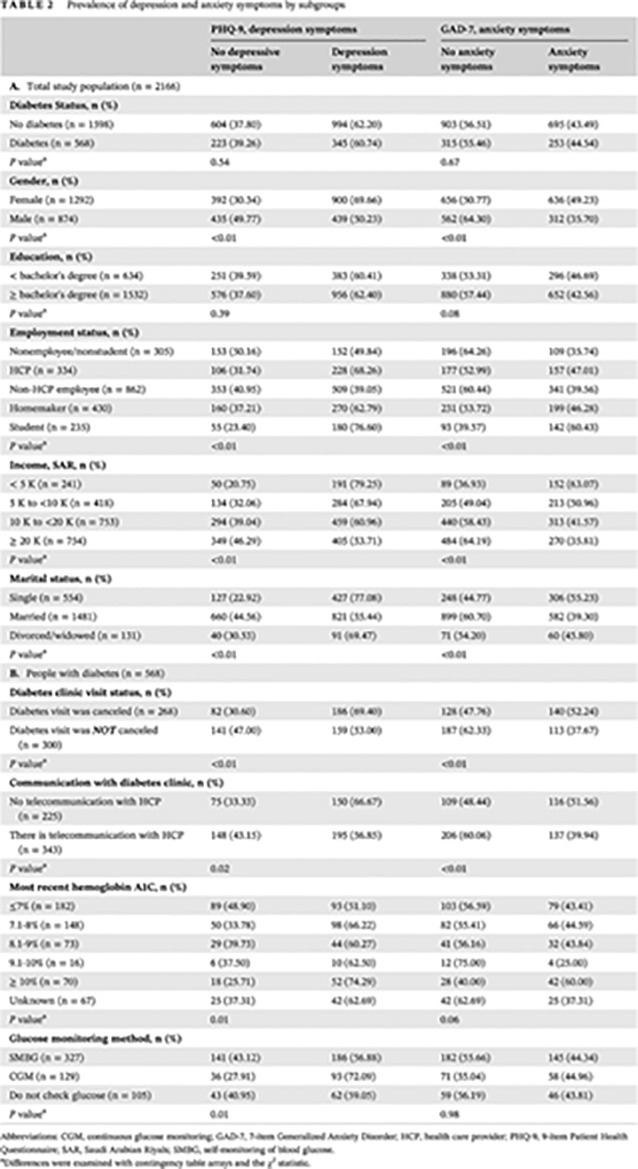
Highlights
- Depression and anxiety symptoms were highly prevalent during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic regardless of diabetes status.
- Women, unmarried individuals, employees (particularly health care providers), students, younger adults, and those with lower income were more vulnerable to psychological distress during the COVID-19 outbreak than others.
- People with diabetes who had their diabetes visit canceled during the pandemic, had no method of telecommunication with HCPs, or A1C≥10%; women; HCPs; students; unmarried individuals; and those with lower income were more likely to report depression and/or anxiety symptoms
Diabetic ketoacidosis drives COVID-19 related hospitalizations in children with type 1 diabetes
