Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Diabetic Kidney Disease
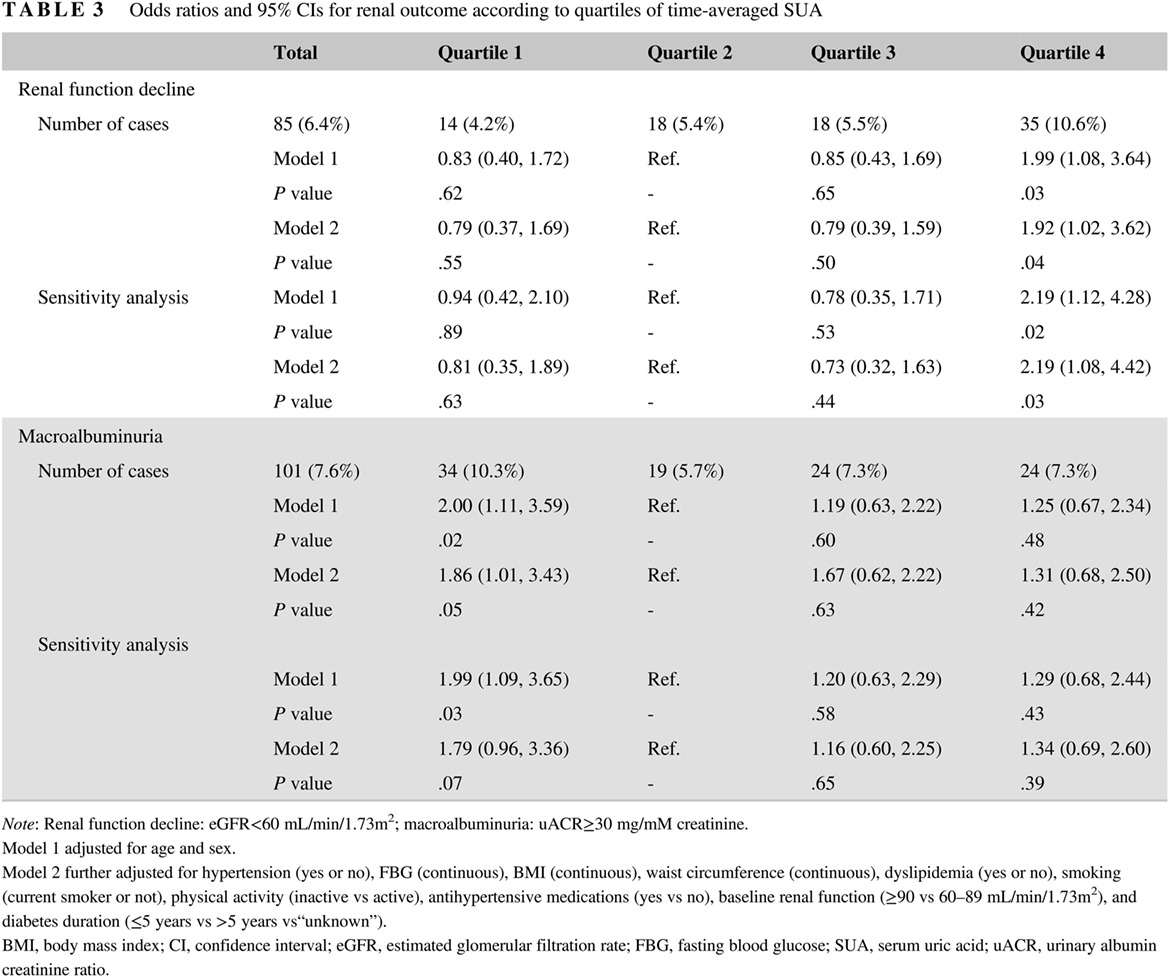
Time-averaged serum uric acid and 10-year incident diabetic kidney disease: A prospective study from China
时均血清尿酸水平与十年新发糖尿病肾病:一项来自中国的前瞻性研究
- First Published: 28 August 2019
Highlights
- Long-term exposure to relatively high SUA, despite within normal range, was associated with nearly 2-fold increased risk of renal function decline.
