Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Neurodegeneration in acute and chronic central nervous system disorders: Novel ideas and approaches
- Pages: 243-245
- First Published: 16 December 2024
REVIEW
Blood-based biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease: Standardization and comprehensiveness
- Pages: 246-254
- First Published: 20 October 2024
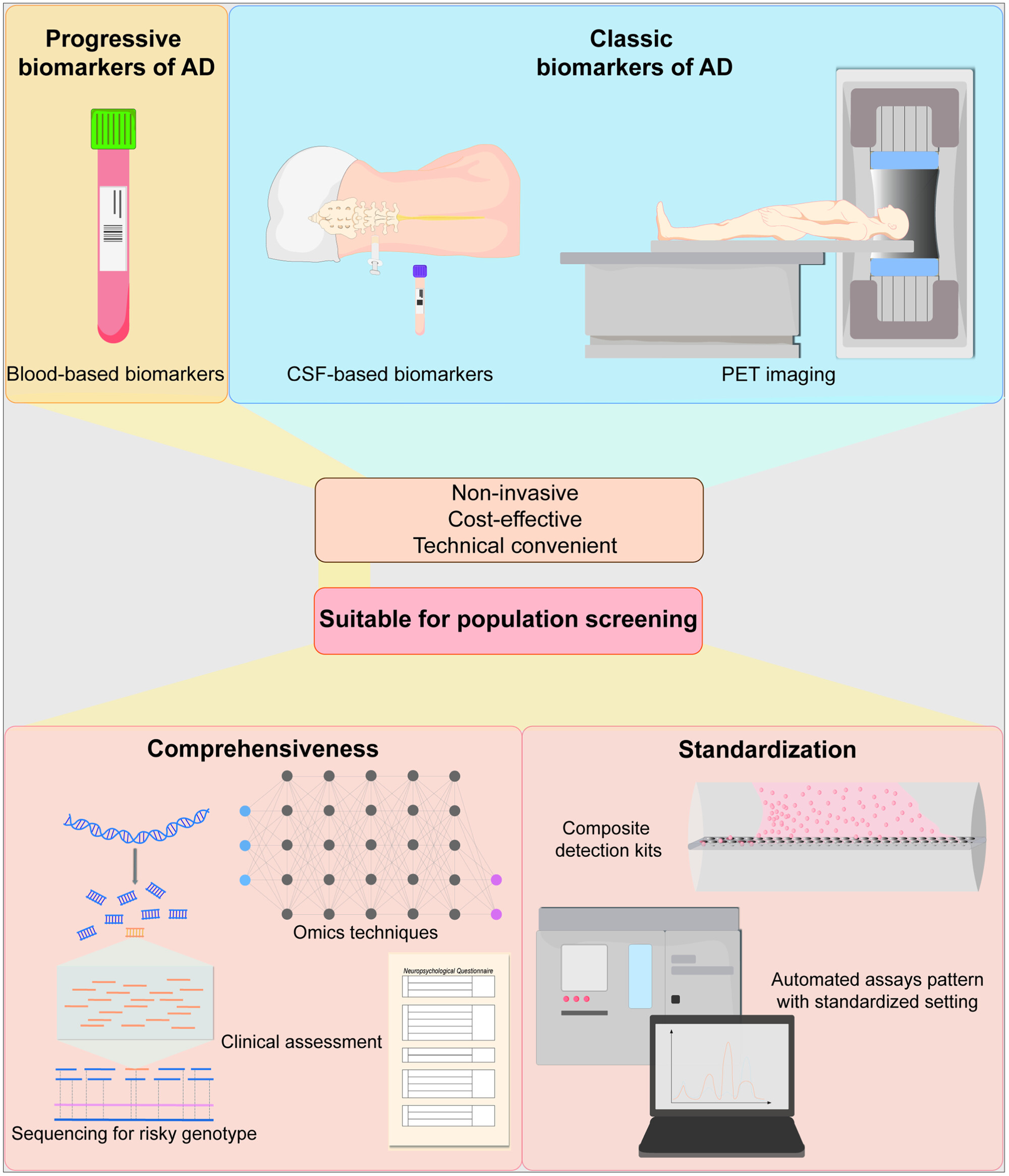
Blood-based biomarkers (BBMs) are noninvasive, cost-effective and technical convenient, thus surpassing cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers and positron emission tomography (PET)-computed tomography imaging in population disease screening of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Relying on the standardization and comprehensiveness in application, BBMs will demonstrate a promising prospect in large-scale identification and prevention of AD.