糖尿病酮症酸中毒促使1型糖尿病儿童发生新型冠状病毒肺炎相关住院治疗
- First Published: 14 April 2021
Inhibition of α-glucosidase and α-amylase by herbal compounds for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: A validation of in silico reverse docking with in vitro enzyme assays
中药复方抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶和α-淀粉酶治疗2型糖尿病:电子反向对接与体外酶试验的验证
- First Published: 06 February 2021
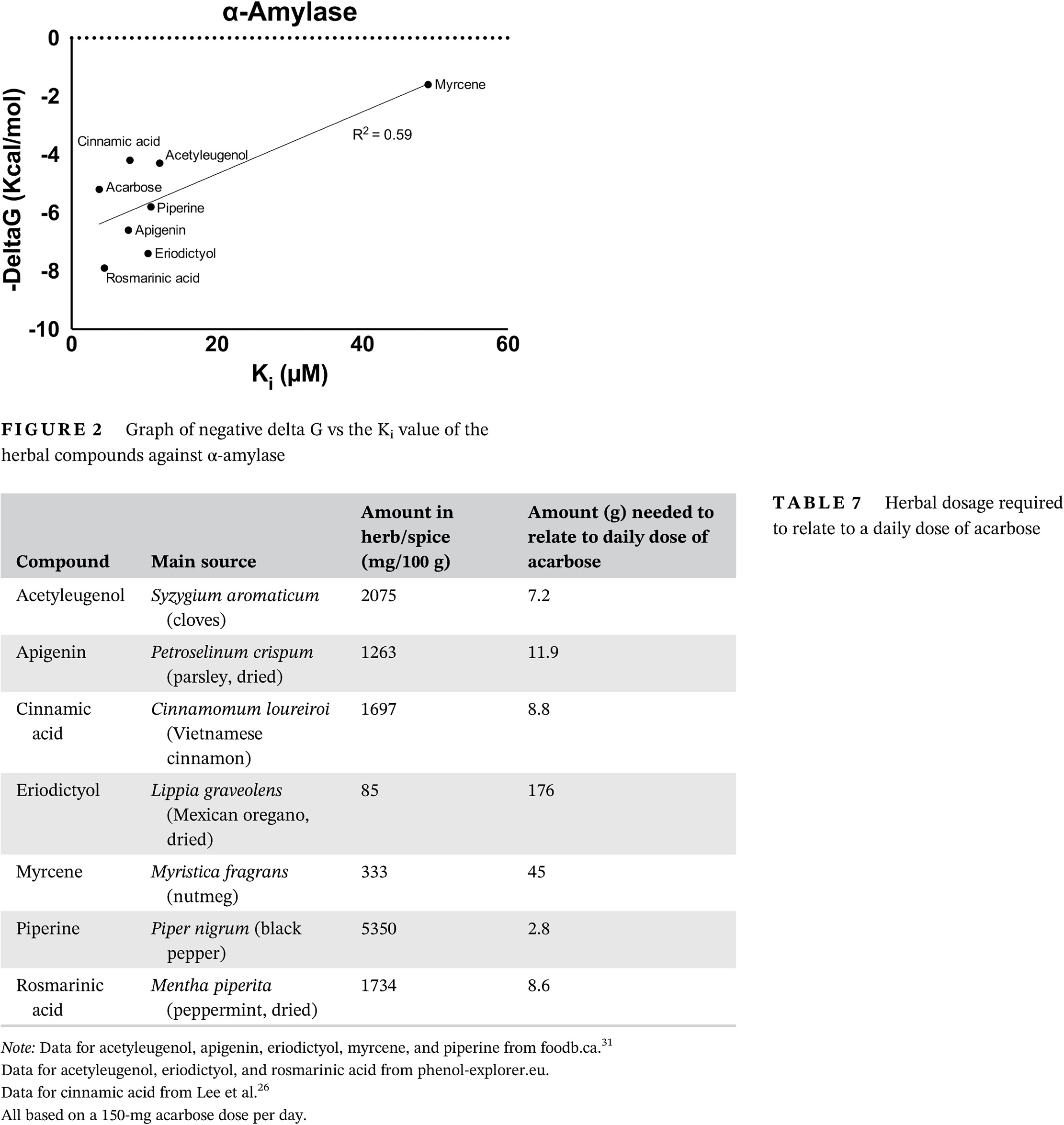
Highlights
- There is a positive relationship between in silico docking and in vitro assays.
- Several of the herbal compounds studied regulate postprandial hyperglycemia.
- Apigenin is a monotherapeutic agent, inhibiting both α-amylase and α-glucosidase.
- Most herbal compounds are not more toxic than acarbose.