- In addition, long-term exposure to relatively low SUA level was also associated with increased risk of albuminuria.
- This study suggested that time-averaged SUA, rather than baseline SUA, is an independent predictor of incident DKD.
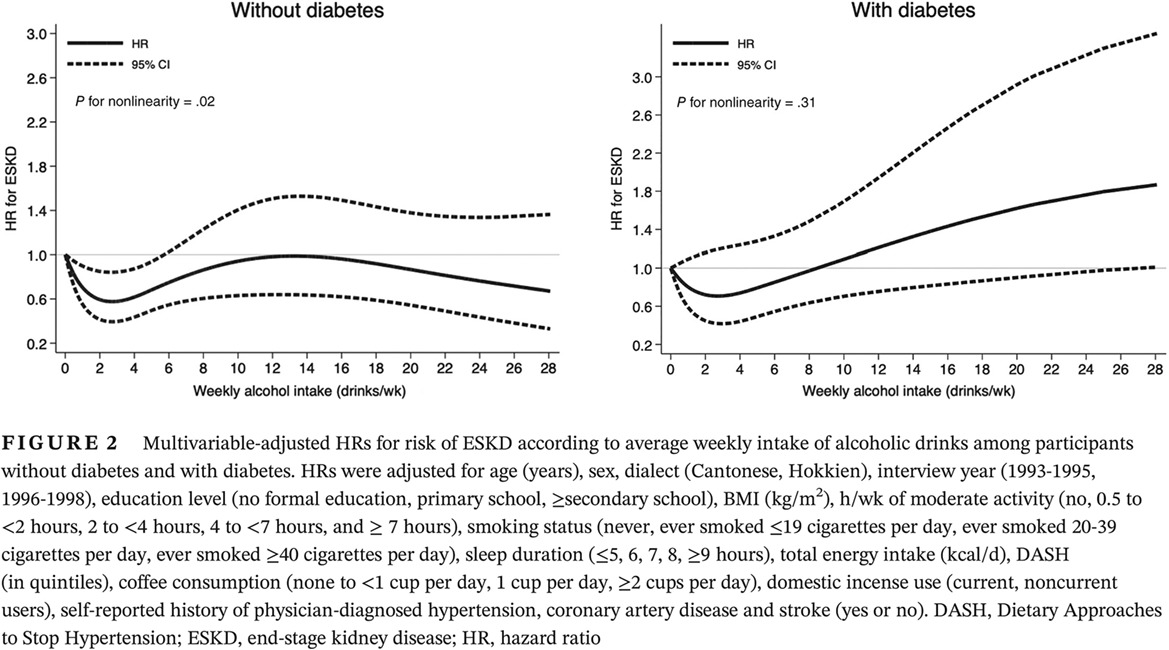
The impact of diabetes on the association between alcohol intake and the risk of end-stage kidney disease in the Singapore Chinese Health Study
在新加坡华人健康研究中探讨糖尿病对酒精摄入与终末期肾病风险关系的影响
- First Published: 06 March 2020
Highlights
- Low-dose intake of alcohol is associated with a lower risk of end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) in nondiabetic participants.
- Joint exposure to heavy drinking and diabetes is associated with a substantially higher risk of ESKD.
- Recommendations on alcohol intake among patients at risk of ESKD should consider the presence of diabetes as a comorbidity.