Recent advances in therapeutic strategies for Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease using protein/peptide co-modified polymer nanoparticles
- Pages: 255-275
- First Published: 28 November 2024
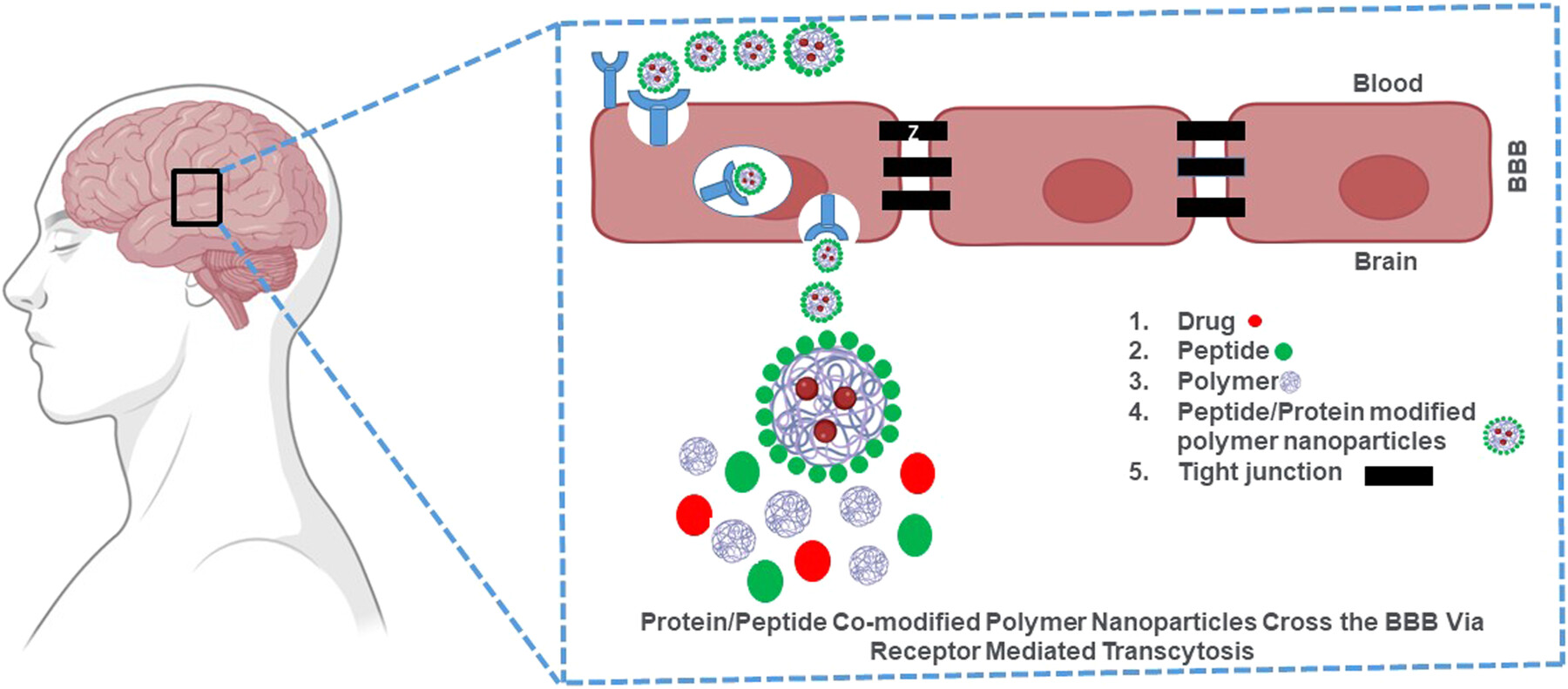
The graphical abstract illustrates that drug-encapsulated polymer nanoparticles are engineered with proteins and peptides to facilitate transport across the blood-brain barrier through receptor-mediated transcytosis and delivery of drugs to targeted regions in the brain, thereby offering a more effective treatment for Parkinson's and Alzheimer's diseases. Various peptides and proteins are used in drug delivery systems because they are only focused on a small class of receptors, such as low-density lipid receptors, Fc-like growth factor receptors, leptin receptors, receptor-associated proteins, insulin receptors, scavenger receptor type B1, cell surface receptors, and transferrin receptor. Polymers are crucial for drug delivery because they offer a versatile, efficient, and secure method of improving the administration and effectiveness of therapeutic agents. BBB, blood-brain barrier.