Predictors of mortality in a multiracial urban cohort of persons with type 2 diabetes and novel coronavirus 19
城市多种族患有2型糖尿病的新型冠状病毒肺炎患者死亡率的预测因素
- First Published: 23 January 2021
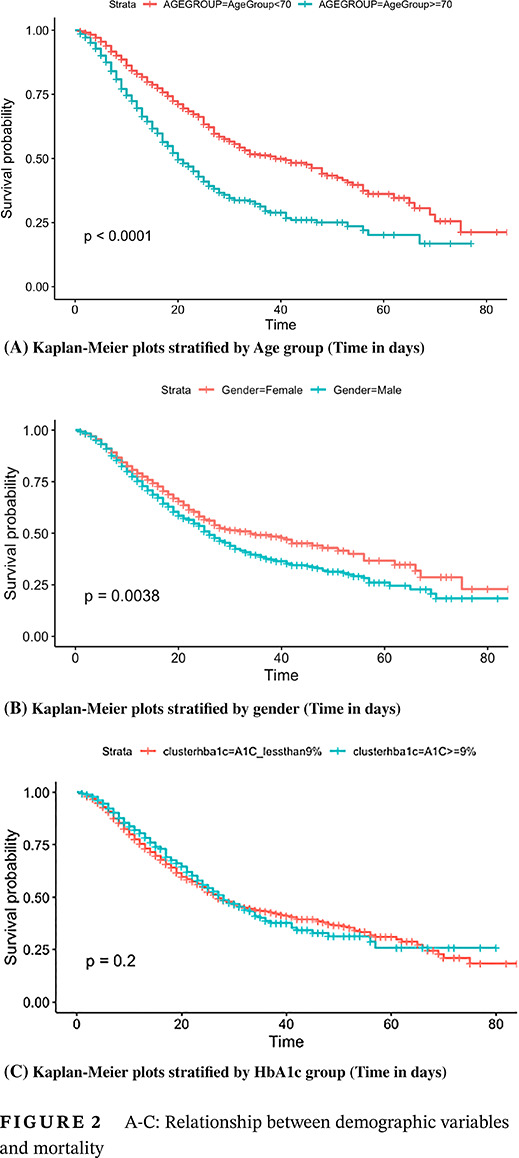
Highlights
- Admission serum or point-of-care glucose is a greater predictor of mortality than glycosylated hemoglobin in persons with type 2 diabetes and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
- Those with diabetes and COVID-19 who were intubated had a higher morality than those who were not intubated.
- Older age, male gender, and history of chronic kidney disease, hypertension, or coronary artery disease increased the risk of mortality. Race and insurance type had no impact on mortality.