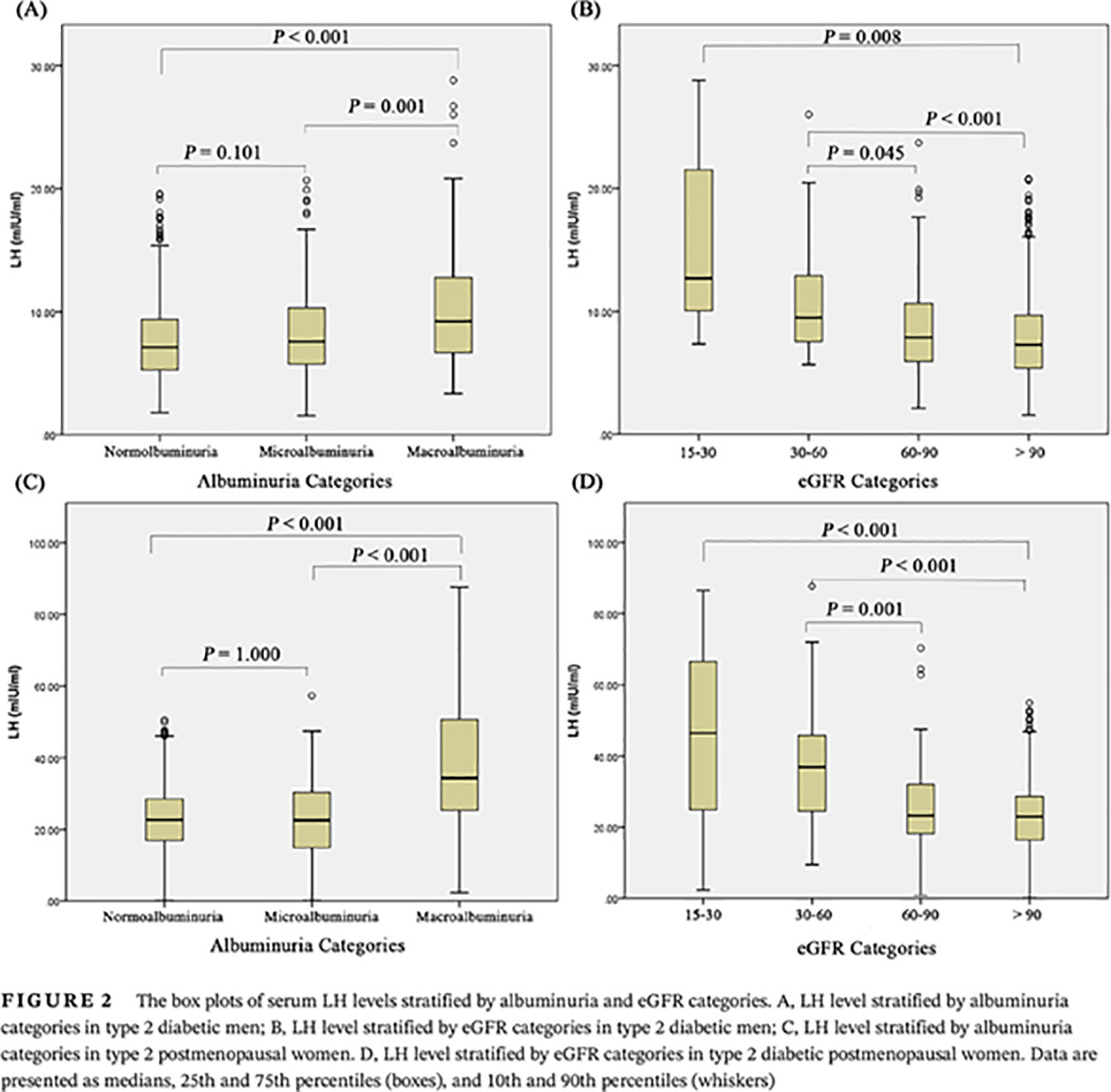
Elevated circulating luteinizing hormone levels are associated with diabetic macroalbuminuria in Chinese men and postmenopausal women: A cross-sectional study
2型糖尿病男性和绝经后女性患者黄体生成素水平与晚期糖尿病肾病的关系:一项横断面研究
- First Published: 31 May 2020
Highlights
- High luteinizing hormone (LH) levels are positively associated with established type 2 diabetic kidney disease (DKD) among Chinese men and postmenopausal women.
- The positive associations between LH and macroalbuminuria risk were independent of age, diabetes duration, or other metabolic factors.