Mass spectrometry-based proteomics for biomarker discovery in the Drosophila model of Parkinson's disease
- Pages: 276-287
- First Published: 22 October 2024

Parkinson's disease (PD) encompasses both sporadic instances and genetic mutations in the SNCA and LRRK2 genes. The utilization of Drosophila melanogaster models, in conjunction with mass spectrometry-based proteomics, has significantly progressed the investigation of PD. These methodologies facilitate the identification of prospective therapeutic targets and biomarkers.
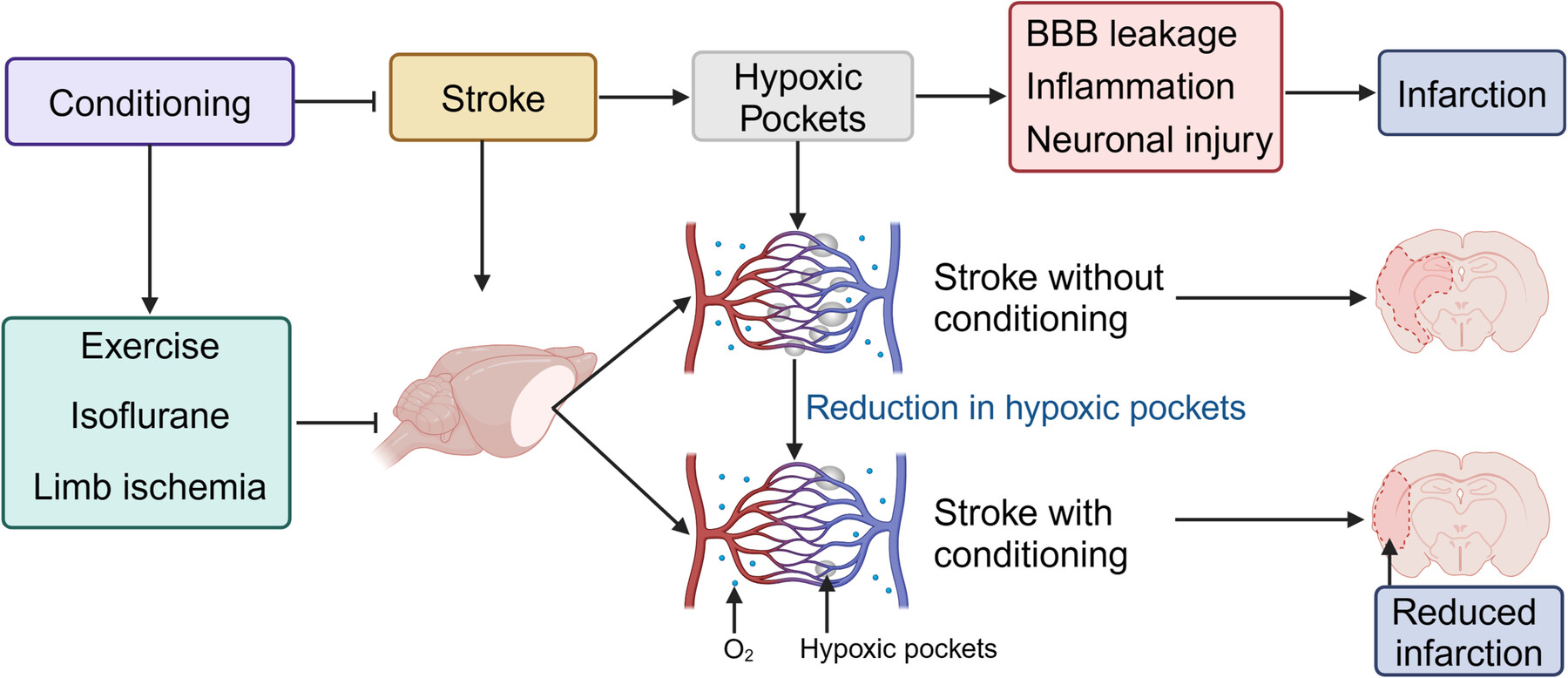
A novel perspective in stroke neuroprotection: Leveraging hypoxic pocket insights for studying preconditioning and postconditioning
- Pages: 288-295
- First Published: 23 October 2024
Rodent ischemic stroke models and their relevance in preclinical research
- Pages: 296-309
- First Published: 04 November 2024
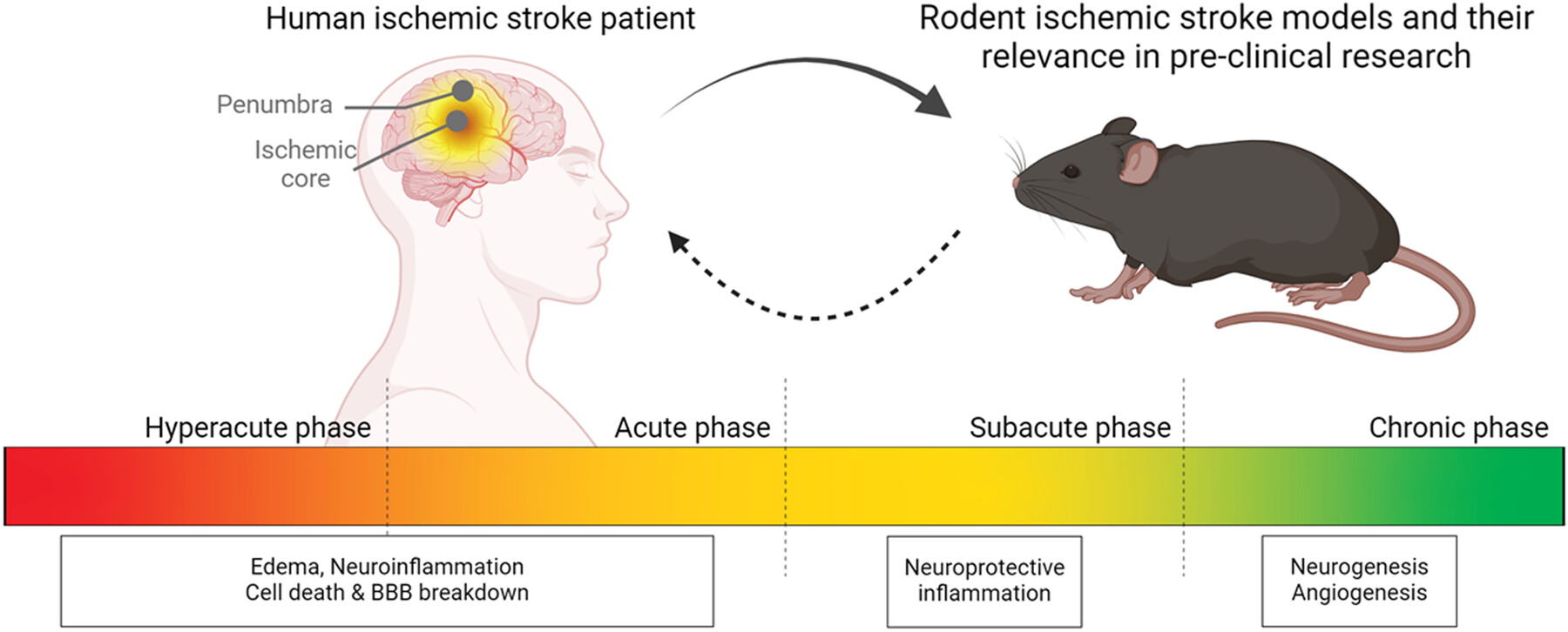