Prevalence and impact of diabetes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis
住院新型冠状病毒肺炎患者糖尿病患病率及其影响的系统回顾和meta分析
- First Published: 23 December 2021
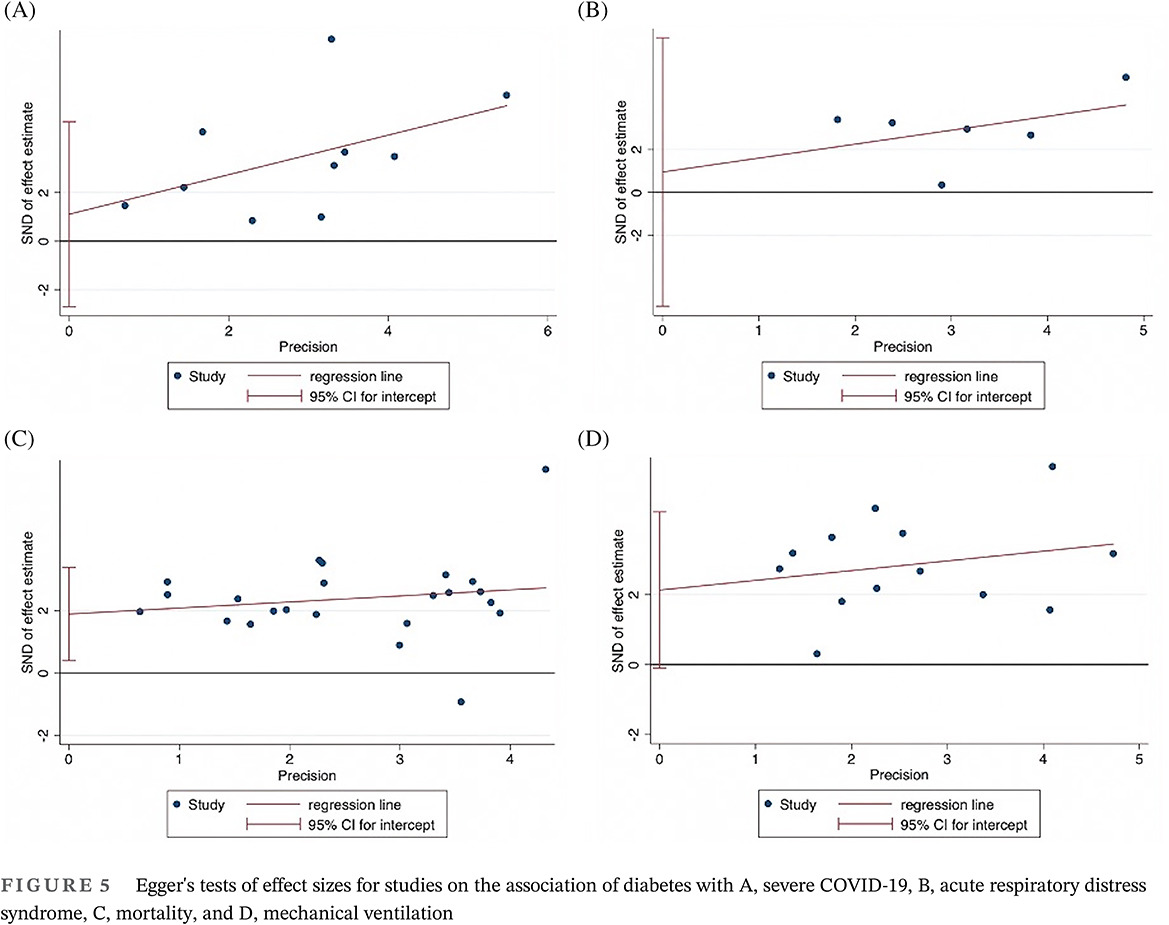
Highlights
- Diabetes may predispose COVID-19 hospitalized patients to worse clinical outcomes.
- Our findings indicate that diabetes is significantly associated with increased odds of severe COVID-19, acute respiratory distress syndrome, mortality, and need for mechanical ventilation in hospitalized patients.
- COVID-19 patients with diabetes are at high risk of morbidity and mortality.