- The increase of circulating LH may be a promising clinical factor for identifying established DKD.
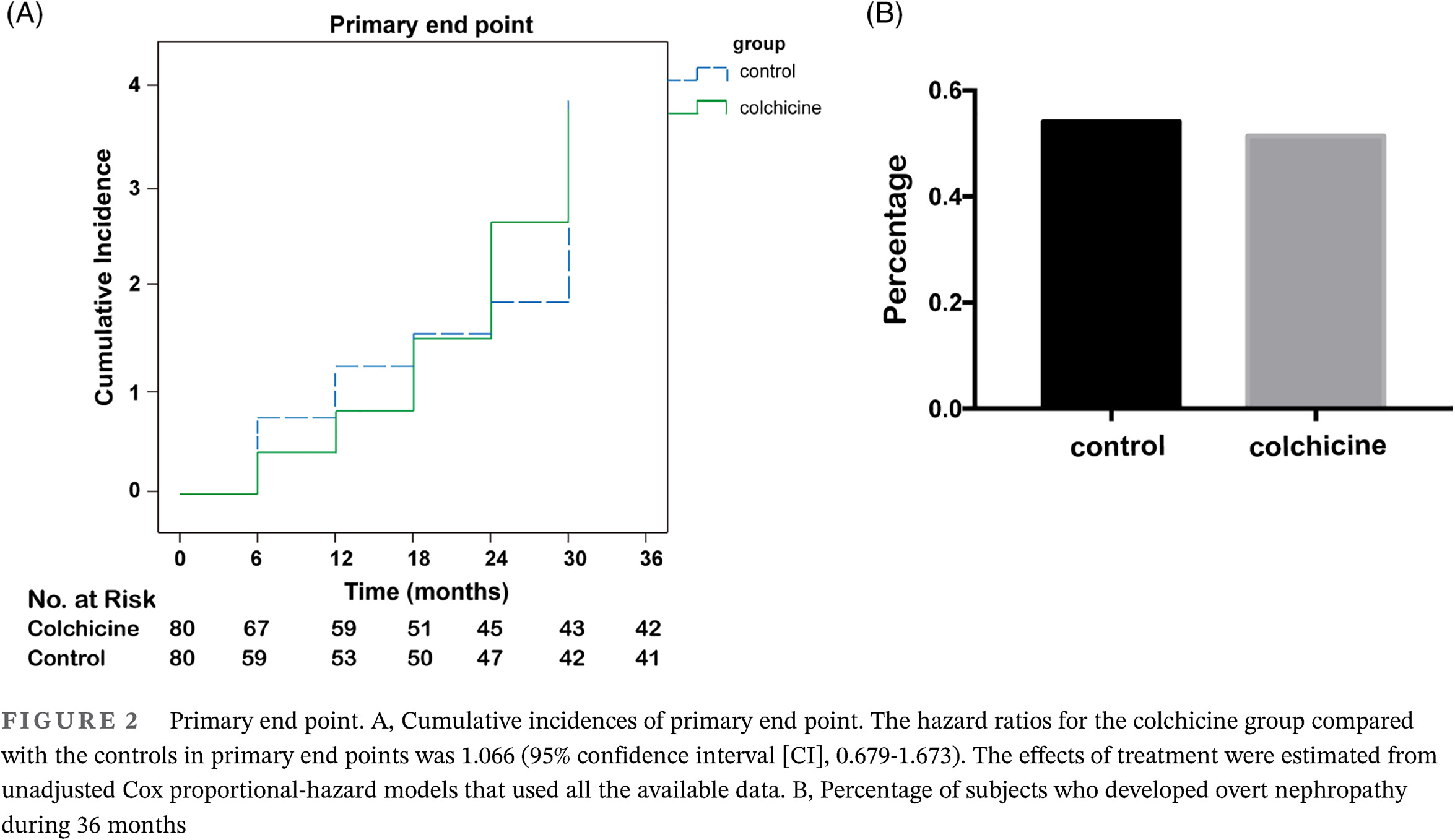
Low-dose colchicine in type 2 diabetes with microalbuminuria: A double-blind randomized clinical trial
低剂量秋水仙碱对2型糖尿病合并微量白蛋白尿的作用:一项随机双盲临床试验
- First Published: 04 March 2021
Economic benefit of prescribing an adjusted renal dose of dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors in type 2 diabetes patients with chronic kidney disease