Ischemic stroke is a leading cause of death and disability, with current treatments limited to recanalization techniques and no approved pharmacological interventions for excitotoxicity and neuroinflammation. This review critically examines the five most commonly used rodent ischemic stroke models, evaluating their ability to replicate human stroke pathophysiology and phenotype, particularly in the acute phases.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Liver enzyme and risk of vascular dementia: A univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization of European descent
- Pages: 310-317
- First Published: 08 December 2024
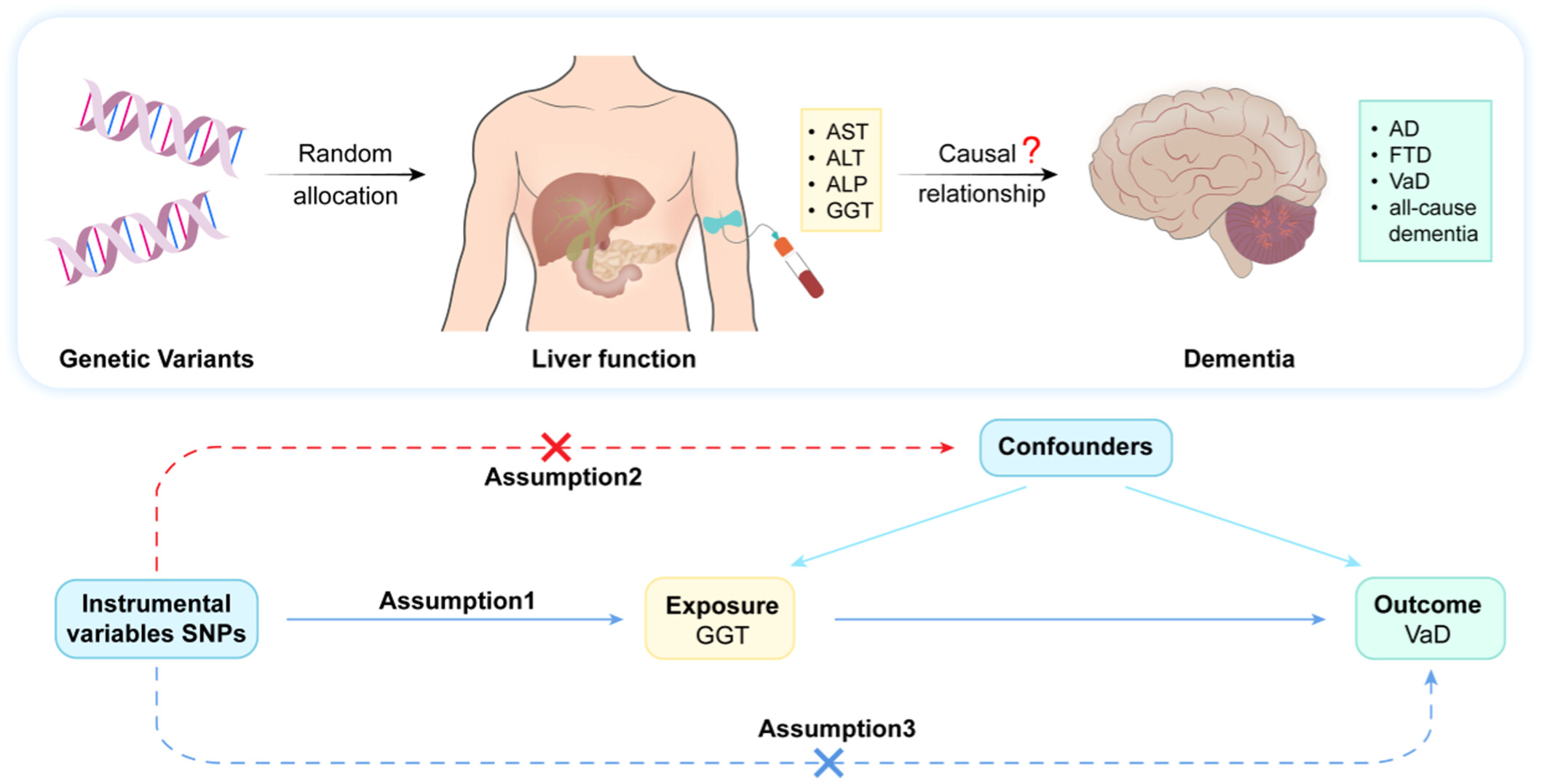
Illustration of our Mendelian randomization investigation examining the potential causal link between liver function and dementia. Assumption 1: Genetic instrumental variables are strongly linked to exposures. Assumption 2: Genetic instrumental variables remain unaffected by confounders that simultaneously affect exposures and outcomes. Assumption 3: Genetic instrumental variables solely influence outcomes via their effect on exposures. AD, Alzheimer's disease; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; FTD, frontotemporal dementia; GGT, γ-glutamyltransferase; OR, odds ratio; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism; VaD, vascular dementia.
STUDY PROTOCOLS
A multicenter single-arm objective performance criteria trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of a dedicated venous sinus thrombectomy device for severe cerebral venous sinus thrombosis
- Pages: 318-328
- First Published: 08 December 2024
CORRECTION
Correction to “Tolerability and first hints for potential efficacy of motor-cognitive training under inspiratory hypoxia in health and neuropsychiatric disorders: A translational viewpoint”
- Page: 329
- First Published: 28 November 2024