A comparison of the stress hyperglycemia ratio, glycemic gap, and glucose to assess the impact of stress-induced hyperglycemia on ischemic stroke outcome
比较应激性高血糖比率, 血糖间隙和葡萄糖评估应激性高血糖对缺血性卒中预后的影响
- First Published: 18 September 2021
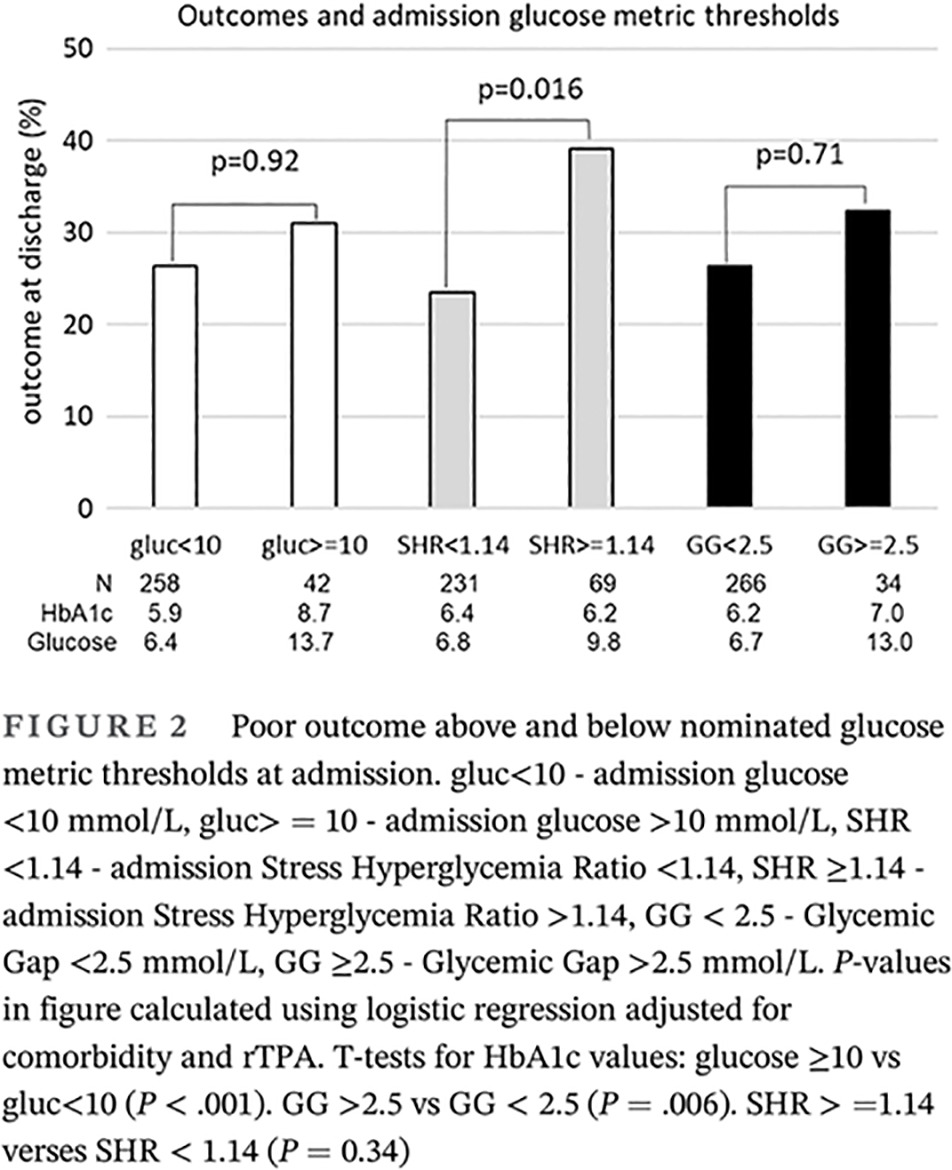
Highlights
- The impact of stress-induced hyperglycemia on outcome is poorly reflected by absolute glucose levels.
- The stress hyperglycemia ratio (SHR) biomarker discriminates between interpatient variation in normal premorbid background glycemia related to glycosylated hemoglobin and the acute relative increase in glucose related to physiological stress that truly represents stress-induced hyperglycemia.
- SHR at admission was superior to glucose in predicting ischemic stroke outcome.
- There is a need for interventional studies based on SHR rather than glucose to best assess management of stress-induced hyperglycemia.