调整二肽基肽酶IV抑制剂的剂量在2型糖尿病合并慢性肾病患者中的经济效益
- First Published: 20 May 2020
Highlights
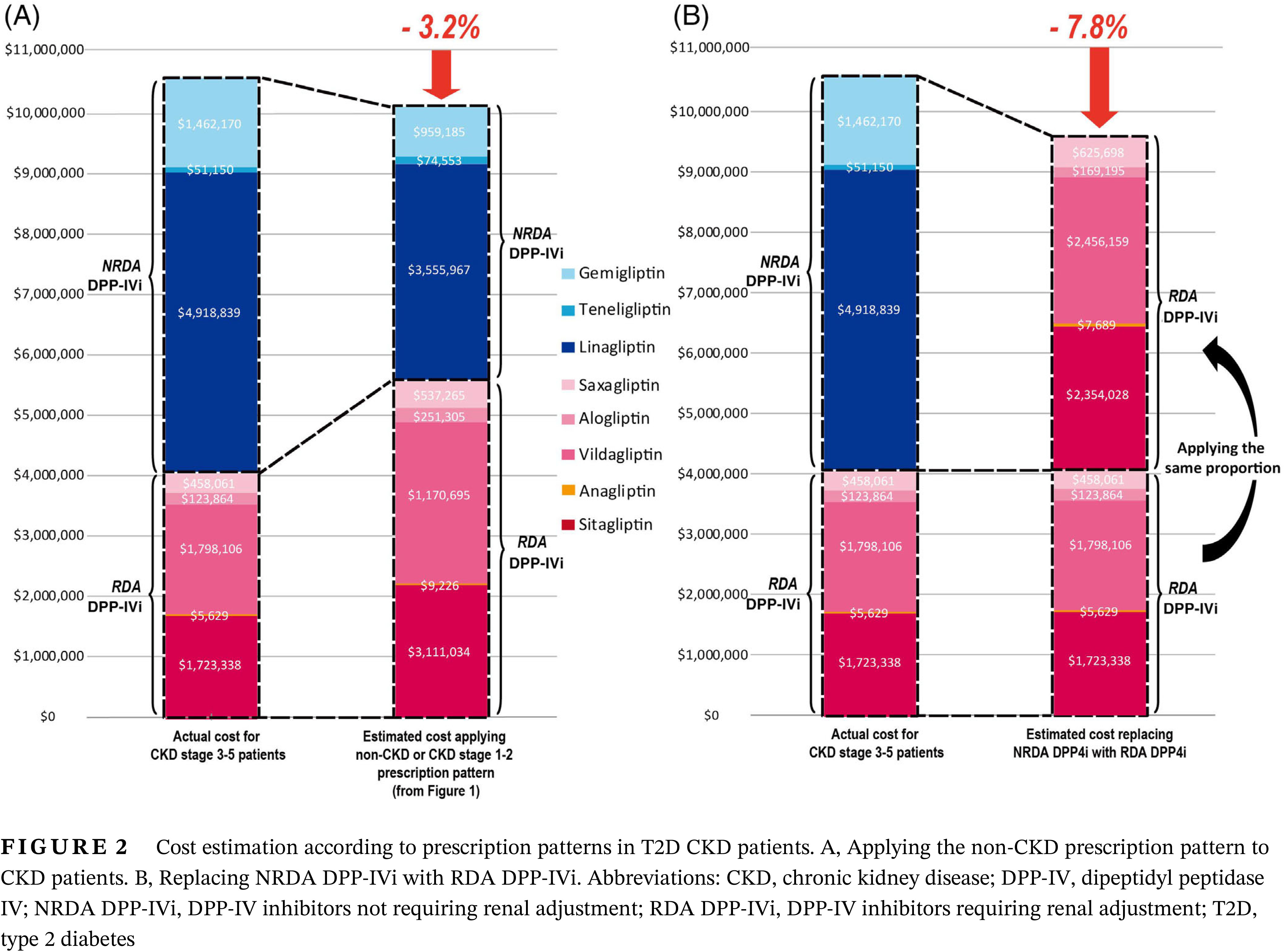
- Based on nationwide insurance data in Korea, the use of dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors (DPP-IVi) not requiring renal dose adjustment (NRDA DPP-IVi) is widespread in the type 2 diabetes chronic kidney disease (T2D CKD) population.
- Instead of prescribing NRDA DPP-IVi, the use of DPP-IVi requiring renal dose adjustment with appropriate renal dose adjustments in T2D CKD patients can achieve a considerable annual cost saving of up to 7.8%.
Antidiabetic drug use trends in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease: A cross-sectional analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
2型糖尿病合并慢性肾病患者抗糖尿病药物使用趋势:国家健康与营养调查的横断面分析
- First Published: 25 October 2019
Highlights
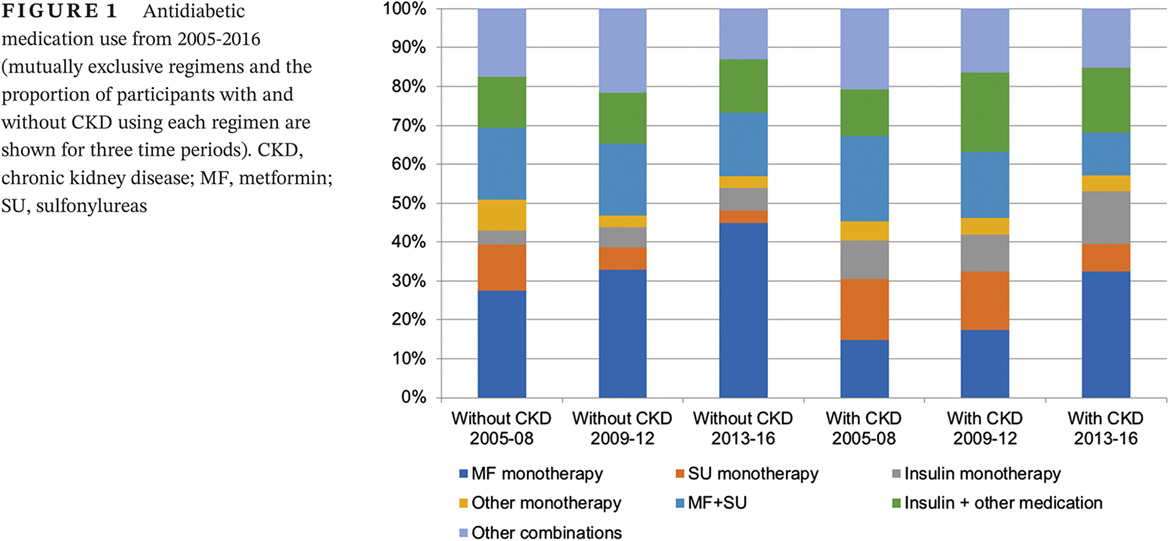
- In a cross-sectional analysis of National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) participants with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and chronic kidney disease (CKD), we observed an increased use of metformin (59%-68%) and a decreased use of sulfonylureas (55%-37%) and thiazolidinediones (25%-5%) in 2013-2016 compared to 2006-2008.
- Guideline-discordant use of metformin (8% of CKD stage 4/5) and glyburide (3% of CKD stages 3-5) observed in 2013-2016 warrants stronger policy implementations regarding inappropriate drug use.