Association of metabolic score for insulin resistance and its 6-year change with incident type 2 diabetes mellitus
胰岛素抵抗代谢评分及其6年变化与2型糖尿病发病的关系
- First Published: 28 February 2021
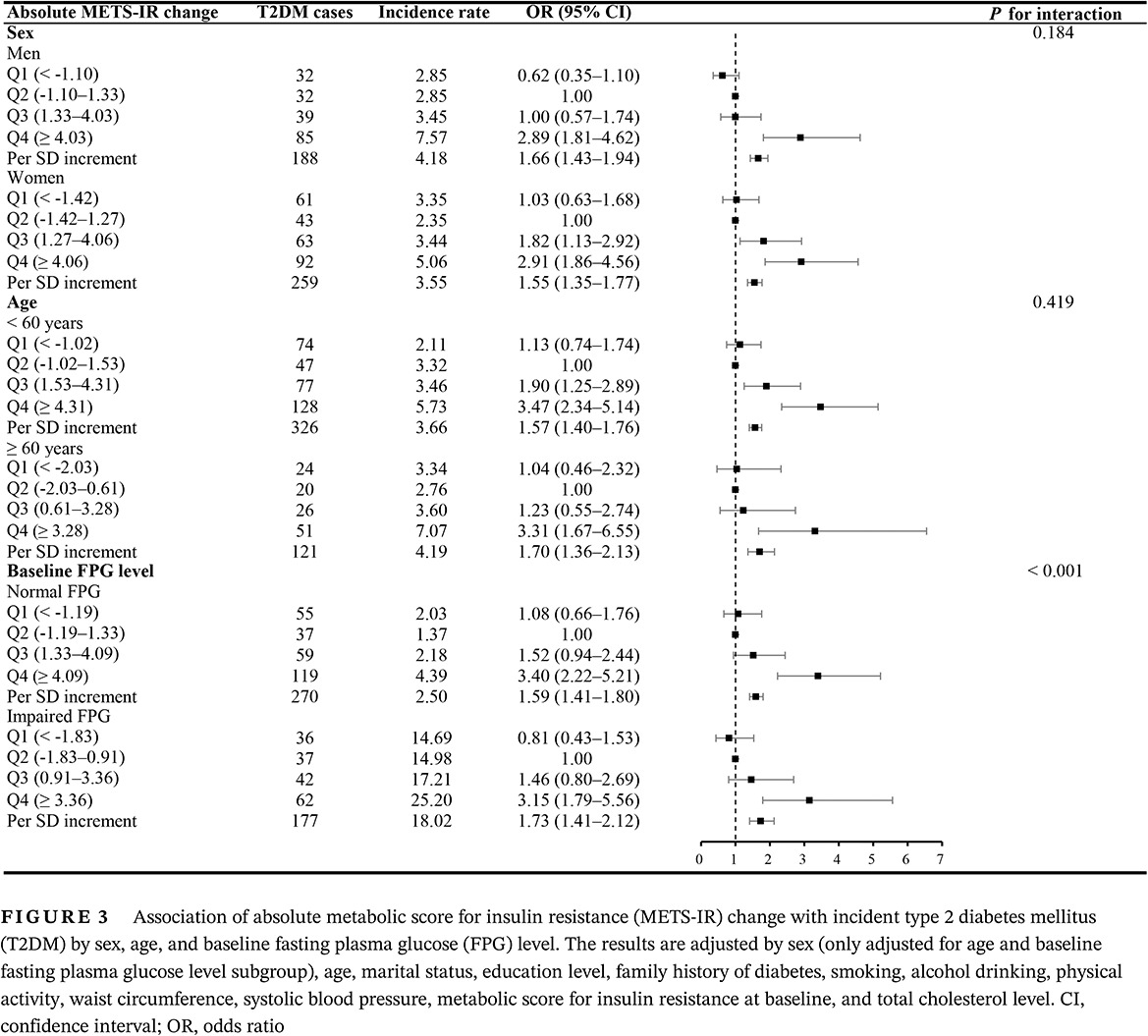
Highlights
- Increased METS-IR and 6-year METS-IR change were positively associated with risk of incident T2DM in a rural Chinese population.
- We observed an association of METS-IR and 6-year METS-IR change with incident T2DM by sex, age, and baseline FPG level.
- Dose-response analysis revealed significantly increased probability of incident T2DM with increasing METS-IR and 6-year METS-IR change.




1753-0407.top-cited-2021articles.cover.gif)