A study on the status of normoalbuminuric renal insufficiency among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: A multicenter study based on a Chinese population
正常蛋白尿的2型糖尿病患者肾功能不全状况的研究:基于中国人群的多中心研究
- First Published: 08 October 2021
Highlights
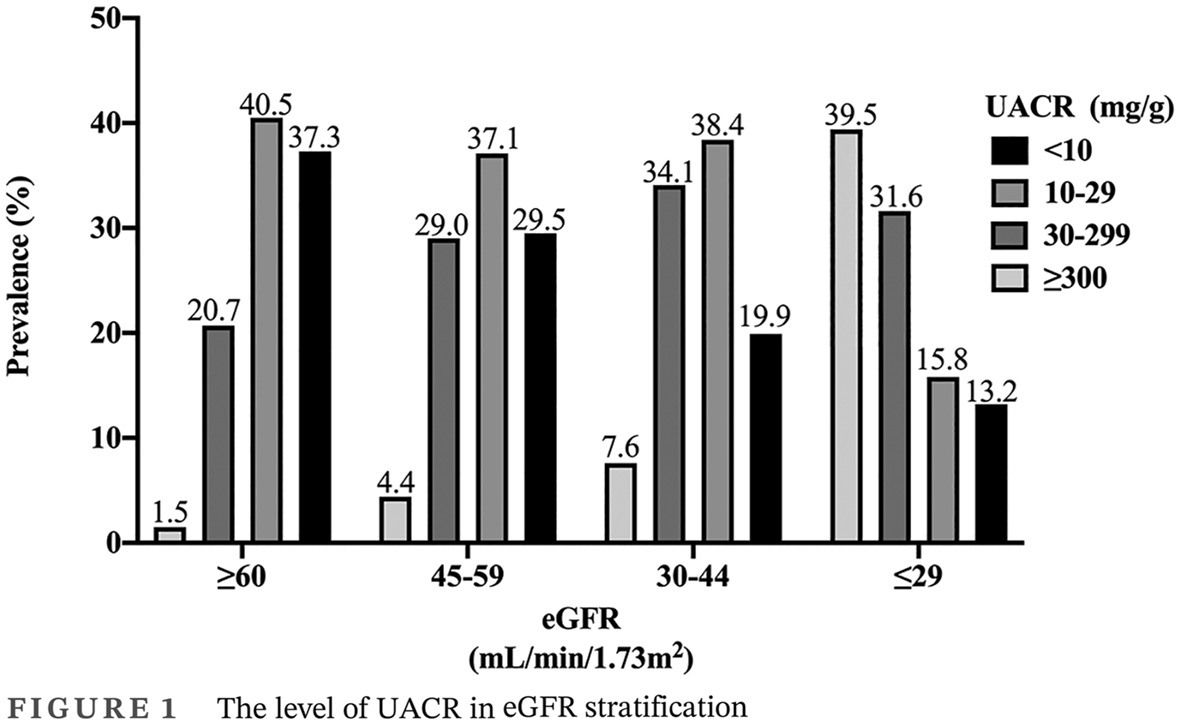
- Approximately 63.6% of diabetes patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 have normal albuminuria.
- The factors related to normoalbuminuria and eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 were male sex, older age, higher triglyceride levels, lower extremity arterial disease, and a longer duration of diabetes.
- Compared with patients with both albuminuria and eGFR decline, those with normoalbuminuria have better control of metabolic indicators.
Urinary C-peptide/creatinine ratio: A useful biomarker of insulin resistance and refined classification of type 2 diabetes mellitus
尿C肽/肌酐比值:一个评估胰岛素抵抗水平并改善2型糖尿病精准分型的有效生物标志物
- First Published: 29 May 2021
Highlights
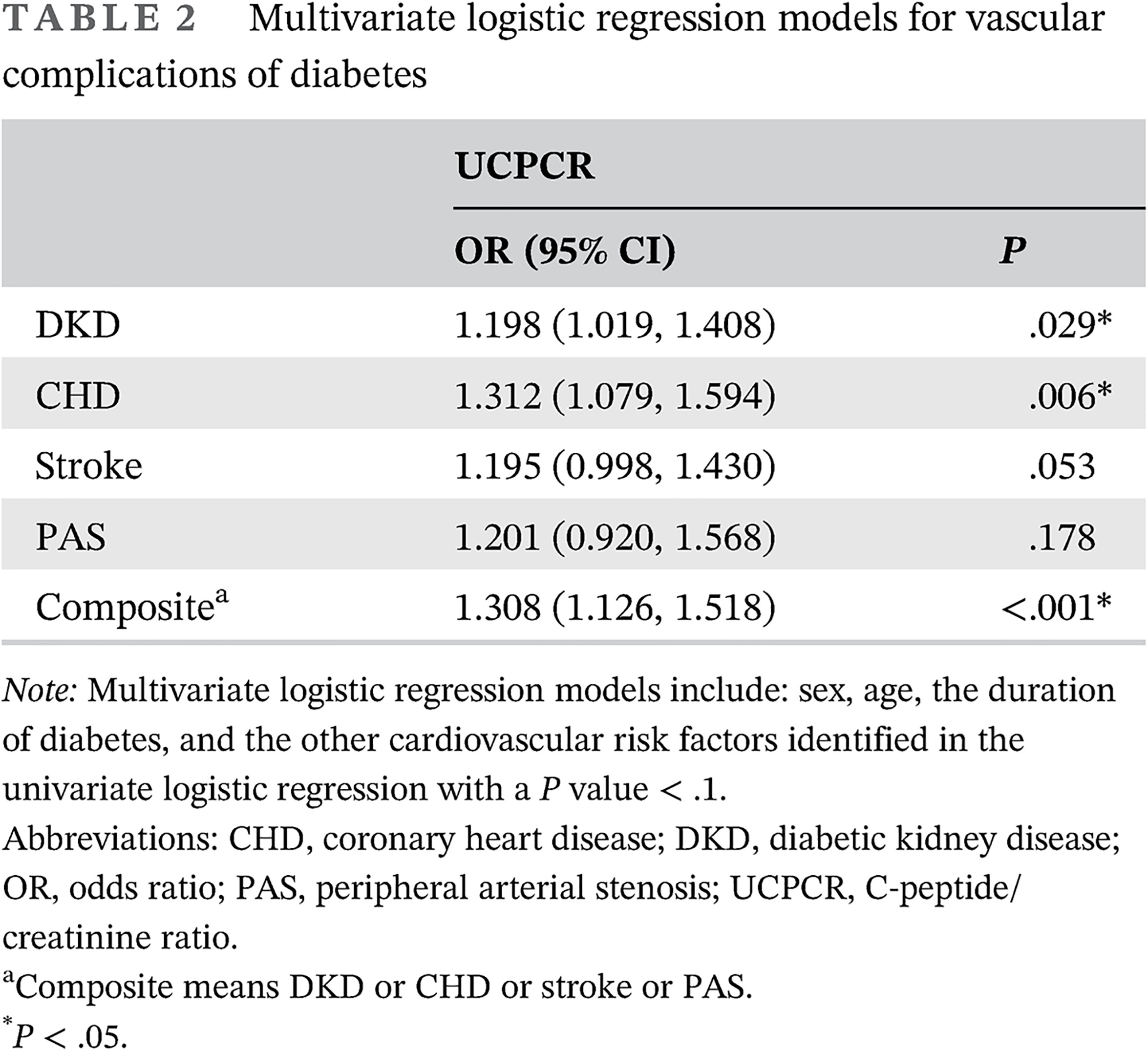
- Urinary C-peptide/creatinine ratio (UCPCR) is a biomarker of insulin resistance.
- High UCPCR is associated with the vascular complications of diabetes.
- The addition of UCPCR could be used to improve the categorization of patients with diabetes, and we present an updated classification comprising subgroups with specific clinical characteristics.




1753-0407.diabetic-kidney-disease.cover.gif)